Reconsidering Anesthesia in Lumbar Surgery: An Umbrella Review of Awake Versus General Anesthesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Analysis and Credibility of the Evidence for the Outcomes of Interest
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Meta-Analysis Characteristics
3.3. Quality Assessment
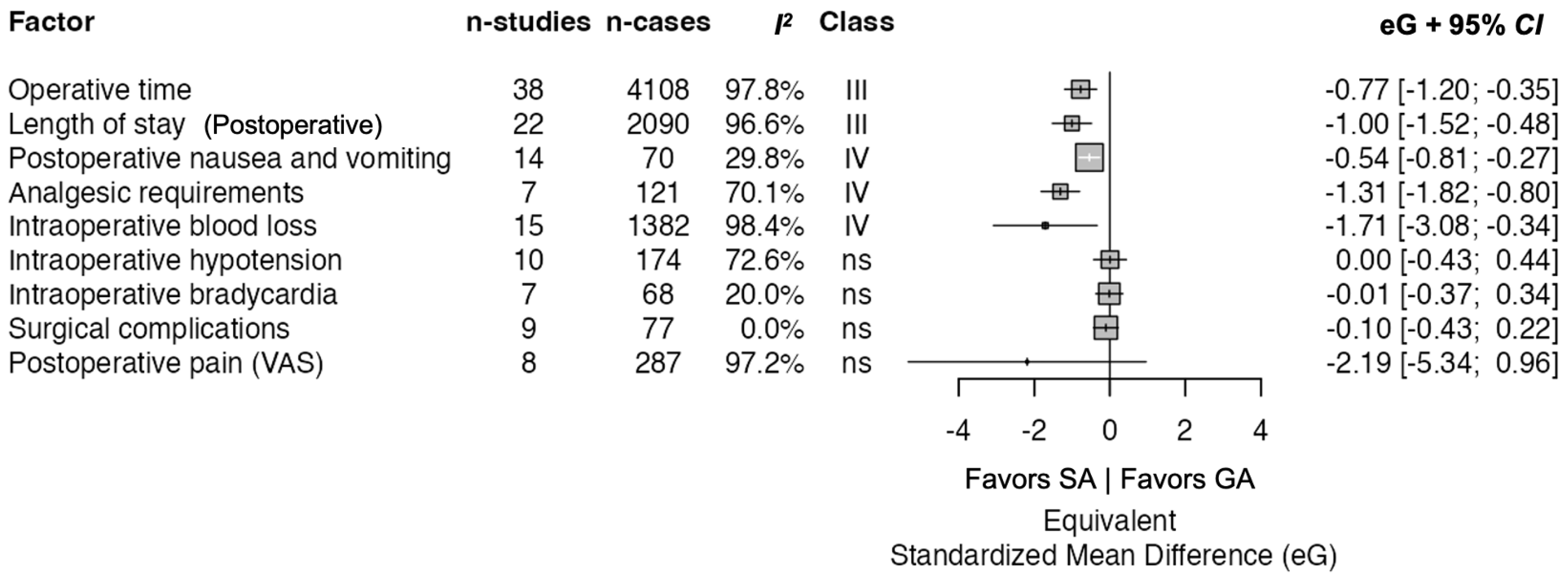
3.4. Summary of Outcomes
3.5. Operative Time
3.6. Intraoperative Blood Loss
3.7. Length of Stay
3.8. Postoperative Pain (VAS)
3.9. Surgical Complications
3.10. Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
3.11. Postoperative Analgesic Requirements
3.12. Intraoperative Hypotension
3.13. Intraoperative Bradycardia
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Contexts
4.2. Observed Benefits of Awake Lumbar Surgery
4.3. Clinical Implications and Future Research
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weber, C.F.; Früh, A.; Jelgersma, C.; Almahozi, A.; Ferdowssian, K.; Hecht, N.; Vajkoczy, P.; Wessels, L. Systematic review and meta-analysis of spinal versus general anesthesia in decompressive surgeries of the lumbar spine. Brain Spine 2025, 5, 104280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Roman, R.J.; Govindarajan, V.; Bryant, J.P.; Wang, M.Y. Spinal anesthesia in awake surgical procedures of the lumbar spine: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 3709 patients. Neurosurg. Focus 2021, 51, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetzlaff, J.E.; Dilger, J.A.; Kodsy, M.; al-Bataineh, J.; Yoon, H.J.; Bell, G.R. Spinal anesthesia for elective lumbar spine surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 1998, 10, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, C.; Lewandrowski, K.U.; Spears, H.; Braxton, E.E. Comparative perioperative narcotic use in tlif patients: Spinal versus general anesthesia in a retrospective cohort study of 180 cases in hospital and ambulatory settings. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2025, 251, 108840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLain, R.F.; Tetzlaff, J.E.; Bell, G.R.; Uwe-Lewandrowski, K.; Yoon, H.J.; Rana, M. Microdiscectomy: Spinal anesthesia offers optimal results in general patient population. J. Surg. Orthop. Adv. 2007, 16, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Attari, M.A.; Mirhosseini, S.A.; Honarmand, A.; Safavi, M.R. Spinal anesthesia versus general anesthesia for elective lumbar spine surgery: A randomized clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 524–529. [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso, K.; Okano, I.; Sarin, M.; Hughes, A.P.; Zelenty, W.D.; Shue, J.; A Sama, A.; Cammisa, F.P.; Girardi, F.P.; Soffin, E.M. Comparative effectiveness of anesthetic technique on outcomes after lumbar spine surgery: A retrospective propensity score-matched analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program, 2009–2019. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2023, 48, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, B.; Wainwright, T.W.; Wang, M.Y.; Sigmundsson, F.G.; Yang, M.M.; Smid-Nanninga, H.; Bonnal, A.; Le Huec, J.-C.; Fawcett, W.J.; Ljungqvist, O.; et al. Consensus statement for perioperative care in lumbar spinal fusion: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society recommendations. Spine J. Off. J. North. Am. Spine Soc. 2021, 21, 729–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Fernandez, R.; Godfrey, C.M.; Holly, C.; Khalil, H.; Tungpunkom, P. Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.J.; Kang, H. Introduction to Umbrella Reviews as a Useful Evidence-Based Practice. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2023, 12, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Zhong, Z.; Meng, L. Impact of spinal anaesthesia vs. general anaesthesia on peri-operative outcome in lumbar spine surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised, controlled trials. Anaesthesia 2017, 72, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadczak, C.N.; Vanjani, N.N.; Pawlowski, H.; Cha, E.D.; Lynch, C.P.; Prabhu, M.C.; Hartman, T.J.; Nie, J.W.; MacGregor, K.R.; Zheng, E.; et al. The Current Status of Awake Endoscopic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2023, 180, e198–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cassai, A.; Geraldini, F.; Boscolo, A.; Pasin, L.; Pettenuzzo, T.; Persona, P.; Munari, M.; Navalesi, P. General Anesthesia Compared to Spinal Anesthesia for Patients Undergoing Lumbar Vertebral Surgery: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajjoub, R.; Ghaith, A.K.; El-Hajj, V.G.; Rios-Zermano, J.; De Biase, G.; Atallah, E.; Tfaily, A.; Saad, H.; Akinduro, O.O.; Elmi-Terander, A.; et al. Comparative outcomes of awake spine surgery under spinal versus general anesthesia: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, M.; Zhao, D.; Xue, Z.; Wu, A. Impact of Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia Versus General Anesthesia on Perioperative Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Spine Surgery: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Spine Surg. 2023, 36, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, M.L.M.; Bojaxhi, E.; Abode-Iyamah, K.O.; Patterson, J.S.A.; White, K.E.A.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Rabai, F.; De Ruyter, M.L.; Riutort, K.T.; Fleissner, Z.J.D.; et al. The Benefits of Awake Spinal Surgery on Minimizing Positioning-related Complications: A Narrative Review. Spine 2025, 50, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.P.; Bonin, B.; Quinones, C.; Kumbhare, D.; Guthikonda, B.; Hoang, S. Spinal Anesthesia for Awake Spine Surgery: A Paradigm Shift for Enhanced Recovery after Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelissen, H.P.; Epema, A.H.; Henning, R.H.; Krijnen, H.J.; Hennis, P.J.; den Hertog, A. Inotropic effects of propofol, thiopental, midazolam, etomidate, and ketamine on isolated human atrial muscle. Anesthesiology 1996, 84, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfel, C.C.; Kranke, P.; Katz, M.H.; Goepfert, C.; Papenfuss, T.; Rauch, S.; Heineck, R.; Greim, C.-A.; Roewer, N. Volatile anaesthetics may be the main cause of early but not delayed postoperative vomiting: A randomized controlled trial of factorial design. Br. J. Anaesth. 2002, 88, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchuman, V.; Agarwal, N.; Mummaneni, V.P.; Wang, M.Y.; Shabani, S.; Patel, A.; Rivera, J.; Haddad, A.F.; Le, V.; Chang, J.M.; et al. Awake spinal surgery: Simplifying the learning curve with a patient selection algorithm. Neurosurg. Focus 2021, 51, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, I.; Barnette, R. Positioning patients for spine surgery: Avoiding uncommon position-related complications. World J. Orthop. 2014, 5, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebl, J.R.; Horlocker, T.T.; Kopp, S.L.; Schroeder, D.R. Neuraxial blockade in patients with preexisting spinal stenosis, lumbar disk disease, or prior spine surgery: Efficacy and neurologic complications. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picetti, E.; Demetriades, A.K.; Catena, F.; Aarabi, B.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Alves, O.L.; Ansaloni, L.; Armonda, R.A.; Badenes, R.; Bala, M.; et al. Early management of adult traumatic spinal cord injury in patients with polytrauma: A consensus and clinical recommendations jointly developed by the World Society of Emergency Surgery (WSES) & the European Association of Neurosurgical Societies (EANS). World J. Emerg. Surg. 2024, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, B.; Ahuja, K.; Sharan, A.D. Awake spinal fusion. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma. 2020, 11, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
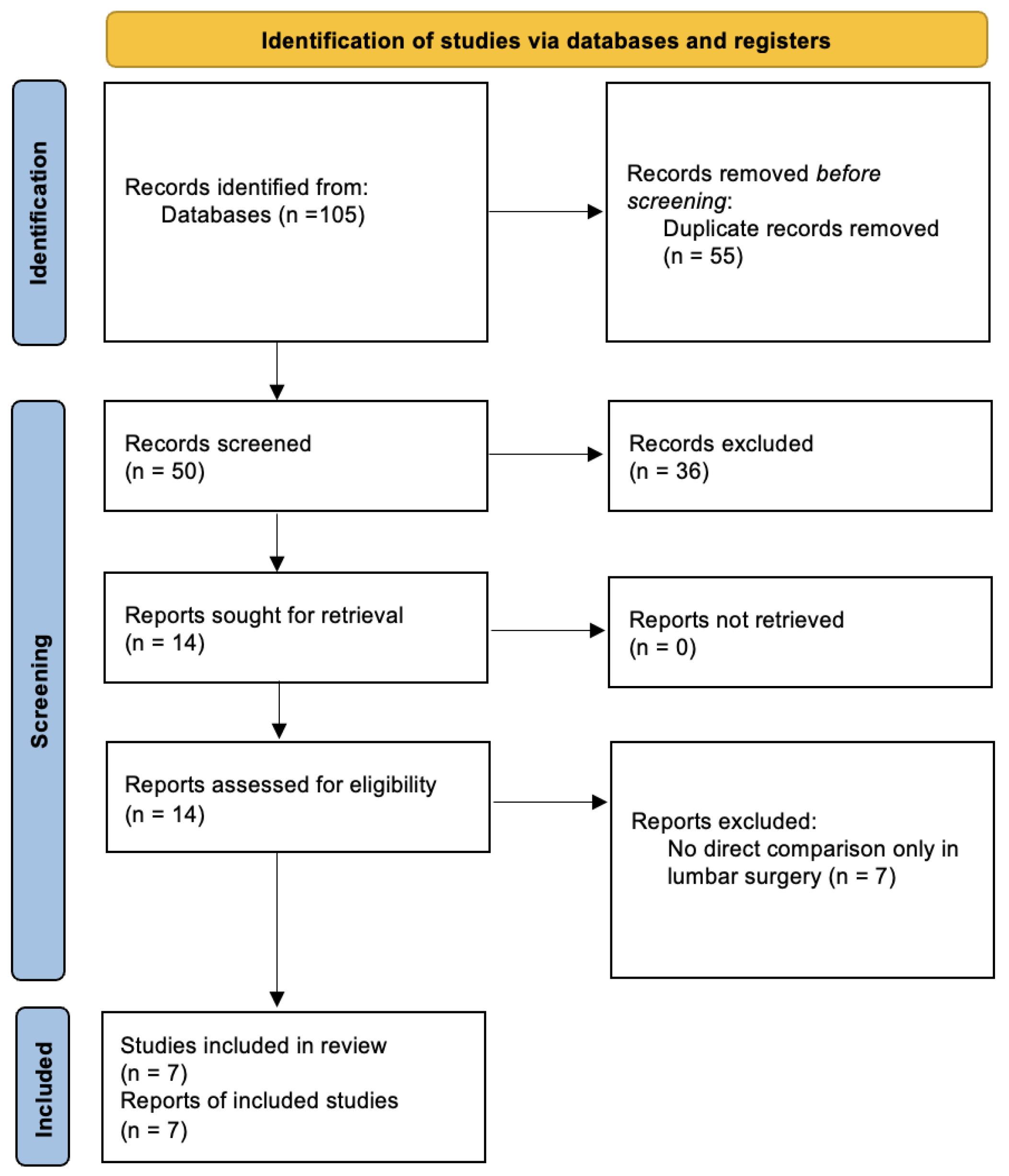
| References | Last Search | Data Sources | Publication Date Range of the Primary Studies | Primary Study Designs | Total Number of Primary Studies | Number of Pooled Patients | Number of Pooled Awake Patients | Number of General Anesthesia Patients | Reported Outcomes of Interest | Surgery Type/Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weber 2025 [1] | Not Reported | Cochrane Library, Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid Embase | 1996–2024 | Prospective and retrospective comparative studies | 11 | 1350 | 688 | 662 | Operative time, intraoperative blood loss, LOS, postoperative pain, postoperative complications, postoperative nausea and vomiting | Lumbar |
| Rajjoub 2024 [14] | 14 April 2023 | Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid Embase, Cochrane Central, and Scopus | 1996–2023 | RCTs, prospective and retrospective comparative studies | 38 | 7820 | 5061 | 2759 | Operative time, intraoperative blood loss, LOS, postoperative complications | Thoracic and lumbar |
| Jadczak 2023 [12] | March 2021 | Embase, PubMed/Medline, Cochrane, and Google Scholar | 2011–2020 | RCTs, prospective and retrospective comparative studies | 26 | 2113 | 1873 | 240 | Postoperative complications, LOS, PROMS | Endoscopic |
| Shui 2023 [15] | 31 May 2020 | Embase, PubMed, Cochrane | 1995–2014 | RCTs | 10 | 733 | 367 | 366 | Intraoperative hemodynamics (hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia), analgesic requirements (PACU, 24h after surgery), postoperative nausea and vomiting, urinary retention, headache, LOS | Lumbar |
| Perez-Roman 2021 [2] | NR | PubMed and Cochrane | 2003–2021 | RCTs, prospective and retrospective comparative studies | 14 | 3709 | 2219 | 1490 | Operative time, anesthesia time, postoperative complications, postoperative pain, LOS | Lumbar |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 6 July 2020 | PubMed, Cochrane, and Google Scholar | 1996–2020 | RCTs | 11 | 896 | 447 | 449 | Postoperative pain, analgesic requirements, blood loss, operative time, intraoperative hemodynamics (hypotension and bradycardia), postoperative nausea and vomiting, urinary retention, LOS, PROM | Lumbar |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 1 July 2016 | PubMed, Embase, Cochrane | 1996–2014 | RCTs | 8 | 625 | 313 | 312 | Intraoperative hemodynamics (hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia), blood loss, operative time, analgesic requirements, postoperative nausea and vomiting, LOS | Lumbar |
| Meta-Analysis | Uses Elements of PICO | Explained Selection of the Study Designs | Comprehensive Literature Search | Study Selection in Duplicate | Excluded Study List Provided | Included Studies Described | Funding Sources Reported | Quality Assessed | Quality Used Appropriately | Satisfactory Discussion of Heterogeneity | Conflicts of Interest Reported | AMSTAR2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weber 2025 [1] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 11 |
| Rajjoub 2024 [14] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 10 | |
| Jadczak 2023 [12] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 9 | |||
| Shui 2023 [15] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 9 | ||
| Perez-Roman 2021 [2] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 9 | ||
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 11 |
| Meng 2017 [11] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | 10 | |
| Total | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 9.86 |
| Outcome | Meta-Analysis | Number of Primary Studies | Number of Pooled Patients | Number of Pooled Awake Patients | Number of Pooled General Anesthesia Patients | Effect Measure | Effect Size | 95% CI | p-Value for Effect (* Computed) | I2 (%) | p-Value for Heterogeneity (* Computed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operative time | Weber 2025 [1] | 8 | 1138 | 574 | 564 | MD | −8.52 | [−14.56, −2.49] | 0.0056 * | 93.49 | <0.0001 * |
| Rajjoub 2024 [14] | 18 | 3101 | 1661 | 1440 | MD | −19.17 | [−29.68, −8.65] | 0.00036 * | 98 | <0.01 | |
| Perez-Roman 2021 [2] | 5 | 1793 | 1281 | 512 | MD | −14.04 | [−21.30, −6.79] | 0.0001 | 88 | <0.00001 | |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 10 | 830 | 414 | 416 | MD | −4.56 | [−12.16, 4.04] | 0.3 | 98 | <0.01 * | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 6 | 503 | 252 | 251 | SMD | 0.41 | [−1.73, 0.91] | 0.54 | 98 | <0.00001 * | |
| Intraoperative blood loss | Weber 2025 [1] | 6 | 695 | 347 | 348 | MD | −27.59 | [−61.85, 6.67] | 0.114 * | 99.77 | <0.00001 * |
| Rajjoub 2024 [14] | 18 | 3101 | 1661 | 1440 | MD | −19.17 | [−29.68, −8.65] | 0.00036 * | 98 | <0.01 | |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 6 | 554 | 286 | 268 | MD | −53.88 | [−98.13,−9.63] | 0.02 | 97 | <0.00001 | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 5 | 434 | 216 | 218 | SMD | 1.56 | [−3.12, 0.00] | 0.05 | 98 | <0.00001 * | |
| Length of stay (LOS) | Weber 2025 [1] | 3 | 343 | 171 | 172 | MD | −1.6 | [−3.95, 0.75] | 0.182 * | 99.89 | <0.00001 |
| Rajjoub 2024 [14] | 13 | 1915 | 807 | 1108 | MD | −0.4 | [−0.64, −0.17] | 0.00085 * | 81 | <0.01 | |
| Jadczak 2023 [12] | 3 | 283 | 163 | 120 | MD | −2.09 | [−3.99, −0.19] | 0.03 | 99.39 | 0.00 | |
| Shui 2023 [15] | 6 | 478 | 239 | 239 | MD | −0.28 | [−0.37, −0.18] | <0.00001 | 32 | 0.2 | |
| Perez-Roman 2021 [2] | 4 | 794 | 412 | 382 | MD | −0.16 | [−0.29 to −0.03] | 0.02 | 0 | 0.58 | |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 7 | 578 | 289 | 289 | MD | −0.31 | [−0.41, −0.21] | <0.00001 | 54 | 0.04 | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 3 | 258 | 131 | 131 | SMD | −1.15 | [−1.98, −0.31] | 0.007 | 89 | 0.00011 * | |
| Postoperative pain (VAS) | Weber 2025 [1] | 2 | 172 | 86 | 86 | MD | −0.22 | [−1.35, 0.92] | 0.705 * | 88.26 | 0.0035 * |
| Perez-Roman 2021 [2] | 2 | 604 | 391 | 213 | MD | −2.50 | [−3.91, −1.09] | 0.0005 | 97 | 0.00001 | |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 4 | 306 | 153 | 153 | SMD | −0.33 | [−0.69, 0.04] | 0.08 | 60 | 0.06 | |
| Postoperative complications | Weber 2025 [1] | 5 | 928 | 443 | 485 | RR | 0.86 | [0.75, 0.99,] | 0.033 | 70.72 | 0.0085 |
| Jadczak 2023 [12] | 6 | 743 | 348 | 395 | OR | 0.97 | [0.22, 4.41] | 0.97 | 87.4 | 0.00 | |
| Perez-Roman 2021 [2] | 6 | 2334 | 1642 | 692 | OR | 0.18 | [0.09, 0.35] | <0.00001 | 79 | 0.0002 | |
| Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) | Weber 2025 [1] | 5 | 845 | 428 | 417 | RR | 0.58 | [0.51, 0.66] | <1 × 10−15 * | 0 | 0.41 * |
| Shui 2023 [15] | 14 | 172 | 51 | 121 | OR | 0.34 | [0.18, 0.66] | 0.001 | 60 | 0.002 | |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 10 | 796 | 397 | 399 | OR | 2.69 | [1.73, 4.20] | <0.0001 | 24 | 0.22 | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 7 | 545 | 273 | 272 | RR | 0.29 | [0.18, 0.46] | <0.00001 | 12 | 0.34 | |
| Analgesic requirements | Shui 2023 [15] | 8 | 380 | 151 | 229 | OR | 0.32 | [0.13, 0.77] | 0.01 | 80 | <0.0001 |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 6 | 534 | 266 | 266 | OR | 11.52 | [5.12, 25.93] | <0.00001 | 57 | 0.04 | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 4 | 362 | 181 | 181 | RR | 0.32 | [0.24, 0.43] | <0.00001 | 0 | 0.96 | |
| Intraoperative hypotension | Shui 2023 [15] | 5 | 388 | 194 | 194 | OR | 1.11 | [0.68, 1.81] | 0.68 | 0 | 0.61 |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 7 | 580 | 289 | 291 | OR | 0.51 | [0.23, 1.11] | 0.09 | 61 | 0.02 | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 5 | 428 | 214 | 214 | RR | 1.48 | [0.75, 2.93] | 0.26 | 73 | 0 | |
| Intraoperative bradycardia | Shui 2023 [15] | 5 | 422 | 211 | 211 | OR | 0.95 | [0.55, 1.62] | 0.84 | 0 | 0.42 |
| De Cassai 2020 [13] | 6 | 520 | 259 | 261 | OR | 0.74 | [0.30, 1.80] | 0.51 | 55 | 0.05 | |
| Meng 2017 [11] | 5 | 428 | 214 | 214 | RR | 0.87 | [0.57, 1.31] | 0.5 | 19 | 0.29 |
| a | ||||||||||||
| Summary Results | ||||||||||||
| Factor | Criteria | Class | n_Studies | Total_n | n_Cases | n_Controls | ||||||
| Length of stay | Ioannidis | III | 22 | 3965 | 2090.0 | 1875.0 | ||||||
| Operative time | Ioannidis | III | 38 | 7029 | 4108.0 | 2921.0 | ||||||
| Analgesic requirements | Ioannidis | IV | 7 | 520 | 121.0 | 399.0 | ||||||
| Intraoperative blood loss | Ioannidis | IV | 15 | 2721 | 1382.0 | 1339.0 | ||||||
| Postoperative nausea and vomiting | Ioannidis | IV | 14 | 279 | 70.0 | 209.0 | ||||||
| Intraoperative bradycardia | Ioannidis | ns | 7 | 150 | 68.0 | 82.0 | ||||||
| Intraoperative hypotension | Ioannidis | ns | 10 | 336 | 174.0 | 162.0 | ||||||
| Postoperative pain (VAS) | Ioannidis | ns | 8 | 672 | 287.0 | 385.0 | ||||||
| Surgical complications | Ioannidis | ns | 9 | 188 | 77.0 | 111.0 | ||||||
| b | ||||||||||||
| Factor | Measure | Value | Value_CI | eG | eG_CI | eOR | eOR_CI | p_Value | ||||
| Length of stay | G | −1.003 | [−1.522, −0.484] | −1.003 | [−1.522, −0.484] | 0.162 | [0.063, 0.415] | 1.50 × 10−4 | ||||
| Operative time | G | −0.773 | [−1.197, −0.349] | −0.773 | [−1.197, −0.349] | 0.246 | [0.114, 0.531] | 3.57 × 10−4 | ||||
| Analgesic requirements | OR | 0.093 | [0.037, 0.234] | −1.310 | [−1.819, −0.801] | 0.093 | [0.037, 0.234] | 4.58 × 10−7 | ||||
| Intraoperative blood loss | G | −1.708 | [−3.081, −0.335] | −1.708 | [−3.081, −0.335] | 0.045 | [0.004, 0.544] | 1.47 × 10−2 | ||||
| Postoperative nausea and vomiting | OR | 0.376 | [0.228, 0.618] | −0.540 | [−0.814, −0.265] | 0.376 | [0.228, 0.618] | 1.16 × 10−4 | ||||
| Intraoperative bradycardia | OR | 0.977 | [0.512, 1.864] | −0.013 | [−0.369, 0.343] | 0.977 | [0.512, 1.864] | 9.43 × 10−1 | ||||
| Intraoperative hypotension | OR | 1.008 | [0.459, 2.214] | 0.004 | [−0.429, 0.438] | 1.008 | [0.459, 2.214] | 9.84 × 10−1 | ||||
| Postoperative pain (VAS) | G | −2.189 | [−5.338, 0.96] | −2.189 | [−5.338, 0.96] | 0.019 | [0, 5.704] | 1.73 × 10−1 | ||||
| Surgical complications | OR | 0.828 | [0.456, 1.501] | −0.104 | [−0.432, 0.224] | 0.828 | [0.456, 1.501] | 5.33 × 10−1 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ononogbu-Uche, F.C.; Tchoumi, C.; Stubbs, N.M.; Sharma, A.; Gardocki, R.J.; Sharan, A.; Abd-El-Barr, M.M.; Braxton, E.E.; Awake Spine Research Group. Reconsidering Anesthesia in Lumbar Surgery: An Umbrella Review of Awake Versus General Anesthesia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238335
Ononogbu-Uche FC, Tchoumi C, Stubbs NM, Sharma A, Gardocki RJ, Sharan A, Abd-El-Barr MM, Braxton EE, Awake Spine Research Group. Reconsidering Anesthesia in Lumbar Surgery: An Umbrella Review of Awake Versus General Anesthesia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238335
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnonogbu-Uche, Favour C., Carl Tchoumi, Nolan M. Stubbs, Arnav Sharma, Raymond J. Gardocki, Alok Sharan, Muhammad M. Abd-El-Barr, Ernest E. Braxton, and Awake Spine Research Group. 2025. "Reconsidering Anesthesia in Lumbar Surgery: An Umbrella Review of Awake Versus General Anesthesia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238335
APA StyleOnonogbu-Uche, F. C., Tchoumi, C., Stubbs, N. M., Sharma, A., Gardocki, R. J., Sharan, A., Abd-El-Barr, M. M., Braxton, E. E., & Awake Spine Research Group. (2025). Reconsidering Anesthesia in Lumbar Surgery: An Umbrella Review of Awake Versus General Anesthesia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8335. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238335






