Short-Term Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Biosimilar Injections in Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ophthalmic Examinations
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the BCVA and IOP
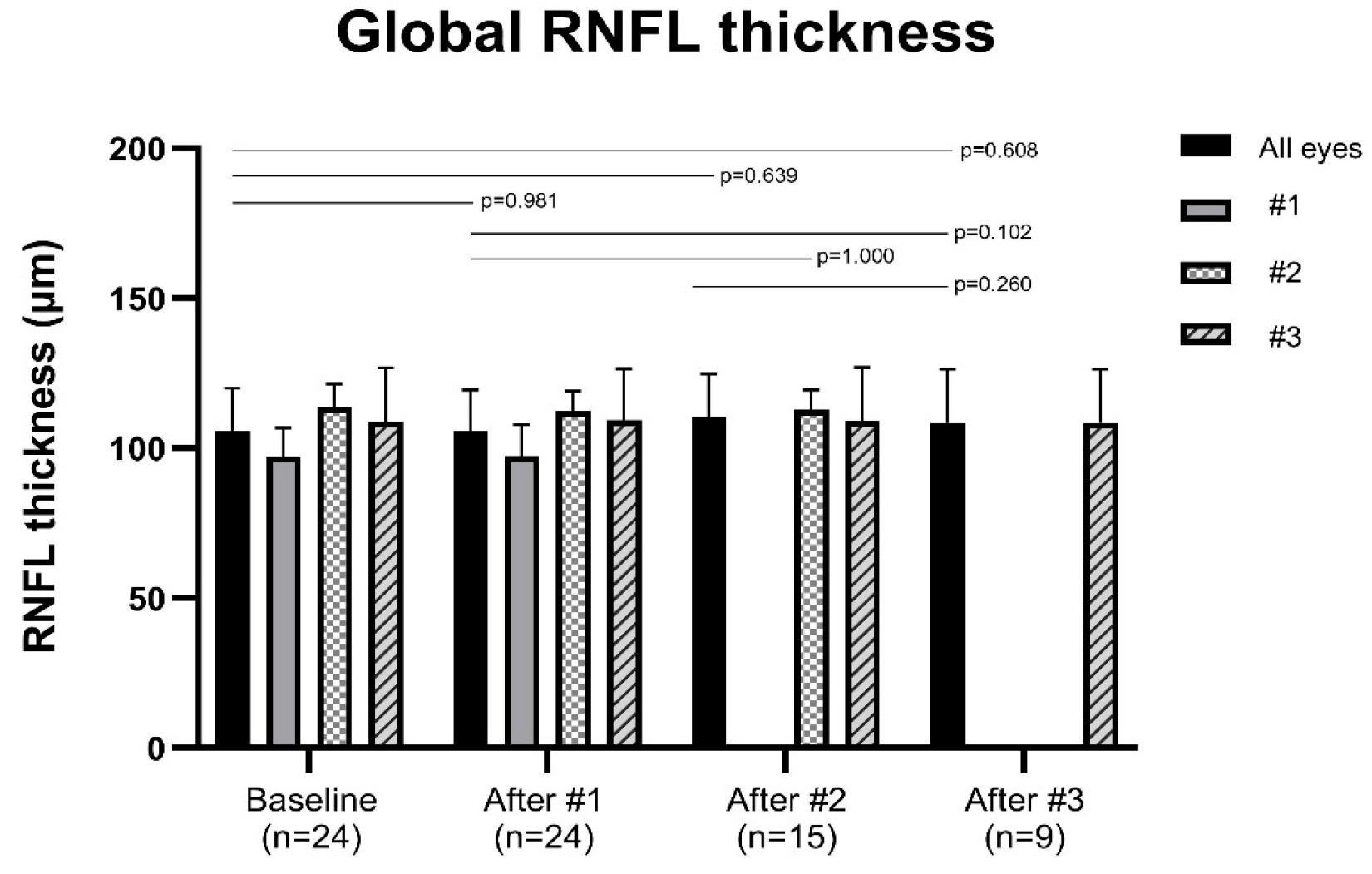
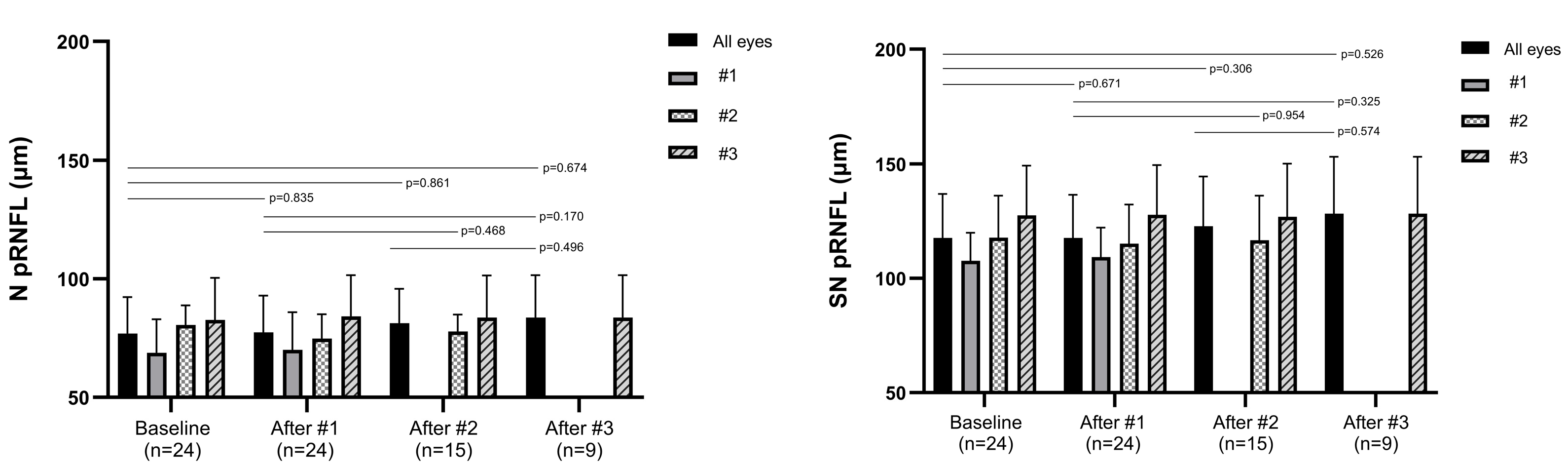
3.2. Changes in the Peripapillary RNFL Thickness
3.3. Changes in the Central Macular Thickness
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RNFL | Retinal nerve fiber layer |
| pRNFL | Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer |
| nAMD | Neovascular age-related macular degeneration |
| OCT | Optical coherence tomography |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| BCVA | Best-corrected visual acuity |
| IOP | Intraocular pressure |
| CMT | Central macular thickness |
| log MAR | Logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution |
| SE | Spherical equivalent |
| CNV | Choroidal neovascularization |
| PCV | Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy |
| RAP | Retinal angiomatous proliferation |
| ART | Automatic real-time |
References
- Mitchell, P.; Liew, G.; Gopinath, B.; Wong, T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2018, 392, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e65–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, P.J.; Brown, D.M.; Heier, J.S.; Boyer, D.S.; Kaiser, P.K.; Chung, C.Y.; Kim, R.Y. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heier, J.S.; Khanani, A.M.; Quezada Ruiz, C.; Basu, K.; Ferrone, P.J.; Brittain, C.; Figueroa, M.S.; Lin, H.; Holz, F.G.; Patel, V.; et al. Efficacy, durability, and safety of intravitreal faricimab up to every 16 weeks for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (TENAYA and LUCERNE): Two randomised, double-masked, phase 3, non-inferiority trials. Lancet 2022, 399, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Shi, F.; Cai, M.; Wu, Y. Conbercept Treatment for Heart-Shaped Vascular Intertwined Nets in Macular Neovascularization: Anti-VEGF Drug Therapy Strategy Based on Vascular Geometry Diagnosed by OCTA. Clin. Case Rep. 2025, 13, e71250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Finkelstein, E.; Lee, J.J.; Too, I.H.K.; Teo, K.Y.C.; Tan, A.C.S.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheung, G.C.M. Understanding patient preferences in anti-VEGF treatment options for age-related macular degeneration. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, P.K.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, M.S.; Holz, F.G. Anti–vascular endothelial growth factor biosimilars in ophthalmology. Retina 2022, 42, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kondo, M.; Iwahashi, C.; Parachuri, N.; Kumar, N.; Bandello, F.; Loewenstein, A.; Kuppermann, B.D. Approved biosimilar ranibizumab—A global update. Eye 2023, 37, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.J.; Veith, M.; Hamouz, J.; Ernest, J.; Zalewski, D.; Studnicka, J.; Vajas, A.; Papp, A.; Gabor, V.; Luu, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Proposed Ranibizumab Biosimilar Product vs a Reference Ranibizumab Product for Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021, 139, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodeller, F.; Alliger, P.; Heyn, J.; Urosevic, D.; Allmannsberger, L.; Wersig, C.; Silva, R. Development of Biosimilar Aflibercept SDZ-AFL. Curr. Ther. Res. 2025, 103, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.K.; Oh, J.; Bae, K.; Park, U.C.; Yu, K.-S.; Yu, H.G. Efficacy and safety of a new ranibizumab biosimilar CKD-701 using a pro re nata treatment regimen in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A phase 3 randomized clinical trial. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, N.M.; Veith, M.; Hamouz, J.; Ernest, J.; Zalewski, D.; Studnička, J.; Vajas, A.; Papp, A.; Vogt, G.; Luu, J.; et al. Biosimilar SB11 versus reference ranibizumab in neovascular age-related macular degeneration: 1-year phase III randomised clinical trial outcomes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, L.M.; DeLeon-Ortega, J.; Sakata, V.; Girkin, C.A. Optical coherence tomography of the retina and optic nerve–a review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.B.; Wheat, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.; Tran, V.; Harwerth, R.S. Agreement between retinal nerve fiber layer measures from Spectralis and Cirrus spectral domain OCT. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, E652–E666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, G.; Hwang, D.D.-J. Long-Term Effect of Intravitreal Brolucizumab Injections on Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Patients with Refractory Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy. J. Retin. 2024, 9, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.Y.; Hwang, D.D.-J. Short-term effect of intravitreal brolucizumab injections in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Damico, L.; Shams, N.; Lowman, H.; Kim, R. Development of ranibizumab, an anti–vascular endothelial growth factor antigen binding fragment, as therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2006, 26, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, B.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.-Y. Twenty Years of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapeutics in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Kim, J.H. Short-term Anatomical Outcomes of Switching from Bevacizumab to the Ranibizumab Biosimilar CKD-701 in Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration. J. Retin. 2024, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Hirayama, K.; Kyo, A.; Misawa, N.; Kinari, G.; Kohno, T.; Honda, S. One-year outcome of intravitreal injection of ranibizumab biosimilar for myopic choroidal neovascularization in Japanese patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Saenz-Frances, F.; Reche-Frutos, J.; Calvo-Gonzalez, C.; Donate-Lopez, J.; Garcia-Feijoo, J. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Changes in Patients with Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treated with Intravitreal Ranibizumab. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6214–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde-Megías, A.; Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Murciano-Cespedosa, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, S.; Martínez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; García-Feijoo, J. Long-term effect of intravitreal ranibizumab therapy on retinal nerve fiber layer in eyes with exudative age-related macular degeneration. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Swaminathan, S.S.; Yang, J.; Barikian, A.; Shi, Y.; Shen, M.; Jiang, X.; Feuer, W.; Gregori, G.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Dose-Response Relationship between Intravitreal Injections and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thinning in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2021, 5, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondell, M.; Lundborg, G.; Kanje, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Has Neurotrophic Activity and Stimulates Axonal Outgrowth, Enhancing Cell Survival and Schwann Cell Proliferation in the Peripheral Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, K.; Ng, Y.-S.; Zhong, L.; Bradley, J.; Schubert, W.; Jo, N.; Akita, J.; Samuelsson, S.J.; Robinson, G.S.; Adamis, A.P.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Is a Survival Factor for Retinal Neurons and a Critical Neuroprotectant during the Adaptive Response to Ischemic Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachary, I. Neuroprotective Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor: Signalling Mechanisms, Biological Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, F.A.; Alencar, L.M.; Zangwill, L.M.; Sample, P.A.; Weinreb, R.N. The relationship between intraocular pressure and progressive retinal nerve fiber layer loss in glaucoma. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 1125–1133.E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.-N.; Chung, H.; Kim, T.-E.; Kim, H.C. Intravitreal anti–vascular endothelial growth factor therapy and retinal nerve fiber layer loss in eyes with age-related macular degeneration: A meta-analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.C.; Chen, C.-L.; Rezaei, K.A.; Chao, J.R.; Vemulakonda, A.; Luttrell, I.; Wang, R.K.; Chen, P.P. Optic nerve head perfusion before and after intravitreal antivascular growth factor injections using optical coherence tomography-based microangiography. J. Glaucoma 2019, 28, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheilian, M.; Karimi, S.; Montahae, T.; Nikkhah, H.; Mosavi, S.A. Effects of intravitreal injection of bevacizumab with or without anterior chamber paracentesis on intraocular pressure and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness: A prospective study. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Shin, K.C.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Change of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Various Retinal Diseases Treated with Multiple Intravitreal Antivascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Jang, K.; Sohn, J.; Park, J.I.; Hwang, D.D.-J. Effect of intravitreal ranibizumab and aflibercept injections on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, R.; Jiang, W.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Mao, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, P.; Shi, M. Effects of anti-VEGF on peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer and papillary/peripapillary blood circulation in retinopathies (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 56, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.S.; Kunkler, A.L.; Quan, A.V.; Medert, C.M.; Vanner, E.A.; Feuer, W.; Chang, T.C. Rates of RNFL thinning in patients with suspected or confirmed glaucoma receiving unilateral intravitreal injections for exudative AMD. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 226, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltz, A.; Spöttl, T.; Huf, W.; Weingessel, B.; Vécsei-Marlovits, V.P. Effect of intravitreal injections due to neovascular age-related macular degeneration on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and minimum rim width: A cross sectional study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024, 24, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, M.; Radosavljevic, A.; Zlatanovic, M.; Jaksic, V.; Davidovic, S.; Stamenkovic, M.; Todorovic, I.; Jaksic, J. Influence of Multiple Anti-VEGF Injections on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Ganglion Cell-Inner Plexiform Layer Thickness in Patients with Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Medicina 2023, 59, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Sim, H.E.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Chang, I.B.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, J.H. Changes in inner retinal layer thickness in patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration during treatment with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor. Medicine 2020, 99, e19955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichrowska, M.; Goździewska, E.; Kocięcki, J. The Safety of Anti-VEGF Treatment, in the Context of the Retinal Nerve Fibre Layer, in Patients with Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Review. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2023, 28, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, K.; Fraser-Bell, S.; Hong, T.; Phan, L.; Wong, J.G.; Chang, A. Long-term anti–vascular endothelial growth factor treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: The LATAR study: Report 1: Ten-year, real-world outcomes. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2021, 5, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rofagha, S.; Bhisitkul, R.B.; Boyer, D.S.; Sadda, S.R.; Zhang, K.; Group, S.-U.S. Seven-year outcomes in ranibizumab-treated patients in ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON: A multicenter cohort study (SEVEN-UP). Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, M.G.; Martin, D.F.; Ying, G.-S.; Jaffe, G.J.; Daniel, E.; Grunwald, J.E.; Toth, C.A.; Ferris, F.L., III; Fine, S.L. Five-year outcomes with anti–vascular endothelial growth factor treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration: The comparison of age-related macular degeneration treatments trials. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.W.; Kim, D.I.; Hwang, D.D. The effect of intravitreal brolucizumab on choroidal thickness in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| No. of patients | 24 |
| Sex, male–female | 13:11 |
| Age of the first ranibizumab biosimilar injection (years) | 74.62 ± 8.99 (range, 55–90) |
| Type of AMD (n %), PCV–typical AMD–RAP | 2 (8.3):21 (87.5):1 (4.2) |
| Laterality, OD:OS | 8:16 |
| Systemic disease | |
| Hypertension (n) | 16 |
| Diabetes (n) | 8 |
| No. of previous anti-VEGF injections | 14.67 ± 15.40 (range, 3–74) |
| Corrective visual acuity (logMAR) | 0.83 ± 0.66 (range, 0.00–2.00) |
| Refractive error (SE) | −0.12 ± 1.06 (range, −2.875–+1.50) |
| IOP (mmHg) | 14.88 ± 2.80 (range, 9–20) |
| Baseline | 1st Injection | 2nd Injection | 3rd Injection | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | 105.58 ± 14.34 | 105.58 ± 13.91 | 110.47 ± 14.28 | 108.44 ± 17.76 |
| (0.981) | (0.639) | (0.608) | ||
| Temporal | 84.88 ± 15.15 | 84.46 ± 14.27 | 87.53 ± 13.40 | 83.22 ± 14.21 |
| (0.294) | (0.692) | (0.610) | ||
| Superior temporal | 137.92 ± 22.82 | 137.13 ± 22.54 | 143.40 ± 25.86 | 143.22 ± 31.78 |
| (0.419) | (0.432) | (0.348) | ||
| Superior nasal | 117.67 ± 19.21 | 117.71 ± 18.88 | 122.80 ± 21.78 | 128.33 ± 24.88 |
| (0.671) | (0.306) | (0.526) | ||
| Nasal | 76.92 ± 15.37 | 77.42 ± 15.57 | 81.33 ± 14.44 | 83.67 ± 17.94 |
| (0.835) | (0.861) | (0.674) | ||
| Inferior nasal | 118.42 ± 25.39 | 118.29 ± 24.82 | 126.73 ± 23.98 | 120.22 ± 29.97 |
| (0.700) | (0.624) | (0.905) | ||
| Inferior temporal | 147.38 ± 23.77 | 147.63 ± 23.56 | 154.13 ± 25.91 | 142.33 ± 23.51 |
| (0.749) | (0.555) | (0.261) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.Y.; Hwang, D.D.-J. Short-Term Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Biosimilar Injections in Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228225
Lee SY, Hwang DD-J. Short-Term Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Biosimilar Injections in Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung Yeon, and Daniel Duck-Jin Hwang. 2025. "Short-Term Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Biosimilar Injections in Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228225
APA StyleLee, S. Y., & Hwang, D. D.-J. (2025). Short-Term Effects of Intravitreal Ranibizumab Biosimilar Injections in Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228225






