Differential NMR Lipoprotein Profiles and Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome by LP-IR Among Adult Chronic Hepatitis B Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Clinical Biochemistry and Measurements of Lipoprotein Profiles
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
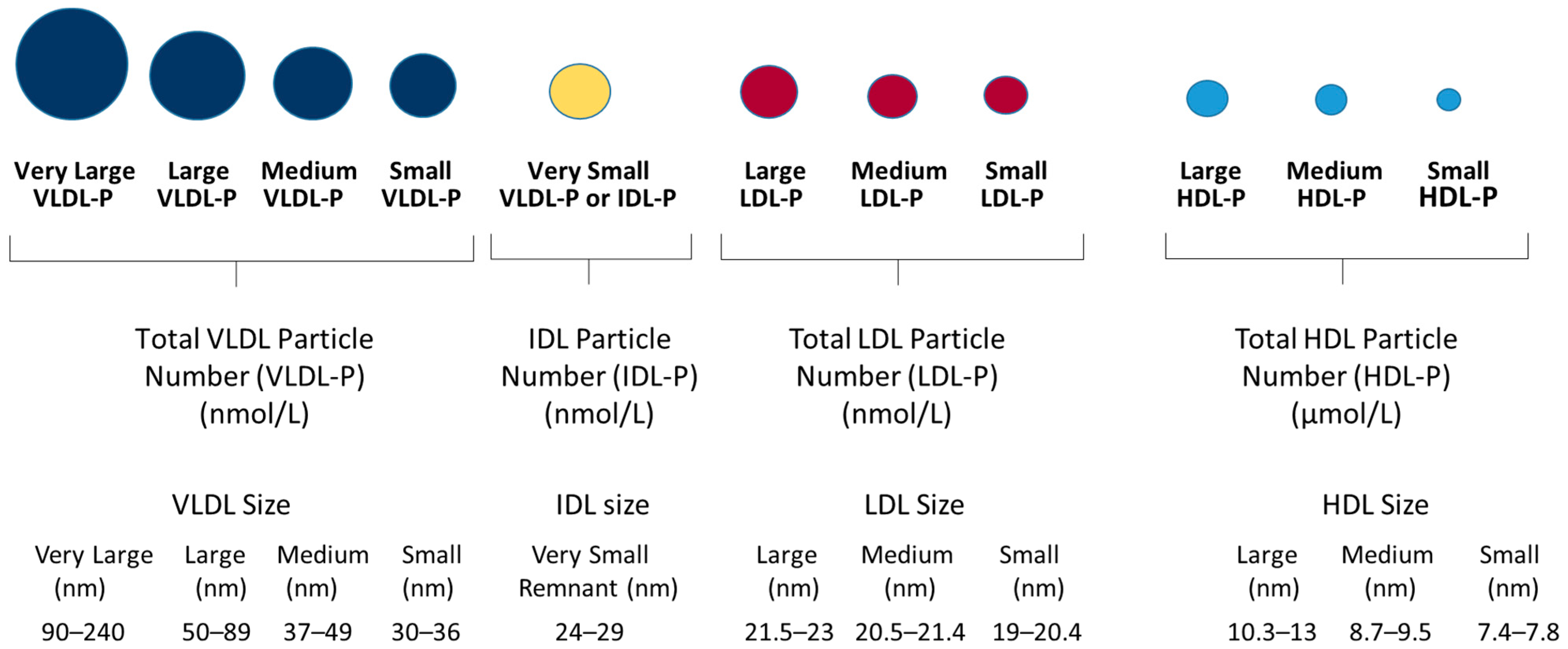
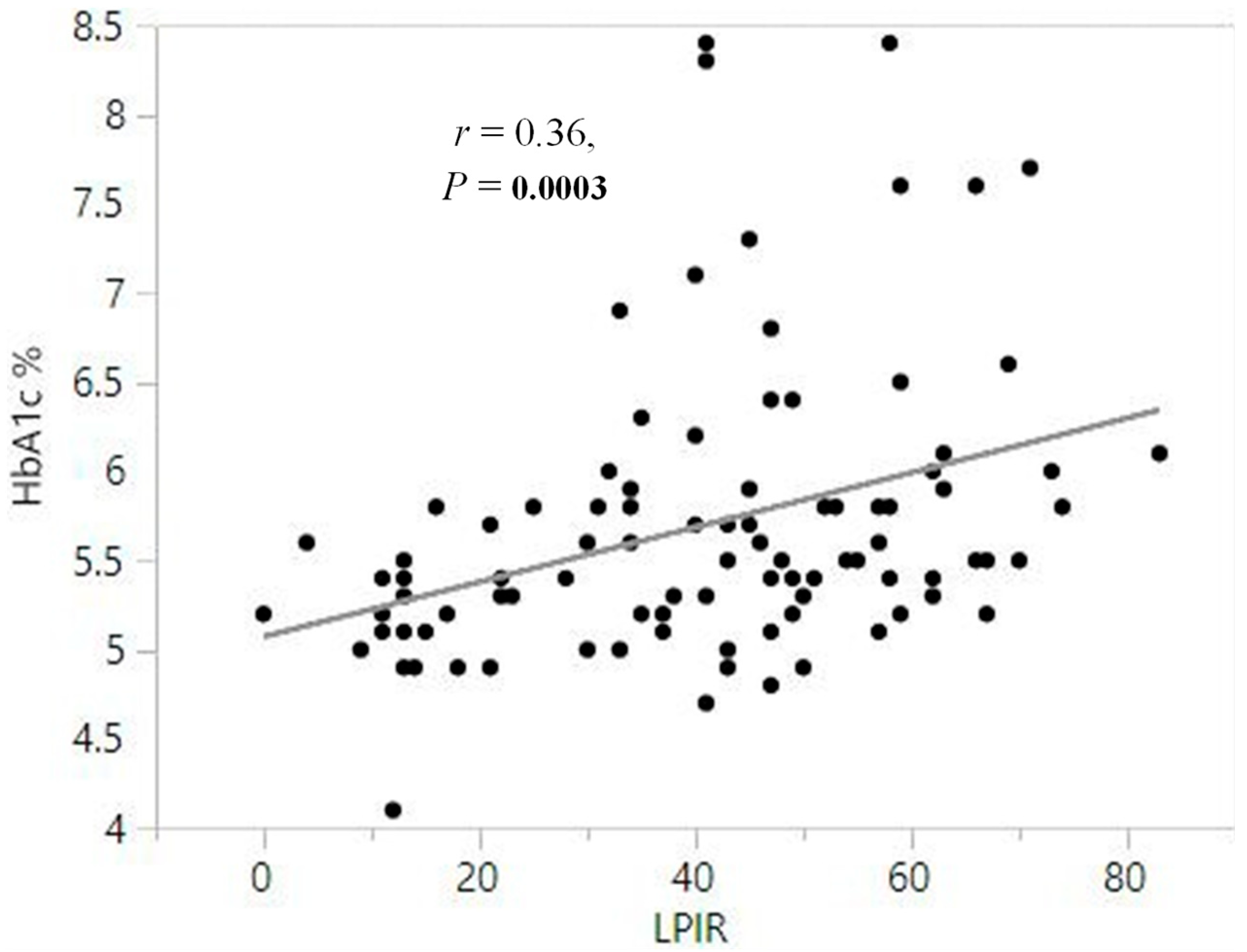
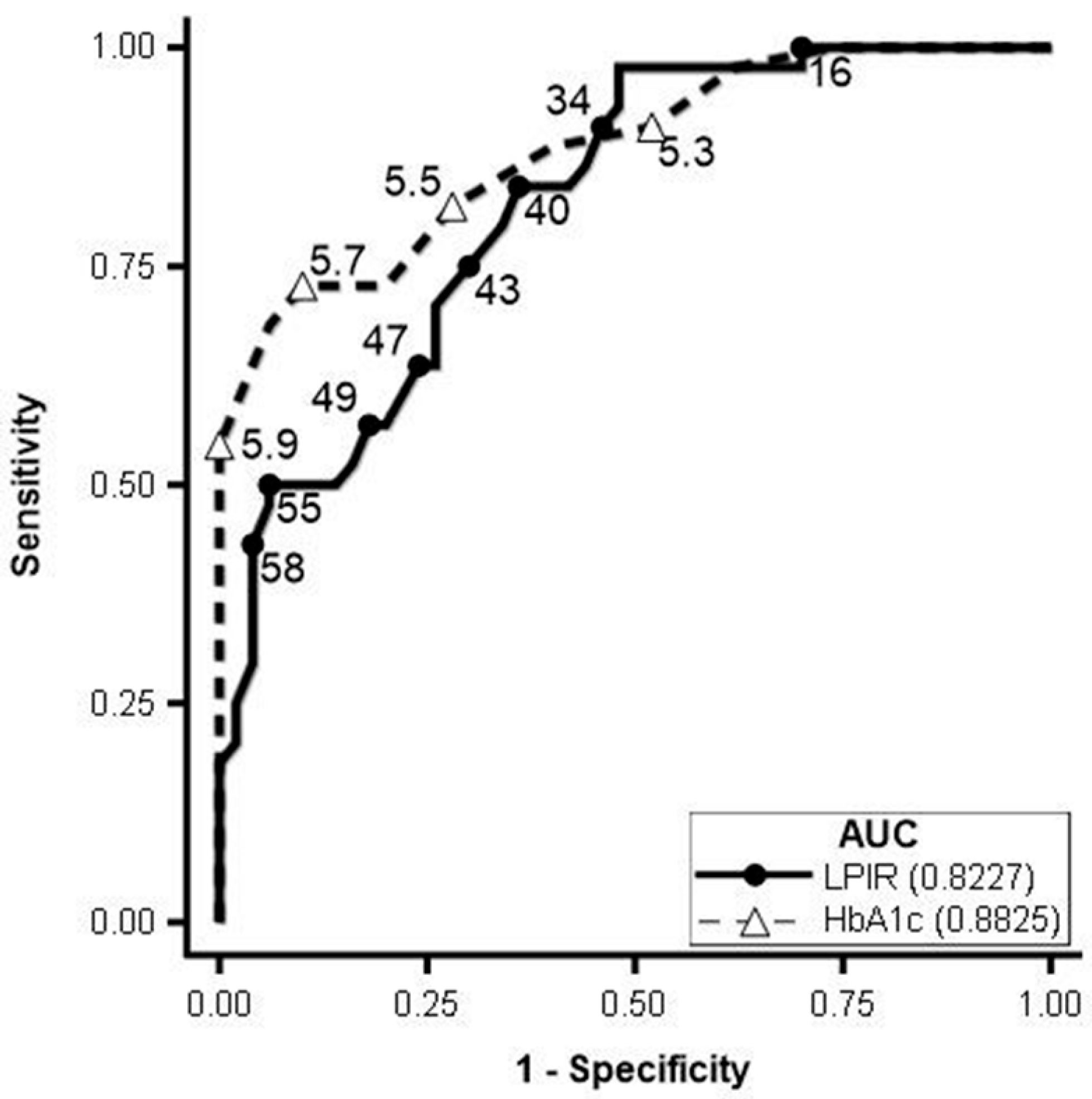
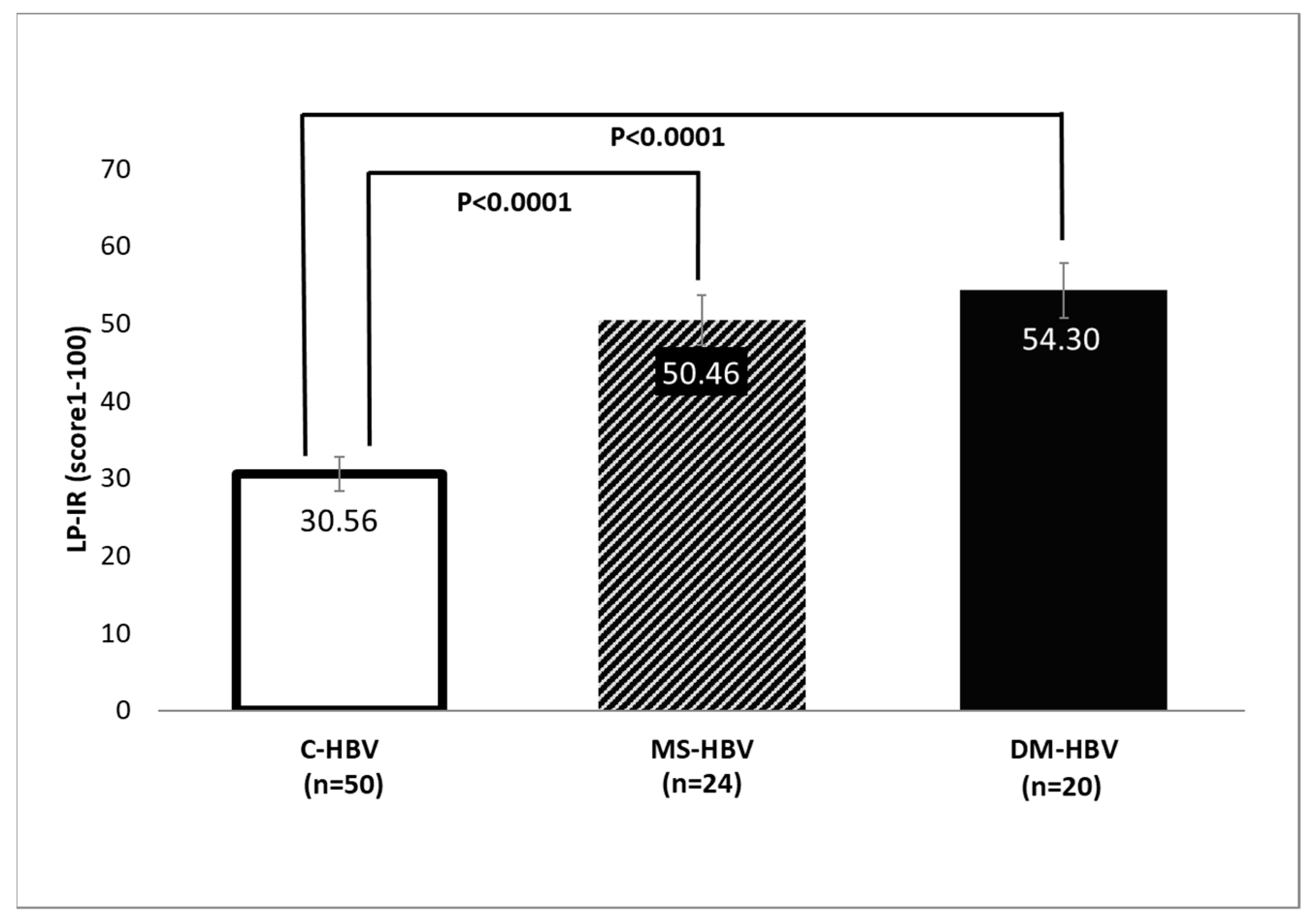
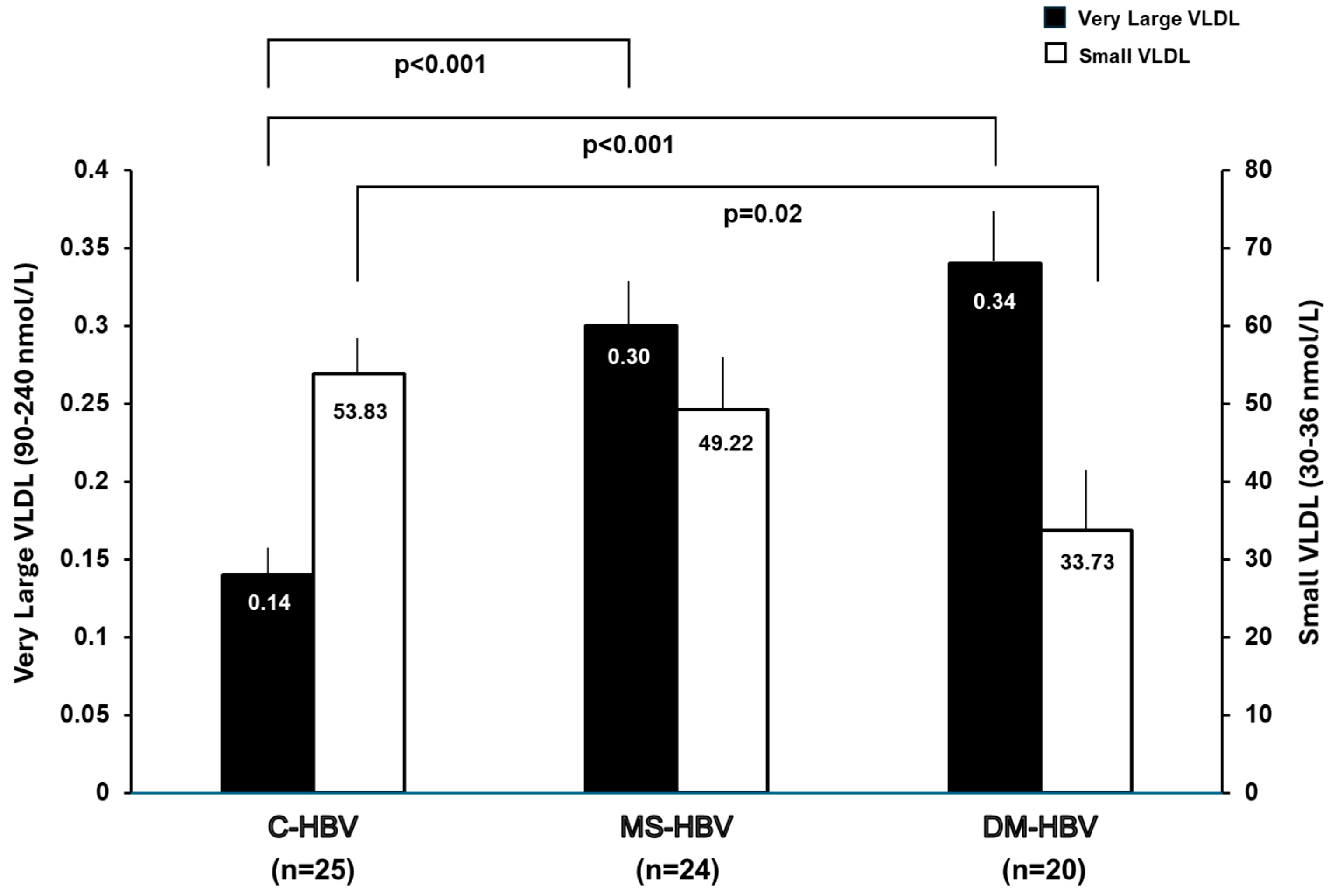
3.2. Lipoprotein Analysis by NMR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AUROC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| BIDMC | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| C-HBV | Patients with hepatitis B virus only |
| DM-HBV | Patients with hepatitis B virus and type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| EMR | Electronic medical records |
| HDL | High density lipoprotein |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance |
| IR-HBV | Patients with hepatitis B virus and insulin resistance |
| LDL | Low density lipoprotein |
| LP-IR | Lipoprotein Insulin Resistance Index |
| MASH | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MRN | Medical record number |
| MS-HBV | Patients with hepatitis B virus and metabolic syndrome |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic curve |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| VLDL | Very low density lipoprotein |
References
- MacLachlan, J.H.; Allard, N.L.; Cowie, B.C. Disparities in hepatitis B vaccine funding in Australian jurisdictions: Limiting access for priority populations. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2015, 39, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.J.; Brouwer, W.P.; Zanjir, W.M.R.; de Man, R.A.; Feld, J.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Patel, K. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Associated With Liver-Related Outcomes and All-Cause Mortality in Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2020, 71, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanoglu, I.; Rivero-Juarez, A.; Ozkaya Sahin, G.; Escmid Study Group For Viral Hepatitis, E. When Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Meets Viral Hepatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J. Past, present and future perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolasevic, I.; Orlic, L.; Franjic, N.; Hauser, G.; Stimac, D.; Milic, S. Transient elastography (FibroScan((R))) with controlled attenuation parameter in the assessment of liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Where do we stand? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7236–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: Where are we? Where do we go? Hepatology 2014, 60, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Issachar, A.; Sneh Arbib, O.; Cohen-Naftaly, M.; Braun, M.; Leshno, M.; Barsheshet, A.; Shlomai, A. Liver steatosis is a strong predictor of mortality and cancer in chronic hepatitis B regardless of viral load. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Su, T.H.; Tseng, T.C.; Hsu, S.J.; Hong, C.M.; Lan, T.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Yang, H.C.; Liu, C.J.; Kao, J.H. All-cause and cause-specific mortality in patients with chronic hepatitis B and concurrent steatotic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2025, 83, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Pongpaibul, A.; Kaosombatwattana, U.; Bhanthumkomol, P.; Bandidniyamanon, W.; Pausawasdi, N.; Tanwandee, T. The prevalence of steatohepatitis in chronic hepatitis B patients and its impact on disease severity and treatment response. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, M.; Zhang, X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An expanded review. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, M.; Shuhart, M.C.; Lombardero, M.; Feld, J.J.; Kleiner, D.E.; Chung, R.T.; Terrault, N.A.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Sanyal, A.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Relationship Between Metabolic Syndrome, Alanine Aminotransferase Levels, and Liver Disease Severity in a Multiethnic North American Cohort With Chronic Hepatitis B. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhai, X.; Baecker, A.; Peng, H.; Qian, J.; Zhou, M.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based cohort study. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, M.; Lombardero, M.; Chung, R.T.; Terrault, N.A.; Ghany, M.G.; Kim, W.R.; Lau, D.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Sanyal, A.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Diabetes and prediabetes in patients with hepatitis B residing in North America. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugianesi, E.; McCullough, A.J.; Marchesini, G. Insulin resistance: A metabolic pathway to chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 42, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Velsen, L.M.; Patmore, L.A.; Feld, J.J.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Piratvisuth, T.; Chien, R.N.; Dongelmans, E.J.; Pavlovic, V.; Yee, L.J.; Brouwer, W.P.; et al. Association of Metabolic Comorbidities With Fibrosis Severity and Fibrosis Regression in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazier-Wood, A.C.; Garvey, W.T.; Dall, T.; Honigberg, R.; Pourfarzib, R. Opportunities for using lipoprotein subclass profile by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in assessing insulin resistance and diabetes prediction. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2012, 10, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Fillmore, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Moore, I.K.; Pypaert, M.; Lutz, E.P.; Kako, Y.; Velez-Carrasco, W.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7522–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dullaart, R.P.; Sluiter, W.J.; Dikkeschei, L.D.; Hoogenberg, K.; Van Tol, A. Effect of adiposity on plasma lipid transfer protein activities: A possible link between insulin resistance and high density lipoprotein metabolism. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 24, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyarajah, E.J.; Cromwell, W.C.; Otvos, J.D. Lipoprotein particle analysis by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin. Lab. Med. 2006, 26, 847–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaurova, I.; Connelly, M.A.; Garvey, W.T.; Otvos, J.D. Lipoprotein insulin resistance index: A lipoprotein particle-derived measure of insulin resistance. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014, 12, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFilippis, A.P.; Blaha, M.J.; Martin, S.S.; Reed, R.M.; Jones, S.R.; Nasir, K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Budoff, M.J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and serum lipoproteins: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiwaku, K.; Anuurad, E.; Enkhmaa, B.; Kitajima, K.; Yamane, Y. Appropriate BMI for Asian populations. Lancet 2004, 363, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Fuchs, M.; Idowu, M.O.; Luketic, V.A.; Boyett, S.; Sargeant, C.; Stravitz, R.T.; Puri, P.; Matherly, S.; Sterling, R.K.; et al. Severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and progression to cirrhosis are associated with atherogenic lipoprotein profile. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1000–1008.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.G.; Tapper, E.B.; Connelly, M.A.; Pimentel, C.F.; Feldbrugge, L.; Kim, M.; Krawczyk, S.; Afdhal, N.; Robson, S.C.; Herman, M.A.; et al. Steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis are predicted by the characteristics of very low density lipoprotein in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyus, S.P.; Braun, P.J.; Wolak-Dinsmore, J.; Jeyarajah, E.J.; Shalaurova, I.; Xu, Y.; Warner, S.M.; Clement, T.S.; Connelly, M.A.; Fischer, T.J. NMR measurement of LDL particle number using the Vantera Clinical Analyzer. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.F.; Hu, G.; Tong, K.K.; Yang, X.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Yu, R. Effect of viral hepatitis on type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Baker, F.; Zeina, A.R.; Natour, R.T.; Mouch, S.A.; Kopelman, Y.; Shibolet, O.; Israel, A. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Hepatitis B Virus Patients: A Large Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 22, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Jie, Y.; Hao, Y.; Gu, J. Assessing the impact of comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus on the disease burden of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and its complications in China from 2006 to 2030: A modeling study. Glob Health Res Policy 2024, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Tang, J.; You, C. Metabolic Syndrome, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and Chronic Hepatitis B: A Narrative Review. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2023, 12, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.A.; Butt, A.S. Hepatitis B virus infection and metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease: Rising pandemic with complex interaction. World J. Hepatol. 2025, 17, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patmore, L.A.; Katwaroe, W.K.; van der Spek, D.; Choi, H.S.J.; Patel, K.; Brakenhoff, S.; van der Meer, A.J.; Brouwer, W.P.; van Kleef, L.A.; de Knegt, R.J.; et al. Association Between the Presence of Metabolic Comorbidities and Liver-Related Events in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 3089–3096.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugivarodom, M.; Pongpaibul, A.; Chainuvati, S.; Nimanong, S.; Chotiyaputta, W.; Tanwandee, T.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P. Prognostic Relevance of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatohepatitis for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzurovic, E.; Topic, G.; Todorovic, N.; Rizzo, M.; Zecevic, K. The prevalence and correlates of advanced fibrosis in patients with and without diabetes mellitus and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2025, 39, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IR-HBV (n = 44) | C-HBV (n = 50) | Standardized Difference (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 50 ± 13 | 47 ± 9 | 0.33 (−0.07–0.74) | 0.117 |
| Gender | 0.46 (0.05–0.087) | 0.03 | ||
| Male | 30 (68.2%) | 23 (46.0%) | ||
| Female | 14 (31.8%) | 27 (54.0%) | ||
| Race | 0.21 (−0.20–0.62) | 0.32 | ||
| White | 3 (6.8%) | 6 (12.0%) | ||
| Black | 6 (13.6%) | 7 (14.0%) | ||
| Asian | 34 (77.3%) | 34 (68.0%) | ||
| Hispanic | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||
| Native American/Alaskan | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||
| More than one race | 1 (2.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||
| Unknown/non-reported | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (6.0%) | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.1 ± 3.4 | 25.0 ± 4.4 | 0.79 (0.37–1.22) | <0.001 |
| ALT, mg/dL | 38.4 ± 26.2 | 27.2 ± 15.6 | 0.53 (0.12–0.94) | 0.01 |
| AST, mg/dL | 27.9 ± 9.4 | 24.8 ± 9.0 | 0.33 (−0.08–0.74) | 0.07 |
| HbA1c, % | 6.2 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 1.45 (0.99–1.90) | <0.0001 |
| HBeAg positive | 4 (9.1%) | 3 (6.0%) | 0.12 (−0.29–0.52) | 0.569 |
| On HBV antiviral treatment | 21 (47.7%) | 21 (42.0%) | 0.12 (−0.29–0.52) | 0.57 |
| Lipoprotein Classes and Subclasses | IR-HBV (n = 44) | C-HBV (n = 50) | Standardized Difference (95% CI) | Wilcoxon p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total VLDL-P | 156.46 ± 59.31 | 114.19 ± 60.43 | 0.71 (0.29–1.12) | 0.0009 |
| Very Large VLDL-P | 0.31 ± 0.20 | 0.14 ± 0.14 | 1.03 (0.60–1.47) | <0.0001 |
| Large VLDL-P | 2.48 ± 1.61 | 1.59 ± 1.46 | 0.58 (0.17–0.99) | 0.0045 |
| Medium VLDL-P | 14.17 ± 7.93 | 10.26 ± 5.92 | 0.56 (0.15–0.98) | 0.0153 |
| Small VLDL-P | 42.18 ± 33.74 | 53.83 ± 36.92 | −0.33 (−0.74–0.08) | 0.0543 |
| Very Small VLDL-P | 97.31 ± 60.18 | 48.38 ± 48.64 | 0.90 (0.48–1.33) | <0.0001 |
| Total LDL-P | 1132.7 ± 506.5 | 1148.9 ± 368.4 | −0.04 (−0.44–0.37) | 0.3227 |
| Large LDL-P | 315.0 ± 252.4 | 512.6 ± 253.5 | −0.78 (−1.2–−0.36) | 0.0003 |
| Medium LDL-P | 157.2 ± 288.5 | 325.6 ± 373.3 | −0.50 (−0.91–−0.09) | 0.0060 |
| Small LDL-P | 660.5 ± 332.0 | 310.9 ± 244.6 | 1.21 (0.77–1.65) | <0.0001 |
| Total HDL-P | 15.38 ± 4.99 | 17.53 ± 5.59 | −0.40 (−0.81–0.01) | 0.0375 |
| Large HDL-P | 0.92 ± 0.59 | 1.93 ± 1.64 | −0.80 (−1.22–−0.38) | 0.0002 |
| Medium HDL-P | 2.29 ± 1.92 | 3.60 ± 2.07 | −0.65 (−1.07–−0.24) | 0.0008 |
| Small HDL-P | 12.17 ± 3.42 | 12.00 ± 3.18 | 0.05 (−0.36–0.45) | 0.8157 |
| VLDL Size | 47.54 ± 6.35 | 42.49 ± 4.88 | 0.90 (0.48–1.33) | <0.0001 |
| LDL Size | 20.72 ± 0.78 | 21.42 ± 0.62 | −0.99 (−1.42–−0.56) | <0.0001 |
| HDL Size | 8.82 ± 0.30 | 9.22 ± 0.41 | −1.09 (−1.52–−0.65) | <0.0001 |
| LP-IR | 52 ± 14 | 31 ± 17 | 1.38 (0.93–1.83) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campoverde Reyes, K.J.; Guevara, J.; Karimi-Sari, H.; Goyes, D.; Lapumnuaypol, K.; Shah, P.A.; Kaur, S.P.; Connelly, M.A.; Jiang, Z.G.; Lau, D.T.-Y. Differential NMR Lipoprotein Profiles and Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome by LP-IR Among Adult Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207405
Campoverde Reyes KJ, Guevara J, Karimi-Sari H, Goyes D, Lapumnuaypol K, Shah PA, Kaur SP, Connelly MA, Jiang ZG, Lau DT-Y. Differential NMR Lipoprotein Profiles and Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome by LP-IR Among Adult Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207405
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampoverde Reyes, Karen J., Javier Guevara, Hamidreza Karimi-Sari, Daniela Goyes, Kamolyut Lapumnuaypol, Pir A. Shah, Satinder P. Kaur, Margery A. Connelly, Z. Gordon Jiang, and Daryl T.-Y. Lau. 2025. "Differential NMR Lipoprotein Profiles and Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome by LP-IR Among Adult Chronic Hepatitis B Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207405
APA StyleCampoverde Reyes, K. J., Guevara, J., Karimi-Sari, H., Goyes, D., Lapumnuaypol, K., Shah, P. A., Kaur, S. P., Connelly, M. A., Jiang, Z. G., & Lau, D. T.-Y. (2025). Differential NMR Lipoprotein Profiles and Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome by LP-IR Among Adult Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7405. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207405







