Isolated Chronic Neutropenia in Adults: Causes, Diagnostic Work-Up, and Management—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction: Definition and Classification
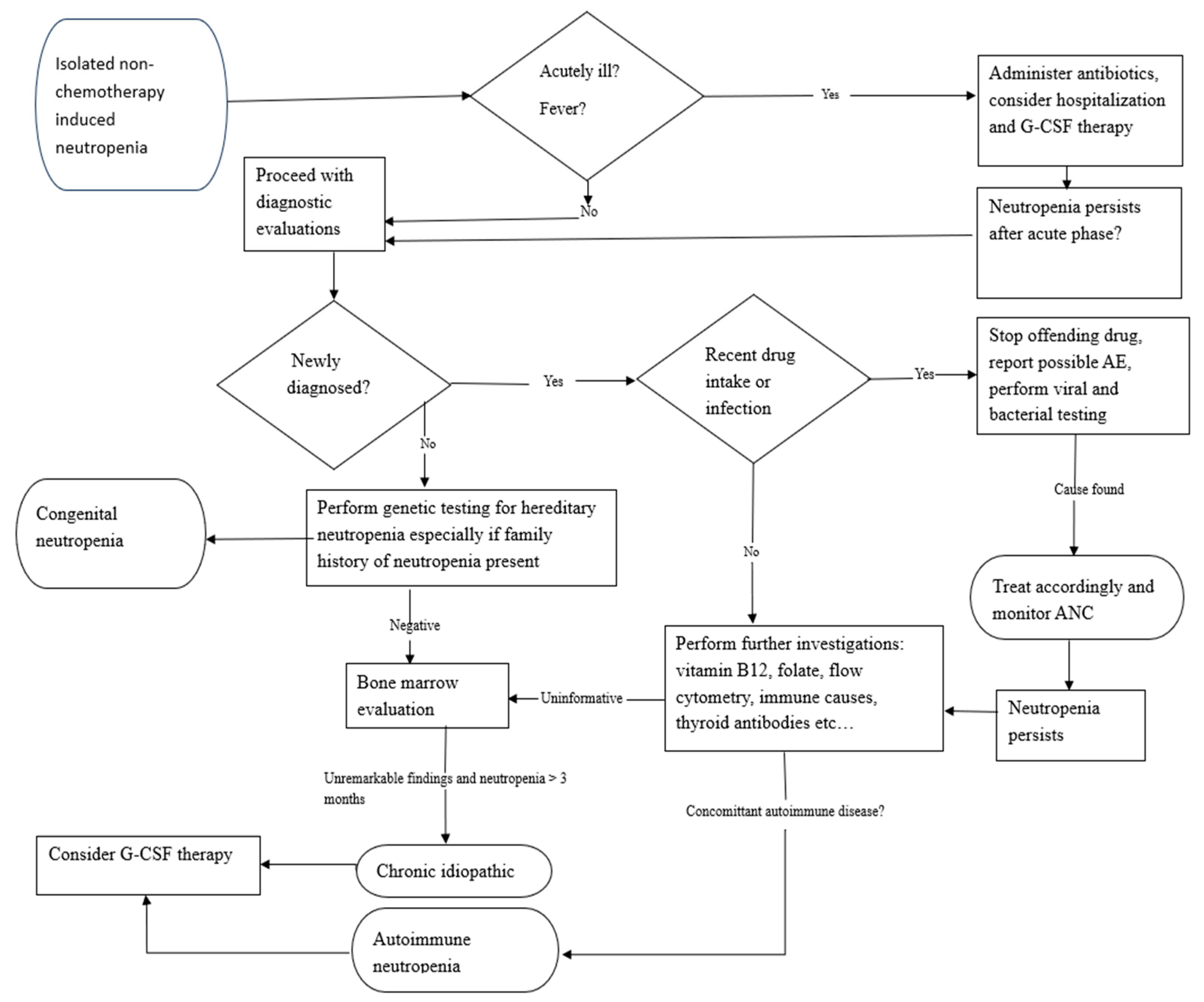
2. Diagnostic Work-Up
3. Etiologies of Chronic Neutropenia
3.1. Drug-Induced Chronic Neutropenia
3.2. Autoimmune Neutropenia (AIN)
3.3. Chronic Idiopathic Neutropenia (CIN)
3.4. Clonal Cytopenia of Undetermined Significance (CCUS)
3.5. Duffy-Null Associated Neutrophil Count (DANC)
3.6. Familial Neutropenia
3.7. Severe Congenital Neutropenia (SCN)
3.8. Cyclic Neutropenia (CyN)
3.9. Congenital Conditions Associated with Neutropenia
4. Treatment of Chronic Neutropenia
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioredda, F.; Skokowa, J.; Tamary, H.; Spanoudakis, M.; Farruggia, P.; Almeida, A.; Guardo, D.; Hoglund, P.; Newburger, P.E.; Palmblad, J.; et al. The European Guidelines on Diagnosis and Management of Neutropenia in Adults and Children: A Consensus Between the European Hematology Association and the EuNet-INNOCHRON COST Action. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njue, L.; Porret, N.; Schnegg-Kaufmann, A.S.; Varra, L.F.; Andres, M.; Rovo, A. Isolated Severe Neutropenia in Adults, Evaluation of Underlying Causes and Outcomes, Real-World Data Collected over a 5-Year Period in a Tertiary Referral Hospital. Medicina 2024, 60, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, P.; Reynolds, S.B.; Zito, P.M. Neutropenia; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.I.; Byeon, S. Diagnosis and management of neutropenia. Blood Res. 2025, 60, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandherr, M.; Stemler, J.; Schalk, E.; Hattenhauer, T.; Hentrich, M.; Hertenstein, B.; Hohmann, C.; Mellinghoff, S.C.; Mispelbaum, R.; Rieger, C.; et al. 2024 update of the AGIHO guideline on diagnosis and empirical treatment of fever of unknown origin (FUO) in adult neutropenic patients with solid tumours and hematological malignancies. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2025, 51, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioredda, F.; Spanoudakis, M.; Skokowa, J.; Tamary, H.; Farruggia, P.; Almeida, A.; Guardo, D.; Palmblad, J.; Hoglund, P.; Touw, I.P.; et al. European guidelines on treatment and supportive measures in chronic neutropenias: A consensus between the European Hematology Association and the EuNet-INNOCHRON COST Action based on a systematic evidence review. Hemasphere 2025, 9, e70113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakilic-Ozturan, E.; Karaman, S.; Soguksu, P.; Mese, S.; Agacfidan, A.; Mutlu, U.D.; Karakas, Z.; Tugcu, D.; Karagenc-Ozkan, A.; Devecioglu, O. The Role of Anti-Neutrophil Antibodies in the Etiologic Classification of Childhood Neutropenia: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Tertiary Center. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 42, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, M.L.W.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Ngeow, J.Y.Y. Telomere biology disorders. npj Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadieu, J.; Beaupain, B.; Fenneteau, O.; Bellanne-Chantelot, C. Congenital neutropenia in the era of genomics: Classification, diagnosis, and natural history. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioredda, F.; Dufour, C.; Hoglund, P.; Papadaki, H.A.; Palmblad, J. Autoimmune Neutropenias: Update on Clinical and Biological Features in Children and Adults. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinauer, M.C. Neutrophil Defects and Diagnosis Disorders of Neutrophil Function: An Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2087, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, E.; Mourot-Cottet, R. Non-chemotherapy drug-induced neutropenia—An update. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 16, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, X.; Huang, S.; Huang, X. Non-chemotherapy drugs inducing agranulocytosis: A disproportionality analysis based on the FAERS database. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1525307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpica Castillo, L.E.; Palmer, S.; Zhu, A.; Deal, A.M.; Chen, S.L.; Moll, S. Incidence and time course of neutropenia in patients treated with rituximab-based therapy for non-malignant immune-mediated hematologic diseases. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, E117–E120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protopapa, M.; Schraad, M.; Pape, K.; Steffen, F.; Steenken, L.; Zipp, F.; Fleischer, V.; Bittner, S. Recurrent late-onset neutropenia following treatment with different B cell-depleting strategies in multiple sclerosis. Med 2025, 6, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.; Higgins, M.; Hammer, B.; Stephenson, P. Clozapine rechallenge and initiation despite neutropenia—A practical, step-by-step guide. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, D.C.; Bolyard, A.A. An update on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic idiopathic neutropenia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegscheider, C.; Ferincz, V.; Schols, K.; Maieron, A. Felty’s syndrome. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1238405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Casanova, J.L.; Boisson, B. Common variable immunodeficiency: Autoimmune cytopenias and advances in molecular diagnosis. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2024, 2024, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliegauf, M.; Kruger, R.; Steiner, S.; Hanitsch, L.G.; Buchel, S.; Wahn, V.; von Bernuth, H.; Grimbacher, B. A Pathogenic Missense Variant in NFKB1 Causes Common Variable Immunodeficiency Due to Detrimental Protein Damage. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 621503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Hayes, K.M.; Ong, M.S.; Mizgerd, J.P.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Dominguez, I.; Barmettler, S.; Farmer, J.R.; Maglione, P.J. Common Variable Immunodeficiency Clinical Manifestations Are Shaped by Presence and Type of Heterozygous NFKB1 Variants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2025, 13, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, R.; Habibi, S.; Sharifi, L.; Azizi, G.; Abolhassani, H.; Olbrich, P.; Aghamohammadi, A. Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, Classification, and Management. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 30, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaknakis, G.; Galli, A.; Papadakis, S.; Kanellou, P.; Elena, C.; Todisco, G.; Bono, E.; Rizzo, E.; Molteni, E.; Fragiadaki, I.; et al. Incidence and prognosis of clonal hematopoiesis in patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia. Blood 2021, 138, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanoudakis, M.; Koutala, H.; Ximeri, M.; Pyrovolaki, K.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Papadaki, H.A. T-cell receptor Vbeta repertoire analysis in patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia demonstrates the presence of aberrant T-cell expansions. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 137, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizymi, N.; Damianaki, A.; Aresti, N.; Karasachinidis, A.; Vlata, Z.; Lavigne, M.; Dialynas, E.; Gounalaki, N.; Stratidaki, I.; Tsaknakis, G.; et al. Characterization of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia. Hemasphere 2024, 8, e70005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattizzo, B.; Bosi, A.; Sorrenti, M.; Murgia, D.; Pettine, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Croci, G.A.; Passamonti, F.; Barcellini, W. Natural history of chronic idiopathic neutropenia of the adult. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atallah-Yunes, S.A.; Ready, A.; Newburger, P.E. Benign ethnic neutropenia. Blood Rev. 2019, 37, 100586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, L.E.; Achebe, M. When non-Whiteness becomes a condition. Blood 2021, 137, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, D.; Nalls, M.A.; Kao, W.H.; Akylbekova, E.L.; Tandon, A.; Patterson, N.; Mullikin, J.; Hsueh, W.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Coresh, J.; et al. Reduced neutrophil count in people of African descent is due to a regulatory variant in the Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines gene. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Luo, H.R. Novel neutrophil biology insights underlying atypical chemokine receptor-1/Duffy antigen receptor of chemokines-associated neutropenia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2024, 31, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmblad, J.; Sohlberg, E.; Nilsson, C.C.; Lindqvist, H.; Deneberg, S.; Ratcliffe, P.; Meinke, S.; Mortberg, A.; Klimkowska, M.; Hoglund, P. Clinical and immunological features in ACKR1/DARC-associated neutropenia. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruenster, M.; Mudde, L.; Bombosi, P.; Dimitrova, S.; Zsak, M.; Middleton, J.; Richmond, A.; Graham, G.J.; Segerer, S.; Nibbs, R.J.; et al. The Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines transports chemokines and supports their promigratory activity. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.; Miyamura, J.; Chen, J.J. Racial/Ethnic-Specific Reference Intervals for Common Laboratory Tests: A Comparison among Asians, Blacks, Hispanics, and White. Hawaii J. Med. Public Health 2015, 74, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Solomou, E.E.; Salamaliki, C.; Lagadinou, M. How to Make the Right Diagnosis in Neutropenia. Clin. Hematol. Int. 2021, 3, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, F.H. Familial benign chronic neutropenia in a Danish family. Ugeskr. Laeger 1990, 152, 2565–2566. [Google Scholar]
- Denic, S.; Showqi, S.; Klein, C.; Takala, M.; Nagelkerke, N.; Agarwal, M.M. Prevalence, phenotype and inheritance of benign neutropenia in Arabs. BMC Blood Disord. 2009, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, A.P.; Lettre, G.; Nalls, M.A.; Ganesh, S.K.; Mathias, R.; Austin, M.A.; Dean, E.; Arepalli, S.; Britton, A.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome-wide association study of white blood cell count in 16,388 African Americans: The continental origins and genetic epidemiology network (COGENT). PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, E.A.; Makaryan, V.; Burt, A.A.; Crosslin, D.R.; Kim, D.S.; Smith, J.D.; Nickerson, D.A.; Reiner, A.P.; Rich, S.S.; Jackson, R.D.; et al. Association Between Absolute Neutrophil Count and Variation at TCIRG1: The NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydzynska, Z.; Pawlik, B.; Krzyzanowski, D.; Mlynarski, W.; Madzio, J. Neutrophil Elastase Defects in Congenital Neutropenia. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 653932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, A.K.; Senthamizhselvi, A.; Hemamalini, S.; Edison, E.S.; Korula, A.; Fouzia, N.A.; George, B.; Mathews, V.; Balasubramanian, P. Spectrum of ELANE mutations in congenital neutropenia: A single-centre study in patients of Indian origin. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, D.C.; Cottle, T.E.; Fier, C.J.; Bolyard, A.A.; Bonilla, M.A.; Boxer, L.A.; Cham, B.; Freedman, M.H.; Kannourakis, G.; Kinsey, S.E.; et al. Severe chronic neutropenia: Treatment and follow-up of patients in the Severe Chronic Neutropenia International Registry. Am. J. Hematol. 2003, 72, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welte, K.; Zeidler, C.; Dale, D.C. Severe congenital neutropenia. Semin. Hematol. 2006, 43, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, D.C.; Bonilla, M.A.; Davis, M.W.; Nakanishi, A.M.; Hammond, W.P.; Kurtzberg, J.; Wang, W.; Jakubowski, A.; Winton, E.; Lalezari, P.; et al. A randomized controlled phase III trial of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim) for treatment of severe chronic neutropenia. Blood 1993, 81, 2496–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fioredda, F.; Iacobelli, S.; van Biezen, A.; Gaspar, B.; Ancliff, P.; Donadieu, J.; Aljurf, M.; Peters, C.; Calvillo, M.; Matthes-Martin, S.; et al. Stem cell transplantation in severe congenital neutropenia: An analysis from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood 2015, 126, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrewa, W.; Bielska, M.; Babol-Pokora, K.; Janczar, S.; Mlynarski, W. Congenital neutropenia: From lab bench to clinic bedside and back. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2024, 793, 108476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Eldomery, M.K.; Maciaszek, J.L.; Klco, J.M. Inherited Predispositions to Myeloid Neoplasms: Pathogenesis and Clinical Implications. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2025, 20, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, D.C.; Bolyard, A.A.; Shannon, J.A.; Connelly, J.A.; Link, D.C.; Bonilla, M.A.; Newburger, P.E. Outcomes for patients with severe chronic neutropenia treated with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3861–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zergham, A.S.; Acharya, U.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R. Cyclic Neutropenia; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Alter, B.P. Diagnosis, genetics, and management of inherited bone marrow failure syndromes. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2007, 2007, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, R.; Braga, J.A.P.; Moritz, E.; Pesquero, J.B.; Bordin, J.O. A novel ELANE variant causing severe congenital neutropenia diagnosed in adulthood. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2025, 113–114, 102940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Koyfman, A. Incidental neutropenia: An emergency medicine focused approach. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2025, 89, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, D.C. How I diagnose and treat neutropenia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, D.C.; Bolyard, A.; Marrero, T.; Makaryan, V.; Bonilla, M.; Link, D.C.; Newburger, P.; Shimamura, A.; Boxer, L.A.; Spiekerman, C. Long-Term Effects of G-CSF Therapy in Cyclic Neutropenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2290–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidler, C.; Grote, U.A.; Nickel, A.; Brand, B.; Carlsson, G.; Cortesao, E.; Dufour, C.; Duhem, C.; Notheis, G.; Papadaki, H.A.; et al. Outcome and management of pregnancies in severe chronic neutropenia patients by the European Branch of the Severe Chronic Neutropenia International Registry. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxer, L.A.; Bolyard, A.A.; Kelley, M.L.; Marrero, T.M.; Phan, L.; Bond, J.M.; Newburger, P.E.; Dale, D.C. Use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor during pregnancy in women with chronic neutropenia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Acute Neutropenia (Duration < 3 Months) | Chronic Neutropenia (Duration > 3 Months) |
|---|---|
| Drugs/toxins | Severe congenital neutropenia |
| Infections | Cyclic neutropenia |
| Autoimmune causes | Chronic idiopathic neutropenia |
| Nutritional deficiencies | Autoimmune neutropenia |
| Radiotherapy | Duffy-null associated neutrophil count |
| Hematological diseases, e.g., AA, AML | Rarely drugs, e.g., rituximab |
| Rheumatological disorders | Hematological diseases, e.g., LGLL, SDS, TBD |
| CIN | AIN | CCUS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cause | No identifiable cause | Usually develops in the presence of autoimmune diseases | Somatic mutations of myeloid neoplasm-linked genes |
| Clonal evolution | Not associated with transformation to myeloid malignancy | Not associated with transformation to myeloid malignancy | Increased risk of progression to myelodysplastic neoplasms |
| Diagnosis | Exclusion of other causes of neutropenia (drugs, malignant disease, infections, nutritional deficiencies, or autoimmune causes) | Detection of anti-neutrophil antibodies possible | NGS myeloid panel showing somatic mutations |
| Clinical course | Generally benign, with mild symptoms/infections | Generally benign with mild symptoms/infections; may be acute or chronic | May be asymptomatic; transformation to myelodysplastic neoplasms is possible |
| Bone marrow examination | Typically normal, without clonal abnormalities | Typically normal, without clonal abnormalities | Typically normal or mild dysplasia |
| Therapy | G-CSF either on-demand or continuously (in patients with frequent infections) | Treatment of underlying autoimmune disease; G-CSF either on-demand or continuously (in patients with frequent infections) | Monitoring; treatment, if progression occurs |
| SCN | Starting dose 5 mcg/kg/day with dose increment by 1–2 mcg/kg/day weekly until target ANC ≥ 1.0 × 109/L is achieved (median dose 7.3 mcg/kg/day) |
| CyN | Median dose 2.5 mcg/kg/d |
| CIN/AIN | Median dose 1.2 mcg/kg/day |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Njue, L.; Porret, N.; Andres, M.; Rovó, A. Isolated Chronic Neutropenia in Adults: Causes, Diagnostic Work-Up, and Management—A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217495
Njue L, Porret N, Andres M, Rovó A. Isolated Chronic Neutropenia in Adults: Causes, Diagnostic Work-Up, and Management—A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217495
Chicago/Turabian StyleNjue, Linet, Naomi Porret, Martin Andres, and Alicia Rovó. 2025. "Isolated Chronic Neutropenia in Adults: Causes, Diagnostic Work-Up, and Management—A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217495
APA StyleNjue, L., Porret, N., Andres, M., & Rovó, A. (2025). Isolated Chronic Neutropenia in Adults: Causes, Diagnostic Work-Up, and Management—A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7495. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217495







