Future Risk After Achieving Clinical Remission in Patients with Severe Asthma: A Comparison of Different Definitions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Definition of Asthma Exacerbation
2.5. Definitions of Clinical Remission
- ♦
- Four-component definitions
- ♦
- Three-component definition
- -
- CR(ACT≥23): no annual exacerbations + no OCS use + ACT ≥ 23 [21]
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Enrolled Patients
3.2. Changes in Clinical Parameters for Assessing CR from Baseline to T24
3.3. Proportion of Patients Achieving CR at T12
3.4. Proportion of CR and Sustained CR at T24 According to Each Definition
3.5. Comparison of CR Definitions for Predicting Exacerbations Between T12 and T24 After Achievement of CR at T12
3.6. Annual FEV1 Change Between T12 and T24 in CR-Positive and CR-Negative Patients at T12
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACQ | Asthma Control Questionnaire |
| ACT | Asthma Control Test |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CR | clinical remission |
| ERS | European Respiratory Society |
| FeNO | Fractional exhaled nitric oxide |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| GETE | Global Evaluation of Treatment Effectiveness |
| GINA | Global Initiative for Asthma |
| ICS | inhaled corticosteroid |
| IgE | total immunoglobulin E |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| JRS | Japanese Respiratory Society |
| LABA | long-acting β-agonist |
| LAMA | long-acting muscarinic antagonist |
| LTRA | leukotriene receptor antagonist |
| NERD | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs exacerbated respiratory disease |
| OCS | oral corticosteroid |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PEF | peak expiratory flow |
| ppb | parts per billion |
| QOL | quality of life |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| SD | standard deviation |
| T0 | baseline |
| T12 | 12 months |
| T24 | 24 months |
| %FEV1 | FEV1% predicted |
References
- Nagase, H.; Adachi, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Yoshida, A.; Okoba, T.; Hayashi, N.; Emoto, K.; Tohda, Y. Prevalence, disease burden, and treatment reality of patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma in Japan. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Woolcock, A.J. Difficult asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Banks-Schlegel, S.; Wenzel, S.E. Pathophysiology of severe asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; Naji, N.; Gauvreau, G.M. Severe asthma: Future treatments. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleecker, E.R.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chanez, P.; Papi, A.; Weinstein, S.F.; Barker, P.; Sproule, S.; Gilmartin, G.; Aurivillius, M.; Werkstrom, V.; et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta(2)-agonists (SIROCCO): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Gurnell, M.; Heaney, L.G.; Corren, J.; Bel, E.H.; Maspero, J.; Harrison, T.; Jackson, D.J.; Price, D.; Lugogo, N.; et al. Oral corticosteroid elimination via a personalised reduction algorithm in adults with severe, eosinophlic asthma treated with benralizumab (PONENTE): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Bafadhel, M.; Busse, W.W.; Casale, T.B.; Kocks, J.W.H.; Pavord, I.D.; Szefler, S.J.; Woodruff, P.G.; de Giorgio-Miller, A.; Trudo, F.; et al. An expert consensus framework for asthma remission as a treatment goal. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canonica, G.W.; Blasi, F.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Guida, G.; Heffler, E.; Paggiaro, P.; Allegrini, C.; Antonelli, A.; Aruanno, A.; Bacci, E.; et al. Severe Asthma Network Italy Definition of Clinical Remission in Severe Asthma: A Delphi Consensus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 3629–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaiss, M.; Oppenheimer, J.; Corbett, M.; Bacharier, L.; Bernstein, J.; Carr, T.; Chipps, B.; Couillard, S.; Forno, E.; Grant, T.; et al. Consensus of an American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, and American Thoracic Society workgroup on definition of clinical remission in asthma on treatment. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 131, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Criee, C.P.; de Jong, C.C.M.; Gappa, M.; Gessner, C.; Gerstlauer, M.; Hamalainen, N.; Haidl, P.; Hamelmann, E.; Horak, F.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of asthma: A guideline for respiratory specialists 2023—Published by the German Respiratory Society (DGP) e. V. Pneumologie 2023, 77, 461–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; McDonald, V.M.; Stevens, S.; Harvey, E.S.; Baraket, M.; Bardin, P.; Bowden, J.J.; Bowler, S.; Chien, J.; Chung, L.P.; et al. Biologics (mepolizumab and omalizumab) induced remission in severe asthma patients. Allergy 2024, 79, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavord, I.; Gardiner, F.; Heaney, L.G.; Domingo, C.; Price, R.G.; Pullan, A.; Oppenheimer, J.; Brusselle, G.; Nagase, H.; Chupp, G.; et al. Remission outcomes in severe eosinophilic asthma with mepolizumab therapy: Analysis of the REDES study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1150162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.F.; Wenzel, S.E.; Brozek, J.L.; Bush, A.; Castro, M.; Sterk, P.J.; Adcock, I.M.; Bateman, E.D.; Bel, E.H.; Bleecker, E.R.; et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.A.; Sorkness, C.A.; Kosinski, M.; Schatz, M.; Li, J.T.; Marcus, P.; Murray, J.J.; Pendergraft, T.B. Development of the asthma control test: A survey for assessing asthma control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, K. An official JRS statement: The principles of fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) measurement and interpretation of the results in clinical practice. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic, S.; European Respiratory, S. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddel, H.K.; Taylor, D.R.; Bateman, E.D.; Boulet, L.P.; Boushey, H.A.; Busse, W.W.; Casale, T.B.; Chanez, P.; Enright, P.L.; Gibson, P.G.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Asthma control and exacerbations: Standardizing endpoints for clinical asthma trials and clinical practice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 59–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milger, K.; Suhling, H.; Skowasch, D.; Holtdirk, A.; Kneidinger, N.; Behr, J.; Timmermann, H.; Schulz, C.; Schmidt, O.; Ehmann, R.; et al. Response to Biologics and Clinical Remission in the Adult German Asthma Net Severe Asthma Registry Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 2701–2712.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basagana, M.; Martinez-Rivera, C.; Padro, C.; Garcia-Olive, I.; Martinez-Colls, M.; Navarro, J.; Pardo, L.; Cruz, P.; Cardona Peitx, G.; Carabias, L.; et al. Clinical characteristics of complete responders versus non-complete responders to omalizumab, benralizumab and mepolizumab in patients with severe asthma: A long-term retrospective analysis. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2317356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaoki, J.; Nagase, H.; Sano, H.; Kaneko, T.; Gon, Y.; Miyahara, N.; Sagara, H.; Tanaka, A.; Horiguchi, T.; Tagaya, E.; et al. Practical Guidelines for Asthma Management (PGAM): Digest edition. Respir. Investig. 2025, 63, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J. Persistency of response to omalizumab therapy in severe allergic (IgE-mediated) asthma. Allergy 2011, 66, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelo, G.; Tran, T.N.; Le, T.T.; Fageras, M.; Dorscheid, D.; Busby, J.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Al-Lehebi, R.; Altraja, A.; Beastall, A.; et al. Exploring Definitions and Predictors of Response to Biologics for Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2024. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/GINA-2024-Strategy-Report-24_05_22_WMS.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Niimi, A.; Fukunaga, K.; Taniguchi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Tagaya, E.; Horiguchi, T.; Yokoyama, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nagata, M. Executive summary: Japanese guidelines for adult asthma (JGL) 2021. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, A.; Hoyte, F.L.; Price, D.B.; Cohen, D.; Barker, P.; Kreindler, J.; Jison, M.; Brooks, C.L.; Papeleu, P.; Katial, R. Clinical Remission in Severe Asthma: A Pooled Post Hoc Analysis of the Patient Journey with Benralizumab. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 2065–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleford, A.; Heaney, L.G.; Redmond, C.; McDowell, P.J.; Busby, J. Clinical remission attainment, definitions, and correlates among patients with severe asthma treated with biologics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 13, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-de-Llano, L.; Scelo, G.; Tran, T.N.; Le, T.T.; Fageras, M.; Cosio, B.G.; Peters, M.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Al-Lehebi, R.O.; et al. Exploring Definitions and Predictors of Severe Asthma Clinical Remission after Biologic Treatment in Adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimi, C.; Nolasco, S.; Noto, A.; Maglio, A.; Quaranta, V.N.; Di Bona, D.; Scioscia, G.; Papia, F.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Calabrese, C.; et al. Long-Term Clinical and Sustained REMIssion in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma Treated With Mepolizumab: The REMI-M Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 3315–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, S. Super-responder and clinical remission in patients with asthma on treatment with single biologic therapy or cycling therapy using dupilumab in a real-world setting. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 62, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslavsky, A. Comparison of clinical remission criteria for severe asthma patients receiving biologic therapy. Respir. Med. 2024, 222, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Crimi, C.; Benfante, A.; Caiaffa, M.F.; Campisi, R.; Candia, C.; Carpagnano, G.E.; Carrieri, I.; D’Amato, M.; Detoraki, A.; et al. Sustained remission induced by 2 years of treatment with benralizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma and nasal polyposis. Respirology 2024, 29, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarato, C.M.I.; Tondo, P.; Lacedonia, D.; Soccio, P.; Pescatore, D.; Baccellieri, M.L.; Lepore, G.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Scioscia, G. Long-Term Clinical Remission on Benralizumab Treatment in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Four-Year Real-Life Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, L.; Bagnasco, D.; Beghe, B.; Braido, F.; Cameli, P.; Caminati, M.; Caruso, C.; Crimi, C.; Guarnieri, G.; Latorre, M.; et al. Unlocking the Long-Term Effectiveness of Benralizumab in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: A Three-Year Real-Life Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarato, C.M.I.; Tondo, P.; Lacedonia, D.; Soccio, P.; Fuso, P.; Sabato, E.; Hoxhallari, A.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Scioscia, G. Clinical Remission in Patients Affected by Severe Eosinophilic Asthma on Dupilumab Therapy: A Long-Term Real-Life Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
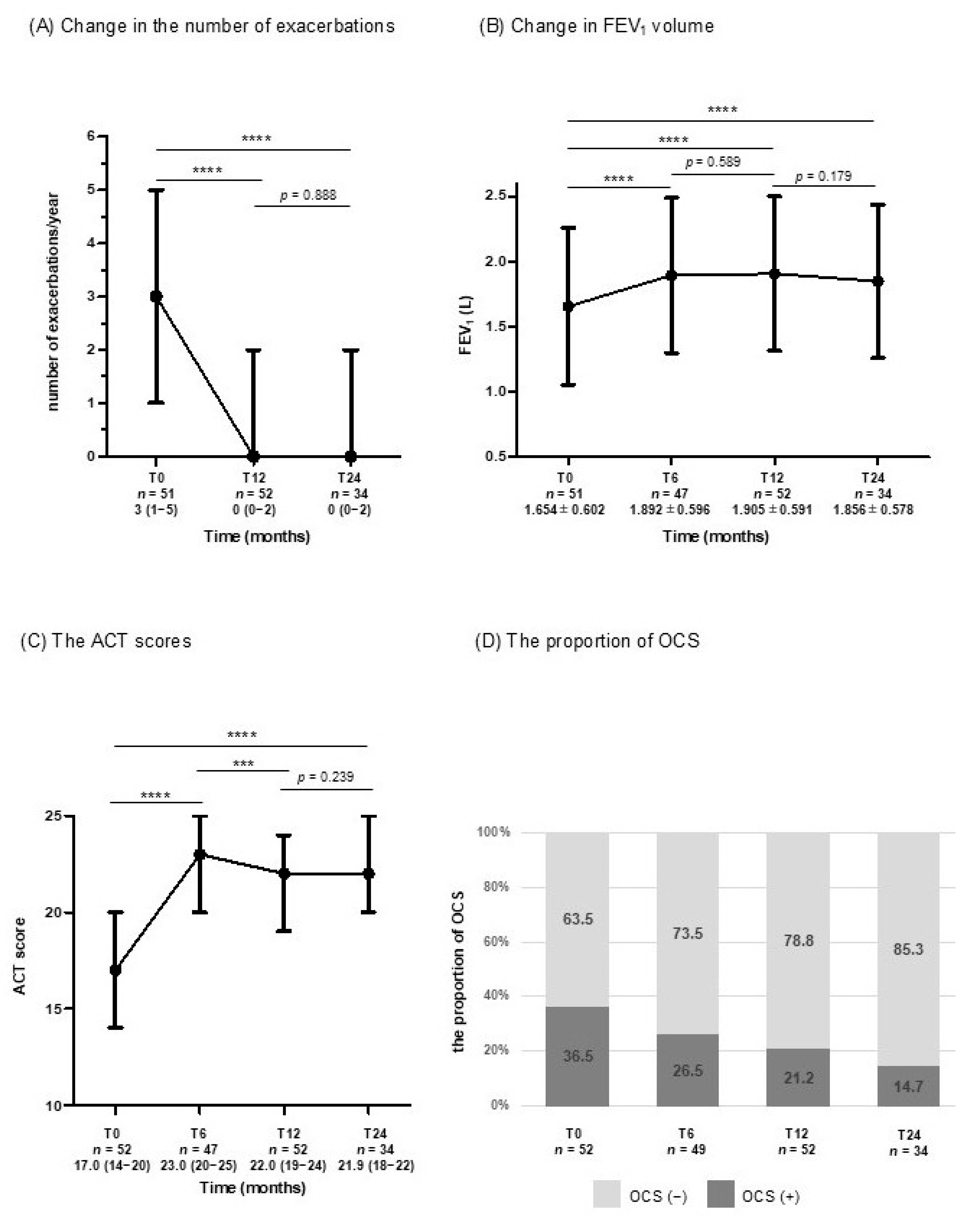
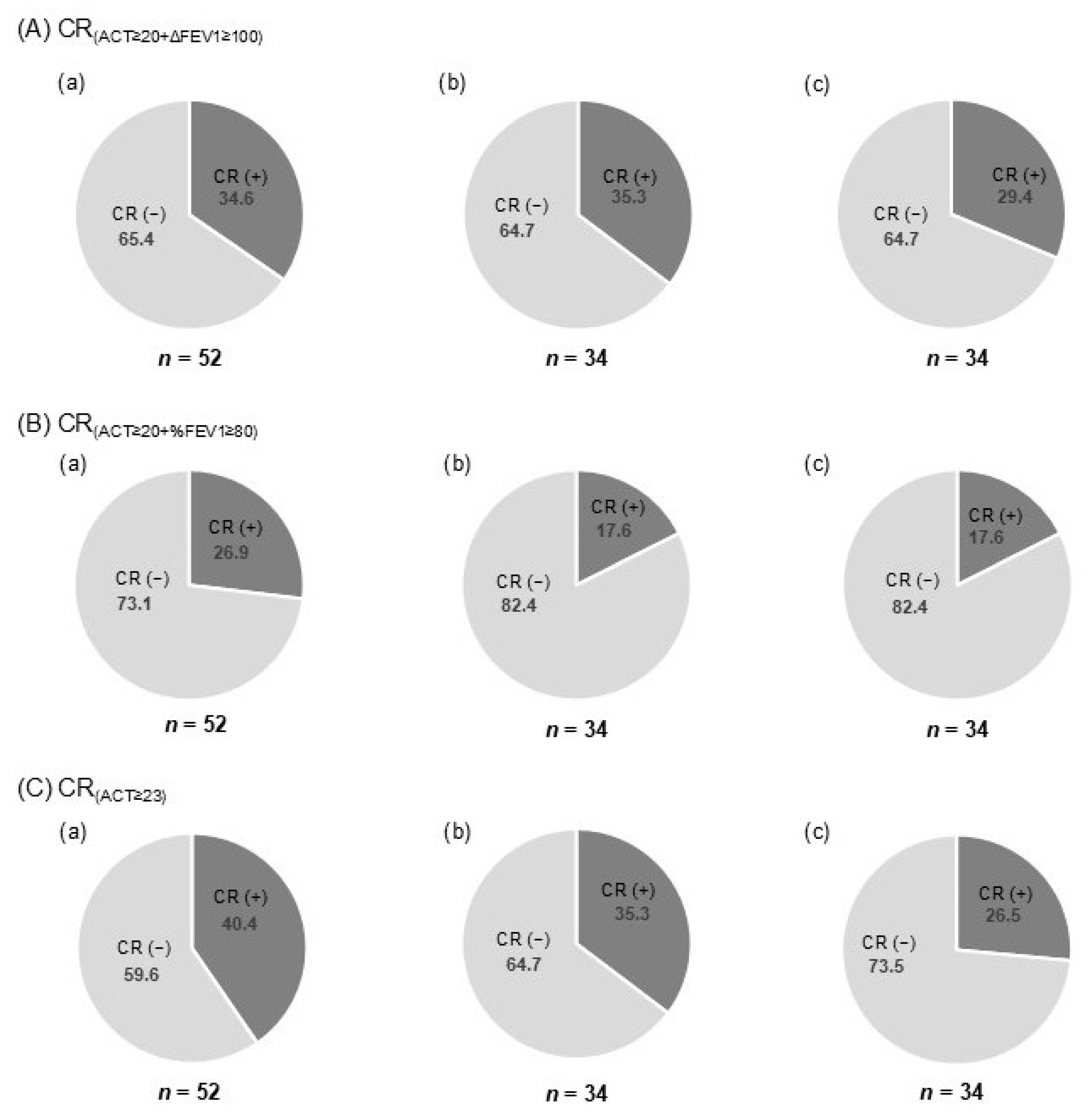
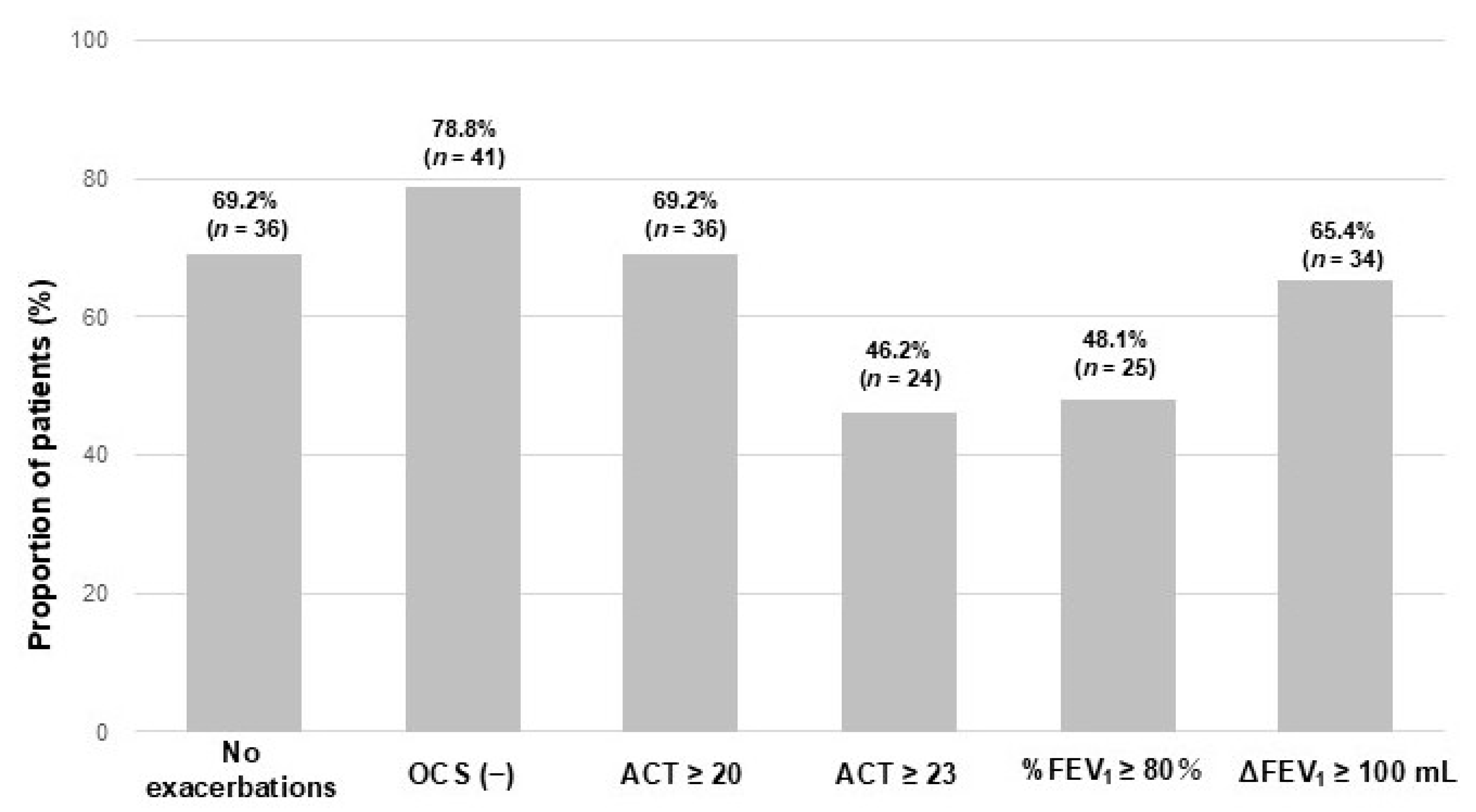
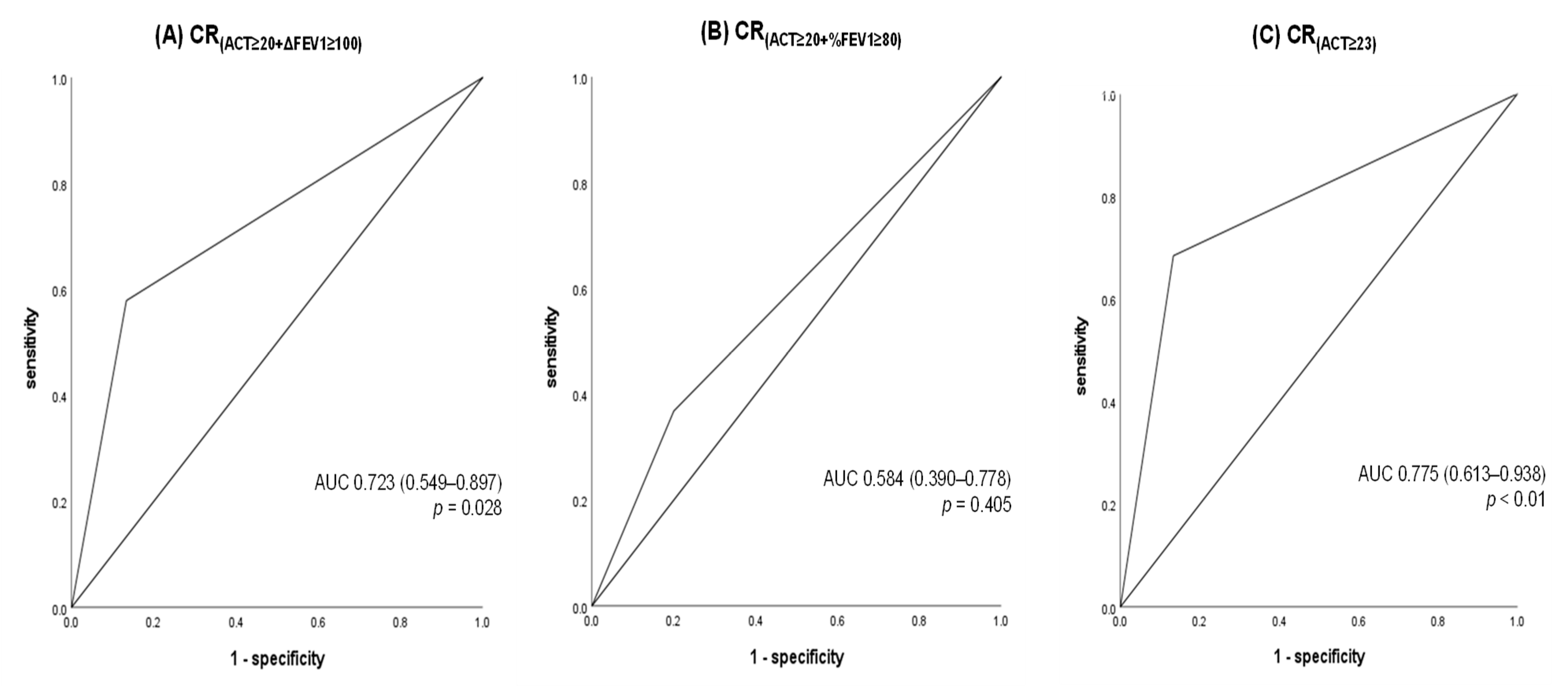

| Total Population (n = 52) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63 (55–69) |
| Sex (male/female), n (%) | 24 (46.2)/28 (53.8) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.3 (21.5–29.6) |
| Duration of asthma (years) | 15 (9–21) |
| Smoking history (never/former/current), n (%) | 34 (65.4)/16 (30.8)/2 (3.8) |
| Exacerbations in the past year | 3.0 (1.0–5.0) |
| Blood eosinophils (/μL) | 436.0 (125.3–748.5) |
| Blood IgE (IU/mL) | 367.0 (153.0–708.0) |
| Sputum eosinophils (%) | 48.0 (11.0–71.7) |
| Sputum neutrophils (%) | 31.4 (6.1–49.0) |
| FeNO (ppb) | 71.0 (36.9–126.1) |
| FEV1 (L) | 1.53 (1.21–1.98) |
| FEV1/FVC ratio (%) | 60.8 (50.5–71.6) |
| FEV1% predicted | 67.5 (49.7–80.9) |
| ACT score (points) | 17 (14–20) |
| Initial treatments | |
| - ICS/LABA, n (%) | 52 (100) |
| - ICS dose (fluticasone equivalent), µg/day | 1000 (640–1400) |
| - LAMA, n (%) | 37 (71.2) |
| - LTRA, n (%) | 43 (82.7) |
| - Omalizumab, n (%) | 18 (34.6) |
| - Mepolizumab or Benralizumab, n (%) | 17 (32.7) |
| - Dupilumab, n (%) | 17 (32.7) |
| - Xanthine derivatives, n (%) | 34 (65.4) |
| - Maintenance OCS therapy, n (%) | 19 (36.5) |
| - OCS daily dose, mg/day | 0.0 (0.0–5.0) |
| Previous biologics | |
| - Omalizumab, n (%) | 8 (15.4) |
| - Mepolizumab or Benralizumab, n (%) | 7 (13.5) |
| - Dupilumab, n (%) | 0 (0.0) |
| Comorbidities | |
| - Childhood asthma, n (%) | 5 (9.6) |
| - Allergic rhinitis, n (%) | 35 (67.3) |
| - Chronic rhinosinusitis, n (%) | 22 (42.3) |
| - Atopic dermatitis, n (%) | 3 (5.8) |
| - Allergic conjunctivitis, n (%) | 8 (15.4) |
| - Anxiety/depression, n (%) | 4 (7.7) |
| - NERD, n (%) | 3 (5.8) |
| (A) no annual exacerbations + no OCS use + ACT ≥ 20 + ΔFEV1 ≥ 100 mL from baseline | |||
| Exacerbations (+) | Exacerbations (−) | Total | |
| Clinical remission at 12 months (+) | 2 | 11 | 13 |
| Clinical remission at 12 months (−) | 13 | 8 | 21 |
| Total | 15 | 19 | 34 |
| OR = 0.112, p = 0.013 | |||
| (B) no annual exacerbations + no OCS use + ACT ≥ 20 + FEV1% predicted ≥ 80% | |||
| Exacerbations (+) | Exacerbations (−) | Total | |
| Clinical remission at 12 months (+) | 3 | 7 | 10 |
| Clinical remission at 12 months (−) | 12 | 12 | 24 |
| Total | 15 | 19 | 34 |
| p = 0.451 | |||
| (C) no annual exacerbations + no OCS use + ACT ≥ 23 | |||
| Exacerbations (+) | Exacerbations (−) | Total | |
| Clinical remission at 12 months (+) | 2 | 13 | 15 |
| Clinical remission at 12 months (−) | 13 | 6 | 19 |
| Total | 15 | 19 | 34 |
| OR = 0.071, p = 0.002 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rikimaru, M.; Saito, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Sato, S.; Fukuhara, A.; Yamada, R.; Shibata, Y. Future Risk After Achieving Clinical Remission in Patients with Severe Asthma: A Comparison of Different Definitions. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228201
Rikimaru M, Saito J, Suzuki Y, Kikuchi M, Sato S, Fukuhara A, Yamada R, Shibata Y. Future Risk After Achieving Clinical Remission in Patients with Severe Asthma: A Comparison of Different Definitions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228201
Chicago/Turabian StyleRikimaru, Mami, Junpei Saito, Yasuhito Suzuki, Masami Kikuchi, Suguru Sato, Atsuro Fukuhara, Ryuki Yamada, and Yoko Shibata. 2025. "Future Risk After Achieving Clinical Remission in Patients with Severe Asthma: A Comparison of Different Definitions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228201
APA StyleRikimaru, M., Saito, J., Suzuki, Y., Kikuchi, M., Sato, S., Fukuhara, A., Yamada, R., & Shibata, Y. (2025). Future Risk After Achieving Clinical Remission in Patients with Severe Asthma: A Comparison of Different Definitions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8201. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228201






