Early Results of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Software System
2.2. Reading Protocols
2.3. Statistical Analysis
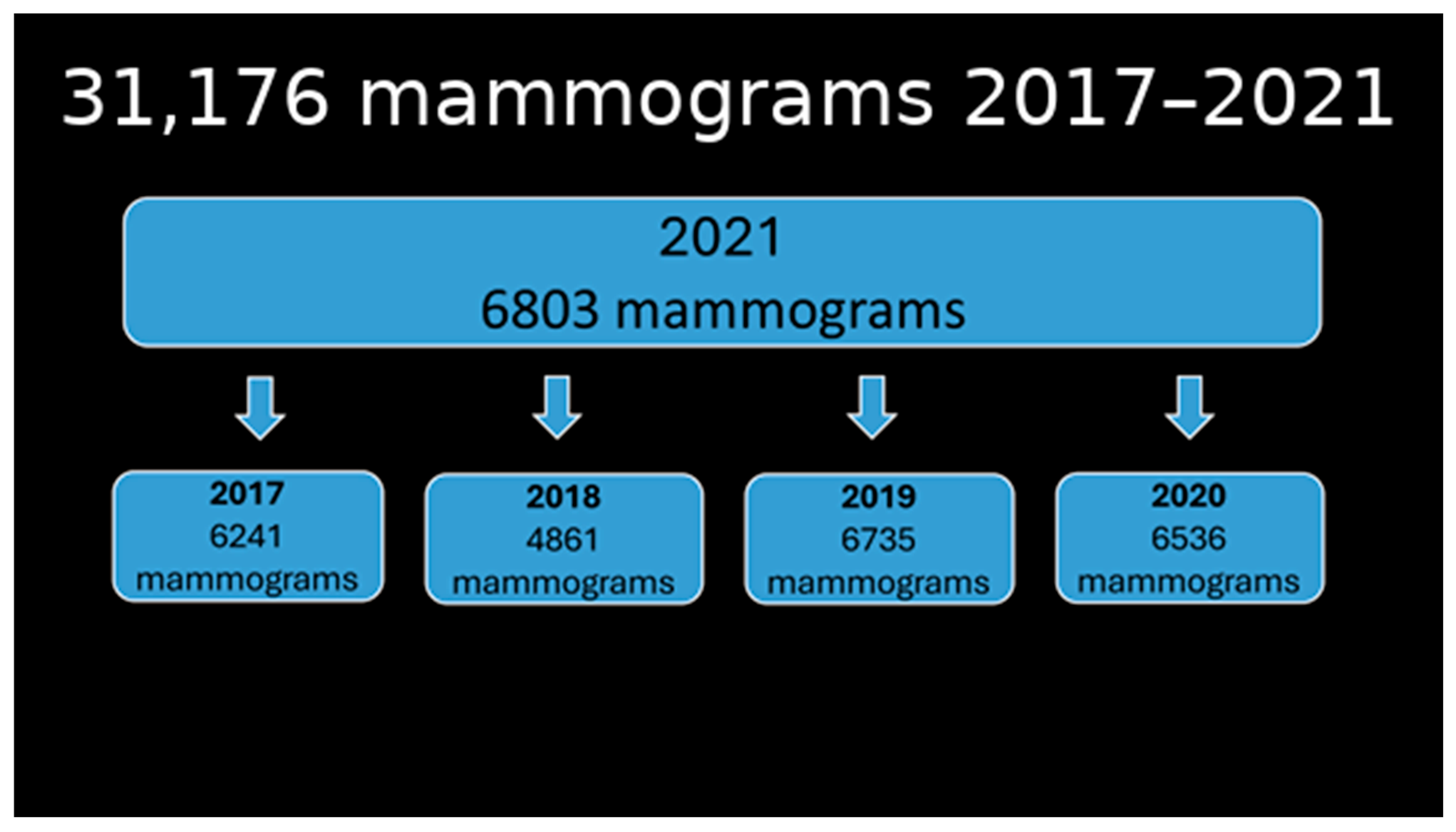
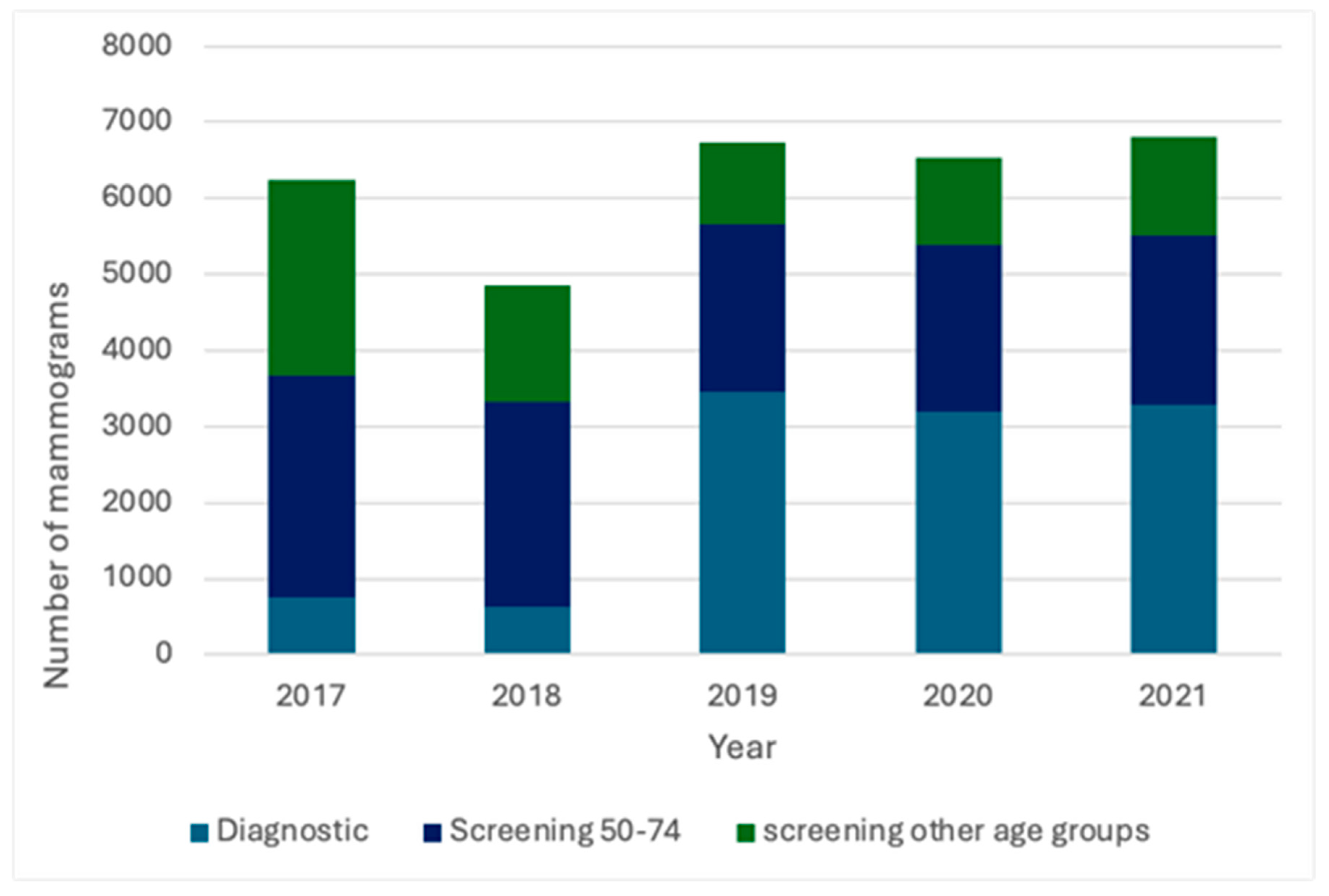
3. Results
3.1. Mammography Categories
3.2. Screening Benchmarks
3.3. Cancer Stage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, A.; Lång, K.; Gubern-Merida, A.; Broeders, M.; Gennaro, G.; Clauser, P.; Helbich, T.H.; Chevalier, M.; Tan, T.; Mertelmeier, T.; et al. Stand-Alone Artificial Intelligence for Breast Cancer Detection in Mammography: Comparison with 101 Radiologists. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacilè, S.; Lopez, J.; Chone, P.; Bertinotti, T.; Grouin, J.-M.; Fillard, P. Improving Breast Cancer Detection Accuracy of Mammography with the Concurrent Use of an Artificial Intelligence Tool. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e190208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, L.; Andersson, I.; Bjurstam, N.; Frisell, J.; Nordenskjöld, B.; Rutqvist, L.E. Long-Term Effects of Mammography Screening: Updated Overview of the Swedish Randomised Trials. Lancet 2002, 359, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.D.; Abraham, R.F.; Smith, B.L.; Lehman, J.M.; Buist, D.S.; Kerlikowske, K.; Henderson, L.M.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; Rauscher, G.H.; et al. National Performance Benchmarks for Modern Screening Digital Mammography: Update from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. Radiology 2017, 283, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritzen, A.D.; Lillholm, M.; Lynge, E.; Nielsen, M.; Karssemeijer, N.; Vejborg, I. Early Indicators of the Impact of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer. Radiology 2024, 311, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paci, E.; Broeders, M.; Hofvind, S.; Duffy, S.W. Summary of the Evidence of Breast Cancer Screening Outcomes in Europe and First Estimate of the Benefit and Harm Balance Sheet. J. Med. Screen. 2012, 19, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.M.; Wale, C.; Smith, R.; Evans, A.; Cuckle, H.; Duffy, S.W. Effect of Mammographic Screening from Age 40 Years on Breast Cancer Mortality in the UK Age Trial at 17 Years’ Follow-Up: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elías-Cabot, E.; Romero-Martín, S.; Raya-Povedano, J.L.; Brehl, A.K.; Álvarez-Benito, M. Impact of Real-Life Use of Artificial Intelligence as Support for Human Reading in a Population-Based Breast Cancer Screening Program with Mammography and Tomosynthesis. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 3958–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sechopoulos, I.; Teuwen, J.; Mann, R. Artificial Intelligence for Breast Cancer Detection in Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: State of the Art. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 72, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; Krupinski, E.; Mordang, J.J.; Schilling, K.; Heywang-Köbrunner, S.H.; Sechopoulos, I.; Mann, R.M. Detection of Breast Cancer with Mammography: Effect of an Artificial Intelligence Support System. Radiology 2019, 290, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritzen, A.D.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; von Euler-Chelpin, M.C.; Lynge, E.; Vejborg, I.; Nielsen, M.; Karssemeijer, N.; Lillholm, M. An Artificial Intelligence–Based Mammography Screening Protocol for Breast Cancer: Outcome and Radiologist Workload. Radiology 2022, 304, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, A.; Lång, K.; Gubern-Merida, A.; Teuwen, J.; Broeders, M.; Gennaro, G.; Clauser, P.; Helbich, T.H.; Chevalier, M.; Mertelmeier, T.; et al. Can We Reduce the Workload of Mammographic Screening by Automatic Identification of Normal Exams with Artificial Intelligence? A Feasibility Study. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, L.R.; Lehman, C.D.; Gastounioti, A.; Conant, E.F.; Bahl, M. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Screening Mammography, from the AJR Special Series on AI Applications. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.Y.; Oberije, C.J.G.; Ambrózay, É.; Szabó, E.; Serfőző, O.; Karpati, E.; Fox, G.; Glocker, B.; Morris, E.A.; Forrai, G.; et al. Prospective Implementation of AI-Assisted Screen Reading to Improve Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3044–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisemann, N.; Bunk, S.; Mukama, T.; Baltus, H.; Elsner, S.A.; Gomille, T.; Hecht, G.; Heywang-Köbrunner, S.; Rathmann, R.; Siegmann-Luz, K.; et al. Nationwide Real-World Implementation of AI for Cancer Detection in Population-Based Mammography Screening. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.; Agarwal, S.; Coombs, L.; Wald, C.; Dreyer, K. 2020 ACR Data Science Institute Artificial Intelligence Survey. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orsi, C.J.; Sickles, E.A.; Mendelson, E.B.; Morris, E.A. ACR BI-RADS® Atlas: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.E.; Joines, M.; Capiro, N.; Dawar, R.; Sears, C.; Sayre, J.; Chalfant, J.; Fischer, C.; Hoyt, A.C.; Hsu, W.; et al. Commercial Artificial Intelligence Versus Radiologists: NPV and Recall Rate in Large Population-Based Digital Mammography and Tomosynthesis Screening Mammography Cohorts. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2025, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall cancers detected | 52 p = 0.3 | 52 p = 0.4 | 64 |
| Cancers detected on mammography | 42 (80.7%) p = 0.05 | 47 (90.3%) p = 0.2 | 63 (98.4%) |
| Malignancy detected in screening mammography in ages 50–74 | 14 p = 0.3 | 8 p = 0.8 | 9 |
| CDR | 6.2/1000 p = 0.02 | 7.2/1000 p = 0.1 | 9.3/1000 |
| CDR in ages 50–74 | 3.2/1000 p = 0.004 | 3.2/1000 p = 0.003 | 1.8/1000 |
| FN in mammographic screening in ages 50–74 | 13% p = 0.02 | 13% p = 0.02 | 0% |
| Stage 1 cancers detected | 57.1% p = 0.05 | 100% p = 0.9 | 100% |
| Percent of DCIS detected | 36.4% p = 0.6 | 12.5% p = 0.7 | 20% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandler Rahat, H.; Friehmann, T.; Shemesh, M.D.; Tamir, S.; Atar, E.; Shochat, T.; Makori, A.; Grubstein, A. Early Results of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217886
Sandler Rahat H, Friehmann T, Shemesh MD, Tamir S, Atar E, Shochat T, Makori A, Grubstein A. Early Results of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217886
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandler Rahat, Hadar, Tal Friehmann, Marva Dahan Shemesh, Shlomit Tamir, Eli Atar, Tzippy Shochat, Arnon Makori, and Ahuva Grubstein. 2025. "Early Results of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217886
APA StyleSandler Rahat, H., Friehmann, T., Shemesh, M. D., Tamir, S., Atar, E., Shochat, T., Makori, A., & Grubstein, A. (2025). Early Results of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217886






