Lipedema and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders Sharing Pathophysiology: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
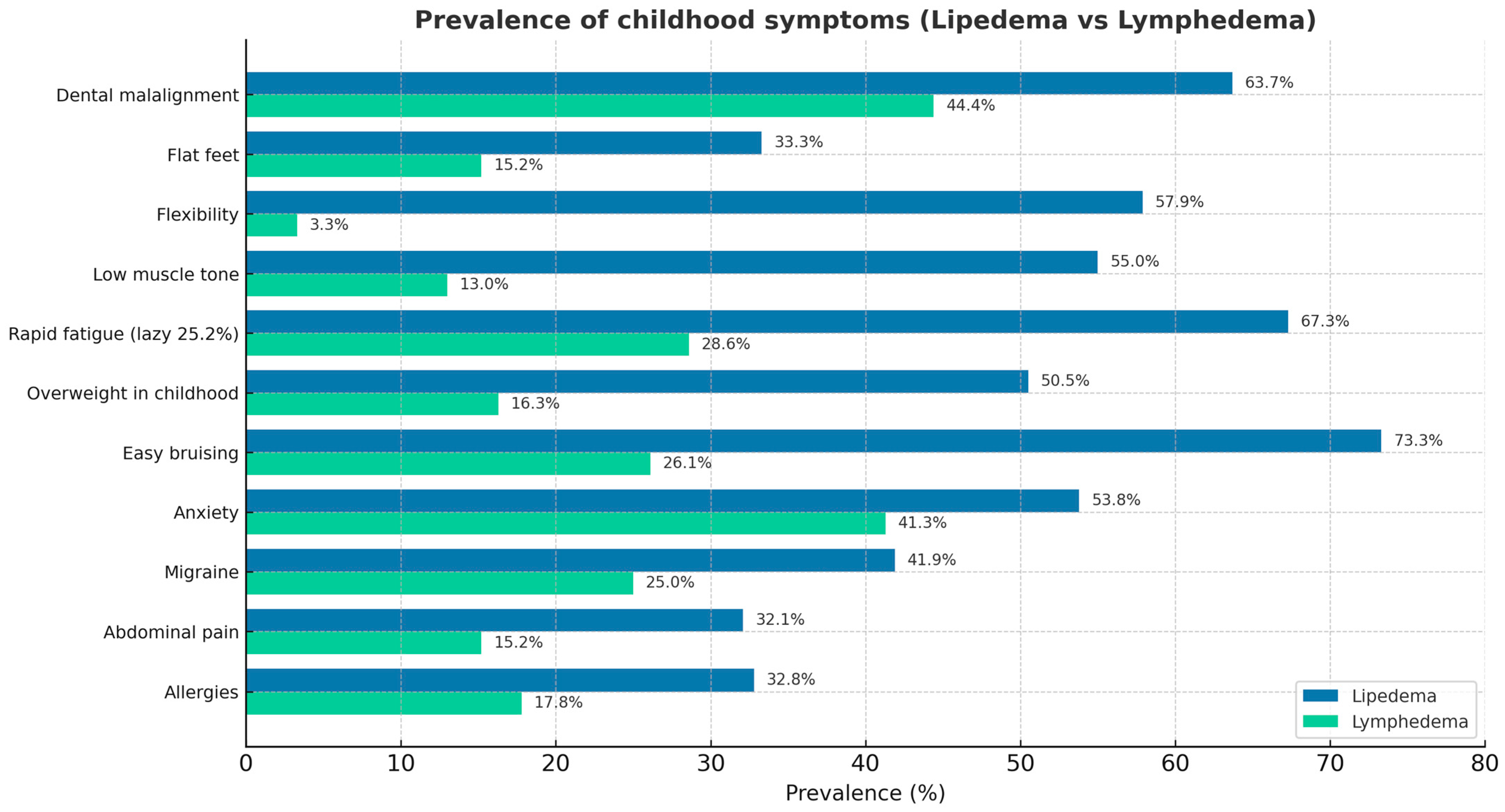
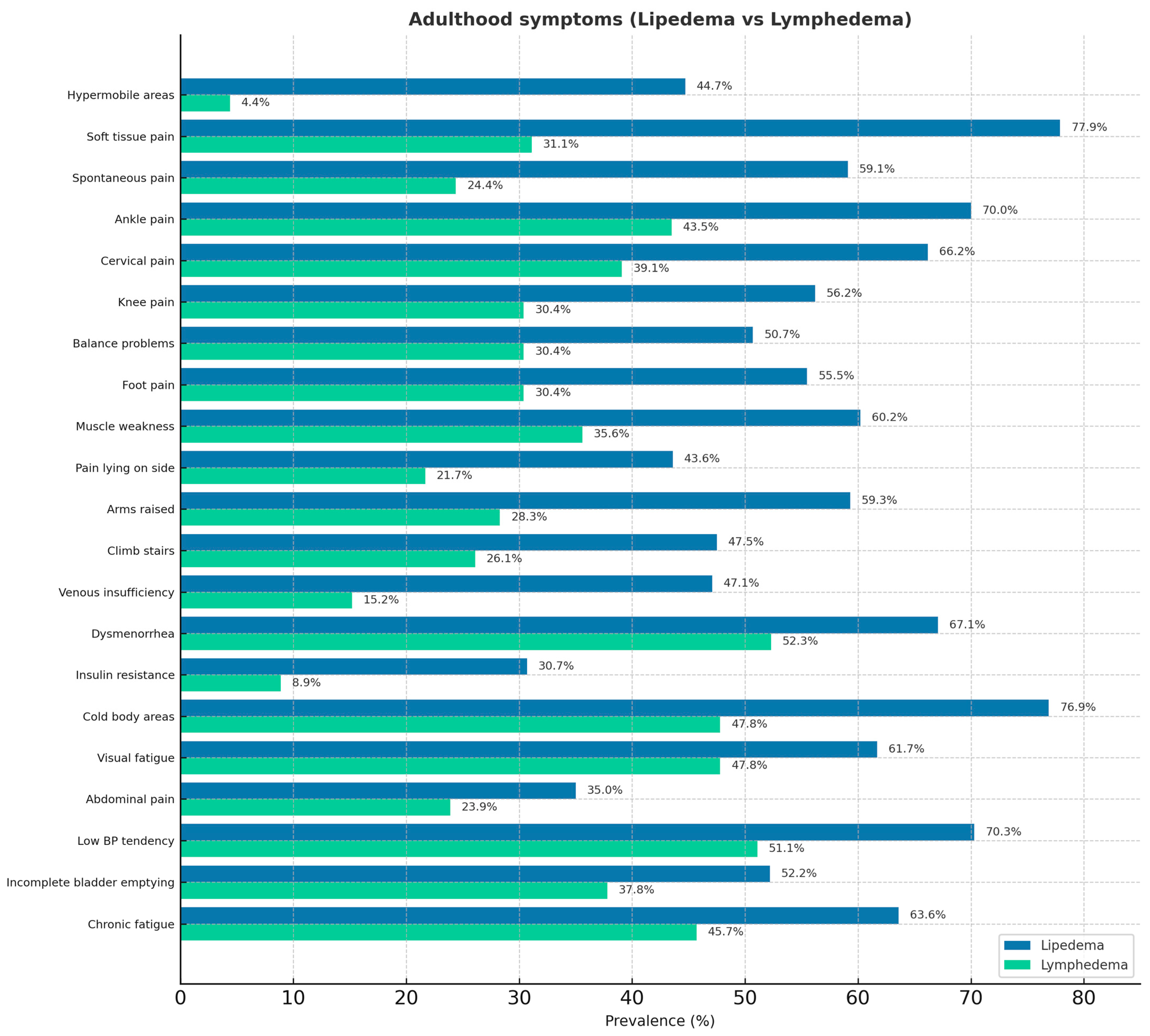
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
7. Final Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michelini, S.; Chiurazzi, P.; Marino, V.; Dell’Orco, D.; Manara, E.; Baglivo, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Maltese, P.E.; Pinelli, M.; Herbst, K.L.; et al. Aldo-Keto Reductase 1C1 (AKR1C1) as the First Mutated Gene in a Family with Nonsyndromic Primary Lipedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Isern, S.U.; Herbst, K.L.; Bunnell, B.A. The Expression of Adipogenic Marker Is Significantly Increased in Estrogen-Treated Lipedema Adipocytes Differentiated from Adipose Stem Cells In Vitro. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzi, R.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Weakley, S.; Garza, M.; Donahue, M.J.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema and Dercum’s Disease: A New Application of Bioimpedance. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2019, 17, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruppa, P.; Gohlke, S.; Łapiński, K.; Garcia-Carrizo, F.; Soultoukis, G.A.; Infanger, M.; Schulz, T.J.; Ghods, M. Lipedema stage affects adipocyte hypertrophy, subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammation and interstitial fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1223264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelini, S.; Greco, S.; Vaia, N.; Puleo, V.; Pellegrino, P.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Michelini, S.; Herbst, K.L.; Goteri, G.; Luca, T.; et al. Endothelial cell alterations in capillaries of adipose tissue from patients affected by lipedema. Obesity 2025, 33, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Schwartz, M.; Herbst, K.L. Interstitial Fluid in Lipedema and Control Skin. Women’s Health Rep. 2020, 1, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Executive Committee of the International Society of Lymphology. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Lymphedema: 2023 Consensum document of the International Society of Lymphology. Lymphology 2023, 56, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rockson, S.G. Advances in Lymphedema. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 2003–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, K.S.; Kamps-Schmitt, K.A.; Borge, R. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Malfait, F.; Francomano, C.; Byers, P.; Belmont, J.; Berglund, B.; Black, J.; Bloom, L.; Bowen, J.M.; Brady, A.F.; Burrows, N.P.; et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers–Danlos syndromes. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daylor, V.; Griggs, M.; Weintraub, A.; Byrd, R.; Petrucci, T.; Huff, M.; Byerly, K.; Fenner, R.; Severance, S.; Griggs, C.; et al. Defining the Chronic Complexities of hEDS and HSD: A Global Survey of Diagnostic Challenges, Life-Long Comorbidities, and Unmet Needs. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, C.M.E.; Clayton, E.W.; Garcia Sierra, A.; Francomano, C. Patients with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome on the diagnostic odyssey: Rethinking complexity and difficulty as a hero’s journey. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2021, 187, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkle, B.T.; Levy, H.P. Symptomatic Joint Hypermobility: The Hypermobile Type of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and the Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensemer, C.; Burks, R.; Kautz, S.; Judge, D.P.; Lavallee, M.; Norris, R.A. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: Complex phenotypes, challenging diagnoses, and poorly understood causes. Dev. Dyn. 2021, 250, 318–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, Y.S.; Wadeea, R.; Rosas, V.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: Friend and foe. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 33, 20170076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L.; Kahn, L.A.; Iker, E.; Ehrlich, C.; Wright, T.; McHutchison, L.; Schwartz, J.; Sleigh, M.; Donahue, P.M.; Lisson, K.H.; et al. Standard of care for lipedema in the United States. Phlebology 2021, 36, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltran, K.; Herbst, K.L. Differentiating lipedema and Dercum’s disease. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aday, A.W.; Donahue, P.M.; Garza, M.; Crain, V.N.; Patel, N.J.; Beasley, J.A.; Herbst, K.L.; Beckman, J.A.; Taylor, S.L.; Pridmore, M.; et al. National survey of patient symptoms and therapies among 707 women with a lipedema phenotype in the United States. Vasc. Med. 2024, 29, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, T.; Babula, M.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, C.; Danesh, N.; Herbst, K. Lipedema Reduction Surgery Improves Pain, Mobility, Physical Function, and Quality of Life: Case Series Report. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cione, E.; Michelini, S.; Abrego-Guandique, D.M.; Vaia, N.; Michelini, S.; Puleo, V.; Bertelli, M.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cannataro, R. Identification of Specific microRNAs in Adipose Tissue Affected by Lipedema. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 11957–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Gil, H.J.; Escobedo, N.; Benito-Martín, A.; Ximénez-Embún, P.; Muñoz, J.; Peinado, H.; Rockson, S.G.; Oliver, G. Platelet factor 4 is a biomarker for lymphatic-promoted disorders. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e135109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, F.; Benz, T.; Lehmann, S.; Sandor, P.; Wagner, S. Common and Contrasting Characteristics of the Chronic Soft-Tissue Pain Conditions Fibromyalgia and Lipedema. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolkan Günaydın, E.; Ünlü, Z.; Ay, S.; Karapınar, T.O. Lipedema awareness in fibromyalgia. Phlebology 2025, 40, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliyan Turk, A.; Erden, E.; Eker Buyuksireci, D.; Umaroglu, M.; Borman, P. Prevalence of Fibromyalgia Syndrome in Women with Lipedema and Its Effect on Anxiety, Depression, and Quality of Life. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2024, 22, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, L.; Ricolfi, L.; Bortolon, M.; Gabriele, G.; Zolesio, P.; Cione, E.; Cannataro, R. Observational Study on a Large Italian Population with Lipedema: Biochemical and Hormonal Profile, Anatomical and Clinical Evaluation, Self-Reported History. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felmerer, G.; Stylianaki, A.; Hägerling, R.; Wang, A.; Ströbel, P.; Hollmén, M.; Lindenblatt, N.; Gousopoulos, E. Adipose Tissue Hypertrophy, An Aberrant Biochemical Profile and Distinct Gene Expression in Lipedema. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 253, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, G.; Zingaretti, N.; Busato, A.; Quintero Sierra, L.; Amuso, D.; Scarano, A.; Iorio, E.L.; Amore, R.; Ossanna, R.; Negri, A.; et al. Gluteal femoral subcutaneous and dermal adipose tissue in female. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 2726–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbarbati, A.; Accorsi, D.; Benati, D.; Marchetti, L.; Orsini, G.; Rigotti, G.; Panettiere, P. Subcutaneous adipose tissue classification. Eur. J. Histochem. 2010, 54, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, N.; Ritelli, M.; Zoppi, N.; Colombi, M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in the Pathogenesis of Classical, Vascular, and Hypermobile Ehlers—Danlos Syndromes. Genes 2019, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, S.; Zoccante, L.; Smania, N.; Sbarbati, A. Stretch marks: A visible expression of connective’s involvement in autism spectrum disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1155854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiengo, E.; Sbarbati, A. Lipedema and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders Sharing Pathophysiology: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207195
Fiengo E, Sbarbati A. Lipedema and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders Sharing Pathophysiology: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207195
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiengo, Elettra, and Andrea Sbarbati. 2025. "Lipedema and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders Sharing Pathophysiology: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207195
APA StyleFiengo, E., & Sbarbati, A. (2025). Lipedema and Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders Sharing Pathophysiology: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207195






