Effects of a Reclining Position on Postoperative Dysphagia After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Patients
2.3. Swallowing Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Swallowing Assessment Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global Burden of 5 Major Types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, L.; Seesing, M.F.; Ruurda, J.P.; Boone, J.; van Hillegersberg, R. Worldwide trends in surgical techniques in the treatment of esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finks, J.F.; Osborne, N.H.; Birkmeyer, J.D. Trends in hospital volume and operative mortality for high-risk surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2128–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ra, J.; Paulson, E.C.; Kucharczuk, J.; Armstrong, K.; Wirtalla, C.; Rapaport-Kelz, R.; Kaiser, L.R.; Spitz, F.R. Postoperative mortality after esophagectomy for cancer: Development of a preoperative risk prediction model. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Journo, X.B.; Boulate, D.; Fourdrain, A.; Loundou, A.; Henegouwen, M.I.v.B.; Gisbertz, S.S.; O’neill, J.R.; Hoelscher, A.; Piessen, G.; van Lanschot, J.; et al. Risk prediction model of 90-day mortality after esophagectomy for cancer. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.H.; Bull, D.A.; Harpole, D.H.; Rentz, J.J.; Neumayer, L.A.; Pappas, T.N.; Daley, J.; Henderson, W.G.; Krasnicka, B.; Khuri, S.F. Outcomes after esophagectomy: A ten-year prospective cohort. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 75, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, R.C.; Reuben, B.C.; Neumayer, L.A.; Bull, D.A. Comparing outcomes after transthoracic and transhiatal esophagectomy: A 5-year prospective cohort of 17,395 patients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2007, 205, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutegård, M.; Lagergren, P.; Rouvelas, I.; Mason, R.; Lagergren, J. Surgical complications and long-term survival after esophagectomy for cancer in a nationwide Swedish cohort study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 38, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Miyata, H.; Gotoh, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Baba, H.; Kimura, W.; Tomita, N.; Nakagoe, T.; Shimada, M.; Sugihara, K.; et al. A risk model for esophagectomy using data of 5354 patients included in a Japanese nationwide web-based database. Ann Surg. 2014, 260, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Vashist, Y.; Goyal, A.; Shetty, P.; Girnyi, S.; Cwalinski, T.; Skokowski, J.; Malerba, S.; Prete, F.P.; Mocarski, P.; Kania, M.K.; et al. Evaluating postoperative morbidity and outcomes of robotic-assisted esophagectomy in esophageal cancer treatment—A comprehensive review on behalf of TROGSS (The Robotic Global Surgical Society) and EFISDS (European Federation International Society for Digestive Surgery) Joint Working Group. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Booka, E.; Takeuchi, H.; Suda, K.; Fukuda, K.; Nakamura, R.; Wada, N.; Kawakubo, H.; Kitagawa, Y. Meta-analysis of the impact of postoperative complications on survival after oesophagectomy for cancer. BJS Open. 2018, 2, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, L.E.; Law, S.; Wong, K.H.; Kwok, K.-F.; Wong, J. The influence of technical complications on postoperative outcome and survival after esophagectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 13, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrott, P.W.; Markar, S.R.; Kuppusamy, M.K.; Traverso, W.L.; Low, D.E. Accordion severity grading system: Assessment of relationship between costs, length of hospital stay, and survival in patients with complications after esophagectomy for cancer. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 215, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamana, I.; Takeno, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Maki, K.; Shibata, R.; Shiwaku, H.; Shimaoka, H.; Shiota, E.; Yamashita, Y. Randomized controlled study to evaluate the efficacy of a preoperative respiratory rehabilitation program to prevent postoperative pulmonary complications after esophagectomy. Dig. Surg. 2015, 32, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, D.; Zhao, J. Association between preoperative diagnosis of sarcopenia and postoperative pneumonia in resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1144516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, M.F.; Atkins, B.Z.; Tong, B.C.; Harpole, D.H.; D’AMico, T.A.; Onaitis, M.W. A comprehensive evaluation for aspiration after esophagectomy reduces the incidence of postoperative pneumonia. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 140, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumai, Y.; Samejima, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yumoto, E. Videofluoroscopic evaluation of pharyngeal swallowing dysfunction after esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cheon, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Shim, Y.M.; Zo, J.I.; Hwang, J.H. Clinical predictors of aspiration after esophagectomy in esophageal cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leder, S.B.; Bayar, S.; Sasaki, C.T.; Salem, R.R. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in assessing aspiration after transhiatal esophagectomy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2007, 205, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneoka, A.; Yang, S.; Inokuchi, H.; Ueha, R.; Yamashita, H.; Nito, T.; Seto, Y.; Haga, N. Presentation of oropharyngeal dysphagia and rehabilitative intervention following esophagectomy: A systematic review. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, J.; Higaki, E.; Hosoi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Abe, T.; Shimizu, Y. Clinical benefits of a swallowing intervention for esophageal cancer patients after esophagectomy. Dis. Esophagus 2021, 34, doaa094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zou, L.; Li, L.; Zou, Q.; Chen, P.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, X. Effect of Chin-down-plus-larynx-tightening maneuver on swallowing function after minimally invasive esophagectomy: A randomized controlled trail. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5889–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.H.; Seo, J.H.; Ko, M.H.; Park, S.-H. Effect of 45° reclining sitting posture on swallowing in patients with dysphagia. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjapornlert, P.; Kagaya, H.; Inamoto, Y.; Mizokoshi, E.; Shibata, S.; Saitoh, E. The effect of reclining position on swallowing function in stroke patients with dysphagia. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2020, 47, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, Y.; Mikushi, S.; Amagasa, T.; Omura, K.; Uematsu, H. Effect of the reclining position in patients after oral tumor surgery. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2011, 58, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Langmore, S.E.; Schatz, K.; Olsen, N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: A new procedure. Dysphagia 1988, 2, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbek, J.C.; Robbins, J.A.; Roecker, E.B.; Coyle, J.L.; Wood, J.L. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 1996, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, M.A.; Mann, G.D.; Groher, M.E. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.T.Y.; Tsang, R.K.; Wong, I.Y.H.; Chan, D.K.K.; Chan, F.S.Y.; Law, S.Y.K. Long-term pharyngeal dysphagia after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer—An investigation using videofluoroscopic swallow studies. Dis. Esophagus 2019, 32, doy068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.E.; Letsos, P.; Taves, D.H.; Inculet, R.I.; Johnston, H.; Preiksaitis, H.G. Oropharyngeal dysphagia in esophageal cancer before and after transhiatal esophagectomy. Dysphagia 2001, 16, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, C.S.; Bousamra, M., 2nd; Lang, I.M.; Kern, M.K.; Nitschke, T.; Bardan, E.; Shaker, R. Pharyngeal dysphagia in postesophagectomy patients: Correlation with deglutitive biomechanics. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 69, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.E.; White, C.J.; Leonard, R.J.; Belafsky, P.C. Prevalence of penetration and aspiration on videofluoroscopy in normal individuals without dysphagia. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 142, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoi, M.; Kayashita, J.; Yamagata, Y.; Tanimoto, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Sakurama, K. Suitable food textures for videofluoroscopic studies of swallowing in esophageal cancer cases to prevent aspiration pneumonia. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 3259–3263. [Google Scholar]
- Périé, S.; Laccourreye, O.; Bou-Malhab, F.; Brasnu, D. Aspiration in unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis after surgery. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1998, 19, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seesing, M.F.J.; Wirsching, A.; van Rossum, P.S.N.; Weijs, T.J.; Ruurda, J.P.; van Hillegersberg, R.; Low, D.E. Defining pneumonia after esophagectomy for cancer: Validation of the Uniform Pneumonia Score in a high volume center in North America. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, doy002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booka, E.; Takeuchi, H.; Nishi, T.; Matsuda, S.; Kaburagi, T.; Fukuda, K.; Nakamura, R.; Takahashi, T.; Wada, N.; Kawakubo, H.; et al. The impact of postoperative complications on survivals after esophagectomy for esophageal Cancer. Cancer Med 2015, 94, e1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Score | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 1 | Contrast does not enter the airway |
| Penetration | 2 | Contrast enters the airway, remains above vocal folds; no residue |
| 3 | Contrast remains above the vocal folds; visible residue present | |
| 4 | Contrast contacts vocal folds; no residue | |
| 5 | Contrast contacts vocal folds; visible residue present | |
| Aspiration | 6 | Contrast passes glottis; no subglottic residue visible |
| 7 | Contrast passes glottis; visible subglottic residue despite patient’s response | |
| 8 | Contrast passes glottis; visible subglottic residue; no patient response |
| Score | Performance | Implication | Deficit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aspirates saliva/tube-dependent | Nothing by mouth | Profound |
| 2 | Tube-dependent | Nothing by mouth/minimal trials | Profound |
| 3 | Tube-dependent | Full trials by mouth | Severe |
| 4 | Total oral | Single-texture trials | Moderate |
| 5 | Total oral | Multiple-texture trials | Mild |
| 6 | Total oral | By mouth/restrictions | Minimal |
| 7 | Regular diet | By mouth/no restrictions | None |
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic | ||
| Age (years), median (range) | 68 (43–85) | |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 72 | 82.8 |
| Female | 15 | 17.2 |
| Interval between surgery and VFSS (days), median (range) | 9 (7–30) | |
| Clinical characteristics | ||
| Histological type | ||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 70 | 80.5 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 17 | 19.5 |
| Pathological tumor stage (UICC 8th) | ||
| T0 | 4 | 4.5 |
| T1a | 15 | 11.5 |
| T1b | 24 | 27.6 |
| T2 | 9 | 10.3 |
| T3 | 31 | 34.5 |
| T4a | 4 | 4.6 |
| T4b | 0 | 0 |
| Pathological nodal stage (UICC 8th) | ||
| N0 | 33 | 37.9 |
| N1 | 28 | 32.2 |
| N2 | 10 | 11.5 |
| N3 | 16 | 18.3 |
| Location of tumor | ||
| Cervical | 2 | 2.3 |
| Upper thoracic | 13 | 14.9 |
| Middle thoracic | 28 | 32.2 |
| Lower thoracic | 28 | 32.2 |
| Abdominal | 16 | 18.4 |
| Treatment | ||
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | ||
| Yes | 38 | 43.7 |
| No | 49 | 56.3 |
| Operation time (min), median (range) | 542 (402–748) | |
| Operative approach | ||
| Thoracotomy | 23 | 26.4 |
| Thoracoscopy | 64 | 73.6 |
| Laparotomy | 25 | 28.7 |
| Laparoscopy | 62 | 71.3 |
| Abdominal/transhiatal | 0 | 0.0 |
| Lymphadenectomy | ||
| 3-Field | 58 | 66.7 |
| 2-Field | 29 | 33.3 |
| Reconstruction | ||
| Posterior mediastinal | 78 | 89.7 |
| Antethoracic | 0 | 0.0 |
| Retrosternal | 9 | 10.3 |
| Complications in postoperative period | ||
| Vocal cord palsy | ||
| Bilateral | 0 | 0.0 |
| Left | 17 | 19.5 |
| Right | 5 | 5.7 |
| Postoperative pulmonary complication | ||
| Yes | 10 | 11.5 |
| No | 77 | 88.5 |
| 90-Degree | 45-Degree | p Value a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |||
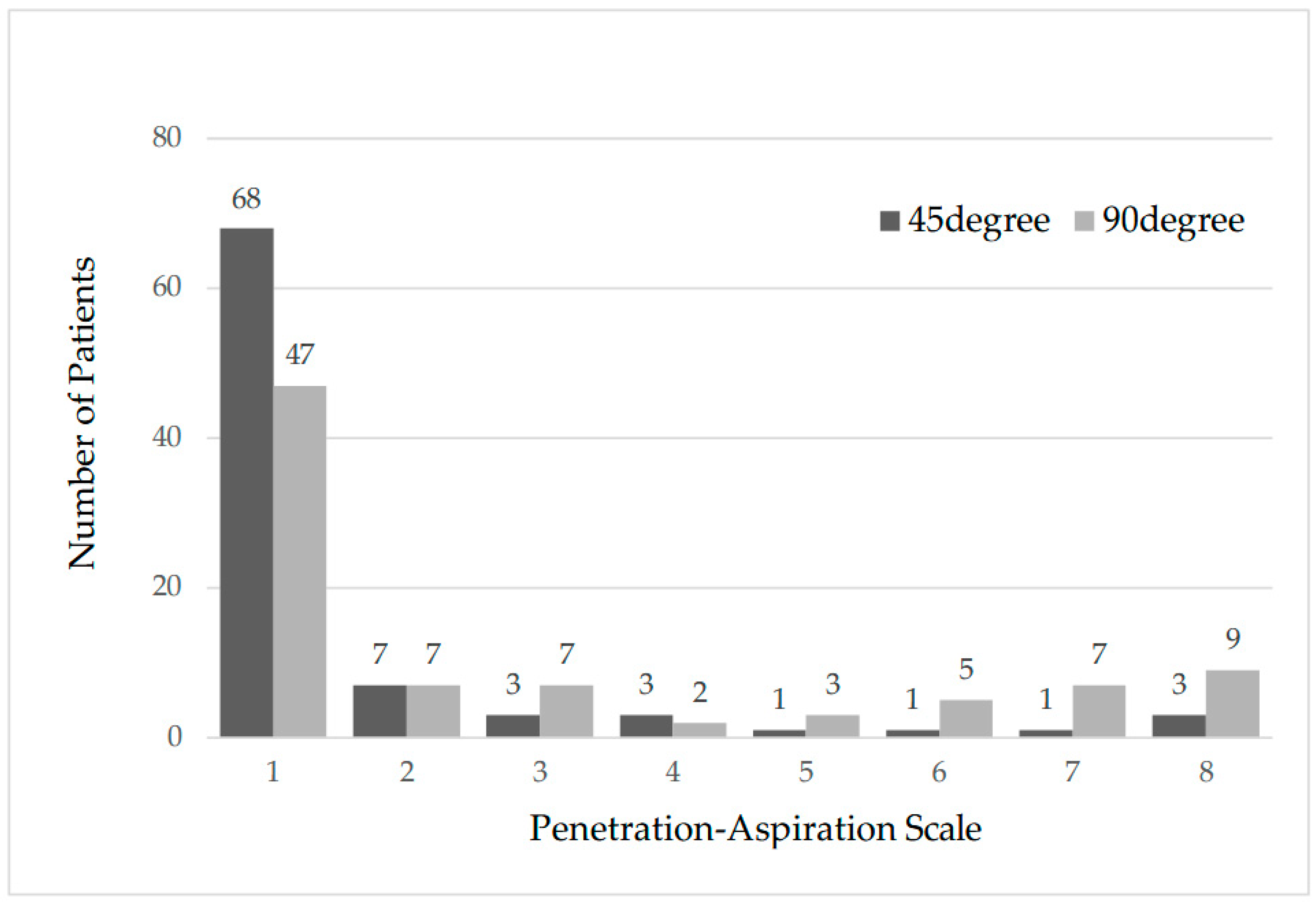
| PAS All (n = 88) | p < 0.05 | |||||
| 1 | Normal | 47 | 54.0 | 68 | 79.2 | |
| 2–5 | Penetration | 19 | 21.8 | 14 | 16.1 | |
| 6–8 | Aspiration | 21 | 24.1 | 5 | 5.7 | |
| RLNP (n = 22) | p < 0.05 | |||||
| 1 | Normal | 7 | 31.8 | 18 | 81.8 | |
| 2–5 | Penetration | 6 | 27.3 | 2 | 9.1 | |
| 6–8 | Aspiration | 9 | 40.9 | 2 | 9.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ariga, T.; Nagafusa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Takahashi, M.; Takashima, S.; Hasui, M.; Honke, J.; Kawata, S.; Murakami, T.; Booka, E.; et al. Effects of a Reclining Position on Postoperative Dysphagia After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207401
Ariga T, Nagafusa T, Watanabe K, Takahashi M, Takashima S, Hasui M, Honke J, Kawata S, Murakami T, Booka E, et al. Effects of a Reclining Position on Postoperative Dysphagia After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207401
Chicago/Turabian StyleAriga, Takahiro, Tetsuyuki Nagafusa, Kouji Watanabe, Mami Takahashi, Shunji Takashima, Makoto Hasui, Junko Honke, Sanshiro Kawata, Tomohiro Murakami, Eisuke Booka, and et al. 2025. "Effects of a Reclining Position on Postoperative Dysphagia After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207401
APA StyleAriga, T., Nagafusa, T., Watanabe, K., Takahashi, M., Takashima, S., Hasui, M., Honke, J., Kawata, S., Murakami, T., Booka, E., Matsumoto, T., Kikuchi, H., Takeuchi, H., Yamauchi, K., & Hiramatsu, Y. (2025). Effects of a Reclining Position on Postoperative Dysphagia After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7401. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207401





