Diagnostic and Prognostic Evaluation of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Using the Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DIC | disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| SIC | sepsis-induced coagulopathy |
| TMA | thrombotic microangiopathy |
| SIRS | systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| JMHLW | Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare |
| ISTH | International Society of Thrombosis Hemostasis |
| JAAM | Japanese Association for Acute Medicine |
| PT | prothrombin time |
| INR | international normalized ratio |
| FDP | fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products |
| sCLEC-2 | soluble C-type lectin-like receptor 2 |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| r | correlation coefficient |
| AUC | area under the curve |
References
- Adelborg, K.; Larsen, J.B.; Hvas, A.M. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: Epidemiology, biomarkers, and management. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levi, M.; Thachil, J.; Levy, J.H. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: The Past, Present, and Future Considerations. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 48, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Sivapalaratnam, S. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: An update on pathogenesis and diagnosis. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtiaud, A.; Iba, T.; Angles-Cano, E.; Meziani, F.; Helms, J. Biomarkers of sepsis-induced coagulopathy: Diagnostic insights and potential therapeutic implications. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2025, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Levi, M.; Levy, J.H. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Cate, H.; Leader, A. Management of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Acute Leukemias. Hamostaseologie 2021, 41, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Cancer: An Update. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, O.; Othman, M.; Rabinovich, A.; Leron, E.; Gotsch, F.; Thachil, J. DIC in Pregnancy—Pathophysiology, Clinical Characteristics, Diagnostic Scores, and Treatments. J. Blood Med. 2022, 13, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gando, S. Hemostasis and thrombosis in trauma patients. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Asakura, H. Therapeutic Strategies for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Associated with Aortic Aneurysm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Asakura, H.; Okamoto, K.; Iba, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Kawasugi, K.; Koga, S.; Myumi, T.; Koike, K.; Gando, S.; et al. Expert consensus for the treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation in Japan. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Japanese Society of Thrombosis Hemostasis/DIC Subcommittee; Okamoto, K.; Iba, T.; Kushimoto, S.; Kawasugi, K.; Gando, S.; Madoiwa, S.; Uchiyama, T.; Mayumi, T.; et al. Addition of recommendations for the use of recombinant human thrombomodulin to the “Expert consensus for the treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation in Japan”. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Toh, C.H.; Thachil, J.; Watson, H.G. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of disseminated intravascular coagulation. British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nisio, M.; Baudo, F.; Cosmi, B.; D’Angelo, A.; De Gasperi, A.; Malato, A.; Schiavoni, M.; Squizzato, A.; Italian Society for Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation: Guidelines of the Italian Society for Haemostasis and Thrombosis (SISET). Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, e177–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, H.; Thachil, J.; Di Nisio, M.; Mathew, P.; Kurosawa, S.; Gando, S.; Kim, H.K.; Nielsen, J.D.; Dempfle, C.E.; Levi, M.; et al. The Scientific Standardization Committee on DIC of the International Society on Thrombosis Haemostasis.: Guidance for diagnosis and treatment of DIC from harmonization of the recommendations from three guidelines. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.L.; Kavanagh, D. Diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic microangiopathy. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2022, 44 (Suppl. 1), 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Imai, H.; Katayama, N.; Iba, T.; Matsumoto, M. Differences and similarities between disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombotic microangiopathy. Thromb. J. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Maegawa, T.; Takada, M.; Tanaka, H.; Gonmori, H. Criteria for diagnosis of DIC based on the analysis of clinical and laboratory findings in 345 DIC patients collected by the Research Committee on DIC in Japan. Bibl. Haematol. 1983, 49, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H.; Maier, C.L.; Helms, J.; Umemura, Y.; Moore, H.; Othman, M.; Thachil, J.; Connors, J.M.; Levi, M.; et al. Updated definition and scoring of disseminated intravascular coagulation in 2025: Communication from the ISTH SSC Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2025, 23, 356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gando, S.; Iba, T.; Eguchi, Y.; Ohtomo, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Koseki, K.; Mayumi, T.; Murata, A.; Ikeda, T.; Ishikura, H.; et al. A multicenter, prospective validation of disseminated intravascular coagulation diagnostic criteria for critically ill patients: Comparing current criteria. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Takahashi, H.; Uchiyama, T.; Eguchi, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Kawasugi, K.; Madoiwa, S.; Asakura, H.; DIC Subcommittee of the Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis. The approval of revised diagnostic criteria for DIC from the Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Thromb. J. 2017, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Helms, J.; Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. The pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Intensive Care 2023, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H.; Warkentin, T.E.; Thachil, J.; van der Poll, T.; Levi, M.; Scientific and Standardization Committee on DIC, and the Scientific and Standardization Committee on Perioperative and Critical Care of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Helms, J.; Levy, J.H. Sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) in the management of sepsis. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2024, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemitsu, T.; Wada, H.; Hatada, T.; Ohmori, Y.; Ishikura, K.; Takeda, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamada, N.; Maruyama, K.; Katayama, N.; et al. Prospective evaluation of three different diagnostic criteria for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempfle, C.E. D-dimer: Standardization versus harmonization. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.D.; Schell, J.C.; Rodgers, G.M. The D-dimer assay. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Tomida, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Ezaki, M.; Masuda, J.; Yoshida, M.; Fukui, S.; Moritani, I.; Inoue, H.; et al. Proposal of Quick Diagnostic Criteria for Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Wada, H.; Tomida, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Ezaki, M.; Shiraki, K.; Shimaoka, M.; Iba, T.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Kawamura, M.; et al. Super Formula for Diagnosing Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Using Soluble C-Type Lectin-like Receptor 2. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Fuller, G.L.; Garcia, A.; Eble, J.A.; Pohlmann, S.; Inoue, O.; Gartner, T.K.; Hughan, S.C.; Pearce, A.C.; Laing, G.D.; et al. A novel Syk-dependent mechanism of platelet activation by the C-type lectin receptor sCLEC-2. Blood 2006, 107, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, M.; Ueda, M.; Matsushita, S.; Sasaki, T.; Furuyama, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Shirai, T.; Kazama, F.; Suzuki-Inoue, K. Development of an automated chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for the measurement of soluble C-type lectin-like receptor 2 (sCLEC-2) and molecular forms of sCLEC-2 measured in patient plasma. Platelets 2024, 35, 2420949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowski, N.A.; Bullen, J.A. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves: Review of methods with applications in diagnostic medicine. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 07TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, M.; Peng, X.; Yang, J.; Niu, T. Comparison of Three Different Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Criteria and Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Antithrombin Investigation in Patients with Confirmed Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy (SIC). Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 30, 10760296241271334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, H.; Kamikubo, Y.; Goto, A.; Shiratori, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Jokaji, H.; Saito, M.; Uotani, C.; Kumabashiri, I.; Morishita, E.; et al. Role of tissue factor in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb. Res. 1995, 80, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yamakawa, K.; Ogura, H.; Koh, T.; Matsumoto, N.; Shimazu, T. Clinical Significance of Tissue Factor and CD13 Double-Positive Microparticles in Sirs Patients with Trauma and Severe Sepsis. Shock 2017, 47, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikura, H.; Irie, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Hoshino, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Mizunuma, M.; Maruyama, J.; Nakashio, M.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Kitamura, T. Early recognition of sepsis-induced coagulopathy using the C2PAC index: A ratio of soluble type C lectin-like receptor 2 (sCLEC-2) level and platelet count. Platelets 2022, 33, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorgalaleh, A.; Favaloro, E.J.; Bahraini, M.; Rad, F. Standardization of Prothrombin Time/International Normalized Ratio (PT/INR). Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nasa, V.; Tandon, M. Perioperative monitoring in liver transplant patients. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2012, 2, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Kabata, D.; Abe, T.; Fujishima, S.; Kushimoto, S.; Mayumi, T.; Ogura, H.; Saitoh, D.; Shiraishi, A.; et al. Sepsis-related coagulopathy treatment based on the disseminated intravascular coagulation diagnostic criteria: A post-hoc analysis of a prospective multicenter observational study. J. Intensive Care 2023, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantes, A.G.; Parastatidou, S.; Tsantes, E.A.; Bonova, E.; Tsante, K.A.; Mantzios, P.G.; Vaiopoulos, A.G.; Tsalas, S.; Konstantinidi, A.; Houhoula, D.; et al. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: An Update on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers, and Current Guidelines. Life 2023, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, F.; Bird, R. How I approach new onset thrombocytopenia. Platelets 2020, 31, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, R.L. Diagnosis and management of aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Oncology 2002, 16, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Gando, S.; Levi, M.; Toh, C.H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; Scully, M. How I treat disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood 2018, 131, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.N.; Nester, C.M. Syndromes of thrombotic microangiopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Moake, J.; Dong, J.F. Molecular basis of thrombotic microangiopathy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2025, 23, 3019–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauthier, L.; Favresse, J.; Hardy, M.; Douxfils, J.; Le Gal, G.; Roy, P.M.; van Es, N.; Ay, C.; Ten Cate, H.; Lecompte, T.; et al. D-dimer testing: A narrative review. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2023, 114, 151–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Focosi, D.; Pezzo, M.P.; Mannucci, P.M. How we manage a high D-dimer. Haematologica 2024, 109, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.M. D-dimer assays in diagnosis and management of thrombotic and bleeding disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.J. Laboratory testing in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limonta, G.; Intra, J.; Brambilla, P.J. The clinical utility of D-dimer/platelet count ratio in pregnant women. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 3602–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ding, Q. D-dimer-to-platelet count ratio as a novel indicator for predicting prognosis in HBV-related decompensated cirrhosis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmaz, A.; Seremet Keskin, A.; Kizilates, F. A Prognostic Marker in COVID-19 Disease Severity and Mortality: D-Dimer/Platelet Ratio. Cureus 2023, 15, e39580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, H.; Wakita, Y.; Nakase, T.; Shimura, M.; Hiyoyama, K.; Nagaya, S.; Mori, Y.; Shiku, H. Outcome of disseminated intravascular coagulation in relation to the score when treatment was begun. Mie DIC Study Group. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 74, 848–852. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson Chornenki, N.L.; Dwivedi, D.J.; Kwong, A.C.; Zamir, N.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Liaw, P.C.; Canadian Critical Care Translational Biology Group. Identification of hemostatic markers that define the pre-DIC state: A multi-center observational study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2524–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, J.; Song, Z.; Xue, M.; Shao, M. Comparison between sepsis-induced coagulopathy and Tsepsis-associated coagulopathy criteria in identifying sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation. World J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 15, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Zou, L.; Pittet, J.F.; Chao, W. Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies. Anesth. Analg. 2024, 138, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.; Cui, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, W.; Hua, T.; Zhu, H.; et al. Interpretable machine learning model for early prediction of 28-day mortality in ICU patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy: Development and validation. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, K.; Umemura, Y.; Mochizuki, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Wada, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Iba, T.; Ohtomo, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Mayumi, T.; et al. Proposal and Validation of a Clinically Relevant Modification of the Japanese Association for Acute Medicine Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Diagnostic Criteria for Sepsis. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 124, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Umemura, Y.; Ushio, N.; Hisamune, R.; Okamoto, K.; Honmma, K.; Sasaki, J. The modified Japanese Association for Acute Medicine disseminated intravascular coagulation diagnostic criteria in sepsis is useful for an indicator of initiating treatment for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb. Res. 2025, 253, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
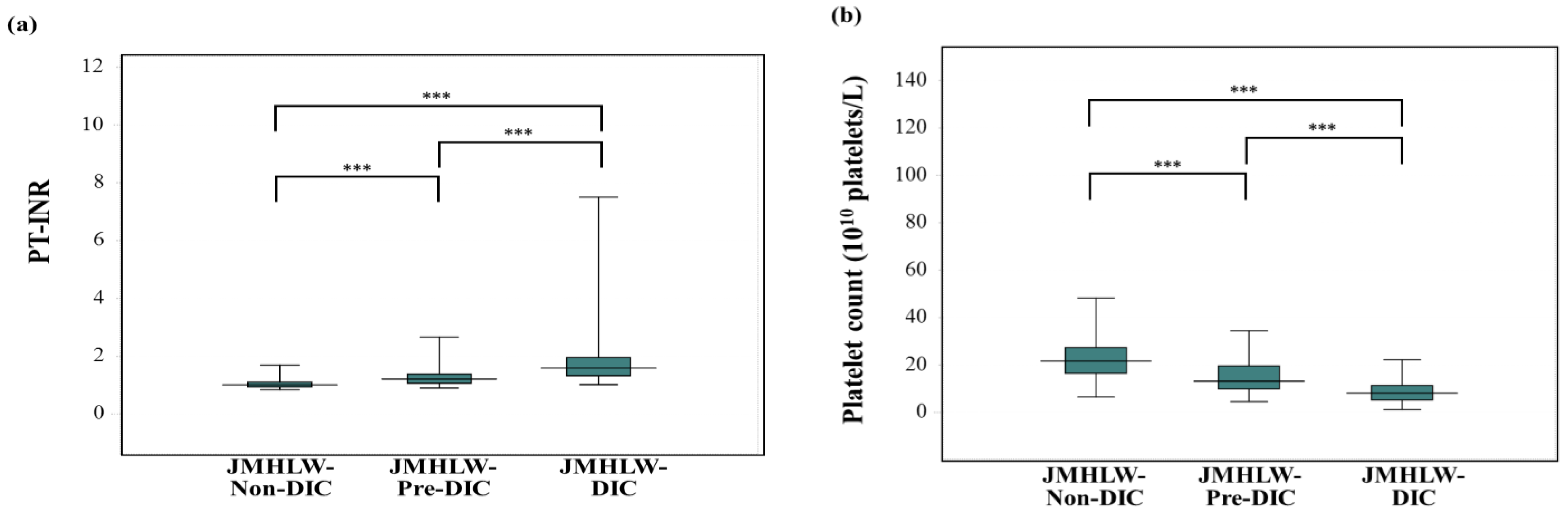
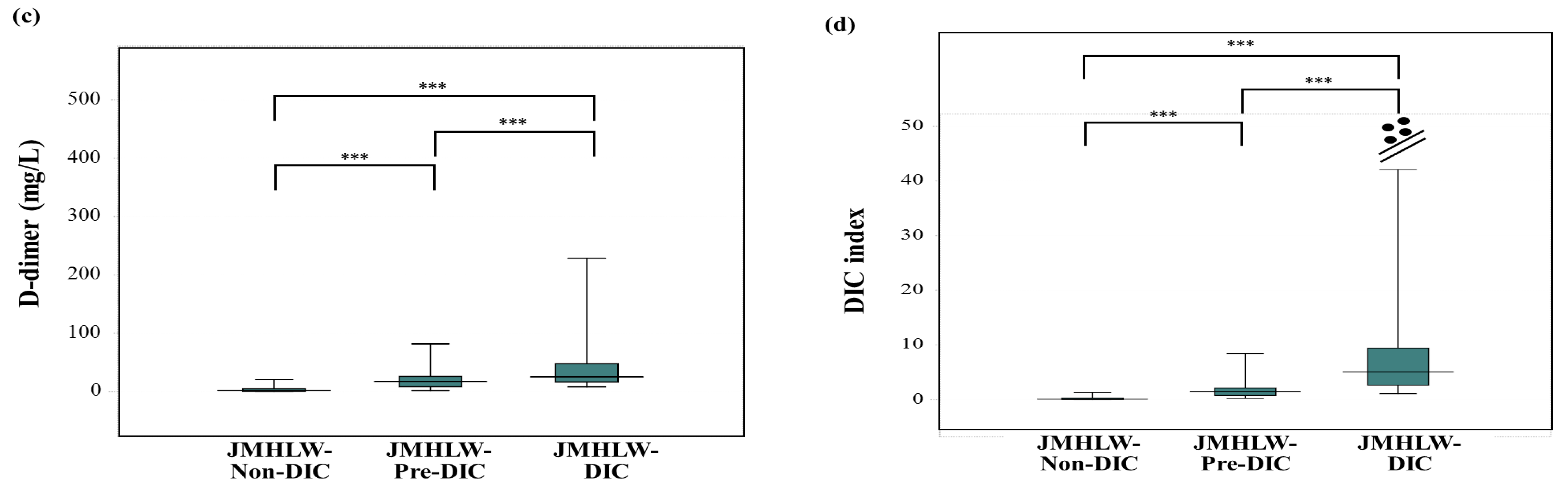

| DIC | JMHLW-DIC | ISTH-DIC | mJAAM-DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT-INR, PT (s) | ≥1.25, 1 P ≥1.67, 2 P | ≥3 s, 1 P ≥6 s, 2 P | ≥1.2, 1 P |
| FDP (mg/L) | ≥10, 1 P ≥20, 2 P ≥40, 3 P | ≥10, 1 P ≥25, 3 P | |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | ≥5, 2 P ≥10, 3 P | ||
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | ≤1.5, 1 P ≤1.0, 2 P | ≤1.0, 1 P | |
| Platelet count (×1010/μL) | ≤12, 1 P ≤ 8, 2 P ≤ 5, 3 P | ≤10. 1 P ≤5, 2 P | ≤12, 1 P ≤8, 3 P |
| Bleeding symptom | Positive, 1 P | ||
| Organ failure | Positive, 1 P | ||
| DIC | ≥7 P | ≥5 P | ≥3 or 4 P |
| JMHLW DIC Criteria | JMHLW-DIC | JMHLW- Pre-DIC | JMHLW-Non-DIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 74 (66–84) | 77 (60–82) | 71 (55–82) |
| Sex (F:M) | 21:51 | 45:67 | 601:715 |
| Infectious disease | 30 | 47 | 212 |
| Digestive system disease | 1 | 2 | 85 |
| Chest or abdominal aneurysm | 3 | 8 | 75 |
| Hematological malignancy | 1 | 2 | 64 |
| Trauma | 6 | 7 | 54 |
| Obstetrics disease | 2 | 1 | 48 |
| Respiratory disease | 1 | 3 | 34 |
| Arrhythmia | 2 | 1 | 18 |
| Thrombosis of peripheral artery | 1 | 1 | 14 |
| Heat illness | 1 | 1 | 33 |
| Cardiac pulmonary arrest | 21 | 14 | 32 |
| Solid cancer | 3 | 4 | 29 |
| Acute coronary syndrome | 0 | 5 | 67 |
| Heart failure | 0 | 5 | 81 |
| Convulsive disorder | 0 | 1 | 25 |
| Metabolic and endocrine diseases | 0 | 1 | 19 |
| Venous thromboembolism | 0 | 2 | 41 |
| Cerebral bleeding | 0 | 5 | 53 |
| Non-malignant hematological disease | 0 | 0 | 38 |
| Cerebral thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 145 |
| Indefinite compliant syndrome | 0 | 0 | 88 |
| Others | 0 | 0 | 61 |
| Total | 72 | 112 | 1316 |
| Parameter | Evaluation |
|---|---|
| PT-INR | Consumption of coagulation factors |
| 1/Platelet count | Activation and consumption of platelet |
| D-dimer | Fibrin formation and degradation |
| PT-INRxD-dimer/Platelet count | Disseminated microvascular coagulation |
| Parameter | r | Formular | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT-INR | 0.449 | Y = −0.226 + 1.814X | p < 0.001 |
| 1/Platelet | 0.159 | Y = 0.049 + 0.015X | p < 0.001 |
| D-dimer | 0.542 | Y = −1.494 + 5.289X | p < 0.001 |
| DIC index | 0.192 | Y = −7.084 + 6.021X, | p < 0.001 |
| JMHLW-DIC vs. JMHLW-Non-DIC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Cutoff | Sensitivity | AUC | Odds Ratio |
| PT-INR | 1.21 | 82.2% | 0.893 | 20.9 |
| Platelet count | 13.9 | 85.7% | 0.910 | 36.7 |
| D-dimer | 10.1 | 92.5% | 0.971 | 137 |
| PT-INR/Platelet count | 0.10 | 92.5% | 0.965 | 134 |
| PT-INRxD-dimer | 13.3 | 93.3% | 0.980 | 177 |
| D-dimer/Platelet count | 11.2 | 95.6% | 0.990 | 1132 |
| DIC index | 1.216 | 97.2% | 0.995 | 1138 |
| JMHLW-DIC or -Pre-DIC vs. JMHLW-Non-DIC | ||||
| PT-INR | 1.10 | 76.2% | 0.828 | 9.88 |
| Platelet count | 16.3 | 75.8% | 0.812 | 9.75 |
| D-dimer | 7.76 | 86.9% | 0.930 | 44.3 |
| PT-INR/Platelet count | 0.07 | 80.2% | 0.879 | 15.6 |
| PT-INRxD-dimer | 8.90 | 86.9% | 0.938 | 43.7 |
| D-dimer/Platelet count | 0.49 | 89.1% | 0.959 | 65.2 |
| DIC index | 0.59 | 90.2 | 0.964 | 87.1 |
| ROC Analyses | Cutoff | Sensitivity | AUC | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JMHLW-DIC vs. JMHLW-non-DIC | 1.216 | 97.2% | 0.995 | 1138 |
| JMHLW-DIC + Pre-DIC vs. JMHLW-non-DIC | 0.590 | 90.2% | 0.964 | 87.1 |
| ISTH overt-DIC vs. non-ISTH-overt DIC | 1.199 | 91.0% | 0.979 | 228 |
| mJAAM-DIC (score of ≥4) vs. non-mJAAM DIC | 0.682 | 93.9% | 0.984 | 240 |
| mJAAM-DIC (score of ≥3) vs. non-mJAAM DIC | 0.449 | 88.8% | 0.954 | 54.0 |
| Outcome | Survivors | Non-Survivors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT-INR | 1.02 (0.94–1.12) | 1.28 (1.09–1.70) | p < 0.001 |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | 1.88 (0.71–6.81) | 10.6 (3.5–29.0) | p < 0.001 |
| Platelet count (1 × 1010) | 20.0 (15.8–27.2) | 14.4 (9.0–21.6) | p < 0.001 |
| JMHLW-DIC score | 1.0 (0.0–2.0) | 5.0 (3.0–7.0) | p < 0.001 |
| DIC index | 0.002 (0.001–0.005) | 0.976 (0.315–3.731) | p < 0.001 |
| ISTH-DIC score | 1.0 (0.0–2.0) | 5.0 (3.5–7.0) | p < 0.001 |
| mJAAM DIC score | 1.0 (0.0–2.0) | 5.0 (4.0–7.0) | p < 0.001 |
| ROC Analyses | Cutoff | Sensitivity | AUC | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT-INR | 1.10 | 72.9% | 0.794 | 7.3 |
| D-dimer | 18.5 | 64.0% | 0.712 | 3.3 |
| Platelet count | 5.0 | 69.7% | 0.778 | 5.5 |
| DIC index | 0.33 | 74.2% | 0.815 | 8.30 |
| JMHLW-DIC score | 2.0 | 77.3% | 0.867 | 11.6 |
| ISTH-DIC score | 1.96 | 77.6% | 0.869 | 13.5 |
| mJAAM-DIC score | 2.0 | 77.9% | 0.868 | 12.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakano, E.; Wada, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Tomida, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Shiraki, K.; Shimaoka, M.; Shimpo, H.; Tawara, I. Diagnostic and Prognostic Evaluation of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Using the Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Index. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217478
Nakano E, Wada H, Yamamoto A, Tomida M, Ichikawa Y, Shiraki K, Shimaoka M, Shimpo H, Tawara I. Diagnostic and Prognostic Evaluation of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Using the Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Index. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217478
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakano, Eri, Hideo Wada, Akitaka Yamamoto, Masaki Tomida, Yuhuko Ichikawa, Katsuya Shiraki, Motomu Shimaoka, Hideto Shimpo, and Isao Tawara. 2025. "Diagnostic and Prognostic Evaluation of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Using the Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Index" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217478
APA StyleNakano, E., Wada, H., Yamamoto, A., Tomida, M., Ichikawa, Y., Shiraki, K., Shimaoka, M., Shimpo, H., & Tawara, I. (2025). Diagnostic and Prognostic Evaluation of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Using the Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Index. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217478







