Sagittal Alignment Correction in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion with Unilateral vs. Bilateral Facetectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Clinical Analysis
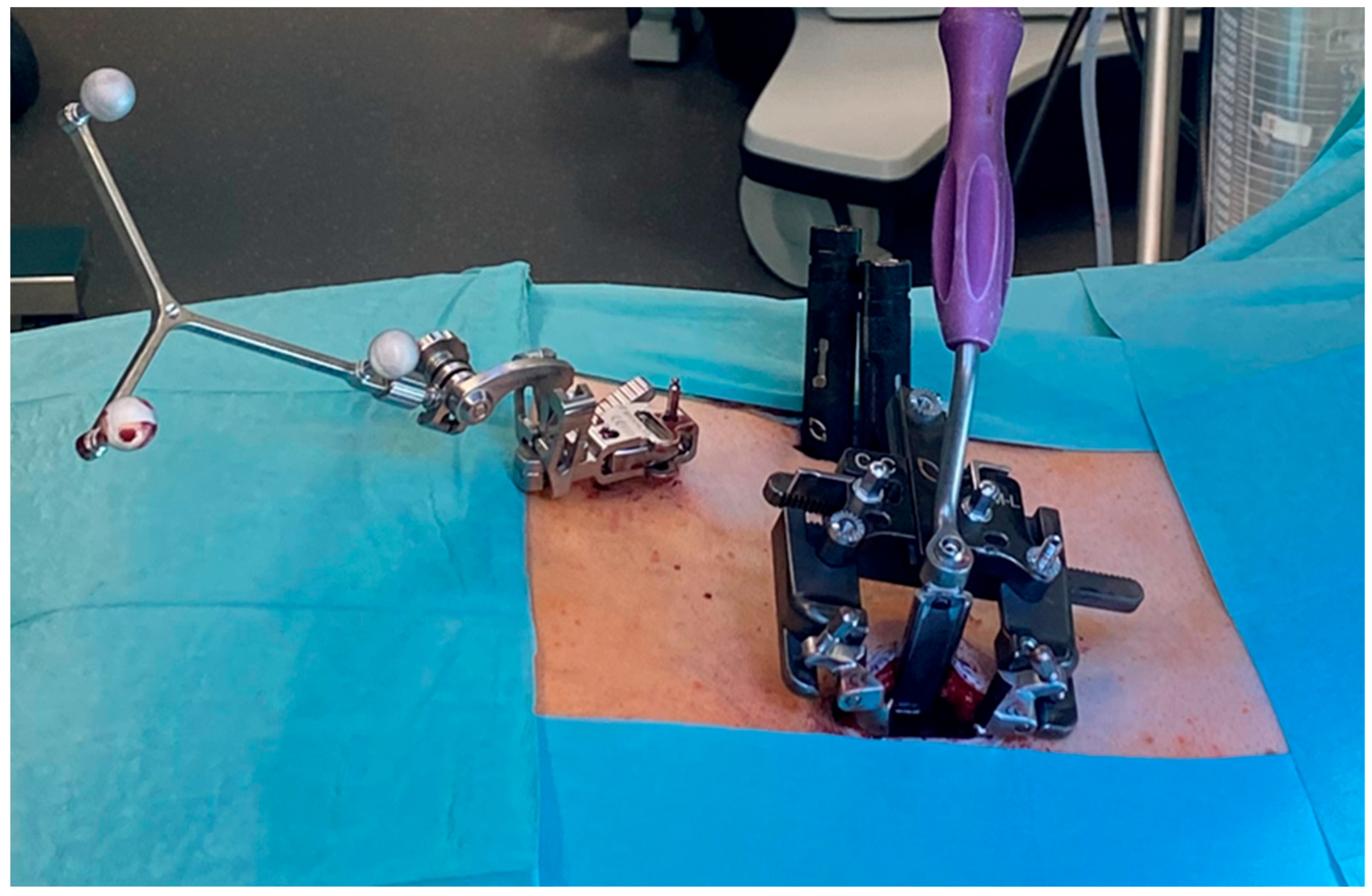
2.2. Surgical Technique
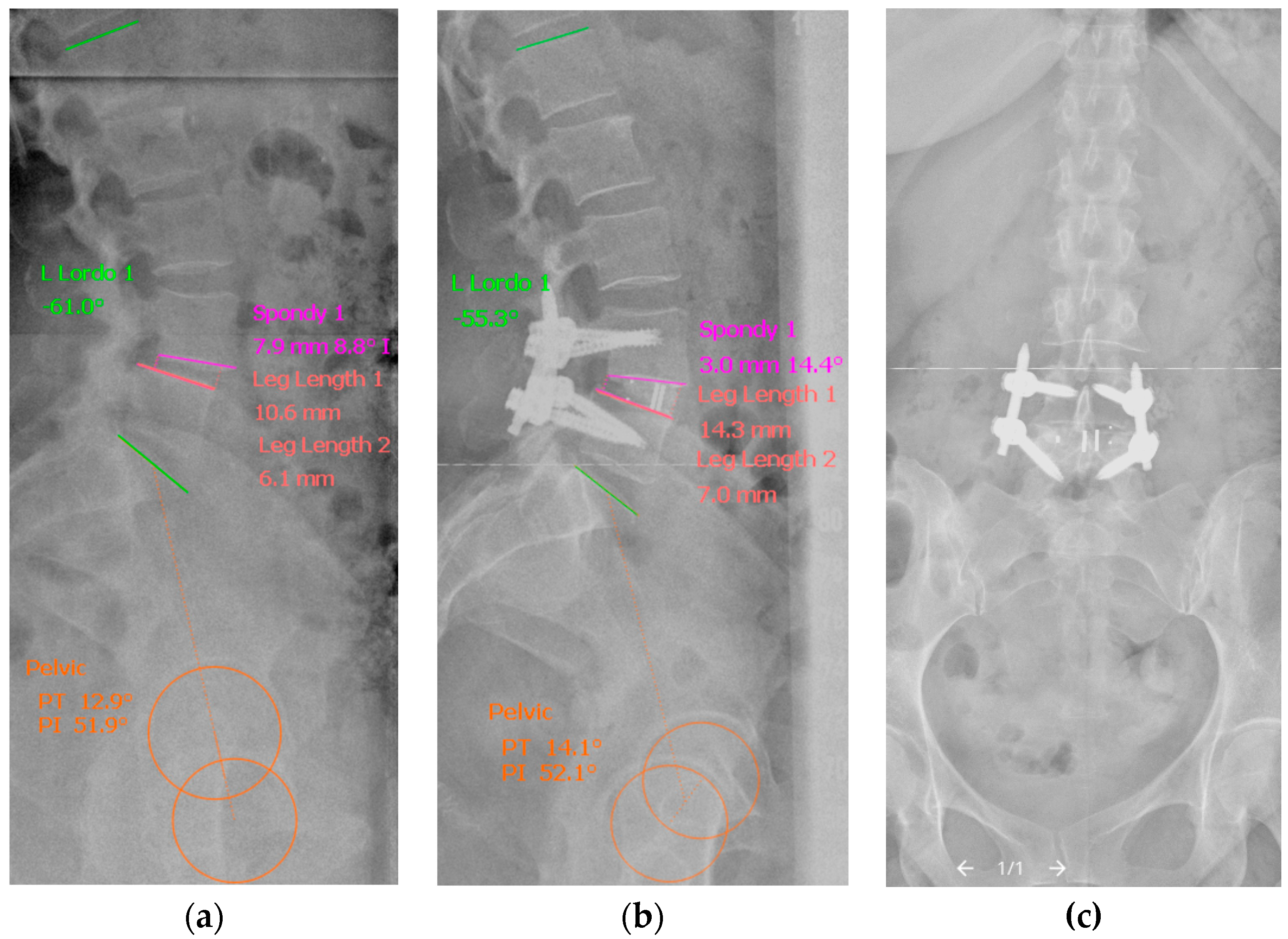
2.3. Radiological Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADH | Anterior disc height |
| ASA | General health status according to ASA grade |
| BF | Bilateral facetectomy |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| LLA | Lumbar lordosis angle |
| MI-TLIF | Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion |
| NRS | Numeric rating scale |
| OD-HA | Odontoid–hip axis |
| PDH | Posterior disc height |
| PI | Pelvic incidence |
| PT | Pelvic tilt |
| SL | Spondylolisthesis |
| SLA | Segmental lordosis angle |
| SS | Sacral slope |
| SVA | Sagittal vertical axis |
| UF | Unilateral facetectomy |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Cole, C.D.; McCall, T.D.; Schmidt, M.H.; Dailey, A.T. Comparison of Low Back Fusion Techniques: Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) or Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Approaches. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2009, 2, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, H.T.; Castro, F.P.J.; Majd, M.E.; Holt, R.T.; Myers, L. Anterior/Posterior Lumbar Fusion versus Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Analysis of Complications and Predictive Factors. J. Spinal Disord. 2001, 14, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, B.K.; Freedman, B.A.; Verwiebe, E.G.; Hall, J.M.; Polly, D.W.J.; Kuklo, T.R. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Clinical and Radiographic Results and Complications in 100 Consecutive Patients. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2005, 18, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villavicencio, A.T.; Burneikiene, S.; Bulsara, K.R.; Thramann, J.J. Perioperative Complications in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion versus Anterior-Posterior Reconstruction for Lumbar Disc Degeneration and Instability. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2006, 19, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.L.; Pei, F.X.; Li, J.; Soo, C.L. Comparative Study of PILF and TLIF Treatment in Adult Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.X.; Chen, Q.X.; Li, F.C. Unilateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Review of the Technique, Indications and Graft Materials. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.H.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, J.Y. Usefulness of Contralateral Indirect Decompression through Minimally Invasive Unilateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2014, 8, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Hioki, A.; Fushimi, K.; Ohno, T.; Shimizu, K. Morphologic Changes in Contralateral Lumbar Foramen in Unilateral Cantilever Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Kidney-Type Intervertebral Spacers. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2015, 28, E270–E276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yson, S.C.; Santos, E.R.G.; Sembrano, J.N.; Polly, D.W. Segmental Lumbar Sagittal Correction after Bilateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2012, 17, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, J.S.; Harris, J.E.; Beckman, J.M.; Turner, A.W.L.; Mundis, G.M.; Akbarnia, B.A. Finite Element Analysis of Lordosis Restoration with Anterior Longitudinal Ligament Release and Lateral Hyperlordotic Cage Placement. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24 (Suppl. S3), 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwaring, J.C.; Bach, K.; Ahmadian, A.A.; Deukmedjian, A.R.; Smith, D.A.; Uribe, J.S. Management of Sagittal Balance in Adult Spinal Deformity with Minimally Invasive Anterolateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Preliminary Radiographic Study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 20, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, J.; Sansur, C.A.; Oskouian, R.J.J.; Fu, K.-M.; Shaffrey, C.I. Radiographic Restoration of Lumbar Alignment after Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 954–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Jin, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Selective Segmental Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Combined with Posterior Spinal Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. ANZ J. Surg. 2014, 84, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, L.A.; Lehrman, J.N.; Menon, R.K.; Godzik, J.; Newcomb, A.G.U.S.; Kelly, B.P. Biomechanical Implications of Unilateral Facetectomy, Unilateral Facetectomy plus Partial Contralateral Facetectomy, and Complete Bilateral Facetectomy in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 31, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talia, A.J.; Wong, M.L.; Lau, H.C.; Kaye, A.H. Outcomes of Extended Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Spondylosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tye, E.Y.; Alentado, V.J.; Mroz, T.E.; Orr, R.D.; Steinmetz, M.P. Comparison of Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes in Patients Receiving Single-Level Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Removal of Unilateral or Bilateral Facet Joints. Spine 2016, 41, E1039–E1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Ramirez, R.; Lang, G.; Moriguchi, Y.; Elowitz, E.; Corredor, J.A.; Avila, M.J.; Gotfryd, A.; Alimi, M.; Gandevia, L.; Härtl, R. Are Locked Facets a Contraindication for Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion? World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas Edwards, W.; Chen, D.; Fay, L.A.; Lok, J.; Yuan, P.; Yuan, H.A. Increasing Neuroforaminal Volume by Anterior Interbody Distraction in Degenerative Lumbar Spine. Spine 1995, 20, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, M.H.; Hanley, E.N.; Matteri, R.E.; Wilder, D.G.; Frymoyer, J.W. Measurement of Intervertebral Disc Space Height. Spine 1977, 2, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval-Beaupère, G.; Schmidt, C.; Cosson, P. A Barycentremetric Study of the Sagittal Shape of Spine and Pelvis: The Conditions Required for an Economic Standing Position. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 20, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.P.; McManus, A.C. Radiographic Analysis of Sagittal Plane Alignment and Balance in Standing Volunteers and Patients with Low Back Pain Matched for Age, Sex, and Size. A Prospective Controlled Clinical Study. Spine 1994, 19, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrey, C.; Jund, J.; Noseda, O.; Roussouly, P. Sagittal Balance of the Pelvis-Spine Complex and Lumbar Degenerative Diseases. A Comparative Study about 85 Cases. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabile, C.; Pillet, H.; Lafage, V.; Barrey, C.; Vital, J.M.; Skalli, W. A New Quasi-Invariant Parameter Characterizing the Postural Alignment of Young Asymptomatic Adults. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3666–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaupt, D.; Zanetti, M.; Boos, N.; Hodler, J. MR Imaging and CT in Osteoarthritis of the Lumbar Facet Joints. Skelet. Radiol. 1999, 28, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.; Shen, F.H.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Arlet, V. Contralateral Radiculopathy after Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16 (Suppl. S3), 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingsakmongkol, W.; Jitpakdee, K.; Varakornpipat, P.; Choentrakool, C.; Tanasansomboon, T.; Limthongkul, W.; Singhatanadgige, W.; Kotheeranurak, V. Clinical and Radiographic Comparisons among Minimally Invasive Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Comparison with Three-Way Matching. Asian Spine J. 2022, 16, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhatanadgige, W.; Promsuwan, M.; Tanasansomboon, T.; Yingsakmongkol, W.; Limthongkul, W. Is Unilateral Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Sufficient in Patients with Claudication? A Comparative Matched Cohort Study. World Neurosurg. 2021, 150, e735–e740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasis, A.G.; Marshman, L.A.G.; Krishna, M.; Bhatia, C.K. Significantly Improved Outcomes with a Less Invasive Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Incorporating Total Facetectomy. Spine 2009, 34, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | UF | BF | p | Available n for UF/BF * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean patient age (yrs) | 64 ± 11 | 62.4 ± 10.6 | 0.46 | 81/23 |
| Gender (f:m, %) | 60:40 | 52:48 | 0.48 | 81/23 |
| Mean BMI | 29.6 ± 7 | 28.9 ± 5.7 | 0.56 | 80/23 |
| Distribution of ASA grades (1:2:3, %) | 6:67:27 | 17:52:31 | 0.22 | 78/23 |
| General medical conditions, % (n): | >0.1 | 81/23 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 14.8 (12) | 8.7 (2) | ||
| Obesity | 48.1 (39) | 34.8 (8) | ||
| Atherosclerosis | 13.6 (11) | 13 (3) | ||
| Prior thrombosis w/o PE | 7.4 (6) | 4.3 (1) | ||
| Smoking history | 29.6 (24) | 34.8 (8) | ||
| Anticoagulant drugs | 2.5 (2) | 4.3. (1) | ||
| COPD | 12.3 (10) | 8.7 (2) |
| Parameters | UF | BF | p | Available n for UF/BF * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous spinal surgery at treated or adjacent level, % (n) | 38.3 (31) | 21.7 (5) | 0.21 | 81/23 |
| Diagnosis related to surgery, % (n): | 0.005 * | 81/23 | ||
| Degenerative spondylolisthesis | 74.1 (60) | 65.2 (15) | ||
| Recurrent disc herniation | 7.4 (6) | - | ||
| Isthmic spondylolisthesis | 4.9 (4) | 30.4 (7) | ||
| Symptomatic foraminal stenosis | 7.4 (6) | 4.4 (1) | ||
| Osteochondrosis | 6.2 (5) | - | ||
| Bastrup phenomenon, % (n) | 57 (45) | 39.1 (9) | 0.13 | 79/23 |
| Grade of facet joint degeneration [17,18], % (n) | 0.09 | 79/23 | ||
| Grade 2 | 20.3 (16) | 34.8 (8) | ||
| Grade 3 | 50.6 (40) | 56.5 (13) | ||
| Grade 4 (locked facets) | 29.1 (23) | 8.7 (2) | ||
| Need for pain killers at admission (WHO grade), median (range) | 2 (1–3) | 1 (1–3) | 0.29 | 41/16 |
| Median postop. wound pain levels (NRS) | 2 (0–8) | 2.5 (0–4) | 0.66 | 63/14 |
| Postop. pain at motion and ambulation, median (range) | 2 (0–10) | 3.5 (0–7) | 0.24 | 63/14 |
| Need for pain killers at discharge (WHO grade), median (range) | 3 (1–3) | 3 (1–3) | 1 | 81/23 |
| Hospital duration (d) | 6.1 ± 2.6 | 6.0 ± 3.1 | 0.16 | 81/23 |
| Operated segments, % (n) | >0.1 | 81/23 | ||
| L 1/2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| L 2/3 | 1.2 (1) | 4.3 (1) | ||
| L 3/4 | 8.7 (7) | 0 | ||
| L 4/5 | 75.3 (61) | 74 (17) | ||
| L 5/S1 | 14.8 (12) | 21.7 (5) | ||
| Median cage height (all lordotic 8°), mm | 11 (9–14) | 11 (9–12) | 0.73 | 81/23 |
| Cage position, % (n): Ventral | 59.5 (47) | 56.5 (13) | 0.79 | 79/23 |
| Middle | 40.5 (32) | 43.5 (10) | ||
| Medial intraoperative blood loss (mL) | 437 ± 207 | 803 ± 347 | <0.001 * | 81/23 |
| Medial operative time (min) | 197 ± 37 | 240 ± 48 | 0.001 * |
| Parameters | UF (n = 27) | BF (n = 13) | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preop. | Postop. | p | Preop. | Postop. | p | ||
| Segmental Spinal Sagittal Parameters | |||||||
| Segmental lordosis angle (SLA), ° | 8.9 ± 5.6 | 11 ± 4.8 | 0.042 * | 7.98 ± 6.6 | 12.3 ± 4.6 | 0.028 * | |
| SLA gain (Δ post- to preop.), ° | 2.1 ± 5.3 | 4.3 ± 5.4 | 0.32 | ||||
| Spondylolisthesis (SL), mm | 5.1 ± 1.6 | 2.3 ± 1.9 | 0.003 * | 5.4 ± 1.6 | 2.98 ± 1.8 | 0.005 * | |
| SL reduction (Δ post- to preop.), mm | −2.8 ± 2.2 | −2.4 ± 1.9 | 0.73 | ||||
| Posterior disc height (PDH), mm | 5.96 ± 1.8 | 7.3 ± 1.97 | 0.001 * | 6.2 ± 2.3 | 6.6 ± 1.9 | 0.55 | |
| Δ PDH, mm | 1.4 ± 1.9 | 0.4 ± 2.6 | 0.26 | ||||
| Anterior disc height (ADH), mm | 11.3 ± 3.1 | 14.1 ± 2.8 | 0.000 * | 10.4 ± 4.3 | 13.2 ± 2.4 | 0.033 * | |
| Δ ADH, mm | 2.8 ± 2.8 | 2.8 ± 4 | 0.65 | ||||
| Regional Spinal Sagittal Parameters | |||||||
| Lumbar lordosis angle (LLA), ° | 51.6 ± 13.9 | 48.8 ± 12.3 | 0.049 * | 53.8 ± 17.3 | 48.2 ± 24.5 | 0.039 * | |
| Δ LLA, ° | −2.8 ± 8.9 | −5.5 ± 9.4 | 0.42 | ||||
| Pelvic Sagittal Parameters | |||||||
| Pelvic incidence (PI), ° | 55.8 ± 9.2 | 55.6 ± 9.2 | 0.38 | 57.8 ± 9.5 | 58.2 ± 9.6 | 0.39 | |
| Δ PI, ° | −0.2 ± 1.1 | 0.4 ± 2.5 | 0.29 | ||||
| Sacral slope (SS), ° | 37.2 ± 7.1 | 35.9 ± 5.98 | 0.14 | 39.4 ± 7.9 | 38.7 ± 7.4 | 0.28 | |
| Δ SS, ° | −1.3 ± 4.5 | −0.7 ± 3.8 | 0.69 | ||||
| Pelvic tilt (PT), ° | 18.7 ± 8.3 | 19.7 ± 6.9 | 0.13 | 18.5 ± 6.7 | 19.5 ± 5.7 | 0.38 | |
| Δ PT, ° | 1.1 ± 4.7 | 0.96 ± 4.5 | 0.9 | ||||
| Global Spinal Sagittal Parameters | |||||||
| Sagittal vertical axis (SVA), mm | 41.3 ± 42.9 | 49.1 ± 34.4 | 0.07 | 34.1 ± 62.6 | 36.2 ± 31.1 | 0.31 | |
| Δ SVA, mm | 7.8 ± 31.6 | 2 ± 56.4 | 0.94 | ||||
| Odontoid–hip axis (OD-HA), ° | 1.2 ± 3.6 | 1.5 ± 2.4 | 0.67 | 1.8 ± 5.1 | 1.3 ± 4.1 | 0.92 | |
| Δ OD-HA, ° | 0.3 ± 3.6 | −0.5 ± 5.9 | 1.0 | ||||
| Factors | Regression Coefficient | p | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval for OR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Lordosis gain 0–2° | Baastrup phenomenon | −5.247 | 0.179 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 11.033 |
| Grade of facet joint degeneration [17,18] | 2.071 | 0.337 | 7.935 | 0.116 | 544.292 | |
| BF vs. UF | −1.417 | 0.474 | 0.242 | 0.005 | 11.768 | |
| Cage position (ventral vs. middle) | −0.084 | 0.961 | 0.919 | 0.030 | 27.756 | |
| Cage height (all 8° oblique) | 2.236 | 0.087 | 9.360 | 0.726 | 120.744 | |
| Lordosis gain >2° | Baastrup phenomenon | −0.169 | 0.850 | 0.845 | 0.147 | 4.855 |
| Grade of facet joint degeneration [17,18] | −0.874 | 0.304 | 0.417 | 0.079 | 2.208 | |
| BF vs. UF | 0.610 | 0.477 | 1.841 | 0.342 | 9.902 | |
| Cage position (ventral vs. middle) | 0.422 | 0.621 | 1.525 | 0.286 | 8.139 | |
| Cage height (all lordotic 8°) | 0.439 | 0.323 | 1.551 | 0.650 | 3.698 | |
| Parameters | UF (n = 81) | BF (n = 23) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| All cases in total, % (n) | 25.9 (21) | 34.8 (8) | 0.28 |
| Cases with surgical intraoperative adverse events, % (n) | 21 (17) | 21.7 (5) | 0.57 |
| Events of dural lesion on the cage insertion side (ipsilateral) | 21 (17) | 8.7 (2) | |
| Events of screw misplacement | 3.6 (3) | 4.3 (1) | |
| Events of screw dislocation/pullout by reposition/compression | 2.4 (2) | 8.7 (2) | |
| Events of intraoperative cage subsidence | 1.2 (1) | ||
| Cases with early surgical postoperative complications (up to 6 weeks postoperatively), % (n) | 6.2 (5) | 13.04 (3) | 0.25 |
| Events of epidural hematoma/surgical evacuation | 1.2 (1) | 4.3 (1) | |
| Events of lesion of the ipsilateral exiting root | 3.6 (3) | ||
| Events of aseptic superficial wound healing disorder (contralateral) | 8.7 (2) | ||
| Events of superficial wound infection (ipsilateral) | 1.2 (1) | ||
| Events of symptomatic contralateral sequester dislocation | 4.3 (1) | ||
| General intraoperative adverse events and early postoperative complications, % (n) | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Telentschak, S.; Fruechtl, E.; Perrech, M.; Lenschow, M.; von Spreckelsen, N.; Czybulka, D.-M.; Goldbrunner, R.; Neuschmelting, V. Sagittal Alignment Correction in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion with Unilateral vs. Bilateral Facetectomy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217595
Telentschak S, Fruechtl E, Perrech M, Lenschow M, von Spreckelsen N, Czybulka D-M, Goldbrunner R, Neuschmelting V. Sagittal Alignment Correction in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion with Unilateral vs. Bilateral Facetectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217595
Chicago/Turabian StyleTelentschak, Sergej, Eva Fruechtl, Moritz Perrech, Moritz Lenschow, Niklas von Spreckelsen, Dierk-Marko Czybulka, Roland Goldbrunner, and Volker Neuschmelting. 2025. "Sagittal Alignment Correction in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion with Unilateral vs. Bilateral Facetectomy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217595
APA StyleTelentschak, S., Fruechtl, E., Perrech, M., Lenschow, M., von Spreckelsen, N., Czybulka, D.-M., Goldbrunner, R., & Neuschmelting, V. (2025). Sagittal Alignment Correction in Single-Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Interbody Fusion with Unilateral vs. Bilateral Facetectomy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217595





