COVID-19 Infection, Drugs, and Liver Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search Methodology
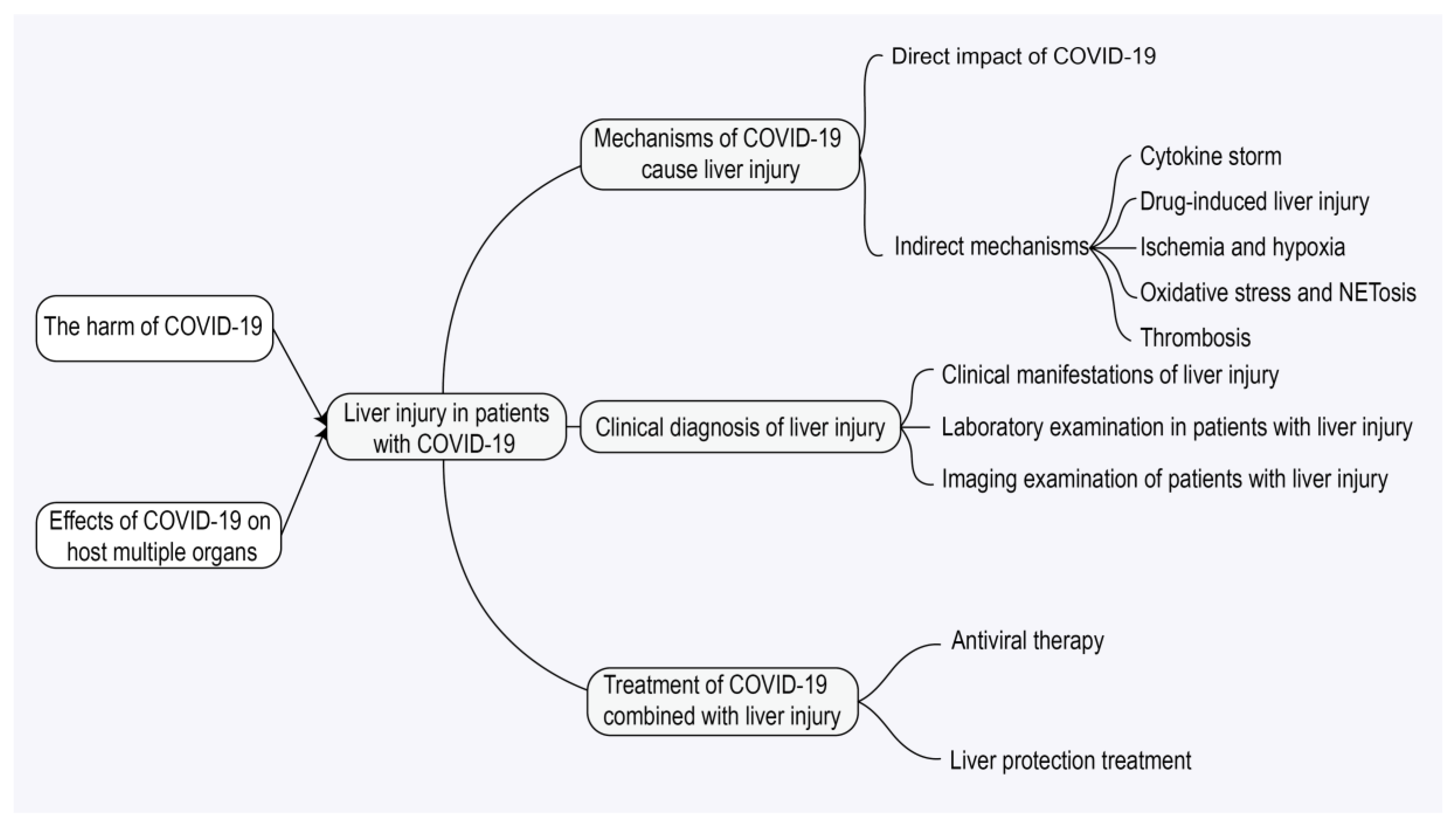
3. The Harm of COVID-19 and Its Effect on Multiple Organs of Host
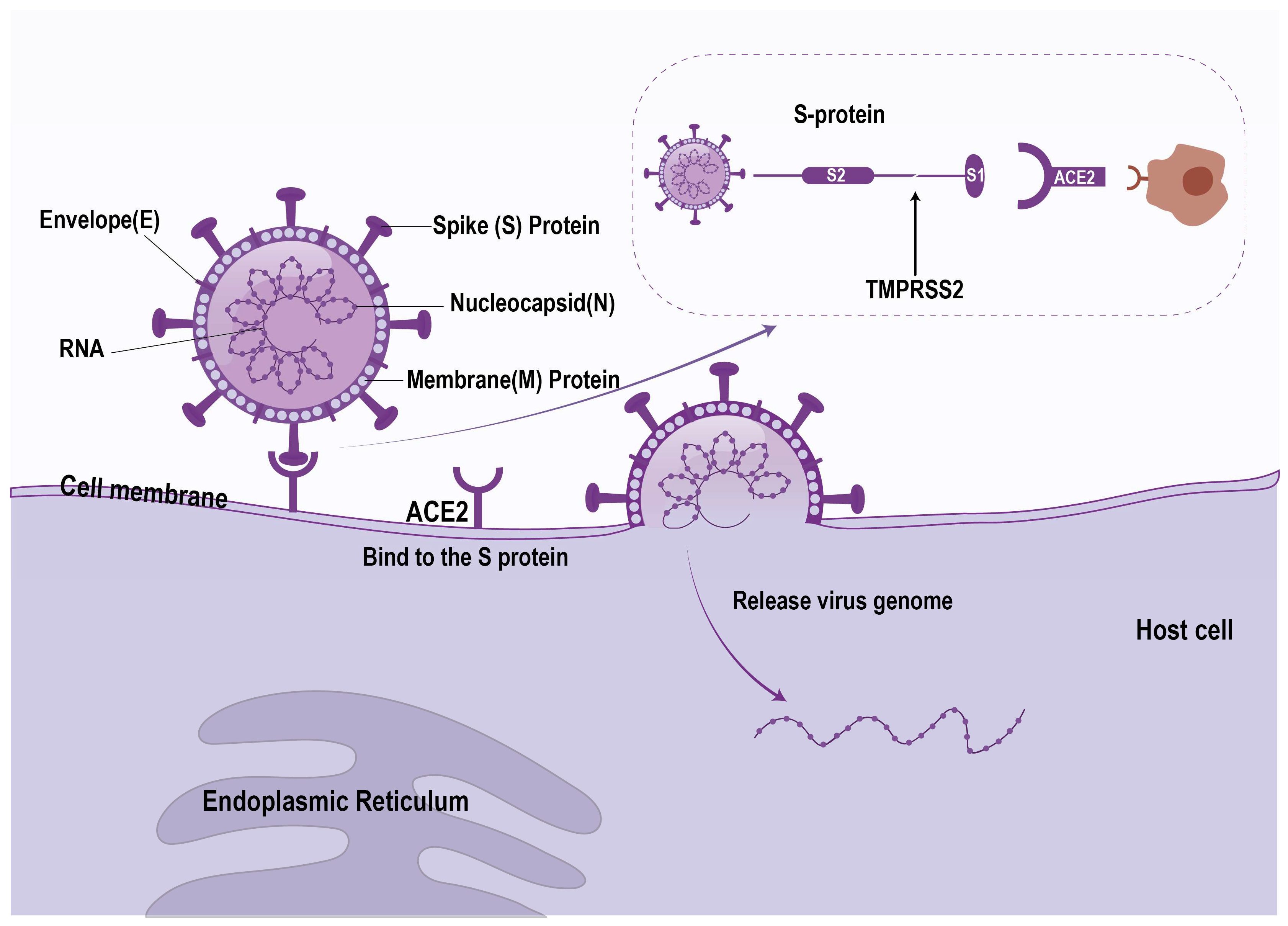
3.1. Virus Characteristics and Infection Mechanism
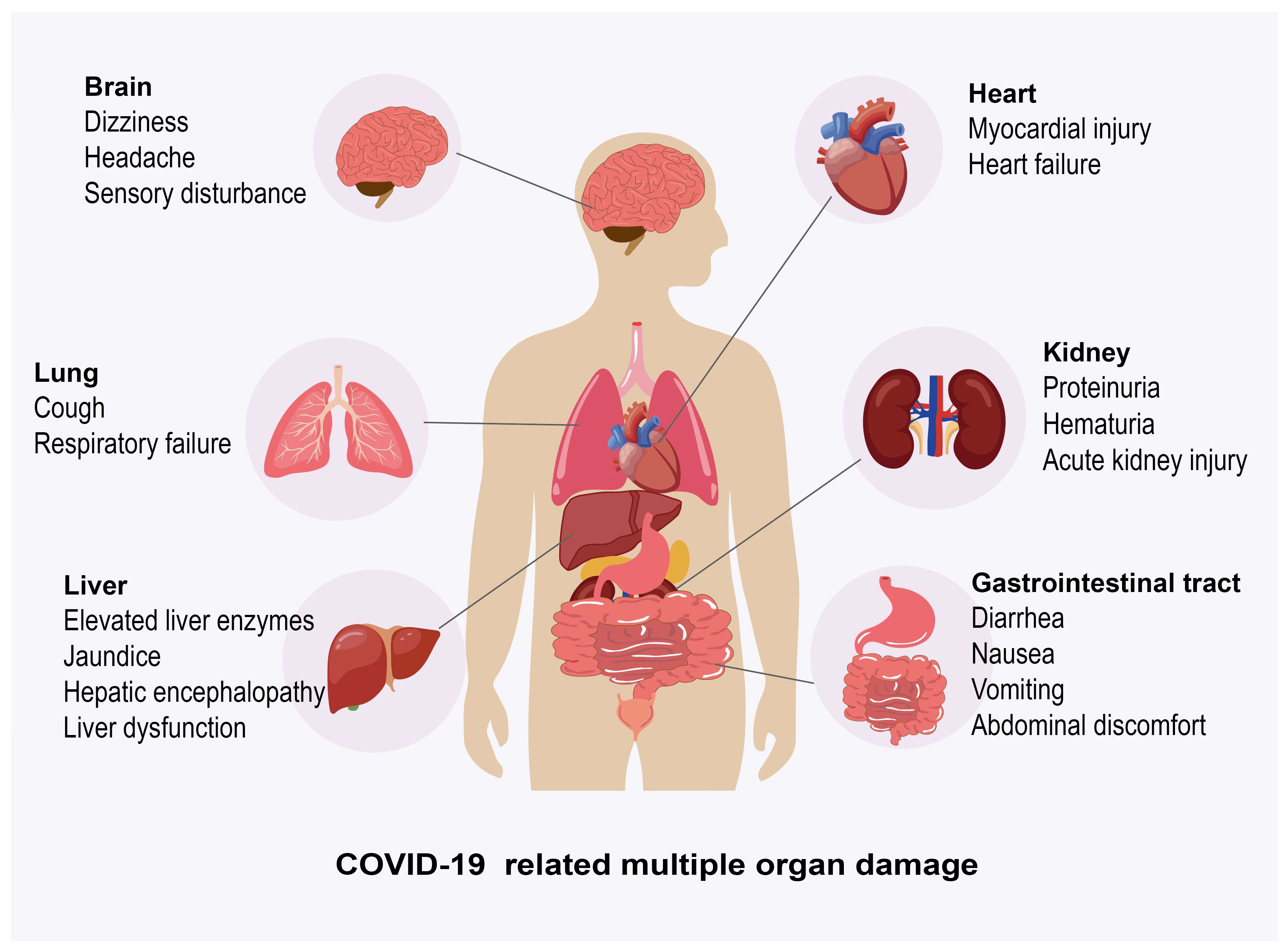
3.2. Effects of COVID-19 on Host’s Multiple Organs
3.2.1. The Effect of COVID-19 on Lung
3.2.2. Effect of COVID-19 on Liver
3.2.3. Effects of COVID-19 on Other Organs
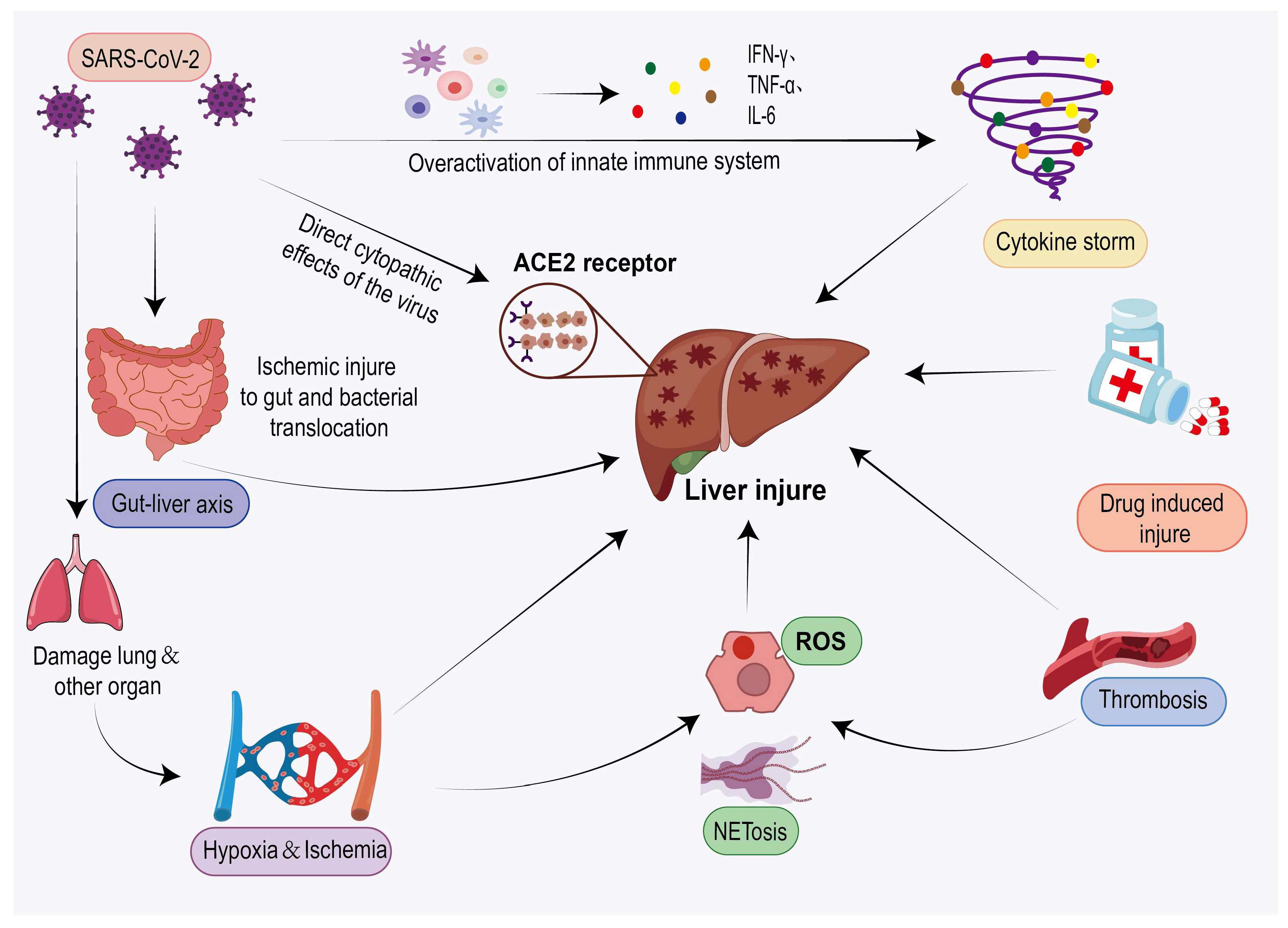
4. Mechanism of Liver Inflammation Caused by COVID-19
4.1. Direct Viral Infection
4.2. Indirect Effects of Viruses
4.2.1. Immune Follow-Up Response (Cytokine Storm)
4.2.2. Ischemic/Hypoxic Liver Injury
4.2.3. Oxidative Stress and NETosis
4.2.4. Thrombosis
4.2.5. Intestinal Hepatic Axis Infection
4.2.6. Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity
5. Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment
5.1. Clinical Diagnosis
5.1.1. Clinical Manifestation
5.1.2. Laboratory Examination
5.1.3. Imaging Examination
5.2. Clinical Treatment
5.2.1. Antiviral Therapy
5.2.2. Treatment of Liver Injury
6. Summary and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus Infections and Immune Responses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.U.; Shafique, L.; Ihsan, A.; Liu, Q. Evolutionary Trajectory for the Emergence of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens 2020, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, J.; Minko, T. Recent Developments on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Approaches for COVID-19. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Manjunath, K.; Ranjan, R.K.; Kaushik, S.; Kumar, S.; Verma, V. COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights into Structure, Function, and hACE2 Receptor Recognition by SARS-CoV-2. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, R.; Agarwal, S. COVID-19: Characteristics and Therapeutics. Cells 2021, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-W.; Wu, X.-X.; Jiang, X.-G.; Xu, K.-J.; Ying, L.-J.; Ma, C.-L.; Li, S.-B.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.-N.; et al. Clinical Findings in a Group of Patients Infected with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) Outside of Wuhan, China: Retrospective Case Series. BMJ 2020, 368, m606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordzadeh-Kermani, E.; Khalili, H.; Karimzadeh, I. Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations and Complications of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 1287–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, M.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Kotfis, K.; Maciejewska, D.; Łoniewski, I.; Lara, L.F.; Pazgan-Simon, M.; Stachowska, E.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Koulaouzidis, A.; et al. COVID-19, MERS and SARS with Concomitant Liver Injury-Systematic Review of the Existing Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, O.K.; Hameed, B.; Fontana, R.J.; Kwok, R.M.; McGuire, B.M.; Mulligan, D.C.; Pratt, D.S.; Russo, M.W.; Schilsky, M.L.; Verna, E.C.; et al. Clinical Best Practice Advice for Hepatology and Liver Transplant Providers During the COVID-19 Pandemic: AASLD Expert Panel Consensus Statement. Hepatology 2020, 72, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-W.; Huang, A.-L.; Tang, K.-F. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Hepatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Regulation, Association, and Therapeutic Implications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinutha, M.; Sharma, U.R.; Swamy, G.; Rohini, S.; Vada, S.; Janandri, S.; Haribabu, T.; Taj, N.; Gayathri, S.; Jyotsna, S.K.; et al. COVID-19-Related Liver Injury: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, Management; Its Impact on Pre-Existing Conditions, Cancer and Liver Transplant: A Comprehensive Review. Life Sci. 2024, 356, 123022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarleri, J.; Delpino, M.V. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying SARS-CoV-2 Hepatotropism and Liver Damage. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danan, G.; Teschke, R. RUCAM in Drug and Herb Induced Liver Injury: The Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danan, G.; Benichou, C. Causality Assessment of Adverse Reactions to Drugs—I. A Novel Method Based on the Conclusions of International Consensus Meetings: Application to Drug-Induced Liver Injuries. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1993, 46, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Eickhoff, A. Liver Injury in COVID-19 Patients with Drugs as Causatives: A Systematic Review of 996 DILI Cases Published 2020/2021 Based on RUCAM as Causality Assessment Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Song, S.; Cao, H.-C.; Li, L.-J. Liver Diseases in COVID-19: Etiology, Treatment and Prognosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.G.; Lin, T.; Wang, P. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Transmission and Pathogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 1100–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadian, M.; Chiti, H.; Shoghli, A.; Biglari, S.; Parsamanesh, N.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. COVID-19: Virology, Biology and Novel Laboratory Diagnosis. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variant Biology: Immune Escape, Transmission and Fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Immune Escape, and Countermeasures. Front. Med. 2022, 16, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisuleyman, E.; Hale, C.; Saito, Y.; Blachere, N.E.; Bergh, M.; Conlon, E.G.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.J.; DaSilva, J.; Muecksch, F.; Gaebler, C.; et al. Vaccine Breakthrough Infections with SARS-CoV-2 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Hu, N.; Lou, J.; Chen, K.; Kang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, N.; Liu, D.; et al. Characteristics of COVID-19 Infection in Beijing. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Deng, Y.; Li, W. Coronavirus Disease 2019: What We Know? J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzotzos, S.J.; Fischer, B.; Fischer, H.; Zeitlinger, M. Incidence of ARDS and Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Global Literature Survey. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arentz, M.; Yim, E.; Klaff, L.; Lokhandwala, S.; Riedo, F.X.; Chong, M.; Lee, M. Characteristics and Outcomes of 21 Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19 in Washington State. JAMA 2020, 323, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestaña, D.; Villar, L.; Gomez-Rojo, M.; Roy, G.; Olmedillo, B.; Giménez, C.; Zambrana, P.; Guisado, G.; Aláez, A.; Bardi, T. Respiratory Mechanics in Late COVID-19 ARDS-a Restrictive Pattern Is Strongly Associated with Death. A Cohort Study. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2022, 54, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrobaa, I.H.; New, K.J. COVID-19: Pulmonary and Extra Pulmonary Manifestations. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 711616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-S. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Cell Receptor Gene ACE2 in a Wide Variety of Human Tissues. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, V.; Kumar, A.B.; Borum, M.L. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Manifestations of COVID-19: Evolving Recognition and Need for Increased Understanding in Vulnerable Populations. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2021, 113, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Krisko, T.; Mehta, A.; Kumar, S.; Schwartz, R.; Fortune, B.; Sharaiha, R.Z. WCM-GI research group∗ Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Manifestations of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease in a Large Cohort of Infected Patients From New York: Clinical Implications. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1137–1140.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasinia, M.; Hormati, A.; Eshagh Hossaini, S.K.; Foroghi Ghomi, S.Y.; Zamani, F.; Afifian, M.; Ahmadpour, S. Clinical Manifestations of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients: An Integrative Review. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2021, 44, E1–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Lian, J.-S.; Hu, J.-H.; Gao, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Hao, S.-R.; Jia, H.-Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, X.-L.; et al. Epidemiological, Clinical and Virological Characteristics of 74 Cases of Coronavirus-Infected Disease 2019 (COVID-19) with Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Gut 2020, 69, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Lv, L.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Luo, R.; Huang, C.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Shah, H. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Manifestations of Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Madhu, D.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, A.; Saraya, A. Special Considerations in the Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in COVID-19 Hotspots: A Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-C.; Huo, T.-I.; Huang, Y.-H. Gastrointestinal and Liver Manifestations in Patients with COVID-19. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, Y.; Song, Y.; Feng, F.; Feng, J.; Song, Q.; Jia, Q.; Wang, J. Clinical Characteristics of 82 Cases of Death from COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Lu, M.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X. Liver Injury during Highly Pathogenic Human Coronavirus Infections. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-F.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Peng, J.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Fu, N.; Lin, H.-L.; Jiang, B.; Tian, Y.-Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients in Hengyang, Hunan Province, China. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 2554–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.D.; et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, M.M.; Barraza, L.H.; LaSota, E.D.; Sobieszczyk, M.E.; Pereira, M.R.; Zheng, E.X.; Fox, A.N.; Zucker, J.; Verna, E.C. Acute Liver Injury in COVID-19: Prevalence and Association with Clinical Outcomes in a Large US Cohort. Hepatology 2020, 72, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.; Khanum, I.; Habib, K.; Wagley, A.; Arshad, A.; Majeed, A. Insight into COVID-19 Associated Liver Injury: Mechanisms, Evaluation, and Clinical Implications. Hepatol. Forum 2024, 5, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.-H.; Ou, C.-Q.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.-L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous Long COVID or Post COVID-19 Syndrome. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 55, 103268. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.-W.; Li, Y.-M.; Li, Y.-L.; Su, C. Liver Injury in COVID-19: Clinical Features, Potential Mechanisms, Risk Factors and Clinical Treatments. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qin, M.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Shen, B.; Yang, F.; Cao, S.; Liu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Characteristics and Clinical Significance of Myocardial Injury in Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukkawar, R.V.; Reddy, H.; Rathod, N.; Kumar, S.; Acharya, S. The Long-Term Cardiovascular Impact of COVID-19: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Cureus 2024, 16, e66554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllis, A.S.; Sfantou, D.; Karapedi, E.; Peteinaki, K.; Kotoulas, S.C.; Saad, R.; Fountoulakis, P.N.; Tsamakis, K.; Tsiptsios, D.; Rallidis, L.; et al. Coronary Implications of COVID-19. Med. Princ. Pract. 2025, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, S.; Orieux, A.; Prevel, R.; Garric, A.; Bats, M.-L.; Dabernat, S.; Camou, F.; Guisset, O.; Issa, N.; Mourissoux, G.; et al. Characterization of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney Disease Is Associated with In-Hospital Death of Patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizi, F.; Nardelli, L.; Regalia, A.; Zanoni, F.; Castellano, G. Are Kidneys Affected by SARS-CoV-2 Infection? An Updated Review on COVID-19-Associated AKI. Pathogens 2024, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.A. COVID-19 Infection and the Kidneys: Learning the Lesson. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, C.; How-Volkman, C.; Spencer, M.; El-Shamy, A.; Mohieldin, A.M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in SARS-CoV-2-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: An Overview. Life 2024, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.H.-Y.; Beghi, E.; Helbok, R.; Moro, E.; Sampson, J.; Altamirano, V.; Mainali, S.; Bassetti, C.; Suarez, J.I.; McNett, M.; et al. Global Incidence of Neurological Manifestations Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19-A Report for the GCS-NeuroCOVID Consortium and the ENERGY Consortium. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2112131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, F.; Prasad, K.; Kumar, V. COVID-19 Associated Nervous System Manifestations. Sleep. Med. 2022, 91, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; De Siati, D.R.; Horoi, M.; Le Bon, S.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Dequanter, D.; Blecic, S.; El Afia, F.; Distinguin, L.; et al. Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunctions as a Clinical Presentation of Mild-to-Moderate Forms of the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Multicenter European Study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht, F.; Mohammadkhanizadeh, A.; Mohammadi, E. How Does the COVID-19 Cause Seizure and Epilepsy in Patients? The Potential Mechanisms. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 46, 102535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisht, A.; Vashisht, V.; Singh, H.; Ahluwalia, P.; Mondal, A.K.; Williams, C.; Farmaha, J.; Woodall, J.; Kolhe, R. Neurological Complications of COVID-19: Unraveling the Pathophysiological Underpinnings and Therapeutic Implications. Viruses 2024, 16, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, H.; Deng, A. COVID-19 Infection May Cause Ketosis and Ketoacidosis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1935–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pp, A.; Ms, B.; Aa, S.; La, K.; Pv, A. Immunity and Coagulation in COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russu, E.; Arbănaşi, E.-M.; Șchiopu, A. Special Issue “COVID-19 Coagulopathy: Advances on Pathophysiology and Therapies”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarella, R.; Marino, M.; Crafa, A.; Bagnara, V.; La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E. Impact of COVID-19 on Testicular Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrine 2024, 85, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediz, C.; Tavukcu, H.H.; Akan, S.; Kizilkan, Y.E.; Alcin, A.; Oz, K.; Yilmaz, O. Is There Any Association of COVID-19 with Testicular Pain and Epididymo-Orchitis? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Gandhi, R.; Satapara, N.; Babaria, D.L.; Vala, R.B.; Murugan, Y. Ophthalmic Manifestations of COVID-19: A Retrospective Study on Prevalence, Characteristics, and Clinical Implications. Cureus 2024, 16, e59177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SeyedAlinaghi, S.; Mehraeen, E.; Afzalian, A.; Dashti, M.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Pashaei, A.; Masoud Afsahi, A.; Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, S.; Amiri Fard, I.; Vafaee, A.; et al. Ocular Manifestations of COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 38, 102608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.J.; Sookoian, S. SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Liver Expression of Host Receptors: Putative Mechanisms of Liver Involvement in COVID-19. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2038–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmelink, M.; De Mendonça, R.; D’Haene, N.; De Clercq, S.; Verocq, C.; Lebrun, L.; Lavis, P.; Racu, M.-L.; Trépant, A.-L.; Maris, C.; et al. Unspecific Post-Mortem Findings despite Multiorgan Viral Spread in COVID-19 Patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Fitzek, A.D.E.; Schaedler, J.; Förster, C.; Kaltschmidt, C.; Hansen, T.; Steinfurth, F.; Windmöller, B.A.; Pilger, C.; Kong, C.; et al. Hepatic Vasculopathy and Regenerative Responses of the Liver in Fatal Cases of COVID-19. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 1726–1729.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagana, S.M.; Kudose, S.; Iuga, A.C.; Lee, M.J.; Fazlollahi, L.; Remotti, H.E.; Del Portillo, A.; De Michele, S.; de Gonzalez, A.K.; Saqi, A.; et al. Hepatic Pathology in Patients Dying of COVID-19: A Series of 40 Cases Including Clinical, Histologic, and Virologic Data. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ni, C.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, J.; Lv, T.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, W.; et al. Recapitulation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cholangiocyte Damage with Human Liver Ductal Organoids. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, A.R.; Misdraji, J. COVID-19: Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Manifestations. Hum. Pathol. 2023, 132, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W.; et al. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients with Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liatsos, G.D. SARS-CoV-2 Induced Liver Injury: Incidence, Risk Factors, Impact on COVID-19 Severity and Prognosis in Different Population Groups. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2397–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.-J.; Lv, G.-Y.; Liu, H.-Q. The Mechanisms and Strategies to Protect from Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Yang, M. Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 Invasion into the Liver and Hepatic Injury in Patients with COVID-19. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 14, e2022003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, S.; Mesa, H.; Aysola, A.; Manivel, J.; Toledo, J.; Borges-Sa, M.; Aldighieri, S.; Reveiz, L. Pathological Findings in Organs and Tissues of Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazarghi, A.; Bazoq, S.; Taziki Balajelini, M.H.; Ebrahimi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Razavi Nikoo, H. Liver Injury in COVID-19: An Insight into Pathobiology and Roles of Risk Factors. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Min, W. Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress and Innate Immunity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobjeva, N.V.; Chernyak, B.V. NETosis: Molecular Mechanisms, Role in Physiology and Pathology. Biochemistry 2020, 85, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. NETosis and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in COVID-19: Immunothrombosis and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 838011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, M.J.; Kawaguchi, N.; Kondo, R.; Sonzogni, A.; Licini, L.; Valle, C.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Sironi, S.; Alessio, M.G.; Previtali, G.; et al. Liver Injury in COVID-19 and IL-6 Trans-Signaling-Induced Endotheliopathy. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Abnormal Coagulation Parameters Are Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Elalamy, I.; Kastritis, E.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Politou, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Gerotziafas, G.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Hematological Findings and Complications of COVID-19. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadid, T.; Kafri, Z.; Al-Katib, A. Coagulation and Anticoagulation in COVID-19. Blood Rev. 2021, 47, 100761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonzogni, A.; Previtali, G.; Seghezzi, M.; Grazia Alessio, M.; Gianatti, A.; Licini, L.; Morotti, D.; Zerbi, P.; Carsana, L.; Rossi, R.; et al. Liver Histopathology in Severe COVID 19 Respiratory Failure Is Suggestive of Vascular Alterations. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassan, M.; Mescoli, C.; Sbaraglia, M.; Guzzardo, V.; Russo, F.P.; Fabris, R.; Trevenzoli, M.; Pelizzaro, F.; Cattelan, A.M.; Basso, C.; et al. Liver Histopathology in COVID-19 Patients: A Mono-Institutional Series of Liver Biopsies and Autopsy Specimens. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 221, 153451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, C. Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Sequelae in Liver Diseases. Life 2025, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Hussain Timraz, J.; Al Ghamdi, N.A.; Metwali, N.Y.; Yaseen, F.A.; Alshaqha, A.M.; Alamri, S.H.; Turkistani, H.; Dwaima, A.; Ali Algarni, I. COVID-19 and Its Effects on the Hepatobiliary System: A Literature Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e80231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, L.; Duan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Gut Microbiota Exaggerates Triclosan-Induced Liver Injury via Gut-Liver Axis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Kumar, P.; Tevethia, H.V.; Premkumar, M.; Arab, J.P.; Candia, R.; Talukdar, R.; Sharma, M.; Qi, X.; Rao, P.N.; et al. Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis: Liver Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Huang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, G.; Gou, J.; Qu, J.; et al. COVID-19: Abnormal Liver Function Tests. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, J. Clinical Features of COVID-19-Related Liver Functional Abnormality. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, A.I.; Lu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; McMahon, D.; Xie, W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Ma, X. Pregnane X Receptor Activation Potentiates Ritonavir Hepatotoxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2898–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leegwater, E.; Strik, A.; Wilms, E.B.; Bosma, L.B.E.; Burger, D.M.; Ottens, T.H.; van Nieuwkoop, C. Drug-Induced Liver Injury in a Patient with Coronavirus Disease 2019: Potential Interaction of Remdesivir with P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1256–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kulkarni, A.; Sharma, M.; Rao, P.N.; Reddy, D.N. Favipiravir-Induced Liver Injury in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhovic, D.; Bojovic, J.; Bulatovic, A.; Vukcevic, B.; Ratkovic, M.; Lazovic, R.; Smolovic, B. First Case of Drug-Induced Liver Injury Associated with the Use of Tocilizumab in a Patient with COVID-19. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, A.; Ramersdorfer, C.; Palitzsch, K.D.; Schölmerich, J.; Lock, G. Fatal liver failure after corticosteroid treatment of a hepatitis B virus carrier. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1999, 124, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, M.; Colletier, K.; Moghe, A. Hepatitis B Reactivation and Liver Failure Because of COVID-19 Infection. ACG Case Rep. J. 2024, 11, e01397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.L.; Rapkiewicz, A.; Maghsoodi-Deerwester, M.; Gupta, M.; Cao, W.; Palaia, T.; Zhou, J.; Ram, B.; Vo, D.; Rafiee, B.; et al. Pathological Findings in the Postmortem Liver of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Hum. Pathol. 2021, 109, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiel, M.I.; El Jamal, S.M.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A.; Gordon, R.E.; Reidy, J.; Bandovic, J.; Advani, R.; Kilaru, S.; Pourmand, K.; Ward, S.; et al. Findings of Hepatic Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Infection. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Manetti, A.C.; Franceschi, F.; La Russa, R.; Bertozzi, G.; Maiese, A.; Savioli, G.; Volonnino, G.; Longhitano, Y. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Therapy. Medicina 2022, 58, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, E.M.; Koretzky, G.A. Review: Cytokine Storm Syndrome: Looking Toward the Precision Medicine Era. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, J.-G. Characteristics and Mechanism of Liver Injury in 2019 Coronavirus Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Dashatan, N.; Koushki, M.; Ghorbani, F.; Naderi, N. Increased Inflammatory Markers Correlate with Liver Damage and Predict Severe COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2020, 13, 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Akkiz, H. Unraveling the Molecular and Cellular Pathogenesis of COVID-19-Associated Liver Injury. Viruses 2023, 15, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polakos, N.K.; Cornejo, J.C.; Murray, D.A.; Wright, K.O.; Treanor, J.J.; Crispe, I.N.; Topham, D.J.; Pierce, R.H. Kupffer Cell-Dependent Hepatitis Occurs during Influenza Infection. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1169–1178; quiz 1404–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Hubscher, S.G. Systemic Viral Infections and Collateral Damage in the Liver. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1057–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelli, A.; Davì, S.; Minoia, F.; Martini, A.; Cron, R.Q. Macrophage Activation Syndrome. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagri, N.K.; Gupta, L.; Sen, E.S.; Ramanan, A.V. Macrophage Activation Syndrome in Children: Diagnosis and Management. Indian. Pediatr. 2021, 58, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojan, A.; Parvu, A.; Zsoldos, I.-A.; Torok, T.; Farcas, A.D. Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Diagnostic Challenge (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Wong, F.; Couch, L.S.; Wang, B.X. Cardiac Complications of COVID-19 in Low-Risk Patients. Viruses 2022, 14, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.G.; Qin, L.; Puah, S.H. COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Clinical Features and Differences from Typical Pre-COVID-19 ARDS. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 213, 54–56.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, X.; Dai, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, L.; Yan, R.; Wang, M.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Hypoxic Hepatitis in COVID-19 Patients in the Intensive Care Unit: A First Retrospective Study. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 607206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Niloofa, R.; De Zoysa, I.M.; Cooray, A.D.; Kariyawasam, J.; Seneviratne, S.L. Neurological Manifestations in COVID-19: A Narrative Review. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120957925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, S.W.; Kim, M.; D’Agati, V.D.; Lee, H.T. Isoflurane Activates Intestinal Sphingosine Kinase to Protect against Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Liver and Intestine Injury. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, R.; Cecchini, A.L. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Pathogenesis Is Related to Oxidative Stress as a Response to Aggression. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 110102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-kappaB Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelová, H.; Hošek, J. TNF-α Signalling and Inflammation: Interactions between Old Acquaintances. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobjeva, N.; Galkin, I.; Pletjushkina, O.; Golyshev, S.; Zinovkin, R.; Prikhodko, A.; Pinegin, V.; Kondratenko, I.; Pinegin, B.; Chernyak, B. Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Is Involved in Oxidative Burst and NETosis of Human Neutrophils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, H.R.; Wong, S.L.; Wagner, D.D.; Waterman, C.M. Cellular Mechanisms of NETosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 36, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S B, M.J.; Chacko, B.; Selvarajan, S.; Peter, J.V.; Geevar, T.; Dave, R.G.; Georgy, J.T.; Zachariah, A.; George, T.; Sathyendra, S.; et al. Biomarkers of Coagulation, Endothelial, Platelet Function, and Fibrinolysis in Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Saito, M.; Nagai, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Ikeuchi, K.; Lim, L.A.; Adachi, E.; Koga, M.; Okushin, K.; Akai, H.; et al. Association of Coagulopathy with Liver Dysfunction in Patients with COVID-19. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, R.; Kawaguchi, N.; McConnell, M.J.; Sonzogni, A.; Licini, L.; Valle, C.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Sironi, S.; Alessio, M.G.; Previtali, G.; et al. Pathological Characteristics of Liver Sinusoidal Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patients: A Series of 43 Cases. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraaijenhagen, R.A.; in’t Anker, P.S.; Koopman, M.M.; Reitsma, P.H.; Prins, M.H.; van den Ende, A.; Büller, H.R. High Plasma Concentration of Factor VIIIc Is a Major Risk Factor for Venous Thromboembolism. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, T.; Blann, A.D.; Briët, E.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Rosendaal, F.R. Role of Clotting Factor VIII in Effect of von Willebrand Factor on Occurrence of Deep-Vein Thrombosis. Lancet 1995, 345, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, G.; Oudot-Mellakh, T.; Dimitromanolakis, A.; Germain, M.; Cohen, W.; Wells, P.; Lathrop, M.; Gagnon, F.; Morange, P.-E.; Tregouet, D.-A. Combined Analysis of Three Genome-Wide Association Studies on vWF and FVIII Plasma Levels. BMC Med. Genet. 2011, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Espada, A.; Salgado-de la Mora, M.; Rodriguez-Paniagua, B.M.; Limon-de la Rosa, N.; Martinez-Gutierrez, M.I.; Pastrana-Brandes, S.; Navarro-Alvarez, N. Histopathological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the Liver: Cellular Damage and Long-Term Complications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2866–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focosi, D.; Franchini, M.; Maggi, F.; Shoham, S. COVID-19 Therapeutics. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0011923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiao, B.; Qu, L.; Yang, D.; Liu, R. The Development of COVID-19 Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1125246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, L.F. Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) Poisoning: The Early Years. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 90, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R.; Danan, G. Worldwide Use of RUCAM for Causality Assessment in 81,856 Idiosyncratic DILI and 14,029 HILI Cases Published 1993-Mid 2020: A Comprehensive Analysis. Medicines 2020, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, A.; Stewart, S.; Urroz, M.; Rodriguez, A.; Borobia, A.M.; Akatbach-Bousaid, I.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M.; Ramirez, E. Characterisation of Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Patients with COVID-19 Detected by a Proactive Pharmacovigilance Program from Laboratory Signals. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olry, A.; Meunier, L.; Délire, B.; Larrey, D.; Horsmans, Y.; Le Louët, H. Drug-Induced Liver Injury and COVID-19 Infection: The Rules Remain the Same. Drug Saf. 2020, 43, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Carmeliet, P. Hypoxia and Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y. Clinical Features and Risk Factors of COVID-19-Associated Liver Injury and Function: A Retrospective Analysis of 830 Cases. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 21, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothimani, D.; Vij, M.; Sanglodkar, U.; Patil, V.; Sachan, D.; Narasimhan, G.; Kaliamoorthy, I.; Rela, M. Severe Jaundice in a COVID-19 Patient-Virus or Drug? J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Sayama, M.; Nakada, T.; Igari, H.; Ishii, I. Suspected Cholestatic Liver Injury Induced by Favipiravir in a Patient with COVID-19. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagiouvanni, I.; Kotoulas, S.-C.; Pataka, A.; Spyratos, D.G.; Porpodis, K.; Boutou, A.K.; Papagiouvannis, G.; Grigoriou, I.; Vettas, C.; Goulis, I. COVID-19 and Liver Injury: An Ongoing Challenge. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, N.; Singla, P.; Arbuckle, E.; Goyal, G.; Liu, Q.; Santos-Zabala, M.L.; Zainah, H. SARS-CoV-2-Induced Autoimmune Hepatitis. Cureus 2023, 15, e38932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbeltagi, R.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Saeed, N.K.; Bediwy, A.S.; Toema, O. May 2022 Acute Hepatitis Outbreak, Is There a Role for COVID-19 and Other Viruses? World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmimass, S.; Kadiri, M.; Borahma, M.; Chabib, F.-Z.; Berhili, C.; Lagdali, N.; Elbarhdadi, I.B.; Ajana, F.-Z. Acute Severe Hepatitis and COVID-19: Case Report. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2024, 49, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melquist, S.; Estepp, K.; Aleksandrovich, Y.; Lee, A.; Beiseker, A.; Hamedani, F.S.; Bassett, J. COVID-19 Presenting as Fulminant Hepatic Failure: A Case Report. Medicine 2020, 99, e22818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J.M.; Worman, H.J. Jaundice in Patients with COVID-19. JGH Open 2021, 5, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Laukkanen, J.A. Hepatic Manifestations and Complications of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e72–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-M, P.; Mishra, S.; Jha, D.K.; Shukla, J.; Choudhury, A.; Mohindra, R.; Mandavdhare, H.S.; Dutta, U.; Sharma, V. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and the Liver: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalvi, S.A.; Rauf, S.A.; Sherali, A.; Ali, S.K.; Shah, H.H.; Jamalvi, F.; Yogeeta, F.; Dave, T. COVID-19 Presenting as Severe Acute Hepatitis in a Pediatric Patient with Thalassemia Minor: A Case Report. Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Du, C.; Song, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; et al. COVID-19-Associated Gastrointestinal and Liver Injury: Clinical Features and Potential Mechanisms. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antala, S.; Diamond, T.; Kociolek, L.K.; Shah, A.A.; Chapin, C.A. Severe Hepatitis in Pediatric Coronavirus Disease 2019. J Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundt, M.A.; Deng, Y.; Ciarleglio, M.M.; Nathanson, M.H.; Lim, J.K. Abnormal Liver Tests in COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study of 1,827 Patients in a Major U.S. Hospital Network. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Liu, Y.-M.; Zhou, F.; Qin, J.-J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.-J.; Cai, J.; Lin, L.; Ouyang, S.; et al. Longitudinal Association Between Markers of Liver Injury and Mortality in COVID-19 in China. Hepatology 2020, 72, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Qiu, Y.; He, J.-S.; Tan, J.-Y.; Li, X.-H.; Liang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhu, L.-R.; Chen, Y.; Iacucci, M.; et al. Manifestations and Prognosis of Gastrointestinal and Liver Involvement in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Ungprasert, P.; Panjawatanan, P.; Harnois, D.M.; Zaver, H.B.; Ahmed, A.; Kim, D. COVID-19 and Liver Injury: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Liu, L.-G.; Wang, Y.-B.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.-H.; Xu, Y.-L.; Gao, G.-J.; Xiong, H.-F.; Fan, Y.; et al. Pattern of Liver Injury in Adult Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Analysis of 105 Patients. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakina, V.; Stundiene, I.; Milaknyte, G.; Bytautiene, R.; Reivytyte, R.; Puronaite, R.; Urbanoviciute, G.; Kazenaite, E. Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver: The Experience of a Single Center. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5735–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, Z. Autoimmune Hepatitis under the COVID-19 Veil: An Analysis of the Nature of Potential Associations. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1510770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J.M.; Worman, H.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Liver Injury: A Retrospective Analysis of Hospitalized Patients in New York City. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, F.-S. Liver Injury in COVID-19: Management and Challenges. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Ye, Q. Hepatic Complications of COVID-19 and Its Treatment. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizaddini, S.; Mani, N. Liver Imaging. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Morana, G.; Beleù, A.; Geraci, L.; Tomaiuolo, L.; Venturini, S. Imaging of the Liver and Pancreas: The Added Value of MRI. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, R.B.; Jayaraman, T.; Khoo, X.-H.; Saravanaa, N.; Kukreja, A.; Johari, B.M.; Gowdh, N.F.M.; Lee, W.-K.; Sooi, C.-Y.; Basri, S.; et al. Liver Dysfunction in Adults with COVID-19 Infection: A Longitudinal Study with Transient Elastography Evaluation. JGH Open 2024, 8, e13118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spogis, J.; Hagen, F.; Thaiss, W.M.; Hoffmann, T.; Malek, N.; Nikolaou, K.; Berg, C.P.; Singer, S.; Bösmüller, H.; Kreth, F.; et al. Sonographic Findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 Associated Liver Damage. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almughalles, S.; Khojaly, S.N.; Nashwan, A.J.; Darweesh, A. Liver Ultrasound Evaluation of Acutely Increased Liver Function Tests of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients. Qatar Med. J. 2024, 2024, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Zhang, L.; Han, P.; Zheng, C.; Tong, Q.; Shang, H.; Yang, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Song, Y. Liver Injury in Patients with COVID-19: Clinical Profiles, CT Findings, the Correlation of the Severity with Liver Injury. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, D.; Maino, C.; Vernuccio, F.; Cannella, R.; Inchingolo, R.; Dezio, M.; Faletti, R.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Gatti, M.; Sironi, S. Liver Involvement in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: A Comprehensive Overview of Diagnostic Imaging Features. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 834–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.; Rockey, D.C. The Utility of Liver Biopsy in 2020. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 36, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on Non-Invasive Tests for Evaluation of Liver Disease Severity and Prognosis-2021 Update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.-S.; Lam, C.-Y.; Tan, P.-H.; Tsang, H.-F.; Wong, S.-C.C. Comprehensive Review of COVID-19: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Advancement in Diagnostic and Detection Techniques, and Post-Pandemic Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xie, K. Development and Validation of a Nomogram to Assess the Occurrence of Liver Dysfunction in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia in the ICU. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, S.M.R.; Sheida, A.; Taghizadieh, M.; Memar, M.Y.; Hamblin, M.R.; Bannazadeh Baghi, H.; Sadri Nahand, J.; Asemi, Z.; Mirzaei, H. Paxlovid (Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir): A New Approach to COVID-19 Therapy? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.; Leister-Tebbe, H.; Gardner, A.; Abreu, P.; Bao, W.; Wisemandle, W.; Baniecki, M.; Hendrick, V.M.; Damle, B.; Simón-Campos, A.; et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, B.; Amani, B. Efficacy and Safety of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID-19: A Rapid Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, K.; Xu, L.; Luo, C.; Luo, C.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhuang, R.; Guo, S. Paxlovid Reduces the 28-Day Mortality of Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, L.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Fung, I.C.-H.; Holme, P.; Cowling, B.J.; Galvani, A.P.; Krug, R.M.; Meyers, L.A. Public Health Impact of Paxlovid as Treatment for COVID-19, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and Chloroquine Effectively Inhibit the Recently Emerged Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, R.L.; Vaca, C.E.; Paredes, R.; Mera, J.; Webb, B.J.; Perez, G.; Oguchi, G.; Ryan, P.; Nielsen, B.U.; Brown, M.; et al. Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe COVID-19 in Outpatients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Laar, S.A.; de Boer, M.G.J.; Gombert-Handoko, K.B.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Zwaveling, J. LUMC-Covid-19 research group Liver and Kidney Function in Patients with COVID-19 Treated with Remdesivir. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4450–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.-X.; et al. Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, B.; Shah, K.C.; Chorawala, M.R.; Shah, N.; Patel, P.; Patel, S.; Shah, P. Molnupiravir: An Antiviral Drug against COVID-19. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Choi, A.Y.; Kopp, J.B.; Winkler, C.A.; Cho, S.K. Review of COVID-19 Therapeutics by Mechanism: From Discovery to Approval. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2024, 39, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayk Bernal, A.; Gomes da Silva, M.M.; Musungaie, D.B.; Kovalchuk, E.; Gonzalez, A.; Delos Reyes, V.; Martín-Quirós, A.; Caraco, Y.; Williams-Diaz, A.; Brown, M.L.; et al. Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, H.A.; Abdul Rab, S.; Butt, M.; Jafar, U.; Shahid, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Lee, K.Y.; Sahra, S.; Sah, R. Molnupiravir for the Treatment of COVID-19 Outpatients: An Updated Meta-Analysis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2024, 57, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Yu, B.; Song, Z.; Han, N.; Luo, H.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Oral Azvudine for Elderly Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter, Retrospective, Real-World Study. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2404450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Liu, X.-F.; Zhou, X.-Z.; Zhong, J.-N.; Zhou, L.-C.; Li, R.; Liu, X.-F. Azvudine Efficacy in Reducing Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, Q.; Tao, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, C. Pharmacotherapies for Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Current Literature Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 806249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Ishtiaq, R.; Inayat, F.; Aziz, M.; Bleibel, W. Gastrointestinal and Liver Manifestations in COVID-19 Population. Middle East. J. Dig. Dis. 2021, 13, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, B.; Mao, J. The Pathogenesis and Treatment of the `Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Yang, L.; Lin, Y.; Deng, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Yi, W.; Xie, Y.; Li, M. Efficacy and Safety of Glycyrrhizic Acid in Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.-X.; Zheng, R.-D.; Fan, J.-G. Etiology and Management of Liver Injury in Patients with COVID-19. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 4753–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Du, Q.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.-G.; He, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, K.; Ouyang, S. Liver Injury in COVID-19: Clinical Features and Treatment Management. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanshad, R.; Roshanshad, A.; Fereidooni, R.; Hosseini-Bensenjan, M. COVID-19 and Liver Injury: Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, Outcome and Management in Special Populations. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Hossain, K. Liver Injury in Severe COVID-19 Infection: Current Insights and Challenges. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 14, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, Z.; Wu, C.; Yu, X.; Li, J. Management of COVID-19 Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases and Liver Transplants. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 100653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mechanism | Description of the Specific Mechanism | Target Cells | Core Molecules | Evidence | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct viral infection | The virus infects hepatocytes or cholangiocytes via the ACE2 receptor (cholangiocytes have higher ACE2 expression) | Cholangiocytes, hepatocytes | ACE2 receptor, spike protein, TMPRSS2 | Autopsy revealed the presence of viral RNA and proteins in the liver | [18,70,71,72,73,74] |
| Immune follow-up response (cytokine storm) | Excessive immune response releases pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α, which triggers hepatocellular inflammation and necrosis | Macrophages, T cells | IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ | Patients have markedly elevated cytokine levels | [12,75,76,77,78] |
| Hypoxia/ischemic injury | Systemic hypoxemia and hepatic microcirculatory disorders due to COVID-19 cause hepatocyte-ischemic-hypoxic injury | Hepatocytes, hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells | ROS | Hepatic pathology shows hypoxia/hypoperfusion lesions | [79,80,81] |
| Oxidative stress and NETosis | SARS-CoV-2 forms a vicious cycle of oxidative damage and NETs release through ROS burst and neutrophil activation | Hepatocytes, neutrophils | ROS, NETs | Mitochondrial dysfunction is found to coexist with microthrombosis/NETs in liver tissue | [82,83,84,85] |
| thrombosis | The virus induces systemic hypercoagulability and hepatic microvascular thrombosis | Hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells, platelets | D-dimer, coagulation factor V, fibrinogen | Autopsy reports microthrombosis of the hepatic sinusoids | [81,86,87,88,89,90,91] |
| Gut–liver axis disorders | Dysbiosis of the intestinal flora leads to endotoxin (LPS) entering the liver, activating Kupffer cells and triggering inflammation | Kupffer cells, intestinal barrier cells | LPS, TLR4/NF-κB pathway | Increased intestinal permeability in patients is associated with liver damage | [92,93,94] |
| Drug-induced liver injury | Hepatotoxicity of antiviral drugs (e.g., remdesivir), immunomodulators | Hepatocytes | CYP3A4 | The incidence of elevated liver enzymes after treatment was 25.4% (57.8% in the lopinavir/ritonavir group) | [95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103] |
| First Author | Drug(s) Involved | Patient Profile and Liver Injury Manifestations | RUCAM Score and Causality Assessment | Key Conclusions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muhović, D. et al. | Tocilizumab | 52-year-old male with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Developed acute hepatocellular injury 1 day after Tocilizumab administration: ALT 1541 IU/L, AST 1076 IU/L (~40× ULN), no bilirubin elevation. | Score: 8 Causality: Probable | First reported case of RUCAM-verified DILI caused by Tocilizumab in a COVID-19 patient. Other causes (viral, ischemic, etc.) were excluded. Liver enzymes normalized 10 days after drug withdrawal. | [101] |
| Chen, F. et al. | Multiple drugs | Retrospective analysis of 830 COVID-19 patients found 27.3% (227/830) had abnormal liver biochemistry. | 32.6% of patients with abnormal liver tests had a RUCAM score > 3 | Suggests a definitive contribution of drug factors to COVID-19-associated liver injury. RUCAM helps avoid misdiagnosis of non-drug-related liver injury. | [141] |
| Delgado, A. et al. | Multiple drugs | DILI was detected in 160 hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Most cases were hepatocellular (57.5%) and mild (87.5%), often with polypharmacy (average 14.7 drugs per patient). | 51.2%: Probable (Score ≥ 6) 48.8%: Possible (Score 3–5) | Remdesivir had the highest incidence rate of DILI (992.7 per 10,000 DDD). Combining RUCAM with LTT testing may improve diagnostic accuracy for DILI involving immune mechanisms. | [138] |
| Jothimani, D. et al. | Dabigatran | 51-year-old male developed severe jaundice (Total Bilirubin 39.1 mg/dL) and pruritus 3 weeks after starting Dabigatran post-COVID-19 discharge. Liver biopsy suggested cholestatic DILI. | Score: 7 Causality: Probable | Other causes (viral, autoimmune, biliary obstruction) were excluded. Suggests Dabigatran may cause cholestatic DILI, potentially via an idiosyncratic reaction. | [142] |
| Kumar, P. et al. | Favipiravir | 3 COVID-19 patients developed liver injury post-treatment (1 hepatocellular, 2 cholestatic), with significant elevations in ALT/AST/ALP. | Score: 7 Causality: Probable | First case series report of Favipiravir-induced DILI. Liver function recovered after drug cessation, indicating its hepatotoxicity may be reversible. | [100] |
| Yamazaki, S. et al. | Favipiravir | A 73-year-old male with severe COVID-19 developed cholestatic liver injury (elevated ALP, γ-GTP, TBIL) after Favipiravir treatment. | Score: 6 Causality: Probable | First reported case of Favipiravir-induced cholestatic liver injury. Underlying liver disease and high dosage were suggested as potential risk factors. | [143] |
| Study Author | Study Type | Sample Size | Incidence of Liver Injury (Parameter Type) | Key Definition of Liver Injury (Core Differences) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hundt et al. | Single-center Retrospective Cohort Study | n = 1827 | At admission: AST elevation: 66.9% ALT elevation: 41.6% ALP elevation: 13.5% TBIL elevation: 4.3% | Based on hospital laboratory reference ranges: AST > 33 U/L, ALT > 34 U/L, ALP > 122 U/L, TBIL > 20.5 μmol/L | [155] |
| McConnell et al. | Multicenter Retrospective Study + Experimental Validation | n = 3780 | ALT ≥ 3 × ULN: 12.7% (481/3780) | ALT ≥ 3 × ULN (Based on local laboratory standards) | [86] |
| Phipps et al. | Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study | n = 2273 | ALT Grading: Mild (>ULN but <2×): 45% Moderate (2–5×): 21% Severe (>5×): 6.4% (95% CI: Not provided) | Grading based on ALT multiples (ULN = 50 U/L) | [44] |
| Chen et al. | Single-center Retrospective Study | n = 99 | ALT or AST elevation: 43.4% (43/99) (95% CI: Not provided) | ALT or AST > Upper Limit of Normal (ALT > 50 U/L, AST > 40 U/L) | [156] |
| Lei et al. | Multicenter Retrospective Study | n = 5771 | ALT elevation: Common in severe cases, median 26.0 U/L (IQR 17.0–45.0) AST elevation: Median in severe cases 31.0 U/L (IQR 21.0–46.0) ALP: Mostly within normal range TBIL: Mild elevation, median 10.6 μmol/L (IQR 7.9–15.0) | Acute liver injury defined as: ALT > 3 × ULN Liver enzyme elevation defined as: >ULN | [157] |
| Mao et al. | Systematic Review (SR) | 35 studies, n = 6686 | Pooled prevalence of liver dysfunction: 19% (95% CI: 9–32; range 1–53; I2 = 96%). Compared with non-severe patients, severe COVID-19 patients had a higher incidence of liver dysfunction, including ALT elevation (OR: 1.89, 95% CI: 1.30–2.76; p = 0.0009; I2 = 10%) and AST elevation (OR: 3.08, 95% CI: 2.14–4.42; p < 0.00001; I2 = 0%). | Based on the indicator abnormality criteria set by the respective included studies. | [158] |
| Wijarnpreecha et al. | Systematic Review (SR) | 64 studies, n = 11,245 | Approximately 25% of COVID-19 patients had elevated liver enzymes. The prevalence of specific parameter elevations were AST 23.2%, ALT 21.2%, Total Bilirubin 9.7%, GGT 15.0%, ALP 4.0%. The prevalence of AST elevation was higher in severe cases (45.5%) compared to non-severe cases (15.0%). Up to 37.6% of COVID-19 patients had concurrent CLD. | Based on the indicator abnormality criteria set by the respective included studies. | [159] |
| Wang et al. | Single-center Retrospective Study | n = 105 | 56.2% of patients had abnormal ALT, AST, or TBIl during the disease course (91.4% of abnormal parameters were ≤3 × ULN); the rate of concurrent ALT + AST elevation was higher in the severe group (46.2%) than in the mild group (12.7%), and 34.6% of severe patients developed new ALT abnormalities after admission. | Defined as exceeding the normal range for ALT (M: 9.0–50.0 U/L; F: 7.0–40.0 U/L), AST (M: 15.0–40.0 U/L; F: 13.0–35.0 U/L), TBil (0–18.8 μmol/L), graded by 1 × ULN, 2 × ULN, 3 × ULN. | [160] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, D.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, H.; Wei, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, M. COVID-19 Infection, Drugs, and Liver Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207228
Qiu D, Cao W, Zhang Y, Hao H, Wei X, Yao L, Wang S, Gao Z, Xie Y, Li M. COVID-19 Infection, Drugs, and Liver Injury. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207228
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Dianya, Weihua Cao, Yaqin Zhang, Hongxiao Hao, Xin Wei, Linmei Yao, Shuojie Wang, Zixuan Gao, Yao Xie, and Minghui Li. 2025. "COVID-19 Infection, Drugs, and Liver Injury" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207228
APA StyleQiu, D., Cao, W., Zhang, Y., Hao, H., Wei, X., Yao, L., Wang, S., Gao, Z., Xie, Y., & Li, M. (2025). COVID-19 Infection, Drugs, and Liver Injury. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207228







