Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Saccadic Eye Movement Time Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participant Enrolment
2.3. Saccadic Duration Test
2.4. Test and Re-Test Methodology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Influence of Age and Sex
3.3. Estimates of Repeatability and Reproducibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buscemi, A.; Mondelli, F.; Biagini, I.; Gueli, S.; D’Agostino, A.; Coco, M. Role of Sport Vision in Performance: Systematic Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Fernandes, P. Static and dynamic visual acuity and refractive errors in elite football players. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tena, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Alonso, X.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Sanchez-Ramos, C.; Alvarez-Peregrina, C. A Descriptive Analysis of Visual and Oculomotor Skills in Federated University Athletes. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetta, K.M.; Brandes, L.E.; Maki, K.; Dziemianowicz, M.S.; Laudano, E.; Allen, M.; Lawler, K.; Sennett, B.; Wiebe, D.; Devick, S.; et al. The King-Devick test and sports-related concussion: Study of a rapid visual screening tool in a collegiate cohort. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 309, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, R.K.; Ortega, J.; Chrisman, S.P.; Kontos, A.P.; Buckley, T.A.; Kaminski, T.W.; Meyer, B.B.P.; Clugston, J.R.; Goldman, J.T.; McAllister, T.; et al. King-Devick Sensitivity and Specificity to Concussion in Collegiate Athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2023, 58, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, A. Spotlight on the Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test. Clin. Optom. 2021, 13, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchin, A.; Maffioletti, S. The Reliability of the DEM Test in the Clinical Environment. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchin, A.; Maffioletti, S.; Daini, R. Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test in Adults: Age-Related Changes and Italian Normative Data. Vision 2025, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadehpur, E.; Aazami, N.; Bolouri, B. Comparison of saccadic eye movements and facility of ocular accommodation in female volleyball players and non-players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2007, 17, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, A.; Lobietti, R.; Squatrito, S. A study of saccadic eye movement dynamics in volleyball: Comparison between athletes and non-athletes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2010, 50, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kishita, Y.; Ueda, H.; Kashino, M. Eye and Head Movements of Elite Baseball Players in Real Batting. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatara, S.; Toda, H.; Maeda, F.; Ito, A.; Handa, T. Comparison of the Saccadic Eye Movement Ability of Female Professional Basketball Players and Non-Athletes. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y. Decreased Saccadic Eye Movement Speed Correlates with Dynamic Balance in Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, G.B. Sports Vision: Vision Care for the Enhancement of Sports Performance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laby, D.M.; Appelbaum, L.G. Review: Vision and On-field Performance: A Critical Review of Visual Assessment and Training Studies with Athletes. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2021, 98, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, C.; Astefanoaei, C.; Pretegiani, E.; Optican, L.; Creanga, D.; Rufa, A.; Cristescu, C. Nonlinear analysis of saccade speed fluctuations during combined action and perception tasks. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 232, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlansky, G.; Hopkins, K.B.; Mitchell, G.L.; Huang, K.; Frazier, M.; Heyman, C.; Scheiman, M. Reliability of the developmental eye movement test. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, M.; Nestor, E.; Parot, C.D.P. A reevaluation of the Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) test’s repeatability. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2004, 81, 934–938. [Google Scholar]
- Tassinari, J.T.; DeLand, P. Developmental Eye Movement Test: Reliability and symptomatology. Optometry 2005, 76, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, Y.; Lederman, R.; Avni, I.; Atzmon, D.; Azoulay, E.; Segal, O. Correlation between reading skills and different measurements of convergence amplitude. Curr. Eye Res. 2002, 25, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Segal, O.; Barkana, Y.; Lederman, R.; Zadok, D.; Pras, E.; Morad, Y. Correlation between asthenopic symptoms and different measurements of convergence and reading comprehension and saccadic fixation eye movements. Optometry 2010, 81, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orduna-Hospital, E.; Hernández-Aranda, D.; Sanchez-Cano, A. Ocular Motility Patterns in Intellectual Disability: Insights from the Developmental Eye Movement Test. Life 2023, 13, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaldi, A.; Sabatini, S.P. The saccade main sequence revised: A fast and repeatable tool for oculomotor analysis. Behav. Res. Methods 2021, 53, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.N.; Calix, R.; Hudson, T.; Rizzo, J.R.; Selesnick, I.; Frucht, S.; Galetta, S.L.; Balcer, L.J.; Rucker, J.C. Accuracy of clinical versus oculographic detection of pathological saccadic slowing. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 442, 120436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Devereux, M.; Gourraud, P.-A.; Jonzzon, S.; Suleiman, L.; Waubant, E.; Green, A.; Graves, J.S. Subclinical Saccadic Eye Movement Dysfunction in Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 34, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Fu, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Relationship between speed perception and eye movement—A case study of crash-involved and crash-not-involved drivers in China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.; Gabriel, R.; Mohiuddin, O.; Whitaker, D.; Wisely, C.E.; Kim, T. Automated Eye Tracking Enables Saccade Performance Evaluation of Patients with Concussion History. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2023, 100, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzoli, D.; Antoniades, C.A.; Kennard, C.; Nyffeler, T.; Bassetti, C.L.; Müri, R.M. Eye movements discriminate fatigue due to chronotypical factors and time spent on task—A double dissociation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobener, E.; Searer, A.; Doettl, S.; Plyler, P. Oculomotor Findings in Videonystagmography across the Lifespan. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2024, 34, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbutt, S.; Harwood, M.R.; Harris, C.M. Infant saccades are not slow. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protasevica, D.; Kassaliete, E.; Klavinska, A.; Alecka, M.; Berzina, A.; Goliskina, V.; Koleda, M.; Mikelsone, R.; Ozola, E.; Ruza, T.; et al. The Computerized Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test: Normative Data for School-Aged Children. Vision 2024, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlinden, C.; Khadka, J.; Pesudovs, K. Precision (repeatability and reproducibility) studies and sample-size calculation. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2015, 41, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRANMO. Sample Size and Power Calculator V 7.12; Inst. Munic. d’Investigació Médica: Barcelona, Spain, 2024; Available online: https://www.datarus.eu/aplicaciones/granmo/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- François, P.B.M. Les techniques d’exploration clinique de la macula. In Physiol. de la macula. Techniques Cliniques d’exploration; Masson: Paris, France, 1997; pp. 27–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ríder-Vázquez, A.; Vega-Holm, M.; Sánchez-González, M.C.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, E. Minimum perceptual time (MPT). Repeatability and reproducibility of variables applied to “sports vision”. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2025, 263, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, H.; Alvarez-Peregrina, C.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Sánchez-Tena, M.Á. Vision in futsal players: Coordination and reaction time. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antona, B.; Barrio, A.; Barra, F.; Gonzalez, E.; Sanchez, I. Repeatability and agreement in the measurement of horizontal fusional vergences. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2008, 28, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstice, N.S.; Davidson, B.; Field, B.; Mathan, J.; Collins, A.V.; Black, J.M. The repeatability and reproducibility of four techniques for measuring horizontal heterophoria: Implications for clinical practice. J. Optom. 2021, 14, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, S.J.; Doyle, L.; Saunders, K.J. Intra- and inter-examiner repeatability of cycloplegic retinoscopy among young children. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2017, 37, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riska, K.M.; Hall, C.D. Reliability and Normative Data for the Dynamic Visual Acuity Test for Vestibular Screening. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, A.; Antona, B.; Puell, M.C. Repeatability of mesopic visual acuity measurements using high- and low-contrast ETDRS letter charts. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, A.C.; Lindsay, P.; Smith, B.G.; Storok, K. Saccadic eye movements as indicators of cognitive function in older adults. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2015, 22, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orduna-Hospital, E.; Navarro-Marqués, A.; López-de-la-Fuente, C.; Sanchez-Cano, A. Eye-Tracker Study of the Developmental Eye Movement Test in Young People without Binocular Dysfunctions. Life 2023, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-la-Fuente, C.; Saz-Onrubia, E.; Orduna-Hospital, E.; Sánchez-Cano, A. Comparison of two visual-verbal tests of ocular motility using an eye-tracker. J. Optom. 2024, 17, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antona, B.; Sanchez, I.; Barrio, A.; Barra, F.; Gonzalez, E. Intra-examiner repeatability and agreement in accommodative response measurements. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2009, 29, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Sparschu, L.; Wang, J. Repeatability of an automated ETDRS contrast threshold measurement. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2021, 41, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Masoudi, S.; Vijay, A.K.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Dumpati, S.; Raj, A.; Willcox, M. Repeatability of lipid layer thickness using LipiView® following removal of contact lenses and its relationship to comfort. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2025, 45, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
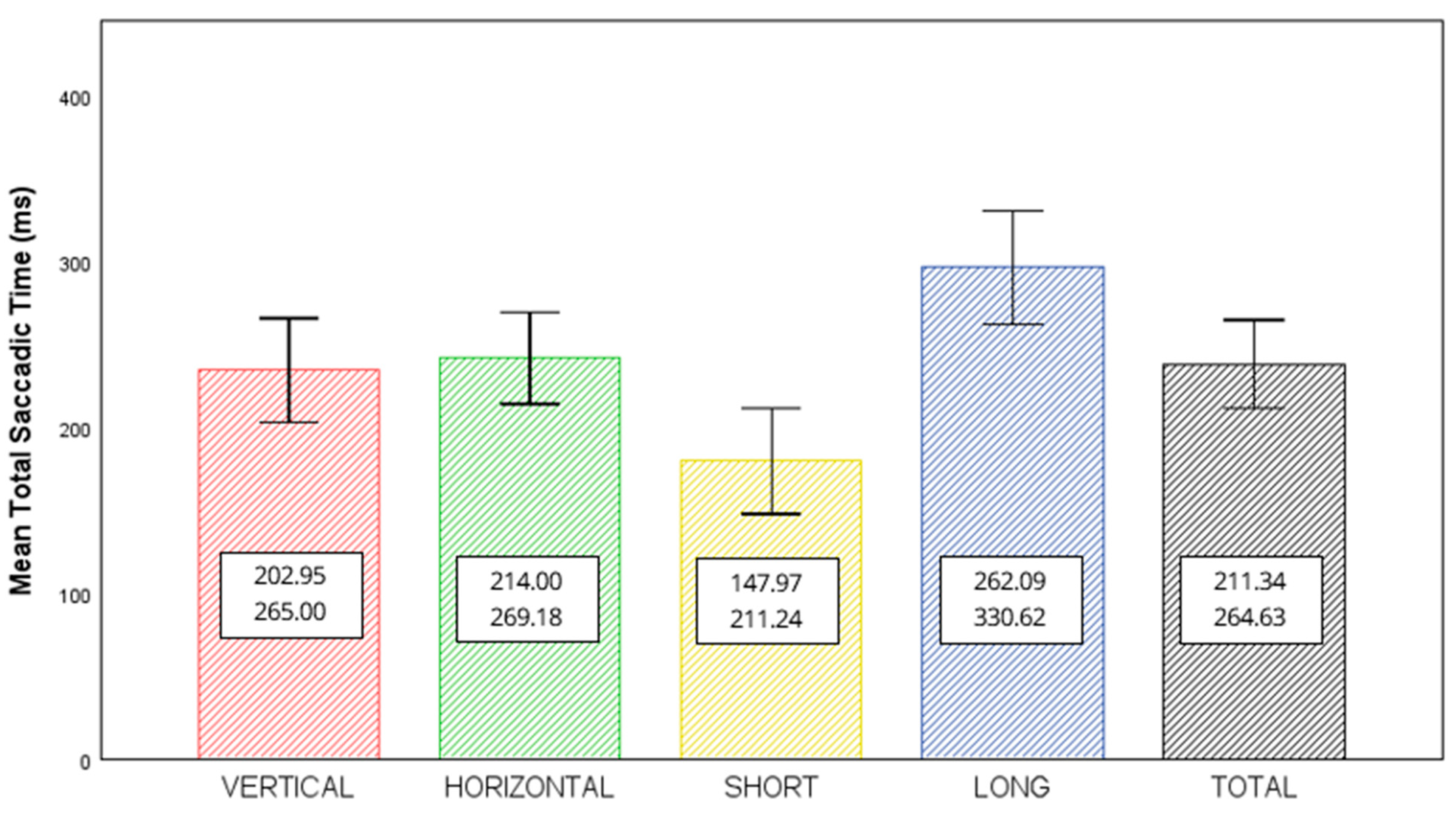

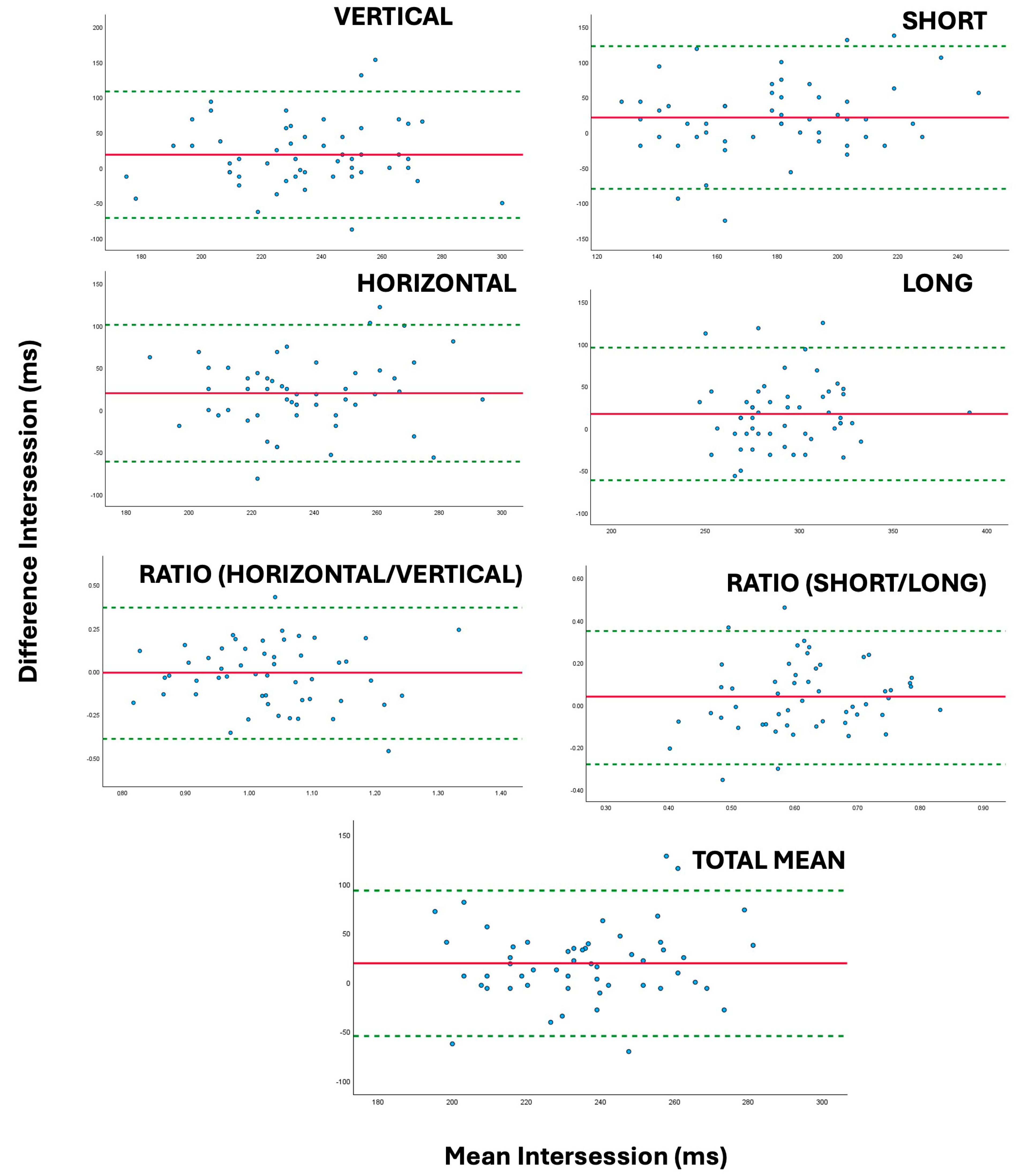
| TEST | Interexaminer Repeatability (Δ) (95% Confidence Limits) | Intersession Repeatability (Δ) (95% Confidence Limits) | ANOVA Interexaminer (p-Valor) | ANOVA Intersession (p-Valor) | Interexaminer Repeatability (ICC) (95% Confidence Limits) | Intersession Repeatability (ICC) (95% Confidence Limits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UP 20° | 1.28 (−112.6 to 115.2) | 7.55 (−93.1 to 108.1) | 0.846 | 0.289 | 0.591 (0.357 to 0.740) | 0.524 (0.179 to 0.725) |
| UP 10° | 2.88 (−136.2 to 141.9) | 19.34 (−92.2 to 130.8) | 0.720 | 0.017 | 0.203 (−0.256 to 0.494) | 0.476 (0.116 to 0.693) |
| LEFT 30° | 4.17 (−105.7 to 114.1) | 12.26 (−91.4 to 115.9) | 0.514 | 0.097 | 0.445 (0.128 to 0.646) | 0.377 (−0.060 to 0.636) |
| LEFT 15° | −7.05 (−149.4 to 135.3) | 20.75 (−141.1 to 182.6) | 0.394 | 0.073 | 0.500 (0.216 to 0.681) | 0.101 (−0.512 to 0.472) |
| RIGHT 15° | 10.58 (−137.3 to 158.4) | 14.62 (−127.4 to 156.6) | 0.219 | 0.148 | 0.240 (−0.187 to 0.514) | 0.144 (−0.460 to 0.502) |
| RIGHT 30° | 13.14 (−108.2 to 134.5) | 32.08 (−90.5 to 154.6) | 0.065 | <0.001 | 0.539 (0.283 to 0.704) | 0.184 (−0.269 to 0.496) |
| DOWN 10° | −3.53 (−145.0 to 137.9) | 30.66 (−159.0 to 220.3) | 0.667 | 0.025 | 0.592 (0.358 to 0.740) | 0.131 (−0.432 to 0.484) |
| DOWN 20° | 7.69 (−105.1 to 120.5) | 16.98 (−124.3 to 158.2) | 0.241 | 0.092 | 0.659 (0.467 to 0.782) | 0.229 (−0.306 to 0.549) |
| TEST | Interexaminer Repeatability (Δ) (95% Confidence Limits) | Intersession Repeatability (Δ) (95% Confidence Limits) | ANOVA Interexaminer (p-Valor) | ANOVA Intersession (p-valor) | Interexaminer Repeatability (ICC) (95% Confidence Limits) | Intersession Repeatability (ICC) (95% Confidence Limits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VERT | 2.08 (−79.8 to 83.9) | 18.63 (−71.1 to 108.4) | 0.661 | 0.005 | 0.561 (0.310 to 0.721) | 0.205 (−0.281 to 0.520) |
| HORIZ | 5.21 (−75.8 to 86.2) | 19.93 (−61.5 to 100.9) | 0.269 | <0.001 | 0.439 (0.121 to 0.641) | 0.183 (−0.281 to 0.498) |
| RATIOhv | 0.02 (−0.45 to 0.48) | −0.01 (−0.39 to 0.37) | 0.548 | 0.803 | 0.065 (−0.472 to 0.406) | 0.201 (−0.398 to 0.542) |
| SHORT | 0.72 (−87.0 to 88.5) | 21.34 (−79.83 to 122.52) | 0.887 | 0.004 | 0.502 (0.217 to 0.683) | 0.196 (−0.290 to 0.514) |
| LONG | 6.57 (−57.5 to 70.7) | 17.22 (−61.3 to 95.7) | 0.080 | 0.003 | 0.767 (0.636 to 0.852) | 0.410 (0.019 to 0.651) |
| RATIOSL | −0.02 (−0.28 to 0.35) | 0.04 (−0.28 to 0.35) | 0.25 | 0.106 | 0.598 (0.371 to 0.743) | 0.343 (−0.118 to 0.617) |
| TOTAL MEAN | 3.65 (−61.8 to 69.1) | 19.28 (−54.6 to 93.1) | 0.34 | <0.001 | 0.607 (0.384 to 0.749) | 0.211 (−0.235 to 0.515) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ríder-Vázquez, A.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, E.; Velasco-Olea, D.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Sánchez-González, M.C. Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Saccadic Eye Movement Time Test. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207170
Ríder-Vázquez A, Gutiérrez-Sánchez E, Velasco-Olea D, Martinez-Perez C, Sánchez-González MC. Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Saccadic Eye Movement Time Test. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(20):7170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207170
Chicago/Turabian StyleRíder-Vázquez, Antonio, Estanislao Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Daniel Velasco-Olea, Clara Martinez-Perez, and María Carmen Sánchez-González. 2025. "Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Saccadic Eye Movement Time Test" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 20: 7170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207170
APA StyleRíder-Vázquez, A., Gutiérrez-Sánchez, E., Velasco-Olea, D., Martinez-Perez, C., & Sánchez-González, M. C. (2025). Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Saccadic Eye Movement Time Test. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(20), 7170. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14207170






