Integrating Computational Modelling into the Ecosystem of Cochlear Implantation: Advancing Access to Diagnostics, Decision-Making, and Post-Implantation Outcomes on a Global Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cochlear Implants Are Not Generally Accessible
3. Computational Models as a Solution?
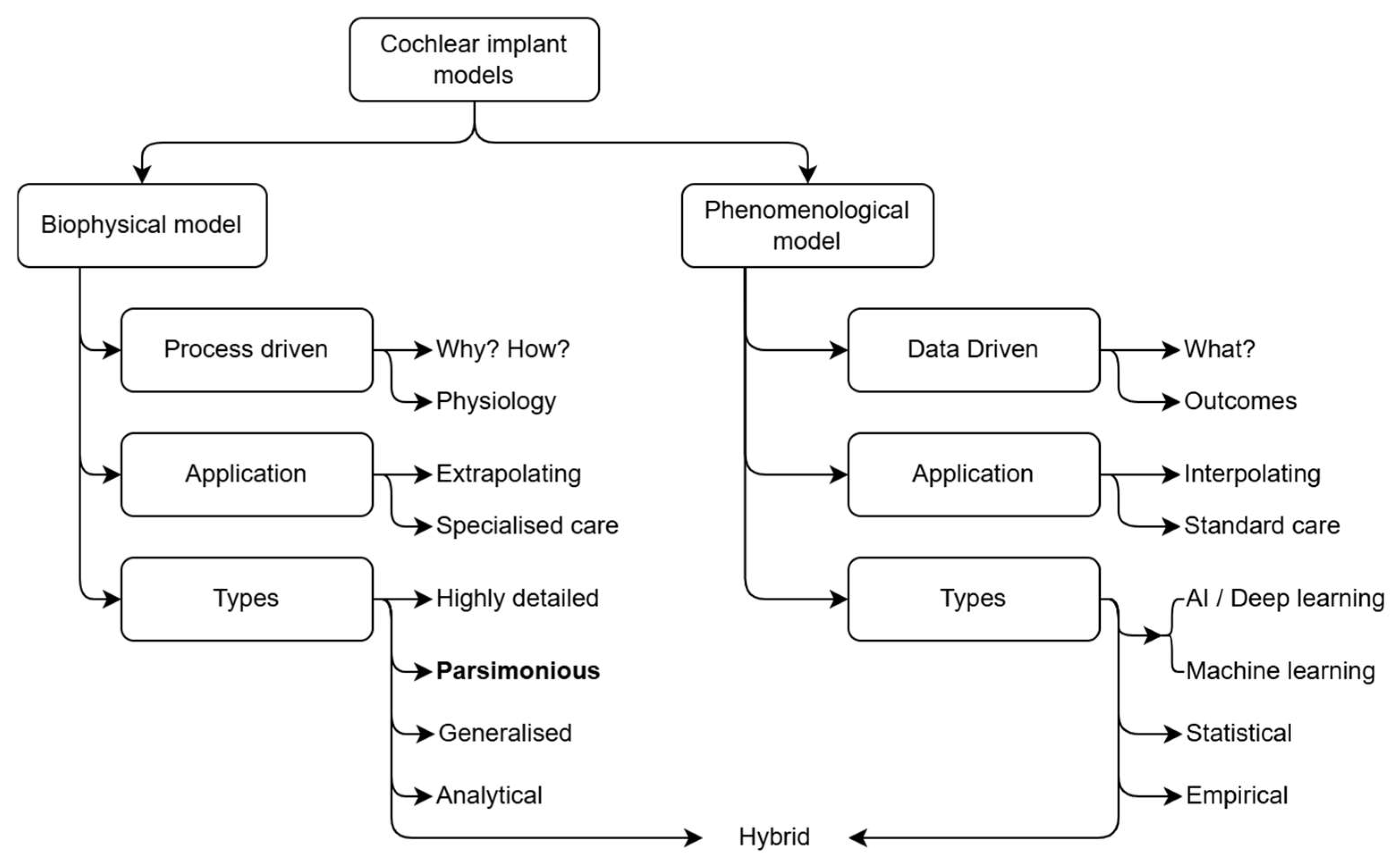
4. The Present Adoption of Biophysical Modelling in Clinical Care Protocols
5. Perspective
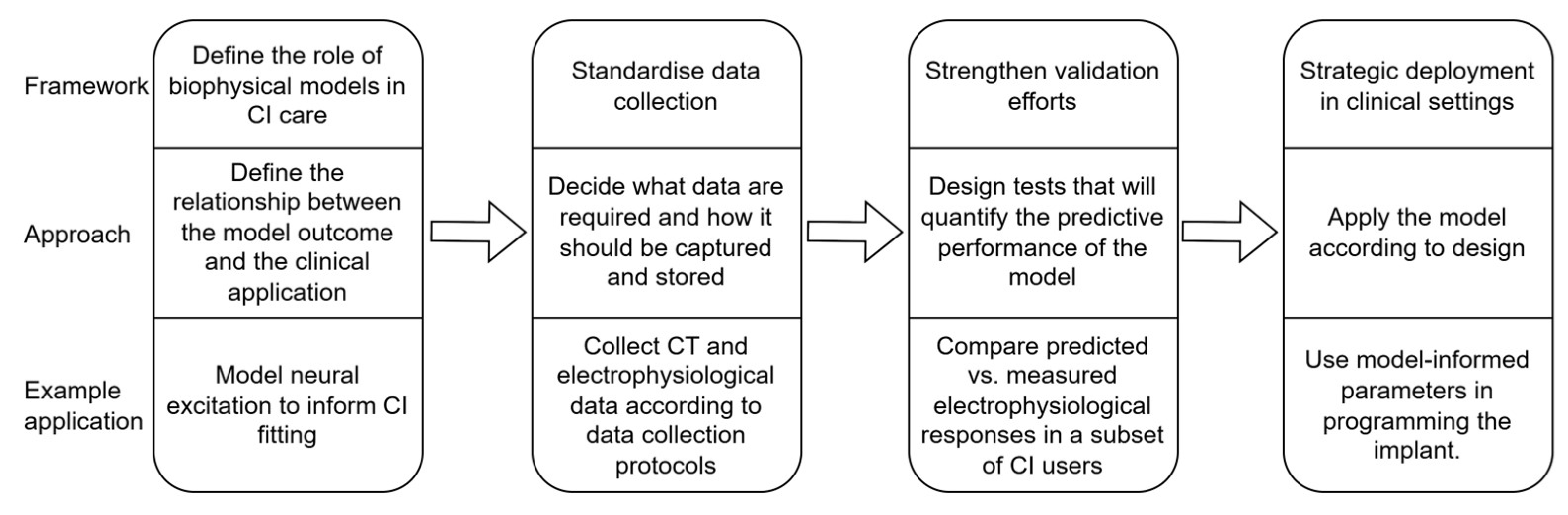
5.1. Defining and Articulating the Role of Biophysical Models in Clinical Care
5.2. Purposeful Data Collection
5.3. Validation of Biophysiological Models
5.4. Strategic Deployment of Models
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CBCT | Cone-beam computed tomography |
| CI | Cochlear implant |
| DR | Dynamic range |
| ECAP | Electrically evoked compound action potential |
| FNS | Facial nerve stimulation |
| FOX | Fitting to outcomes eXpert |
| LMICs | Low- and middle-income countries |
| NAS | Non-auditory stimulation |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
References
- Fagan, J.J.; Tarabichi, M. Cochlear Implants in Developing Countries: Practical and Ethical Considerations. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.H.; McMahon, C.M.; Waterworth, C.J.; Morton, S.N.; Platt, A.C.; Chadha, S.H.; Xu, M.J.; Der, C.M.; Nakku, D.; Seguya, A. Access to Ear and Hearing Care Globally: A Survey of Stakeholder Perceptions from the Lancet Commission on Global Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2025, 46, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Carlson, M.L. Cochlear Implantation in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele Okuba, T.; Lystad, R.P.; Boisvert, I.; McMaugh, A.; Moore, R.C.; Walsan, R.; Mitchell, R.J. Cochlear Implantation Impact on Health Service Utilisation and Social Outcomes: A Systematic Review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, G.; Tuomi, S.; Müller, A. Costs Involved in Using a Cochlear Implant in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Commun. Disord. 2012, 59, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulwafu, W.; Chabaluka, C.; Anderson, I.; Strachan, D.; Raine, C. Development of a Cochlear Implantation Program in Malawi: Audiometric and Speech Perception Results From a Series of Implantees. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 2025, 172, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanekom, T.; Hanekom, J.; Badenhorst, W.; Baron, R.; Le Roux, T.; Uys, A. A Tailored and Transdisciplinary Approach to Cochlear Implants. In Updates on Hearing Loss and Its Rehabilitation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.; Melin, S.; Doerfer, K.; Moberly, A.C.; Harris, M.S. Auditory Rehabilitation Following Cochlear Implantation. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2024, 12, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Madiseh, A.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Bennett, R.J.; Upson, G.S.; Friedland, P.; Swanepoel, D.W.; Atlas, M.D. Factors Influencing Postoperative Experiences in Adult Cochlear Implant Recipients: A Multistakeholder Perspective. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, L.M.; Calvino, M.; Sánchez-Cuadrado, I.; Danesi, G.; Patelli, I.; Zana, M.; Ruiz de Erenchun-Lasa, Í.; del Carmen Zapata, M.; Muñoz Yuste, E.M.; Schaudel, D. Evaluation of Remote Programming of Cochlear Implants under Challenging Conditions; Evaluación de La Programación Remota de Implantes Cocleares En Condiciones Difíciles. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2025, 76, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathour, J.; Govaerts, P.J.; Lacroix, E.; Naïma, D. Effect of a CI Programming Fitting Tool with Artificial Intelligence in Experienced Cochlear Implant Patients. Otol. Neurotol. 2023, 44, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathour, J.; Govaerts, P.J.; Derue, L.; Vanderbemden, S.; Huaux, H.; Lacroix, E.; Deggouj, N. Prospective Comparison between Manual and Computer-Assisted (FOX) Cochlear Implant Fitting in Newly Implanted Patients. Ear Hear. 2023, 44, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaerenberg, B.; Govaerts, P.J.; De Ceulaer, G.; Daemers, K.; Schauwers, K. Experiences of the Use of FOX, an Intelligent Agent, for Programming Cochlear Implant Sound Processors in New Users. Int. J. Audiol. 2010, 50, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthurkkara, S.; Bennett, C. Development of Custom Sound® Pro Software Utilising Big Data and Its Clinical Evaluation. Int. J. Audiol. 2024, 63, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangchuk, P.; Umat, C.; Chong, F.Y.; Mohd-Zaki, F.; Abdullah, A. Speech Perception Outcomes with the Anatomy-Based Fitting Map among Experienced, Adult Cochlear Implant Users: A Longitudinal Study. Audiol. Neurotol. 2025, 30, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, M.W.; Dillon, M.T.; Buss, E.; Pillsbury, H.C.; Brown, K.D.; O’Connell, B.P. Validating a New Tablet-Based Tool in the Determination of Cochlear Implant Angular Insertion Depth. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Távora-Vieira, D.; Voola, M.; Kuthubutheen, J.; Friedland, P.; Gibson, D.; Acharya, A. Evaluation of the Performance of OTOPLAN-Based Cochlear Implant Electrode Array Selection: A Retrospective Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochier, T.; Schlittenlacher, J.; Roberts, I.; Goehring, T.; Jiang, C.; Vickers, D.; Bance, M. From Microphone to Phoneme: An End-to-End Computational Neural Model for Predicting Speech Perception with Cochlear Implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 3300–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essaid, B.; Kheddar, H.; Batel, N.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Lakas, A. Artificial Intelligence for Cochlear Implants: Review of Strategies, Challenges, and Perspectives. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 119015–119038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Robles, J.A. Advances and Challenges in the Development of Visual Prostheses. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, E.; Harris, M. What Happens When a Bionic Body Part Becomes Obsolete?: Blind People with Second Sight’s Retinal Implants Found Out. IEEE Spectr. 2022, 59, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijns, J.H.M.; Briaire, J.J.; Schoonhoven, R. Integrated Use of Volume Conduction and Neural Models to Simulate the Response to Cochlear Implants. Simul. Pract. Theory 2000, 8, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girzon, G. Investigation of Current Flow in the Inner Ear During Electrical Stimulation of Intracochlear Electrodes. Master’s Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Thiselton, J.; Hanekom, T. Parameterisation and Prediction of Intra-Canal Cochlear Structures. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattay, F.; Leao, R.N.; Felix, H. A Model of the Electrically Excited Human Cochlear Neuron. II. Influence of the Three-Dimensional Cochlear Structure on Neural Excitability. Hear. Res. 2001, 153, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejón-Leblic, M.A.; Lazo-Maestre, M.; Fratter, A.; Ropero-Romero, F.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Reina-Tosina, J. A Full-Head Model to Investigate Intra and Extracochlear Electric Fields in Cochlear Implant Stimulation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 155010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Sue, A.; Wong, P.; Li, Q.; Carter, P. Development of HEATHER for Cochlear Implant Stimulation Using a New Modeling Workflow. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Encke, J.; Obando-Leitón, M.; Weiß, R.; Schäfer, F.; Eberharter, J.; Böhnke, F.; Hemmert, W. Electrical Stimulation in the Human Cochlea: A Computational Study Based on High-Resolution Micro-CT Scans. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Westhuizen, J.; Hanekom, T.; Hanekom, J.J. Apical Reference Stimulation: A Possible Solution to Facial Nerve Stimulation. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenhorst, W.; Hanekom, T.; Gross, L.; Hanekom, J.J. Facial Nerve Stimulation in a Post-Meningitic Cochlear Implant User: Using Computational Modelling as a Tool to Probe Mechanisms and Progression of Complications on a Case-by-Case Basis. Cochlear Implants Int. 2021, 22, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, W.; Schurzig, D.; Büchner, D.; Penninger, R.T.; Würfel, W. Validation of a Cochlear Implant Patient-Specific Model of the Voltage Distribution in a Clinical Setting. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Gil, M.; Ramos-De-Miguel, A.; Greiner, D.; Benítez, D.; Ramos-Macías, Á.M.; Escobar, J.M. A Computational Model for Multiobjective Optimization of Multipolar Stimulation in Cochlear Implants: An Enhanced Focusing Approach. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2025, 280, 127472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.T.M.; Hsu, C.H. Conditions for Generating Virtual Channels in Cochlear Prosthesis Systems. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 37, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rader, T.; Nachtigäller, P.; Linke, T.; Weißgerber, T.; Baumann, U. Exponential Fitting of Spread of Excitation Response Measurements in Cochlear Implants. J. Neurosci. Methods 2023, 391, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, F.; Kipping, D.; Nogueira, W. A Computational Model to Simulate Spectral Modulation and Speech Perception Experiments of Cochlear Implant Users. Front. Neuroinform 2023, 17, 934472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresa, M.; Mangado, N.; Andrews, R.J.; Gonzalez Ballester, M.A. Computational Models for Predicting Outcomes of Neuroprosthesis Implantation: The Case of Cochlear Implants. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, A.; Dwyer, R.T.; Noble, J.H. Evaluation of a High-Resolution Patient-Specific Model of the Electrically Stimulated Cochlea. J. Med. Imaging 2017, 4, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opstal, A.J.; Noordanus, E. Towards Personalized and Optimized Fitting of Cochlear Implants. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1183126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangado, N.; Pons-Prats, J.; Coma, M.; Mistrík, P.; Piella, G.; Ceresa, M.; Ballester, M.Á.G. Computational Evaluation of Cochlear Implant Surgery Outcomes Accounting for Uncertainty and Parameter Variability. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velde, H.M.; Rademaker, M.M.; Damen, J.A.A.; Smit, A.L.; Stegeman, I. Prediction Models for Clinical Outcome after Cochlear Implantation: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 137, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelmans, A.G.; Seinen, T.M.; Pera, V.; Markus, A.F.; Fridgeirsson, E.A.; John, L.H.; Schiphof-Godart, L.; Rijnbeek, P.R.; Reps, J.M.; Williams, R.D. Implementation and Updating of Clinical Prediction Models: A Systematic Review. Mayo Clin. Proc. Digit. Health 2025, 3, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanekom, T.; Hanekom, J.J. Three-Dimensional Models of Cochlear Implants: A Review of Their Development and How They could Support Management and Maintenance of Cochlear Implant Performance. Network 2016, 27, 67–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; George, S.; Tran, P.; Sue, A.; Carter, P.; Li, Q. Development and Validation of a High-Fidelity Finite-Element Model of Monopolar Stimulation in the Implanted Guinea Pig Cochlea. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malherbe, T.K.; Hanekom, T.; Hanekom, J.J. The Effect of the Resistive Properties of Bone on Neural Excitation and Electric Fields in Cochlear Implant Models. Hear. Res. 2015, 327, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frijns, J.H.M.; Kalkman, R.K.; Briaire, J.J. Stimulation of the Facial Nerve by Intracochlear Electrodes in Otosclerosis: A Computer Modeling Study. Otol. Neurotol. 2009, 30, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, G.; Nassif, N.; Redaelli de Zinis, L.O. Osteoneogenesis at the Round Window: A Possible Cause of Cochlear Implant Failure? Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiderski, D.L.; Colesa, D.J.; Hughes, A.P.; Raphael, Y.; Pfingst, B.E. Relationships between Intrascalar Tissue, Neuron Survival, and Cochlear Implant Function. JARO—J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2020, 21, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafieibavani, E.; Goudey, B.; Kiral, I.; Zhong, P.; Jimeno-Yepes, A.; Swan, A.; Gambhir, M.; Buechner, A.; Kludt, E.; Eikelboom, R.H.; et al. Predictive Models for Cochlear Implant Outcomes: Performance, Generalizability, and the Impact of Cohort Size. Trends Hear. 2021, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, R.K.; Briaire, J.J.; Dekker, D.M.T.; Frijns, J.H.M. Place Pitch versus Electrode Location in a Realistic Computational Model of the Implanted Human Cochlea. Hear. Res. 2014, 315, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Collins, A.G.E. Ten Simple Rules for the Computational Modeling of Behavioral Data. eLife 2019, 8, e49547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, H.B.; Reese, S.P.; Anderson, A.E.; Weiss, J.A. Validation of Computational Models in Biomechanics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2010, 224, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bang, H.; Kim, D.J. How to Establish Clinical Prediction Models. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.A.; Papsin, B.C.; Harrison, R.V. Toward a Battery of Behavioral and Objective Measures to Achieve Optimal Cochlear Implant Stimulation Levels in Children. Ear Hear. 2004, 25, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasey, B.; Nagendran, M.; Campbell, B.; Clifton, D.A.; Collins, G.S.; Denaxas, S.; Denniston, A.K.; Faes, L.; Geerts, B.; Ibrahim, M.; et al. Reporting Guideline for the Early-Stage Clinical Evaluation of Decision Support Systems Driven by Artificial Intelligence: DECIDE-AI. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füchslin, R.M.; Ambühl, J.; Faggian, A.; Fellermann, H.M.; Flumini, D.; Geller, A.; Hanczyc, M.M.; Klinkert, A.; Krütli, P.; Matuttis, H.-G.; et al. Ethical Aspects of Computational Modelling in Science, Decision Support and Communication. In Artificial Life and Evolutionary Computation; Schneider, J.J., Weyland, M.S., Flumini, D., Füchslin, R.M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 263–293. [Google Scholar]
- Portelli, D.; Lombardo, C.; Loteta, S.; Galletti, C.; Azielli, C.; Ciodaro, F.; Mento, C.; Aguennouz, M.H.; Di Rosa, G.; Alibrandi, A.; et al. Exploring the Hearing Improvement and Parental Stress in Children with Hearing Loss Using Hearing Aids or Cochlear Implants. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SACIG. Quality Standards Cochlear Implant Services for Adults and Children in South Africa. Available online: https://www.sacig.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/SACIG-Guidelines.pdf? (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Besser, J.; Stropahl, M.; Urry, E.; Launer, S. Comorbidities of Hearing Loss and the Implications of Multimorbidity for Audiological Care. Hear. Res. 2018, 369, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanekom, T. Integrating Computational Modelling into the Ecosystem of Cochlear Implantation: Advancing Access to Diagnostics, Decision-Making, and Post-Implantation Outcomes on a Global Scale. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227929
Hanekom T. Integrating Computational Modelling into the Ecosystem of Cochlear Implantation: Advancing Access to Diagnostics, Decision-Making, and Post-Implantation Outcomes on a Global Scale. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227929
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanekom, Tania. 2025. "Integrating Computational Modelling into the Ecosystem of Cochlear Implantation: Advancing Access to Diagnostics, Decision-Making, and Post-Implantation Outcomes on a Global Scale" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227929
APA StyleHanekom, T. (2025). Integrating Computational Modelling into the Ecosystem of Cochlear Implantation: Advancing Access to Diagnostics, Decision-Making, and Post-Implantation Outcomes on a Global Scale. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 7929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14227929







