Differences in Functional Performance and Minimal Detectable Change According to Levels of Ankle Plantar Flexor Spasticity in Patients with Chronic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC scale | Activities-specific Balance Confidence Scale |
| 5xSTS | Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test |
| F8WT | Figure-of-8 Walk Test |
| FSST | Four-Square Step Test |
| MDC | Minimal detectable change |
| TUG | Timed Up and Go Test |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| MAS | Modified Ashworth Scale |
| SEM | Standard error of measurement |
References
- Tang, A.; Rymer, W.Z. Abnormal Force--EMG Relations in Paretic Limbs of Hemiparetic Human Subjects. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1981, 44, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbonnais, D.; Vanden Noven, S. Weakness in Patients with Hemiparesis. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1989, 43, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerfeld, D.K.; Eek, E.U.-B.; Svensson, A.-K.; Holmqvist, L.W.; von Arbin, M.H. Spasticity After Stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, P.P.; Wolf, T.; Uebele, M.; Marx, J.J.; Vogt, T.; Stoeter, P.; Bauermann, T.; Weibrich, C.; Vucurevic, G.D.; Schneider, A.; et al. Occurence and Clinical Predictors of Spasticity after Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2010, 41, 2016–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Woollacott, M.H. Motor Control: Theory and Practical Applications; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-683-30643-9. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, C.L.; Leathley, M.J.; Gregson, J.M.; Moore, A.P.; Smith, T.L.; Sharma, A.K. Prevalence of Spasticity Post Stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 2002, 16, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressel, E.; McNair, P.J. The Effect of Prolonged Static and Cyclic Stretching on Ankle Joint Stiffness, Torque Relaxation, and Gait in People with Stroke. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selles, R.W.; Li, X.; Lin, F.; Chung, S.G.; Roth, E.J.; Zhang, L.-Q. Feedback-Controlled and Programmed Stretching of the Ankle Plantarflexors and Dorsiflexors in Stroke: Effects of a 4-Week Intervention Program. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2330–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.D.; Strike, S.C.; Dabnichki, P. Strategies Used for Unconstrained Direction Change during Walking. Percept. Mot. Skills 2006, 102, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaister, B.C.; Bernatz, G.C.; Klute, G.K.; Orendurff, M.S. Video Task Analysis of Turning during Activities of Daily Living. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, L.E.; Myers, A.M. The Activities-Specific Balance Confidence (ABC) Scale. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1995, 50A, M28–M34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, S.L.; Wrisley, D.M.; Marchetti, G.F.; Gee, M.A.; Redfern, M.S.; Furman, J.M. Clinical Measurement of Sit-to-Stand Performance in People with Balance Disorders: Validity of Data for the Five-Times-Sit-to-Stand Test. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, R.J.; Brach, J.S.; Piva, S.R.; VanSwearingen, J.M. Walking Skill Can Be Assessed in Older Adults: Validity of the Figure-of-8 Walk Test. Phys. Ther. 2010, 90, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dite, W.; Temple, V.A. A Clinical Test of Stepping and Change of Direction to Identify Multiple Falling Older Adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salbach, N.M.; Mayo, N.E.; Higgins, J.; Ahmed, S.; Finch, L.E.; Richards, C.L. Responsiveness and Predictability of Gait Speed and Other Disability Measures in Acute Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.K.-Y.; Dagenais, M.; Alsbury-Nealy, K.; Legasto, J.M.; Scodras, S.; Aravind, G.; Takhar, P.; Nekolaichuk, E.; Salbach, N.M. Distance-Limited Walk Tests Post-Stroke: A Systematic Review of Measurement Properties. NeuroRehabilitation 2021, 48, 413–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The Timed “Up & Go”: A Test of Basic Functional Mobility for Frail Elderly Persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck, P.; Zwingmann, C. The “smallest Real Difference” as a Measure of Sensitivity to Change: A Critical Analysis. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2003, 26, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Liaw, L.-J.; Chen, S.-M.; Lin, J.-H. The Test-Retest Reliability of 2 Mobility Performance Tests in Patients with Chronic Stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2007, 21, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, T.; Seney, M. Test-Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change on Balance and Ambulation Tests, the 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey, and the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale in People with Parkinsonism. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerman, H.; Roebroeck, M.E.; Lankhorst, G.J.; Becher, J.G.; Bezemer, P.D.; Verbeek, A.L. Smallest Real Difference, a Link between Reproducibility and Responsiveness. Qual. Life Res. 2001, 10, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, N.; van der Windt, D.A.; Assendelft, W.J.; Mourits, A.J.; Devillé, W.L.; de Winter, A.F.; Bouter, L.M. Interobserver Reproducibility of the Assessment of Severity of Complaints, Grip Strength, and Pressure Pain Threshold in Patients with Lateral Epicondylitis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiengkaew, V.; Jitaree, K.; Chaiyawat, P. Minimal Detectable Changes of the Berg Balance Scale, Fugl-Meyer Assessment Scale, Timed “Up & Go” Test, Gait Speeds, and 2-Minute Walk Test in Individuals with Chronic Stroke with Different Degrees of Ankle Plantarflexor Tone. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudzadeh, A.; Nakhostin Ansari, N.; Naghdi, S.; Ghasemi, E.; Motamedzadeh, O.; Shaw, B.S.; Shaw, I. Role of Spasticity Severity in the Balance of Post-Stroke Patients. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 783093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radinmehr, H.; Ansari, N.N.; Naghdi, S.; Tabatabaei, A.; Moghimi, E. Comparison of Therapeutic Ultrasound and Radial Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Plantar Flexor Spasticity After Stroke: A Prospective, Single-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botner, E.M.; Miller, W.C.; Eng, J.J. Measurement Properties of the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale among Individuals with Stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. 2005, 27, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishige, S.; Wakui, S.; Miyazawa, Y.; Naito, H. Reliability and Validity of the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence Scale-Japanese (ABC-J) in Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors. Phys. Ther. Res. 2020, 23, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Bermejo, L.; Adsuar, J.C.; Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Barrios-Fernández, S.; Garcia-Gordillo, M.A.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Carlos-Vivas, J. Test-Retest Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh Hollands, K.; Hollands, M.A.; Zietz, D.; Miles Wing, A.; Wright, C.; van Vliet, P. Kinematics of Turning 180° During the Timed Up and Go in Stroke Survivors With and Without Falls History. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2010, 24, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, Y.-C.; Lin, L.-F.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hu, C.-C.; Liang, P.-J.; Lee, S.-C. Association Between Turning Mobility and Cognitive Function in Chronic Poststroke. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 772377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennerhassett, J.M.; Jayalath, V.M. The Four Square Step Test Is a Feasible and Valid Clinical Test of Dynamic Standing Balance for Use in Ambulant People Poststroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 2156–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-J.; Goh, E.Y.; Chua, S.Y.; Ng, S.S. Reliability and Validity of Step Test Scores in Subjects with Chronic Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.E.; McPherson, K.; McNaughton, H.K.; Rochester, L.; Weatherall, M. Community Ambulation after Stroke: How Important and Obtainable Is It and What Measures Appear. Predictive? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.F.; Hui-Chan, C.W. Relief of Hemiparetic Spasticity by TENS Is Associated with Improvement in Reflex and Voluntary Motor Functions. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992, 85, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-M.; Kang, S.-H. The Effects of Task-Oriented Circuit Training Using Unstable Surface on Balance, Walking and Balance Confidence in Subacute Stroke Patients. J. Korean Soc. Integr. Med. 2021, 9, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and Reporting Effect Sizes to Facilitate Cumulative Science: A Practical Primer for t-Tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregson, J.M.; Leathley, M.J.; Moore, A.P.; Smith, T.L.; Sharma, A.K.; Watkins, C.L. Reliability of Measurements of Muscle Tone and Muscle Power in Stroke Patients. Age Ageing 2000, 29, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mong, Y.; Teo, T.W.; Ng, S.S. 5-Repetition Sit-to-Stand Test in Subjects with Chronic Stroke: Reliability and Validity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.S.T.; Yam, M.-S.; Ng, S.S.M. The Figure-of-Eight Walk Test: Reliability and Associations with Stroke-Specific Impairments. Disabil. Rehabil. 2013, 35, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, E.Y.; Chua, S.Y.; Hong, S.-J.; Ng, S.S. Reliability and Concurrent Validity of Four Square Step Test Scores in Subjects with Chronic Stroke: A Pilot Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portney, L.G.; Watkins, M.P. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 892. [Google Scholar]
- Bourke, A.K.; Scotland, A.; Lipsmeier, F.; Gossens, C.; Lindemann, M. Gait Characteristics Harvested during a Smartphone-Based Self-Administered 2-Minute Walk Test in People with Multiple Sclerosis: Test-Retest Reliability and Minimum Detectable Change. Sensors 2020, 20, 5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, C.; Hillier, S.L.; Lynch, E.A. Circuit Class Therapy for Improving Mobility after Stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD007513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Lim, C. Effects of Curved-Path Gait Training on Gait Ability in Middle-Aged Patients with Stroke: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, A.; van Ooijen, M.; Geurts, A.C.H.; Day, B.L.; Janssen, T.W.J.; Beek, P.J.; Roerdink, M.; Weerdesteyn, V. Step by Step: A Proof of Concept Study of C-Mill Gait Adaptability Training in the Chronic Phase after Stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 45, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, C.; Roerdink, M.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Beek, P.J.; Janssen, T.W.J. Walking-Adaptability Therapy after Stroke: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Trials 2021, 22, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrholz, J.; Thomas, S.; Elsner, B. Treadmill Training and Body Weight Support for Walking after Stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 8, CD002840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marigold, D.S.; Eng, J.J. The Relationship of Asymmetric Weight-Bearing with Postural Sway and Visual Reliance in Stroke. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnoff, J.J.; Shin, S.; Motl, R.W. Multiple Sclerosis and Postural Control: The Role of Spasticity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh Khiabani, R.; Mochizuki, G.; Ismail, F.; Boulias, C.; Phadke, C.P.; Gage, W.H. Impact of Spasticity on Balance Control during Quiet Standing in Persons after Stroke. Stroke Res. Treat. 2017, 2017, 6153714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Suzuki, T.; Bean, J.; Fielding, R.A. High Intensity Strength Training Improves Strength and Functional Performance after Stroke. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 79, 369–376, quiz 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomaglio, M.J.; Eng, J.J. Muscle Strength and Weight-Bearing Symmetry Relate to Sit-to-Stand Performance in Individuals with Stroke. Gait Posture 2005, 22, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.S.; Hui-Chan, C.W. The Timed up & Go Test: Its Reliability and Association with Lower-Limb Impairments and Locomotor Capacities in People with Chronic Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.S.M.; Shepherd, R.B. Weakness in Patients with Stroke: Implications for Strength Training in Neurorehabilitation. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2000, 5, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.S.M.; Ng, P.C.M.; Lee, C.Y.W.; Ng, E.S.W.; Tong, M.H.W. Walkway Lengths for Measuring Walking Speed in Stroke Rehabilitation. J. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 44, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.S.M.; Hui-Chan, C.W.Y. Ankle Dorsiflexor, Not Plantarflexor Strength, Predicts the Functional Mobility of People with Spastic Hemiplegia. J. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 45, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, I.-P.; Hsu, M.-J.; Sheu, C.-F.; Lee, S.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Lin, J.-H. Psychometric Comparisons of 2 Versions of the Fugl-Meyer Motor Scale and 2 Versions of the Stroke Rehabilitation Assessment of Movement. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair. 2008, 22, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Description | Reporting Unit | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Items | 16 daily balance activities | 0–100 each | 0 = no confidence; 100 = complete confidence |
| Total score | Mean of 16 item scores | Percentage (0–100%) | Higher = greater confidence |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 60.33 ± 14.48 |
| Sex (male/female) | 32 (59.3)/22 (40.7) |
| Duration (months) | 26.19 ± 9.09 |
| Diagnosis (infarction/hemorrhage) | 34 (63)/20 (37) |
| Paretic side (left/right) | 25 (46.3)/29 (53.7) |
| MMSE-K (score) | 25.87 ± 1.66 |
| Use of walking aid | |
| None/Single point cane/Quadri-pod cane | 15 (26.8)/29 (51.8)/11 (19.6) |
| FMA-L/E (score) | 25.87 ± 6.04 |
| BBS (score) | 44.49 ± 12.29 |
| 10mWT (m/s) | 0.63 ± 0.26 |
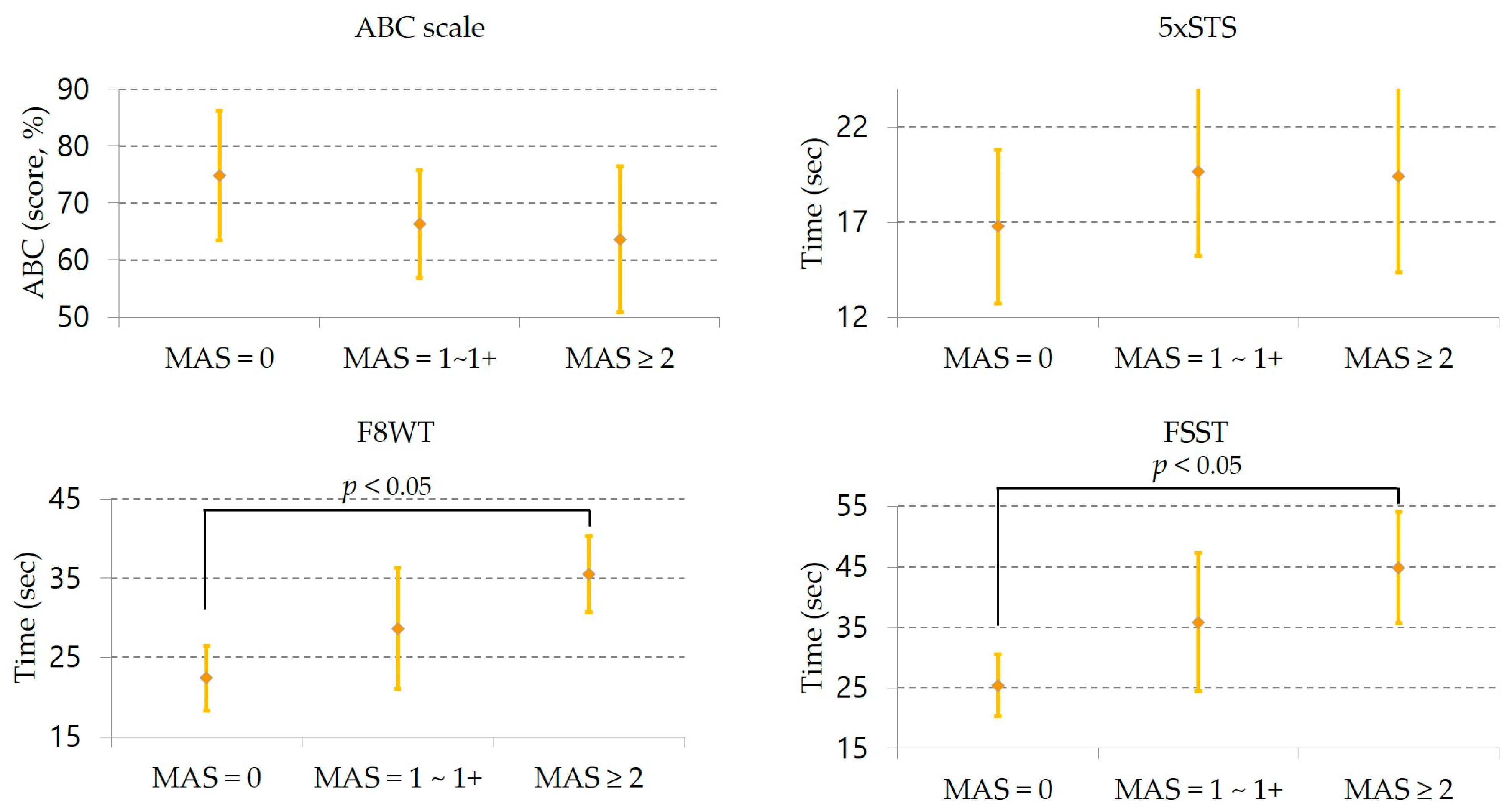
| Measures | Subgroups with Ankle Plantar Flexor Tone Mean ± SD (Min ~ Max) | F | Df | p | Post Hoc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAS = 0 (n = 16) (A) | MAS = 1~1+ (n = 23) (B) | MAS ≥ 2 (n = 15) (C) | |||||
| ABC scale (score, %) | 74.81 ± 23.26 (31~97) | 66.41 ± 23.09 (23~99) | 63.67 ± 25.34 (10~88) | 0.951 | 2 | 0.393 | ns |
| 5xSTS (sec) | 16.77 ± 8.24 (8.03~43.80) | 19.67 ± 10.91 (9.93~46.72) | 19.41 ± 9.98 (7.54~44.61) | 0.451 | 2 | 0.639 | ns |
| F8WT (sec) | 22.40 ± 8.30 (13.06~38.77) | 28.67 ± 18.62 (15.03~91.31) | 35.50 ± 9.57 (23.92~61.71) | 3.409 | 2 | 0.041 | A ∣ C |
| FSST (sec) | 25.42 ± 10.42 (13.87~49.77) | 35.85 ± 27.96 (14.76~140.11) | 44.87 ± 18.09 (10.38~85.73) | 3.205 | 2 | 0.049 | A ∣ C |
| Measures | Subgroups with Ankle Plantar Flexor Tone | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAS = 0 (n = 16) | MAS = 1~1+ (n = 23) | MAS ≥ 2 (n = 15) | |||||||
| 1st | 2nd | ICC | 1st | 2nd | ICC | 1st | 2nd | ICC | |
| ABC scale (score, %) | 75.00 ± 24.18 | 74.63 ± 23.55 | 0.90 (0.75~0.96) | 66.09 ± 24.94 | 66.74 ± 21.91 | 0.95 (0.90~0.98) | 64.27 ± 27.28 | 63.07 ± 23.71 | 0.96 (0.90~0.98) |
| 5xSTS (sec) | 16.84 ± 8.66 | 16.69 ± 7.95 | 0.96 (0.90~0.98) | 19.64 ± 11.12 | 19.70 ± 10.78 | 0.98 (0.96~0.99) | 20.34 ± 10.54 | 18.48 ± 9.43 | 0.96 (0.77~0.98) |
| F8WT (sec) | 22.95 ± 8.58 | 21.85 ± 8.12 | 0.96 (0.89~0.99) | 29.21 ± 18.42 | 28.14 ± 19.20 | 0.95 (0.90~0.98) | 35.74 ± 8.92 | 35.27 ± 10.74 | 0.88 (0.69~0.96) |
| FSST (sec) | 25.44 ± 10.88 | 25.39 ± 10.26 | 0.94 (0.84~0.98) | 36.60 ± 27.70 | 35.09 ± 28.43 | 0.98 (0.95~0.99) | 46.21 ± 18.50 | 43.53 ± 18.68 | 0.89 (0.71~0.96) |
| Measures | Subgroups With Ankle Plantar Flexor Tone | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAS = 0 (n = 16) | MAS = 1~1+ (n = 23) | MAS ≥ 2 (n = 15) | MAS = 0 (n = 16) | MAS = 1~1+ (n = 23) | MAS ≥ 2 (n = 15) | |
| SEM | MDC | |||||
| ABC scale (score, %) | 7.35 | 5.16 | 5.06 | 20.37 | 14.30 | 14.02 |
| 5xSTS (sec) | 1.64 | 1.54 | 1.99 | 4.56 | 4.26 | 5.51 |
| F8WT (sec) | 1.66 | 4.16 | 3.31 | 4.60 | 11.52 | 9.17 |
| FSST (sec) | 2.66 | 3.95 | 5.99 | 7.37 | 10.94 | 16.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, S.; Lee, D.; Park, D.; Lee, K. Differences in Functional Performance and Minimal Detectable Change According to Levels of Ankle Plantar Flexor Spasticity in Patients with Chronic Stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207358
An S, Lee D, Park D, Lee K. Differences in Functional Performance and Minimal Detectable Change According to Levels of Ankle Plantar Flexor Spasticity in Patients with Chronic Stroke. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207358
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, SeungHeon, DongGeon Lee, DongMin Park, and Kyeongbong Lee. 2025. "Differences in Functional Performance and Minimal Detectable Change According to Levels of Ankle Plantar Flexor Spasticity in Patients with Chronic Stroke" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207358
APA StyleAn, S., Lee, D., Park, D., & Lee, K. (2025). Differences in Functional Performance and Minimal Detectable Change According to Levels of Ankle Plantar Flexor Spasticity in Patients with Chronic Stroke. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7358. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207358






