Advanced 3D Facial Scanning in Orthodontics: A Correlative Analysis of Craniofacial Anthropometric Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure Methodology
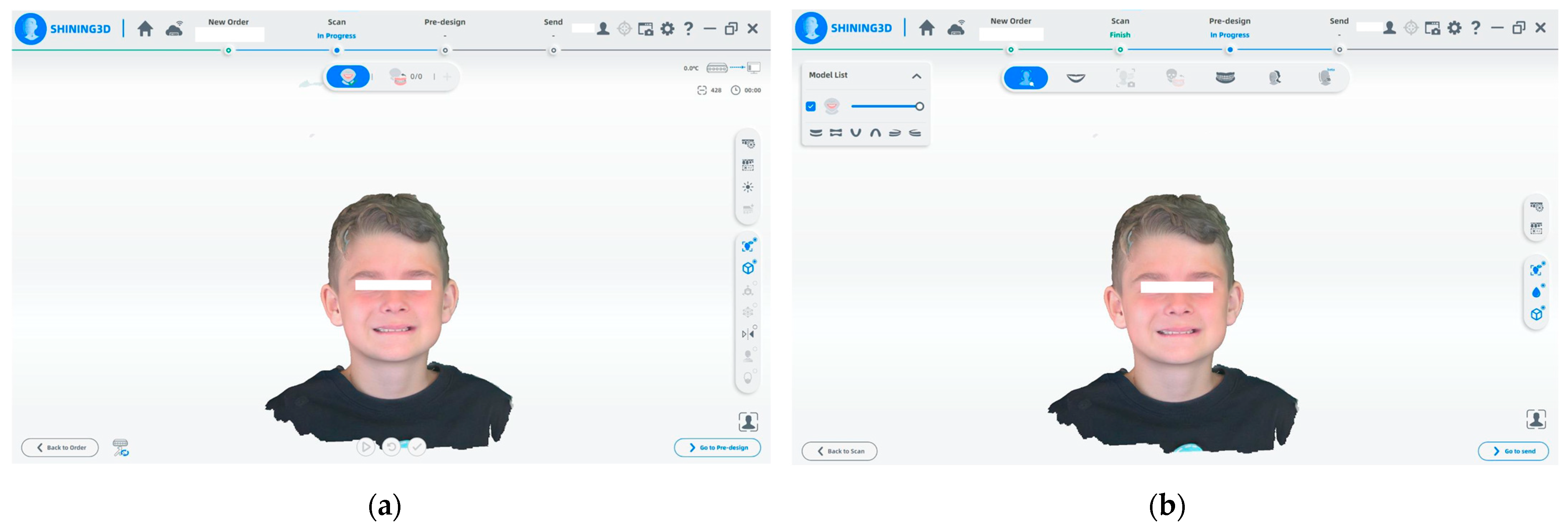
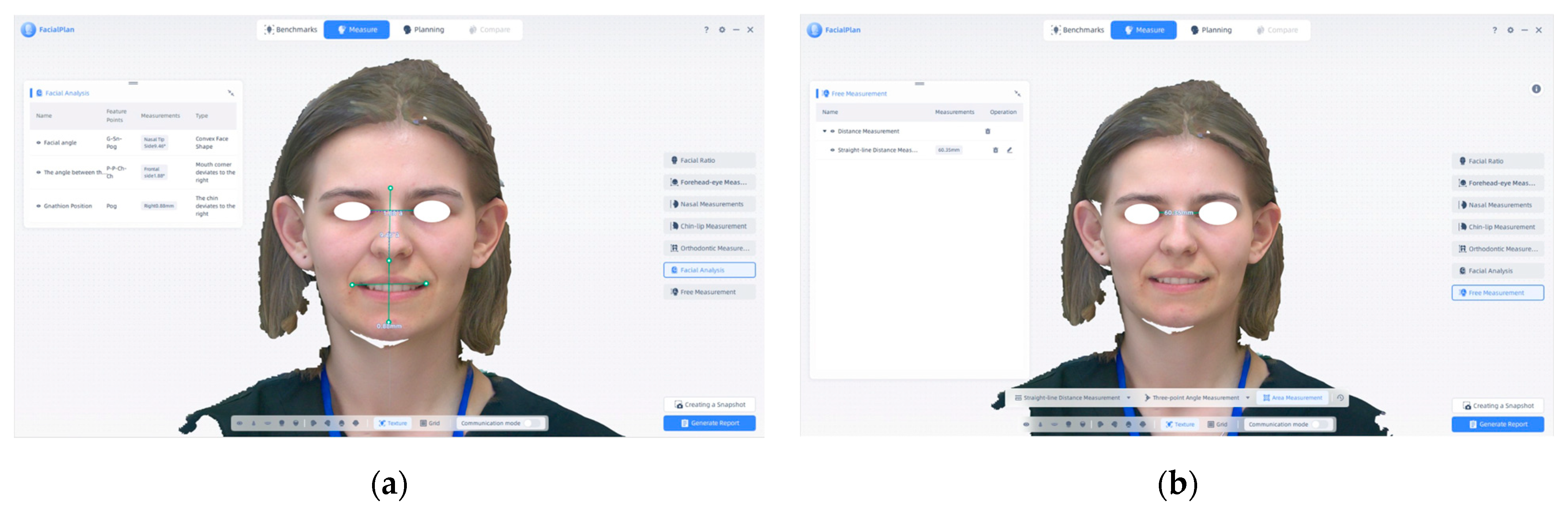
- (a)
- The Shining 3D program is used for the initial facial scanning procedure. Throughout the scan, the 3D model is created in real time. The technology reconstructs the surface geometry of the face using a calibrated camera and structured light projection. The scanning process is displayed on the upper status bar, which tracks the progress.
- (b)
- When the facial scan is complete, the pre-design stage begins. The software offers a precise 3D depiction of the patient’s face following data collection. For additional processing, simulation, or integration with intraoral and CBCT data, the user can proceed to the pre-design module.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
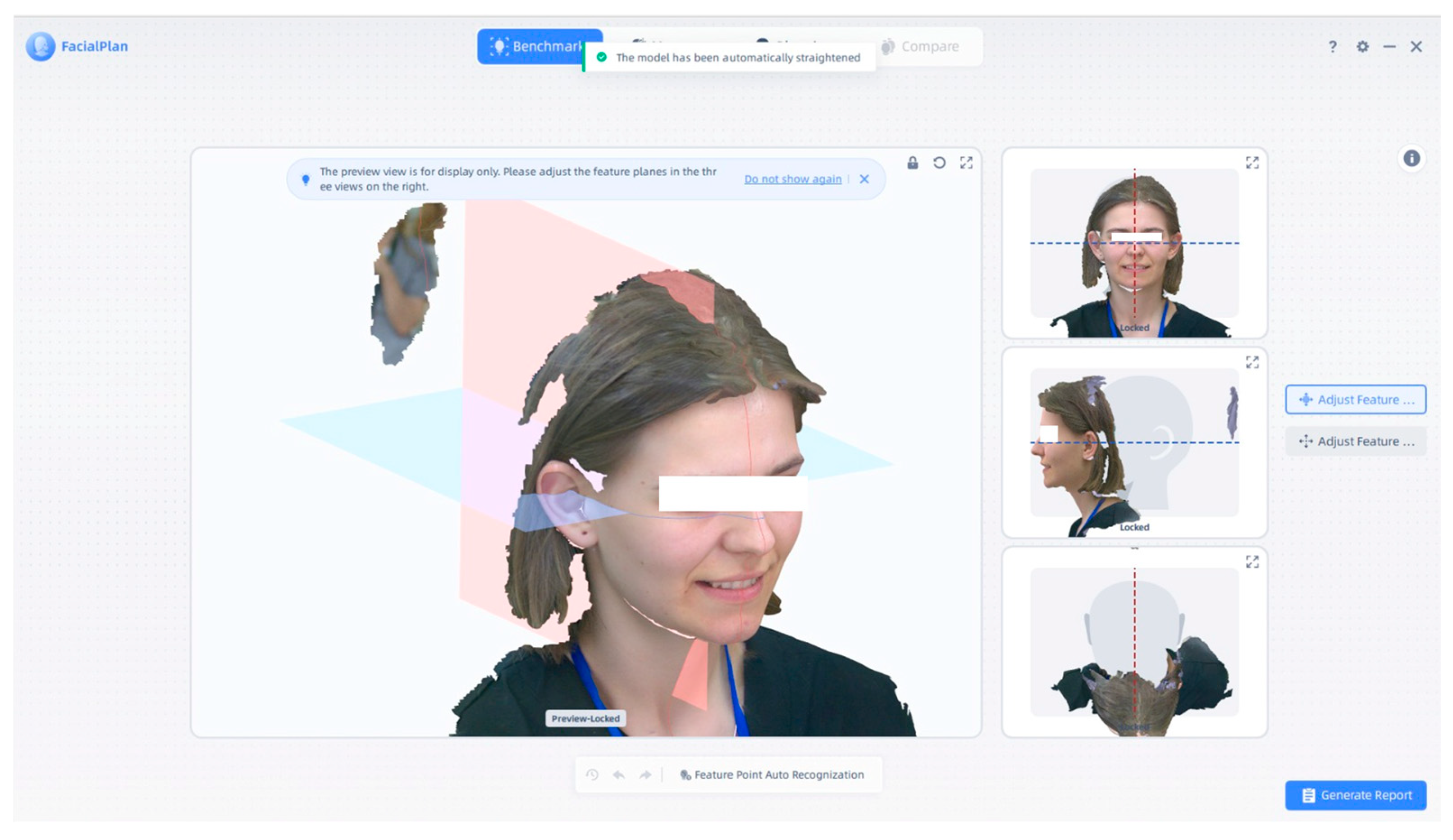
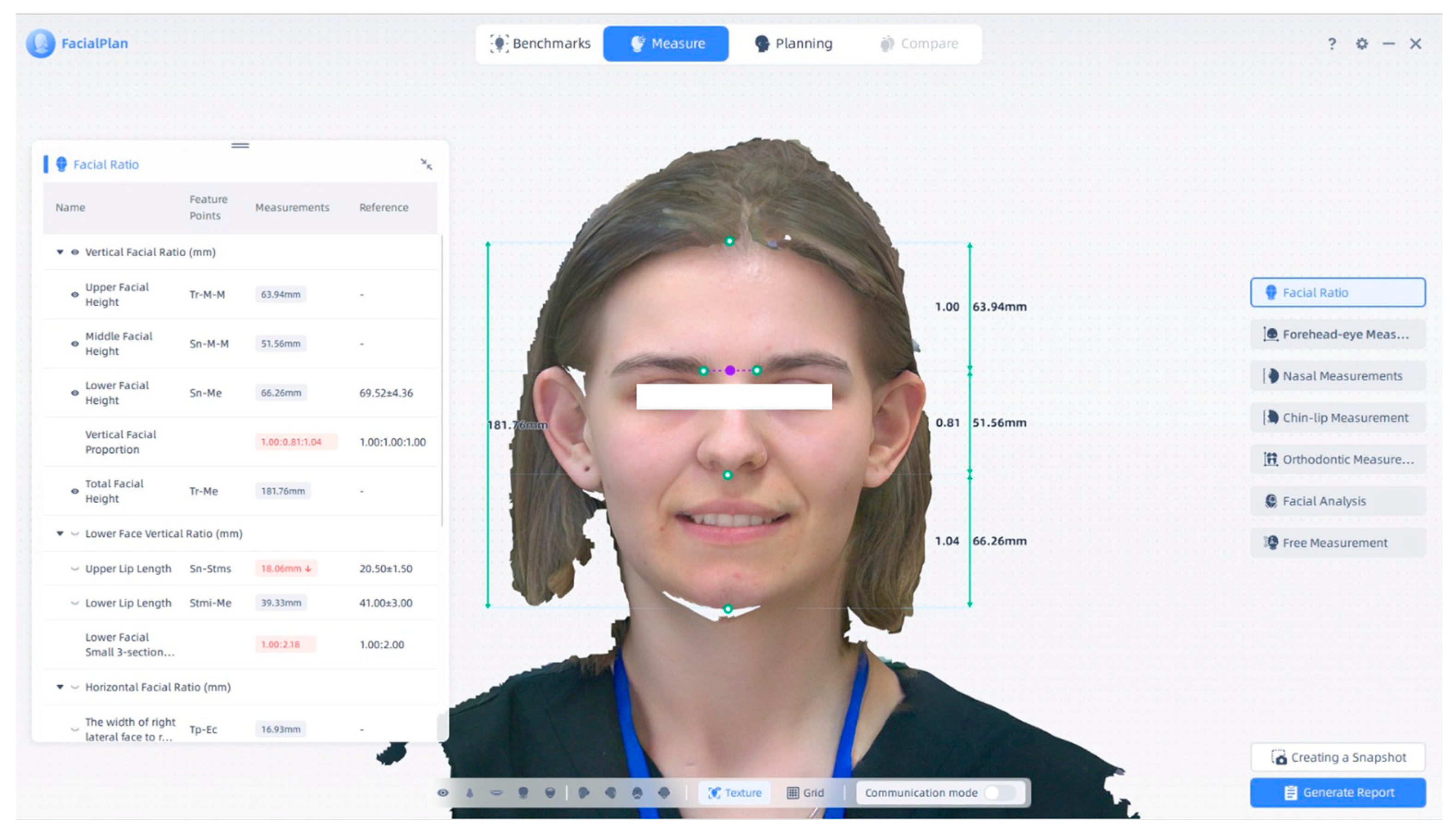
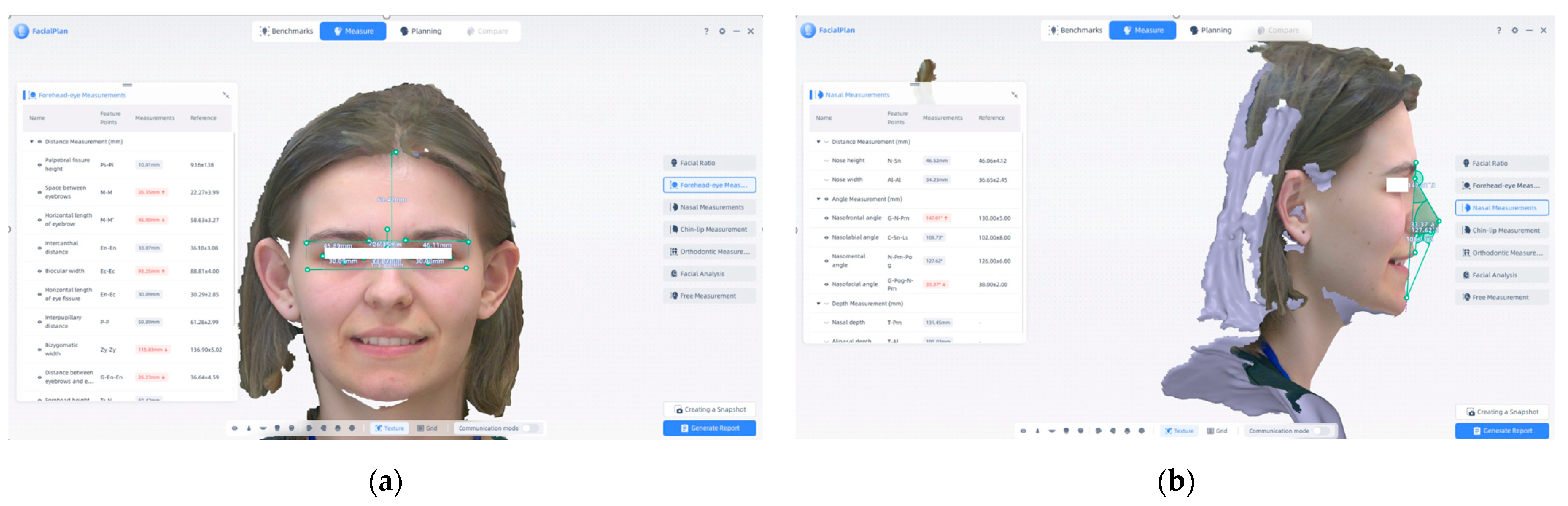
4. Three-Dimensional Facial Visualization and Measurement Reports
5. Discussion
6. Study Limitations and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shuto, T.; Mine, Y.; Tani, A.; Taji, T.; Murayama, T. Facial Scans in Clinical Dentistry and Related Research: A Scoping Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e81662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Nguyen, O.; Lin, Y.-C.; Luu, D.; Kim, S.; Amini, A.; Lee, S.J. Facial Scanners in Dentistry: An Overview. Prosthesis 2022, 4, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.; Gandolfi, A.; Luongo, G.; Logozzo, S. Intraoral scanners in dentistry: A review of the current literature. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, B.; Greven, M.; Wismeijer, D. Integrating 3D facial scanning in a digital workflow to CAD/CAM design and fabricate complete dentures for immediate total mouth rehabilitation. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2017, 9, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohner, L.; Gamba, D.D.; Hanisch, M.; Marcio, B.S.; Neto, P.T.; Laganá, D.C.; Sesma, N. Accuracy of digital technologies for the scanning of facial, skeletal, and intraoral tissues: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Xiong, Y.X.; Wang, Y. Three-Dimensional Accuracy of Facial Scan for Facial Deformities in Clinics: A New Evaluation Method for Facial Scanner Accuracy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornvit, P.; Sanohkan, S. The Accuracy of Digital Face Scans Obtained from 3D Scanners: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Gallucci, G.O. The virtual patient in dental medicine. Clin. Oral Implants. Res. 2015, 26, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurzo, A.; Strunga, M.; Havlínová, R.; Reháková, K.; Urban, R.; Surovková, J.; Kurilová, V. Smartphone-Based Facial Scanning as a Viable Tool for Facially Driven Orthodontics? Sensors 2022, 22, 7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crumpler, W. How Accurate Are Facial Recognition Systems–and Why Does It Matter? Center for Strategic and International Studies. 2020. Available online: https://www.csis.org/blogs/strategic-technologies-blog/how-accurate-are-facial-recognition-systems-and-why-does-it (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Srinivasan, M.; Leles, C.R.; Berisha, F.; Bronzino, I.; Milhomens, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.H. Clinical Evaluation of the Accuracy of Two Face Scanners with Different Scanning Technologies. J. Dent. 2025, 153, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Baker, B.; Ayoub, A.; Ju, X.; Mossey, P. Patch-Based Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Landmark Detection of 3D Facial Images in Clinical Settings. Eur. J. Orthod. 2024, 46, cjae056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, S.; Antonelli, A.; Salviati, M.; Greco, V.; Bennardo, F.; Becker, K.; Giudice, A.; Simeone, M. Accuracy Assessment of EM3D App-Based 3D Facial Scanning Compared to Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbonani, T.M.; L’Abbé, E.N.; Ridel, A.F. Analyzing 3D Facial Morphology: Insights from a Comparative European and South African Study on Population Affinity, Sex, Age, and Allometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 365, 112282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs-Murphy, K.; Brazile, W.J.; Morris, K.; Rosecrance, J. Demographic Differences in Facial Anthropometric Data from 3D Scans and Implications for Respirator Fit. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Taylor, J.M.; Huang, K.X.; Shariati, K.; Chevalier, J.M.; Miller, M.N.; Cronin, B.J.; Lee, J.C. Ethnic Variation in Lower Face Anthropometry on Facial Computed Tomography Scans for Patients Seeking Facial Feminization Surgery. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2024, 77, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shining 3D. MetiSmile—Dental Facial Scanner. Available online: https://www.shining3ddental.com/solution/metismile-face-scanner/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Weinberg, S.M.; Naidoo, S.; Govier, D.P.; Martin, R.A.; Kane, A.A.; Marazita, M.L. Anthropometric Precision and Accuracy of Digital Three-Dimensional Photogrammetry: Comparing the 3dMDface System with Direct Anthropometry and 2D Photographs. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2006, 43, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Yang, H.J.; Huh, K.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Heo, M.-S.; Choi, S.-C.; Hwang, S.J.; Yi, W.-J. Automatic Reproduction of Natural Head Position Using a Portable 3D Scanner Based on Immediate Calibration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentstore. Scanner Facial MetiSmile Shining 3D. Available online: https://dentstore.ro/scanner-cabinet/537918-scanner-facial-metismile-shining-3d-12.html?srsltid=AfmBOoqXRNxS1ftZHJqkiKlHBo5h6NPnz_KOC47MG-k7wDSzl1Fqlu_f (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Shining 3D. MetiSmile User Manual: 3D Facial Scanner Instructions; Version 1.3; Shining 3D Tech Co., Ltd.: Hangzhou, China, 2023; Available online: https://www.shining3d.com (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Rathi, A.; Chhetri, S. Measurements of Lower, Middle, and Upper Facial Heights in Different Sex in a Teaching Hospital of Biratnagar. J. Nepal Dent. Assoc. 2018, 18, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- George, A.M.; Govindaraj, A.K.; Sivakumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Sundari, S. Complexities in Diagnosis and Management of Long Face. J. Contemp. Orthod. 2018, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.R. Flap Classification and Design. In Local Flaps in Facial Reconstruction; Baker, S.R., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 71–107. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Juboori, M.J.; Al-Juboori, A.J.; Wen, T.M.; Ting, J.; Chui, L.S.; Hoe, T.M.; Ali, H. The Relationship between the Lip Length and Smile Line in a Malaysian Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Dent. Oral Craniofac. Res. 2017, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bhullar, M.; Malhotra, Y.; Mittal, S.; Aggarwal, I.; Singla, D.; Goyal, M. Evaluation of Smile Parameters in Nongrowing Subjects Using Photographs. Dent. J. Adv. Stud. 2019, 7, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointer, J.S. The Far Interpupillary Distance. A Gender-Specific Variation with Advancing Age. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1999, 19, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, N.R.; Dixson, B.J. Beyond Facial Width-to-Height Ratios: Bizygomatic Width Is Highly Sexually Dimorphic When Adjusting for Allometry. Biol. Lett. 2022, 18, 20220211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naini, F.B.; Cobourne, M.T.; Garagiola, U.; McDonald, F.; Wertheim, D. Nasofrontal Angle and Nasal Dorsal Aesthetics: A Quantitative Investigation of Idealized and Normative Values. Facial Plast. Surg. 2016, 32, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuhanek, C.; Schiller, A.; Grigore, A.; Popa, L. Ghid Ortodonție; Editura Victor Babeș: Timișoara, România, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Uche, U.L.; Oluseun, A.O.; Nwachuku, M.I.; Babatunde, L.B.; Ikpa, J.O. Anthropometric Study of Inter-Alar Width and Mouth Width Measurements among Nigerians of Delta State Extraction. Eur. J. Biomed. 2020, 7, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Naini, F.B.; Cobourne, M.T.; McDonald, F.; Wertheim, D. Mentolabial Angle and Aesthetic Preference. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Obaidi, H.A.; Abdul-Qadir, M.Y. Evaluation of the Variation of Skeletofacial Angles (Facial, Mandibular, and Gonial Angles) among the Pubertal Age Groups: A Cephalometric Study. Sci. J. Publ. 2007, 19, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hellak, A.; Kirsten, B.; Schauseil, M.; Davids, R. Influence of Maxillary Advancement Surgery on Skeletal and Soft-Tissue Changes in the Nose—A Retrospective Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study. Head Face Med. 2015, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, L.A.; Barbu, H.M.; Iancu, S.A.; Brad, S. Incidence, Size and Orientation of Maxillary Sinus Septa—A Retrospective Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, Ș.; Todor, L.; Zetu, I.N.; Păcurar, M.; Porumb, A.; Milutinovici, R.A.; Popa, M. Radiographic Methods for Locating Impacted Maxillary Canines. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022, 63, 599. [Google Scholar]
- David, A.P.; Brad, S.; Rusu, L.-C.; David, O.T.; Samoila, C.; Leretter, M.T. Automatic Segmentation of the Jaws Used in Guided Insertion of Orthodontic Mini Implants to Improve Their Stability and Precision. Medicina 2024, 60, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, A.; Szuhanek, C.; Brad, S. Accurate Determination for Orthodontic Mini-Implant Placement Using Acrylic Resin Surgical Guide and CBCT. Mater. Plast. 2016, 53, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Nagib, R.; Szuhanek, C.; Moldoveanu, B.; Negrutiu, M.L.; Duma, V.F.; Sinescu, C.; Brad, S. Dimensional Study of Impacted Maxillary Canine Replicas 3D Printed Using Two Types of Resin Materials. Mater. Plast. 2018, 55, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sink, B.A.; Brad, S.; Tanase, A.D.; Brad, A.B. OPG Fine Preoperative Evaluation of Maxillary Inflammatory and Atrophic Lesions with Postoperative Successfully Surgical Solutions Appreciation of Dentoalveollary Reconstructions Using Heterolog Membranes and Materials Together with Metallic Implants. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 4057–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivis, M.; Poenaru, M.; Ionita, H.; Lazar, E.; Haba, D.; Brad, S. The MRI Fine Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathies and Associated Oral Cavity Pathological Conditions. Med. Surg. J. 2013, 117, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Maharjan, S.K.; Mathema, S.R. Measurement of Proportion of Lower Facial Height and Its Significance in Different Age, Sex and Ethnicity. J. Nepal Dent. Assoc. 2014, 14, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.K.; Anand, C.; Ghosh, S.K. Photometric Facial Analysis—A Baseline Study. J. Anat. Soc. India 2004, 53, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sadacharan, C.M. Vertical and Horizontal Facial Proportions of Indian American Men. Anat. Cell Biol. 2016, 49, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husein, O.F.; Sepehr, A.; Garg, R.; Sina-Khadiv, M.; Gattu, S.; Waltzman, J.; Galle, S.E. Anthropometric and Aesthetic Analysis of the Indian American Woman’s Face. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Tripathi, S.; Chopra, A.; Khaneja, K.; Agarwal, S. Vertical and Horizontal Proportions of the Face and Their Correlation to Phi among Indians in Moradabad Population: A Survey. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2015, 15, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniwaa. Shining 3D MetiSmile Scanner. 2024. Available online: https://www.aniwaa.com/product/3d-scanners/shining-3d-dental-metismile (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Top3DShop. Shining 3D MetiSmile Face 3D Scanner Review. 2023. Available online: https://top3dshop.com/product/shining-3d-metismile-face-3d-scanner (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Starcona. MetiSmile AI Software Capabilities for Orthodontics. 2023. Available online: https://starcona.com/products/shining3d-metismile-face-scanner (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Adekunle, A.A.; Olowo, A.Y.; James, O.; Adamson, O.O.; Alade, A.A.; Agbogidi, F.O.; Butali, A. Facial anthropometry measurements using three-dimensional stereophotogrammetry analysis among Nigerians. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2022, 33, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.P.; Medapati, V.; Segwapa, K. Facial anthropometric norms of the young Black South African woman. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpinar, M.; Nahir, M.; Ozdemir, F.; Sahin, B. Photographic nasal soft tissue analysis from preadolescence to young adulthood: Anthropometric measurements. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2022, 33, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkelgosha, V.; Fathinejad, S.; Pakizeh, Z.; Shamsa, M.; Golkari, A. Photographic facial soft tissue analysis by means of linear and angular measurements in an adolescent Persian population. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.K.; Sharma, T.; Prasad, P.N.; Rawat, A.; Joshi, S. Angular photogrammetric analysis for a young adult Garhwali population. Curr. Trends Dent. 2024, 1, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcă, A.; Bucur, S.M.; Păcurar, M. Facial profile characteristics evaluation in a population of Central Romania region. Acta Med. Marisiensis 2014, 60, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Stăncioiu, A.-A.; Vasica, F.; Nagib, R.; Popa, A.; Motofelea, A.C.; Hușanu, A.A.; Szuhanek, C.-A. Cephalometric Evaluation of Facial Height Ratios and Growth Patterns: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stăncioiu, A.-A.; Motofelea, A.C.; Hușanu, A.A.; Vasica, L.; Nagib, R.; Popa, A.; Szuhanek, C. Associations of Digital Measurements: Analysis of Orthopantomography Versus Lateral Cephalograms for Evaluation of Facial Asymmetry. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stăncioiu, A.-A.; Motofelea, A.C.; Hușanu, A.A.; Vasica, L.; Popa, A.; Nagib, R.; Szuhanek, C. Innovative Aesthetic and Functional Orthodontic Planning with Hard and Soft Tissue Analyses. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkarat, F.; Tofighi, O.; Jamilian, A.; Fateh, A.; Abbaszadeh, F. Are Virtually Designed 3D Printed Surgical Splints Accurate Enough for Maxillary Reposition as an Intermediate Orthognathic Surgical Guide? J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2023, 22, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristic | N = 90 |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| F | 57 (63%) |
| M | 33 (37%) |
| Age | 14 (10, 24) |
| Upper Facial Height | 56.2 (53.1, 59.4) |
| Middle Facial Height | 55.7 (51.9, 60.1) |
| Lower Facial Height | 60 (56, 64) |
| Vertical Facial Proportion I-upper region | 1.01 (0.92, 1.06) |
| Vertical Facial Proportion II-lower region | 1.08 (0.99, 1.15) |
| Total Facial Height | 173 (162, 180) |
| Upper Lip Length | 15.88 (13.77, 18.06) |
| Lower Lip Length | 37.1 (33.2, 41.2) |
| Interpupillary distance | 58.8 (55.4, 61.7) |
| Bizygomatic width | 110 (104, 115) |
| Nasofrontal angle | 144 (140, 148) |
| Nasolabial angle | 116 (108, 123) |
| Mouth width | 51 (47, 56) |
| Mentolabial angle | 137 (126, 149) |
| Facial angle | 14.2 (10.0, 19.7) |
| Distance from Labrale superius to E-line | 3.8 (1.6, 6.6) |
| Distance from Labrale inferius to E-line | 2.57 (1.29, 4.54) |
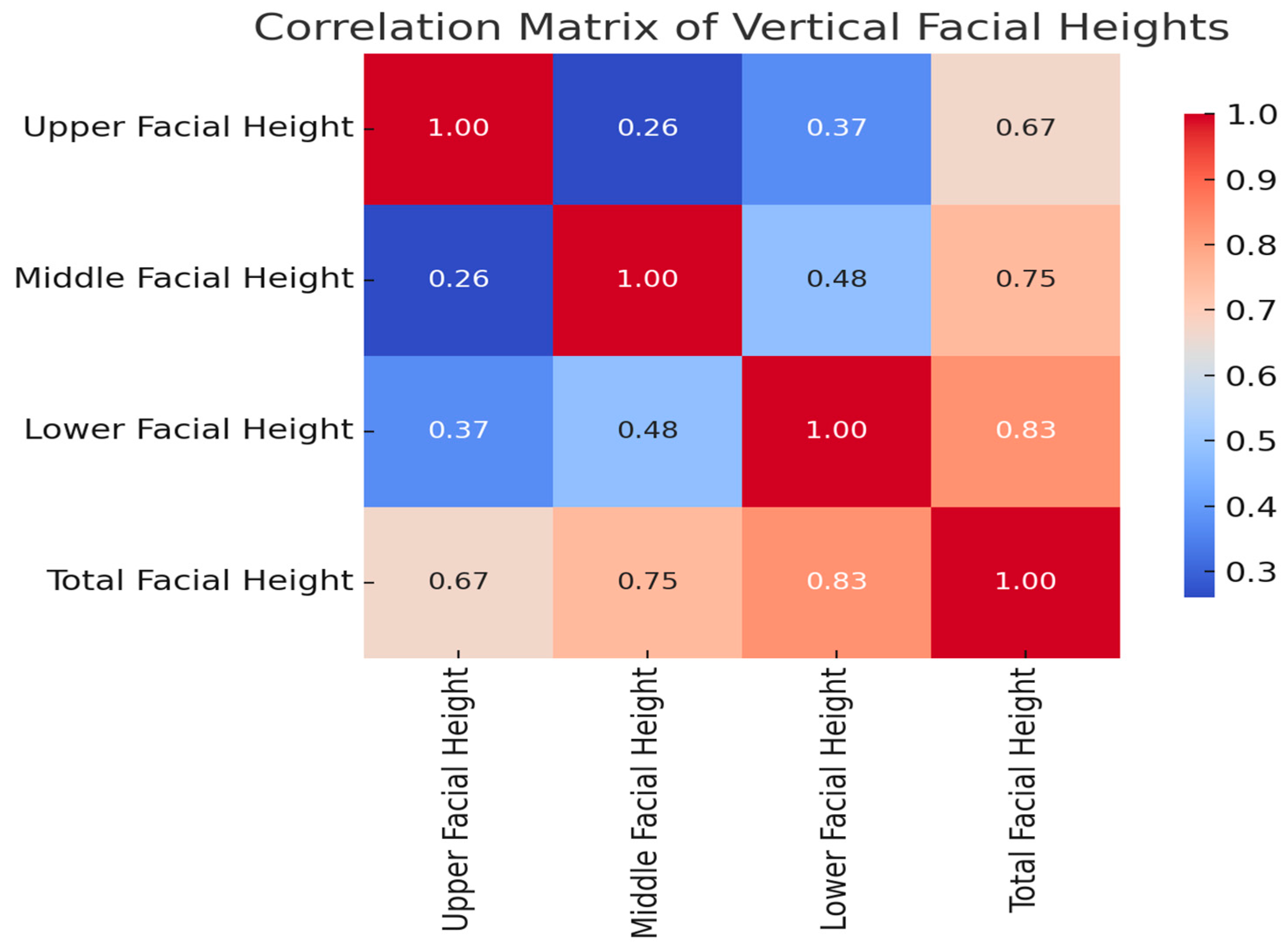
| Age | Upper Facial Height | Middle Facial Height | Lower Facial Height | Vertical Facial Proportion I | Vertical Facial Proportion II | Total Facial Height | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | — | ||||||
| Upper Facial Height | r = 0.334 (95% CI: 0.136 to 0.506), p = 0.001 | — | |||||
| Middle Facial Height | r = 0.631 (95% CI: 0.488 to 0.741), p < 0.001 | r = 0.257 (95% CI: 0.053 to 0.441), p = 0.014 | — | ||||
| Lower Facial Height | r = 0.615 (95% CI: 0.467 to 0.729), p < 0.001 | r = 0.367 (95% CI: 0.173 to 0.534), p < 0.001 | r = 0.479 (95% CI: 0.302 to 0.624), p < 0.001 | — | |||
| Vertical Facial Proportion I | r = 0.198 (95% CI: −0.009 to 0.389), p = 0.061 | r = −0.611 (95% CI: −0.726 to −0.462), p < 0.001 | r = 0.539 (95% CI: 0.374 to 0.671), p < 0.001 | r = 0.090 (95% CI: −0.119 to 0.292), p = 0.398 | — | ||
| Vertical Facial Proportion II | r = 0.258 (95% CI: 0.054 to 0.442), p = 0.014 | r = −0.438 (95% CI: −0.591 to −0.254), p < 0.001 | r = 0.247 (95% CI: 0.042 to 0.432), p = 0.019 | r = 0.600 (95% CI: 0.449 to 0.718), p < 0.001 | r = 0.622 (95% CI: 0.476 to 0.734), p < 0.001 | — | |
| Total Facial Height | r = 0.690 (95% CI: 0.563 to 0.785), p < 0.001 | r = 0.667 (95% CI: 0.534 to 0.768), p < 0.001 | r = 0.748 (95% CI: 0.640 to 0.827), p < 0.001 | r = 0.833 (95% CI: 0.756 to 0.887), p < 0.001 | r = 0.025 (95% CI: −0.183 to 0.231), p = 0.812 | r = 0.218 (95% CI: 0.011 to 0.407), p = 0.039 | — |
| Upper Lip Length | Lower Lip Length | Interpupillary Distance | Bizygomatic Width | Mouth Width | Distance From Labrale Superius to E-Line | Distance From Labrale Inferius to E-Line | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper lip length | — | ||||||
| Lower lip length | r = 0.528 (95% CI: 0.360 to 0.663), p < 0.001 | — | |||||
| Interpupillary distance | r = 0.445 (95% CI: 0.262 to 0.597), p < 0.001 | r = 0.527 (95% CI: 0.359 to 0.662), p < 0.001 | — | ||||
| Bizygomatic width | r = 0.293 (95% CI: 0.091 to 0.471), p = 0.005 | r = 0.584 (95% CI: 0.429 to 0.706), p < 0.001 | r = 0.845 (95% CI: 0.773 to 0.895), p < 0.001 | — | |||
| Mouth width | r = −0.052 (95% CI: −0.256 to 0.157), p = 0.625 | r = 0.278 (95% CI: 0.075 to 0.459), p = 0.008 | r = 0.487 (95% CI: 0.311 to 0.631), p < 0.001 | r = 0.618 (95% CI: 0.471 to 0.731), p < 0.001 | — | ||
| Distance from Labrale superius to E-line | r = −0.201 (95% CI: −0.392 to 0.006), p = 0.057 | r = 0.241 (95% CI: 0.036 to 0.427), p = 0.022 | r = 0.309 (95% CI: 0.109 to 0.485), p = 0.003 | r = 0.448 (95% CI: 0.266 to 0.599), p < 0.001 | r = 0.665 (95% CI: 0.531 to 0.767), p < 0.001 | — | |
| Distance from Labrale inferius to E-line | r = −0.204 (95% CI: −0.394 to 0.003), p = 0.054 | r = 0.126 (95% CI: −0.083 to 0.325), p = 0.235 | r = 0.217 (95% CI: 0.010 to 0.406), p = 0.040 | r = 0.261 (95% CI: 0.057 to 0.444), p = 0.013 | r = 0.490 (95% CI: 0.315 to 0.633), p < 0.001 | r = 0.601 (95% CI: 0.450 to 0.719), p < 0.001 | — |
| Nasofrontal Angle | Nasolabial Angle | Mentolabial Angle | Facial Angle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasofrontal angle | — | |||
| Nasolabial angle | r = −0.001 (95% CI: −0.208 to 0.206), p = 0.990 | — | ||
| Mentolabial angle | r = 0.023 (95% CI: −0.185 to 0.229), p = 0.827 | r = 0.360 (95% CI: 0.165 to 0.528), p < 0.001 | — | |
| Facial angle | r = −0.035 (95% CI: −0.240 to 0.173), p = 0.745 | r = 0.385 (95% CI: 0.193 to 0.548), p < 0.001 | r = −0.391 (95% CI: −0.553 to −0.200), p < 0.001 | — |
| Characteristic | Female (n = 57, 63.3%) | Male (n = 33, 36.7%) | Total (n = 90) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 22.0 (12.0–27.0) | 11.0 (9.0–16.0) | 14.0 (10.0–24.0) | 0.002 |
| Upper facial height, mm | 57.2 (54.5–59.4) | 55.4 (47.9–59.0) | 56.2 (53.1–59.3) | 0.105 |
| Middle facial height, mm | 57.1 (53.2–60.8) | 53.5 (49.0–58.0) | 55.7 (52.0–60.1) | 0.002 |
| Lower facial height, mm | 60.3 (56.3–63.5) | 59.2 (53.7–65.5) | 60.2 (55.6–63.9) | 0.940 |
| Vertical facial proportion I | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 1.0 (0.9–1.1) | 1.0 (0.9–1.1) | 0.335 |
| Vertical facial proportion II | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 1.1 (1.0–1.2) | 1.1 (1.0–1.1) | 0.067 |
| Total facial height, mm | 175.2 (167.6–180.1) | 165.4 (152.9–179.4) | 173.0 (162.2–179.9) | 0.045 |
| Upper lip length, mm | 15.5 (13.7–17.6) | 16.2 (14.6–18.6) | 15.9 (13.8–18.0) | 0.175 |
| Lower lip length, mm | 38.0 (35.1–41.1) | 36.6 (32.1–42.8) | 37.1 (33.2–41.2) | 0.368 |
| Interpupillary distance, mm | 59.1 (56.1–62.1) | 58.6 (55.0–61.7) | 58.8 (55.4–61.7) | 0.506 |
| Bizygomatic width, mm | 110.3 (105.2–115.5) | 107.8 (101.9–112.9) | 109.8 (104.5–115.1) | 0.187 |
| Nasofrontal angle, ° | 144.6 (141.2–150.0) | 142.1 (138.6–146.4) | 144.1 (140.4–147.6) | 0.025 |
| Nasolabial angle, ° | 114.0 (107.0–120.2) | 122.1 (115.2–125.2) | 116.5 (108.5–123.0) | 0.001 |
| Mouth width, mm | 52.0 (47.4–56.3) | 49.7 (43.9–54.1) | 51.0 (46.5–55.7) | 0.152 |
| Mentolabial angle, ° | 136.6 (124.7–145.4) | 139.9 (130.5–150.0) | 137.5 (125.9–148.5) | 0.171 |
| Facial angle, ° | 13.7 (9.5–18.5) | 15.0 (10.1–20.8) | 14.2 (10.0–19.5) | 0.288 |
| Distance from Labrale superius to E-line, mm | 4.5 (2.1–7.1) | 2.8 (1.1–4.9) | 3.8 (1.6–6.6) | 0.041 |
| Distance from Labrale inferius to E-line, mm | 2.6 (1.4–4.8) | 2.5 (1.3–3.6) | 2.6 (1.3–4.5) | 0.269 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stăncioiu, A.-A.; Motofelea, A.C.; Popa, A.; Nagib, R.; Lung, R.-B.; Szuhanek, C. Advanced 3D Facial Scanning in Orthodontics: A Correlative Analysis of Craniofacial Anthropometric Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7578. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217578
Stăncioiu A-A, Motofelea AC, Popa A, Nagib R, Lung R-B, Szuhanek C. Advanced 3D Facial Scanning in Orthodontics: A Correlative Analysis of Craniofacial Anthropometric Parameters. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7578. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217578
Chicago/Turabian StyleStăncioiu, Andra-Alexandra, Alexandru Cătălin Motofelea, Adelina Popa, Riham Nagib, Rareș-Bogdan Lung, and Camelia Szuhanek. 2025. "Advanced 3D Facial Scanning in Orthodontics: A Correlative Analysis of Craniofacial Anthropometric Parameters" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7578. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217578
APA StyleStăncioiu, A.-A., Motofelea, A. C., Popa, A., Nagib, R., Lung, R.-B., & Szuhanek, C. (2025). Advanced 3D Facial Scanning in Orthodontics: A Correlative Analysis of Craniofacial Anthropometric Parameters. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7578. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217578







