Blood Biomarkers as a Non-Invasive Method for the Assessment of the State of the Fontan Circulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characterizing the State of the Fontan Circulation—Current Standard
3. Fontan Failure—Definition and Diagnosis
4. Overview of the Term “Biomarker” and Review Methodology
5. Blood Biomarkers in the Fontan Circulation—Review of Available Evidence on Currently Used Biomarkers
5.1. Natriuretic Peptides
5.2. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
5.3. Cystatin C
5.4. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
5.5. Vitamin D
5.6. Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
5.7. von Willebrand Factor (vWF)
6. Review of Available Evidence on the Most Promising New Blood Biomarkers in the Fontan Circulation
6.1. Carbohydrate Antigen 125 (CA125)
6.2. Lipoproteins
6.3. Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF)
7. Review of Available Evidence for Other Blood Biomarkers Studied in the Fontan Circulation
7.1. Troponins
7.2. ST2 Protein
7.3. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15)
7.4. Galectin-3
7.5. Adrenomedullin (ADM)
7.6. Endothelin-1 (ET-1)
7.7. Components of the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS)
7.8. Norepinephrine (NE)
7.9. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α)
7.10. Uric Acid
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumgartner, H.; De Backer, J.; Babu-Narayan, S.V.; Budts, W.; Chessa, M.; Diller, G.-P.; Lung, B.; Kluin, J.; Lang, I.M.; Meijboom, F.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Adult Congenital Heart Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 563–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittczak, A.; Dryżek, P.; Maciejewski, M.; Kula-Mazurek, A.; Moszura, T.; Bikiewicz, A.; Bielecka-Dabrowa, A. Successful Complex Percutaneous Intervention in Patient with Fontan Circulation and Severe Heart Failure: A Case Report. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychik, J.; Atz, A.M.; Celermajer, D.S.; Deal, B.J.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Gewillig, M.H.; Hsia, T.-Y.; Hsu, D.T.; Kovacs, A.H.; McCrindle, B.W.; et al. Evaluation and Management of the Child and Adult with Fontan Circulation: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e234–e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontan, F.; Baudet, E. Surgical Repair of Tricuspid Atresia. Thorax 1971, 26, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Tan, T.; Liu, X.; Liufu, R.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wen, S.; Zhuang, J.; Yuan, H. Complications and Management of Functional Single Ventricle Patients with Fontan Circulation: From Surgeon’s Point of View. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 917059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kverneland, L.S.; Kramer, P.; Ovroutski, S. Five Decades of the Fontan Operation: A Systematic Review of International Reports on Outcomes after Univentricular Palliation. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2018, 13, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plappert, L.; Edwards, S.; Senatore, A.; De Martini, A. The Epidemiology of Persons Living with Fontan in 2020 and Projections for 2030: Development of an Epidemiology Model Providing Multinational Estimates. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, K.R.; Goldberg, D.J. Biomarkers and the Fontan Circulation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inai, K. Biomarkers for Heart Failure and Prognostic Prediction in Patients with Fontan Circulation. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e14983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, R.W.; Valente, A.M.; Davey, B.; Wu, F.; Drucker, N.; Lombardi, K.; Lee, S.; McCollum, S.; Shabanova, V., St.; Clair, N.; et al. How Good Are Cardiologists at Predicting Major Adverse Events in Fontan Patients? JACC Adv. 2024, 3, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.K.S. The Failing Fontan. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 37, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, H. Where Is the “Optimal” Fontan Hemodynamics? Korean Circ. J. 2017, 47, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puyvelde, J.; Rega, F.; Budts, W.; Van De Bruaene, A.; Cools, B.; Gewillig, M.; Eyskens, B.; Heying, R.; Salaets, T.; Meyns, B. Defining the Causes for Fontan Circulatory Failure in Total Cavopulmonary Connection Patients. Interdiscip. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2024, 39, ivae188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What Are Biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesko, L.J.; Atkinson, A.J., Jr. Use of Biomarkers and Surrogate Endpoints in Drug Development and Regulatory Decision Making: Criteria, Validation, Strategies. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, J.P.; Bruneau, B.G.; Ramos, H.R.; Ogawa, T.; de Bold, M.K.; de Bold, A.J. Cardiac Natriuretic Peptides. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, B. BNP and NT-proBNP as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cardiac Dysfunction in Both Clinical and Forensic Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, H.; Takasugi, H.; Ohashi, H.; Yamada, O.; Watanabe, K.; Yagihara, T.; Echigo, S. Abnormalities of Neurohormonal and Cardiac Autonomic Nervous Activities Relate Poorly to Functional Status in Fontan Patients. Circulation 2004, 110, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inai, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Nakazawa, M. Clinical Correlation and Prognostic Predictive Value of Neurohumoral Factors in Patients Late after the Fontan Operation. Am. Heart J. 2005, 150, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, Y.M.; Ettedgui, J.; Beerman, L.; Maisel, A.; Tofovic, S. Comparison of Plasma B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Levels in Single Ventricle Patients with Systemic Ventricle Heart Failure versus Isolated Cavopulmonary Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.A.; Meurling, C.J.; Holmqvist, F.; Waktare, J.E.P.; Thilén, U.J. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Brain Natriuretic Peptides in Adults with a Systemic Morphologically Right Ventricle or Fontan-Type Circulation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 114, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.M.E.; Zink, S.; Singer, H.; Dittrich, S. B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Levels in Patients with Functionally Univentricular Hearts after Total Cavopulmonary Connection. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, B.-L.; Cheung, Y.-F. Plasma Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Systemic Ventricular Function in Asymptomatic Patients Late after the Fontan Procedure. Heart Vessel. 2007, 22, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, E.; Gitter, R.; Mair, R.; Pinter, M.; Schreier-Lechner, E.; Vondrys, D.; Tulzer, G. Aminoterminal Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels in Children and Adolescents after Fontan Operation Correlate with Congestive Heart Failure. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2008, 29, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojnarska, O.; Gwizdała, A.; Katarzyński, S.; Katarzyńska, A.; Oko-Sarnowska, Z.; Bręborowicz, P.; Grajek, S. Evaluation of Exercise Capacity with Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing and BNP Levels in Adult Patients with Single or Systemic Right Ventricles. Arch. Med. Sci. 2010, 6, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atz, A.M.; Zak, V.; Breitbart, R.E.; Colan, S.D.; Pasquali, S.K.; Hsu, D.T.; Lu, M.; Mahony, L.; Paridon, S.M.; Puchalski, M.D.; et al. Factors Associated with Serum Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels after the Fontan Procedure. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2011, 6, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, P.B.; Müller, J.; Weber, R.; Hager, A. Value of N-Terminal pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels in Different Types of Fontan Circulation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 15, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolcz, J.; Tomkiewicz-Pajak, L.; Wojcik, E.; Podolec, P.; Skalski, J. Prognostic Significance and Correlations of Neurohumoral Factors in Early and Late Postoperative Period after Fontan Procedure. Interdiscip. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2011, 13, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchill, L.J.; Redington, A.N.; Silversides, C.K.; Ross, H.J.; Jimenez-Juan, L.; Mital, S.; Oechslin, E.N.; Dragulescu, A.; Slorach, C.; Mertens, L.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Genotype and Serum BNP in a Contemporary Cohort of Adults Late after Fontan Palliation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 197, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, H.; Negishi, J.; Hayama, Y.; Sasaki, O.; Taniguchi, Y.; Noritake, K.; Miyazaki, A.; Yamada, O. Hyperuricemia Reflects Global Fontan Pathophysiology and Associates with Morbidity and Mortality in Patients after the Fontan Operation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Takeuchi, D.; Inai, K.; Shinohara, T.; Nakanishi, T. Prognostic Value of Multiple Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Mortality in Adult Congenital Heart Disease: Comparisons of Single-/Two-Ventricle Physiology, and Systemic Morphologically Right/Left Ventricles. Heart Vessel. 2016, 31, 1834–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Bruaene, A.; Hickey, E.J.; Kovacs, A.H.; Crean, A.M.; Wald, R.M.; Silversides, C.K.; Redington, A.N.; Ross, H.J.; Alba, A.C.; Billia, F.; et al. Phenotype, Management and Predictors of Outcome in a Large Cohort of Adult Congenital Heart Disease Patients with Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 252, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggen, V.J.M.; van den Bosch, A.E.; Eindhoven, J.A.; Schut, A.-R.W.; Cuypers, J.A.A.E.; Witsenburg, M.; de Waart, M.; van Schaik, R.H.N.; Zijlstra, F.; Boersma, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide, Troponin-T, and Growth-Differentiation Factor 15 in Adult Congenital Heart Disease. Circulation 2017, 135, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, D.; van Melle, J.P.; Willems, T.P.; Bartelds, B.; Ploegstra, M.-J.; Hillege, H.; Ebels, T.; Berger, R.M.F. N-Terminal pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Serum Levels Reflect Attrition of the Fontan Circulation. Cardiol. Young 2020, 30, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Li, S.; Dolgner, S.J.; Steinberg, Z.L.; Buber, J. Utility of Biomarkers in Adult Fontan Patients with Decompensated Heart Failure. Cardiol. Young 2020, 30, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Bosch, E.; Bossers, S.S.M.; Kamphuis, V.P.; Boersma, E.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; Breur, J.M.P.J.; Ten Harkel, A.D.J.; Kapusta, L.; Bartelds, B.; Roest, A.A.W.; et al. Associations Between Blood Biomarkers, Cardiac Function, and Adverse Outcome in a Young Fontan Cohort. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e015022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghelani, S.J.; Opotowsky, A.R.; Harrild, D.M.; Powell, A.J.; Azcue, N.; Ahmad, S.; Clair, N.S.; Bradwin, G.; Rathod, R.H. Characterization of Circulating and Urinary Biomarkers in the Fontan Circulation and Their Correlation with Cardiac Imaging. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 162, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.A.; Pomiato, E.; Palmieri, R.; Di Già, G.; Piemonte, F.; Porzio, O.; Gagliardi, M.G. The Effects of Exercise Training on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing and Cardiac Biomarkers in Adult Patients with Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and Fontan Circulation. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindik, N.; Gökdemir, M.; Varan, B.; Ulubay, G.; Ozkan, M.; Tokel, N.K. Comparison of Serum N-Terminal pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Levels, Conventional Echocardiography, Exercise Parameters, and Dyssynchrony Measurements in Fontan Patients. Cardiol. Young 2023, 33, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, W.R.; Jain, C.C.; Borlaug, B.A.; Jaffe, A.S.; Connolly, H.M.; Burchill, L.J.; Egbe, A.C. Exercise Capacity, NT-proBNP, and Exercise Hemodynamics in Adults Post-Fontan. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, J.; Ono, M.; Niedermaier, C.; Hörer, J.; Hoffmann, G.; Holdenrieder, S.; Klawonn, F.; Ewert, P. Quantification of Ventricular Stress in Univentricular Hearts during Early Childhood Using Age-Independent Zlog-NT-proBNP. Int. J. Cardiol. 2024, 406, 131983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerola, A.; Jokinen, E.; Sairanen, H.; Pihkala, J. During Treatment Protocol for Univentricular Heart Serum Levels of Natriuretic Peptides Decrease. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2010, 38, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Ven, J.P.G.; Kamphuis, V.P.; van den Bosch, E.; Gnanam, D.; Terol, C.; Bogers, A.J.J.C.; Breur, J.M.P.J.; Berger, R.M.F.; Blom, N.A.; Ten Harkel, A.D.J.; et al. Cardiac Function and Serum Biomarkers throughout Staged Fontan Palliation: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpal, S.; Alshawabkeh, L.; Opotowsky, A.R. Current Role of Blood and Urine Biomarkers in the Clinical Care of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2017, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW) and Human Pathology. One Size Fits All. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, C.; Cattazzo, F.; Hu, Z.-D.; Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M. The Role of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Cardiovascular Risk Assessment: Useful or Hype? Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, E.; Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, E402–E411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Quintana, E.; Rodríguez-González, F. Iron Deficiency Anemia Detection from Hematology Parameters in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Patients. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2013, 8, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkiewicz-Pajak, L.; Plazak, W.; Kolcz, J.; Pajak, J.; Kopec, G.; Dluzniewska, N.; Olszowska, M.; Moryl-Bujakowska, A.; Podolec, P. Iron Deficiency and Hematological Changes in Adult Patients after Fontan Operation. J. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, T.; Yasuhara, J.; Kumamoto, T.; Shimizu, H.; Yoshiba, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Sumitomo, N. Usefulness of the Red Blood Cell Distribution Width to Predict Heart Failure in Patients with a Fontan Circulation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buendía Fuentes, F.; Jover Pastor, P.; Arnau Vives, M.Á.; Lozano Edo, S.; Rodríguez Serrano, M.; Aguero, J.; Osa Sáez, A.; Conde Amiel, I.; Aguilera Sancho-Tello, V.; Martínez-Dolz, L.; et al. CA125: A New Biomarker in Patients with Fontan Circulation. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 76, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.C.; Potok, O.A.; Rifkin, D.; Estrella, M.M. Advantages, Limitations, and Clinical Considerations in Using Cystatin C to Estimate GFR. Kidney360 2022, 3, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, M.; Kirby, A.; Stewart, R.A.; Blankenberg, S.; Sullivan, D.; White, H.D.; Hunt, D.; Marschner, I.; Janus, E.; Kritharides, L.; et al. Circulating Cystatin C Is an Independent Risk Marker for Cardiovascular Outcomes, Development of Renal Impairment, and Long-Term Mortality in Patients With Stable Coronary Heart Disease: The LIPID Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e020745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, G.; Zhang, S. Association Between Cystatin C and Cardiac Function and Long-Term Prognosis in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e919422-1–e919422-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opotowsky, A.R.; Baraona, F.R.; Mc Causland, F.R.; Loukas, B.; Landzberg, E.; Landzberg, M.J.; Sabbisetti, V.; Waikar, S.S. Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urine Biomarkers in Patients with Single-Ventricle Fontan Circulation. Heart 2017, 103, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opotowsky, A.R.; Carazo, M.; Singh, M.N.; Dimopoulos, K.; Cardona-Estrada, D.A.; Elantably, A.; Waikar, S.S.; Mc Causland, F.R.; Veldtman, G.; Grewal, J.; et al. Creatinine versus Cystatin C to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: Results of the Boston Adult Congenital Heart Disease Biobank. Am. Heart J. 2019, 214, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemello, L.; Padalino, M.; Zanon, C.; Benvegnu’, L.; Biffanti, R.; Mancuso, D.; Cavalletto, L. Role of Transient Elastography to Stage Fontan-Associated Liver Disease (FALD) in Adults with Single Ventricle Congenital Heart Disease Correction. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.; De Staercke, C.; Everitt, I.; Haouzi, A.; Ko, Y.-A.; Jennings, S.; Kim, J.H.; Rodriguez, F.H.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; Quyyumi, A.; et al. Biomarker Profile in Stable Fontan Patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 305, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, D.A.; Gao, Z.; Freytag, J.; Mahendran, A.; Szugye, C.; Woodly, S.; Alvarez, T.C.E.; Lubert, A.M.; Alsaied, T.; Goldstein, S.L.; et al. Associations Between Characteristics of Individuals with Fontan Circulation with Blood and Urine Biomarkers of Kidney Injury and Dysfunction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxmann, A.C.; Ahmed, M.S.; Marques, N.C.; Menon, V.B.; Pereira, A.B.; Kirsztajn, G.M.; Heilberg, I.P. Influence of Muscle Mass and Physical Activity on Serum and Urinary Creatinine and Serum Cystatin C. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banait, T.; Wanjari, A.; Danade, V.; Banait, S.; Jain, J. Role of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (Hs-CRP) in Non-Communicable Diseases: A Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rost, N.S.; Wolf, P.A.; Kase, C.S.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Silbershatz, H.; Massaro, J.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Franzblau, C.; Wilson, P.W. Plasma Concentration of C-Reactive Protein and Risk of Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: The Framingham Study. Stroke 2001, 32, 2575–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opotowsky, A.R.; Valente, A.M.; Alshawabkeh, L.; Cheng, S.; Bradley, A.; Rimm, E.B.; Landzberg, M.J. Prospective Cohort Study of C-Reactive Protein as a Predictor of Clinical Events in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: Results of the Boston Adult Congenital Heart Disease Biobank. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opotowsky, A.R.; Loukas, B.; Ellervik, C.; Moko, L.E.; Singh, M.N.; Landzberg, E.I.; Rimm, E.B.; Landzberg, M.J. Design and Implementation of a Prospective Adult Congenital Heart Disease Biobank. World J. Pediatr. Congenit. Heart Surg. 2016, 7, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, J.A.; Muthurangu, V.; Pandya, B.; Michel-Behnke, I.; Taylor, A.M.; Demyanets, S. Postprandial Variability of Novel Heart Failure Biomarkers in Fontan Patients Compared to Healthy Volunteers. Int. J. Cardiol. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2021, 3, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, H.; Asano, R.; Mori, A.; Ishibashi, T.; Motooka, D.; Nakai, M.; Nakaoka, Y. Gut Dysbiosis in Patients with Fontan Circulation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e034538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Maseeh, A. Vitamin D: The “Sunshine” Vitamin. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2012, 3, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D Metabolism, Mechanism of Action, and Clinical Applications. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demay, M.B.; Pittas, A.G.; Bikle, D.D.; Diab, D.L.; Kiely, M.E.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Lips, P.; Mitchell, D.M.; Murad, M.H.; Powers, S.; et al. Vitamin D for the Prevention of Disease: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1907–1947. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/109/8/1907/7685305?login=false (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Hazique, M.; Khan, K.I.; Ramesh, P.; Kanagalingam, S.; Zargham Ul Haq, F.; Victory Srinivasan, N.; Khan, A.I.; Mashat, G.D.; Khan, S. A Study of Vitamin D and Its Correlation with Severity and Complication of Congestive Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e28873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avitabile, C.M.; Leonard, M.B.; Zemel, B.S.; Brodsky, J.L.; Lee, D.; Dodds, K.; Hayden-Rush, C.; Whitehead, K.K.; Goldmuntz, E.; Paridon, S.M.; et al. Lean Mass Deficits, Vitamin D Status and Exercise Capacity in Children and Young Adults after Fontan Palliation. Heart 2014, 100, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avitabile, C.M.; Goldberg, D.J.; Zemel, B.S.; Brodsky, J.L.; Dodds, K.; Hayden-Rush, C.; Whitehead, K.K.; Goldmuntz, E.; Rychik, J.; Leonard, M.B. Deficits in Bone Density and Structure in Children and Young Adults Following Fontan Palliation. Bone 2015, 77, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holler, F.; Hannes, T.; Germund, I.; Emmel, M.; Hoyer-Kuhn, H.; Khalil, M.; Sreeram, N.; Udink Ten Cate, F.E.A. Low Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Fontan Patients. Cardiol. Young 2016, 26, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancilla, E.E.; Zielonka, B.; Brodsky, J.; Roizen, J.; Zemel, B.; Goldberg, D.J.; Dodds, K.M.; Rychik, J. Abstract 19714: Growth Parameters, Bone Mineral Density and Secondary Hyperparathyroidism After Fontan Operation: Results from the Multidisciplinary Clinic at the CHOP Single Ventricle Survivorship Program. Circulation 2016, 134, A19714. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, S.G.; Godang, K.; Müller, L.-S.O.; Almaas, R.; de Lange, C.; Brunvand, L.; Hansen, K.M.; Myhre, A.G.; Døhlen, G.; Thaulow, E.; et al. Progressive Loss of Bone Mass in Children with Fontan Circulation. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2019, 14, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, P.; Tran, D.; Verrall, C.E.; Attard, C.; Singh, M.F.; Ayer, J.; d’Udekem, Y.; Twigg, S.; Celermajer, D.S.; Cordina, R. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Low Bone Density in Adults with a Fontan Circulation. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2019, 14, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, S.J.; Dodds, K.M.; Burstein, D.S.; Huang, J.; Rand, E.B.; Mancilla, E.; Heimall, J.R.; McBride, M.G.; Paridon, S.M.; Goldberg, D.J.; et al. End-Organ Function and Exercise Performance in Patients with Fontan Circulation: What Characterizes the High Performers? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.; Sandberg, C.; Öhlund, I.; Lind, T.; Sthen Bergdahl, M.; Wiklund, U.; Rylander Hedlund, E.; Sjöberg, G.; Rydberg, A. Vitamin D, Liver-Related Biomarkers, and Distribution of Fat and Lean Mass in Young Patients with Fontan Circulation. Cardiol. Young 2022, 32, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina-Ruedy, E.; Rosen, C.J. Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis: An Old Dog Teaches Us New Tricks. Mol. Metab. 2022, 60, 101480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.J.; Ruppe, M.D.; Tabatabai, L.S. The Parathyroid Gland and Heart Disease. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2017, 13, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Lin, B. Parathyroid Hormone and Risk of Heart Failure in the General Population. Medicine 2016, 95, e4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Ruebner, R.L.; Furth, S.L.; Dodds, K.M.; Rychik, J.; Goldberg, D.J. Assessment of Kidney Function in Survivors Following Fontan Palliation. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2016, 11, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenting, P.J.; Christophe, O.D.; Denis, C.V. Von Willebrand Factor Biosynthesis, Secretion, and Clearance: Connecting the Far Ends. Blood 2015, 125, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Feng, S.; Zhao, J.; Liao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Liu, J. Prognostic Value of Plasma von Willebrand Factor Levels in Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombos, T.; Makó, V.; Cervenak, L.; Papassotiriou, J.; Kunde, J.; Hársfalvi, J.; Förhécz, Z.; Pozsonyi, Z.; Borgulya, G.; Jánoskuti, L.; et al. Levels of von Willebrand Factor Antigen and von Willebrand Factor Cleaving Protease (ADAMTS13) Activity Predict Clinical Events in Chronic Heart Failure. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleber, M.E.; Koller, L.; Goliasch, G.; Sulzgruber, P.; Scharnagl, H.; Silbernagel, G.; Grammer, T.B.; Delgado, G.; Tomaschitz, A.; Pilz, S.; et al. Von Willebrand Factor Improves Risk Prediction in Addition to N-Terminal pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Patients Referred to Coronary Angiography and Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binotto, M.A.; Maeda, N.Y.; Lopes, A.A. Altered Endothelial Function Following the Fontan Procedure. Cardiol. Young 2008, 18, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkiewicz-Pajak, L.; Hoffman, P.; Trojnarska, O.; Lipczyńska, M.; Podolec, P.; Undas, A. Abnormalities in Blood Coagulation, Fibrinolysis, and Platelet Activation in Adult Patients after the Fontan Procedure. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkiewicz-Pajak, L.; Wojcik, T.; Chłopicki, S.; Olszowska, M.; Pajak, J.; Podolec, J.; Sitek, B.; Musiałek, P.; Rubis, P.; Komar, M.; et al. Aspirin Resistance in Adult Patients after Fontan Surgery. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 181, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, H.; Hayama, Y.; Miike, H.; Suzuki, D.; Nakajima, K.; Iwasa, T.; Konagai, N.; Sakaguchi, H.; Miyazaki, A.; Shiraishi, I.; et al. Prognostic Value of von Willebrand Factor in Adult Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. Heart 2020, 106, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinel, K.; Korak, F.; Dusleag, M.; Strini, T.; Baumgartner, D.; Burmas, A.; Sallmon, H.; Zieger, B.; Schlagenhauf, A.; Koestenberger, M. Mild Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome and Cholestasis in Pediatric and Adult Patients with Fontan Circulation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, J.; de la Espriella, R.; Miñana, G.; Santas, E.; Llácer, P.; Núñez, E.; Palau, P.; Bodí, V.; Chorro, F.J.; Sanchis, J.; et al. Antigen Carbohydrate 125 as a Biomarker in Heart Failure: A Narrative Review. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhchi, P.; Cybulski, C.; Gronwald, J.; Wong, F.O.; Narod, S.A.; Akbari, M.R. CA125 and Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Marín, G.; de la Espriella, R.; Santas, E.; Lorenzo, M.; Miñana, G.; Núñez, E.; Bodí, V.; González, M.; Górriz, J.L.; Bonanad, C.; et al. CA125 but Not NT-proBNP Predicts the Presence of a Congestive Intrarenal Venous Flow in Patients with Acute Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk: The Task Force for the Management of Dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutzouri, E.; Elisaf, M.; Liberopoulos, E.N. Hypocholesterolemia. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 9, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, W.; Tan, M.; Yu, S.; Rocchini, A. Low Total, Low-Density Lipoprotein, High-Density Lipoprotein, and Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Patients with Complex Congenital Heart Disease after Fontan Palliation. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, W.; Tan, M.; Ostlund, R.E.; Yu, S.; Ma, L.; Rocchini, A. Altered Cholesterol Metabolism and Hypocholesterolemia in Patients with Single Ventricle Following Fontan Palliation. J. Pediatr. 2016, 171, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubert, A.M.; Alsaied, T.; Palermo, J.J.; Anwar, N.; Urbina, E.M.; Brown, N.M.; Alexander, C.; Almeneisi, H.; Wu, F.; Leventhal, A.R.; et al. Fontan-Associated Dyslipidemia. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.; Mihas, A.A.; Abou-Assi, S.G.; Williams, L.M.; Gavis, E.; Pandak, W.M.; Heuman, D.M. High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol as an Indicator of Liver Function and Prognosis in Noncholestatic Cirrhotics. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, G.; Spadaro, L.; Marchisello, S.; Fede, G.; Purrello, F. Abnormalities of Lipoprotein Levels in Liver Cirrhosis: Clinical Relevance. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-W.; Wu, C.-H.; Huang, M.-T.; Lee, C.-S.; Chen, H.-L.; Lin, M.-T.; Chiu, S.-N.; Tseng, W.-C.; Chen, C.-A.; Wang, J.-K.; et al. Liver Fibrosis Detected by Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Functional Correlates in Fontan Patients. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 66, ezae249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, R.A.; Ogunmoroti, O.; Zhao, D.; Ndumele, C.E.; Rao, V.; Pandey, A.; Larson, N.B.; Bielinski, S.J.; Michos, E.D. Hepatocyte Growth Factor and Incident Heart Failure Subtypes: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Shoji, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Fujii, T.; Nakazawa, M. Elevated Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels Are Associated with Aortopulmonary Collateral Vessels in Patients before and after the Fontan Procedure. Am. Heart J. 2007, 153, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.B.; Kwon, B.S.; Bae, E.J.; Noh, C.I.; Choi, J.Y. Significance of Circulating Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Protein-Losing Enteropathy after Fontan Operation. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2011, 32, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Taki, M.; Toda, K.; Muraji, S.; Yoshiba, S.; Kobayshi, T.; Sumitomo, N. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Predicts Failure of Fontan Circulation. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 3738–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, D.R.; Lazar, F.-L.; Homorodean, C.; Cainap, C.; Focsan, M.; Cainap, S.; Olinic, D.M. High-Sensitivity Troponin: A Review on Characteristics, Assessment, and Clinical Implications. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 9713326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber, I.; McCarthy, C.P.; Januzzi, J.L. A Test in Context: Interpretation of High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Assays in Different Clinical Settings. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willinger, L.; Brudy, L.; Meyer, M.; Oberhoffer-Fritz, R.; Ewert, P.; Müller, J. Prognostic Value of Non-Acute High Sensitive Troponin-T for Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eindhoven, J.A.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; van den Bosch, A.E.; Kardys, I.; Cheng, J.M.; Veenis, J.F.; Cuypers, J.A.A.E.; Witsenburg, M.; van Schaik, R.H.N.; Boersma, E. High-Sensitive Troponin-T in Adult Congenital Heart Disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerola, A.; Poutanen, T.; Savukoski, T.; Pettersson, K.; Sairanen, H.; Jokinen, E.; Pihkala, J. Cardiac Troponin I, Cardiac Troponin-Specific Autoantibodies and Natriuretic Peptides in Children with Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome. Interact. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2014, 18, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abiko, M.; Inai, K.; Shimada, E.; Asagai, S.; Nakanishi, T. The Prognostic Value of High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. J. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, M.M.; Cortese, F.; Gesualdo, M.; Riccardi, R.; Di Nunzio, D.; Moncelli, M.; Iacoviello, M.; Scicchitano, P. A Novel Cardiac Bio-Marker: ST2: A Review. Molecules 2013, 18, 15314–15328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Kałużna-Oleksy, M.; Migaj, J.; Straburzyńska-Migaj, E. Clinical Value of Soluble ST2 in Cardiology. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Vergaro, G.; Sciarrone, P.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. Clinical and Prognostic Significance of sST2 in Heart Failure: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laqqan, M.; Schwaighofer, C.; Graeber, S.; Raedle-Hurst, T. Predictive Value of Soluble ST2 in Adolescent and Adult Patients with Complex Congenital Heart Disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geenen, L.W.; Baggen, V.J.M.; van den Bosch, A.E.; Eindhoven, J.A.; Cuypers, J.A.A.E.; Witsenburg, M.; Boersma, E.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W. Prognostic Value of Soluble ST2 in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease. Heart 2019, 105, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollert, K.C.; Kempf, T.; Wallentin, L. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 as a Biomarker in Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, E.T.; Morrow, D.A.; Guo, J.; Berg, D.D.; Blazing, M.A.; Bohula, E.A.; Bonaca, M.P.; Cannon, C.P.; de Lemos, J.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 and Cardiovascular Risk: Individual Patient Meta-Analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raedle-Hurst, T.M.; Koenigstein, K.; Gruenhage, F.; Raedle, J.; Herrmann, E.; Abdul-Khaliq, H. Growth Differentiation Factor 15—An Early Marker of Abnormal Function of the Fontan Circuit in Patients with Univentricular Hearts. Am. Heart J. 2010, 160, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.L.; Wolff, D.; Ridderbos, F.S.; Eshuis, G.; Hillege, H.; Willems, T.P.; Ebels, T.; van Melle, J.P.; Berger, R.M.F. GDF-15 (Growth Differentiation Factor 15) Is Associated with Hospitalization and Mortality in Patients with a Fontan Circulation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborska, B.; Sikora-Frąc, M.; Smarż, K.; Pilichowska-Paszkiet, E.; Budaj, A.; Sitkiewicz, D.; Sygitowicz, G. The Role of Galectin-3 in Heart Failure—The Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Potential—Where Do We Stand? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.Z.; Amin, L.Z.; Wijaya, I.P. Galectin-3: A Novel Biomarker for the Prognosis of Heart Failure. Clujul Med. 2017, 90, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, R.A.; Voors, A.A.; Muntendam, P.; van Gilst, W.H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J. Galectin-3: A Novel Mediator of Heart Failure Development and Progression. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrynchyshyn, N.; Jourdain, P.; Desnos, M.; Diebold, B.; Funck, F. Galectin-3: A New Biomarker for the Diagnosis, Analysis and Prognosis of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 106, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opotowsky, A.R.; Baraona, F.; Owumi, J.; Loukas, B.; Singh, M.N.; Valente, A.M.; Wu, F.; Cheng, S.; Veldtman, G.; Rimm, E.B.; et al. Galectin-3 Is Elevated and Associated with Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Single-Ventricle Fontan Circulation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; Kangawa, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Ichiki, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuo, H.; Eto, T. Adrenomedullin: A Novel Hypotensive Peptide Isolated from Human Pheochromocytoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 192, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; Kremer, D.; Geven, C.; ter Maaten, J.M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Pickkers, P.; Metra, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Düngen, H.; et al. Adrenomedullin in Heart Failure: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Application. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, R.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Wilkens, H.; Herrmann, E.; Raedle-Hurst, T.M. Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin: An Indicator of the Failing Fontan Circuit in Patients with Univentricular Hearts? Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2014, 16, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, T.; Imai, Y.; Takanashi, Y.; Seo, K.; Terada, M.; Aoki, M.; Nakazawa, M. Time Course of Endothelin-1 and Adrenomedullin after the Fontan Procedure. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1999, 68, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Nishikimi, T.; Takamuro, M.; Yasuda, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Tanabe, S.; Yamada, O.; Yagihara, T.; Suga, S.; Kangawa, K.; et al. Possible Role of Adrenomedullin in the Regulation of Fontan Circulation: Mature Form of Plasma Adrenomedullin Is Extracted in the Lung in Patients with Fontan Procedure. Regul. Pept. 2007, 141, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, A.P.; Hyndman, K.A.; Dhaun, N.; Southan, C.; Kohan, D.E.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M.; Webb, D.J.; Maguire, J.J. Endothelin. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 357–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banecki, K.M.R.M.; Dora, K.A. Endothelin-1 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galié, N.; Manes, A.; Branzi, A. The Endothelin System in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 61, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Moukarbel, G.V.; Gupta, R.; Frank, S.M.; Anderson, A.M.; Liu, L.C.; Khouri, S.J. Endothelin 1 Is Associated with Heart Failure Hospitalization and Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Pulmonary Hypertension. Cardiology 2019, 143, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Kogaki, S.; Ichimori, H.; Narita, J.; Nawa, N.; Ueno, T.; Takahashi, K.; Kayatani, F.; Kishimoto, H.; Nakayama, M.; et al. Overexpression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelin Receptors in the Pulmonary Arteries of Failed Fontan Patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 159, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Udekem, Y.; Cheung, M.M.H.; Setyapranata, S.; Iyengar, A.J.; Kelly, P.; Buckland, N.; Grigg, L.E.; Weintraub, R.G.; Vance, A.; Brizard, C.P.; et al. How Good Is a Good Fontan? Quality of Life and Exercise Capacity of Fontans without Arrhythmias. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 88, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, M.; Kurosawa, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Nomura, K.; Kitamura, N. The Role of Plasma Endothelin in the Fontan Circulation. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 43, 793–797. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, E.; d’Udekem, Y.; Cheung, M.; Sari, C.I.; Inman, J.; Ahimastos, A.; Eikelis, N.; Pathak, A.; King, I.; Grigg, L.; et al. Sympathetic and Vascular Dysfunction in Adult Patients with Fontan Circulation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, S.H.; Hu, L.; Andò, S.; Pirklbauer, M.; Säemann, M.D.; Ruotolo, C.; Zaza, G.; La Manna, G.; De Nicola, L.; Mayer, G.; et al. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System: From History to Practice of a Secular Topic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, M.; Battistoni, A.; Chin, D.; Rubattu, S.; Tocci, G. Renin as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease in Clinical Practice. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainwaring, R.D.; Lamberti, J.J.; Moore, J.W.; Billman, G.F.; Nelson, J.C. Comparison of the Hormonal Response after Bidirectional Glenn and Fontan Procedures. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1994, 57, 59–63; discussion 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainwaring, R.D.; Lamberti, J.J.; Carter, T.L.; Moore, J.W.; Nelson, J.C. Renin, Angiotensin II, and the Development of Effusions Following Bidirectional Glenn and Fontan Procedures. J. Card. Surg. 1995, 10, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, K.; Bové, T.; De Groote, K.; Panzer, J.; Vandekerckhove, K.; Suys, B.; De Wolf, D.; Van Nooten, G. Pleural Effusions, Water Balance Mediators and the Influence of Lisinopril after Completion Fontan Procedures. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2009, 36, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohuchi, H.; Negishi, J.; Ono, S.; Miyake, A.; Toyota, N.; Tamaki, W.; Miyazaki, A.; Yamada, O. Hyponatremia and Its Association with the Neurohormonal Activity and Adverse Clinical Events in Children and Young Adult Patients after the Fontan Operation. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2011, 6, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Saiki, H.; Tamai, A.; Seki, M.; Inuzuka, R.; Masutani, S.; Senzaki, H. Ventricular Fibrogenesis Activity Assessed by Serum Levels of Procollagen Type III N-Terminal Amino Peptide during the Staged Fontan Procedure. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 151, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaudet, L.; Calderari, B.; Pacher, P. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Catecholamine and Cocaine-Mediated Cardiotoxicity. Heart Fail. Rev. 2014, 19, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.E.; Januzzi, J.L. Established and Emerging Roles of Biomarkers in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, C.R.; Shelton, B.; Johnstone, D.E.; Francis, G.; Greenberg, B.; Konstam, M.; Probstfield, J.L.; Yusuf, S. Prognostic Significance of Plasma Norepinephrine in Patients with Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Dysfunction. SOLVD Investigators. Circulation 1996, 94, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabassi, A.; de Champlain, J.; Maggiore, U.; Parenti, E.; Coghi, P.; Vicini, V.; Tedeschi, S.; Cremaschi, E.; Binno, S.; Rocco, R.; et al. Prealbumin Improves Death Risk Prediction of BNP-Added Seattle Heart Failure Model: Results from a Pilot Study in Elderly Chronic Heart Failure Patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3334–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohuchi, H.; Negishi, J.; Miyake, A.; Sakaguchi, H.; Miyazaki, A.; Yamada, O. Long-Term Prognostic Value of Cardiac Autonomic Nervous Activity in Postoperative Patients with Congenital Heart Disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 151, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.-H.; Luo, M.-Y.; Liang, N.; Gong, S.-X.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.-Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, A.-P. Interleukin-6: A Novel Target for Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 745061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, L.L.; Mariano, D.; Lemos, R.P.; Bialves, T.S.; Oliveira, C.J.F.; de Melo-Minardi, R.C. The Role of Structural Bioinformatics in Understanding Tumor Necrosis Factor α-Interacting Protein Mechanisms in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: A Review. Immuno 2024, 4, 14–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urschel, K.; Cicha, I. TNF-Alpha in the Cardiovascular System: From Physiology to Therapy. Int. J. Interferon Cytokine Mediat. Res. 2015, 7, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainwaring, R.D.; Lamberti, J.J.; Hugli, T.E. Complement Activation and Cytokine Generation after Modified Fontan Procedure. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 65, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.A.; Beshish, A.G.; Bush, L.B.; Lowery, R.E.; Wong, J.H.; Schumacher, K.R.; Halligan, N.L.N.; Cornell, T.T.; Rocchini, A.P. Analysis of Inflammatory Cytokines in Postoperative Fontan Pleural Drainage. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2019, 40, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrow, A.M.; Freeze, H.; Rychik, J. Protein-Losing Enteropathy after Fontan Operation: Investigations into Possible Pathophysiologic Mechanisms. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de Santiago, E.; Téllez, L.; Garrido-Lestache Rodríguez-Monte, E.; Garrido-Gómez, E.; Aguilera-Castro, L.; Álvarez-Fuente, M.; Del Cerro, M.J.; Albillos, A. Fontan Protein-Losing Enteropathy Is Associated with Advanced Liver Disease and a Proinflammatory Intestinal and Systemic State. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Node, K.; Kobayashi, Y. Uric Acid and Cardiovascular Disease: A Clinical Review. J. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumrić, M.; Borovac, J.A.; Kurir, T.T.; Božić, J. Clinical Implications of Uric Acid in Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Review. Life 2021, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, M.; Renaud, D.; Schmidt, R.; Einkemmer, M.; Laser, L.V.; Michel, E.; Dubowy, K.O.; Karall, D.; Laser, K.T.; Scholl-Bürgi, S. Altered Serum Proteins Suggest Inflammation, Fibrogenesis and Angiogenesis in Adult Patients with a Fontan Circulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Turcato, G.; Cervellin, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in Heart Failure: A Narrative Review. World J. Cardiol. 2018, 10, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Tang, Q. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width: A Novel Predictive Indicator for Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 7089493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandsen, E.J.; Randers, E. Reference Intervals for Plasma Cystatin C and Plasma Creatinine in Adults Using Methods Traceable to International Calibrators and Reference Methods. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M. A Test in Context: High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1911–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier, E. Parathyroid Hormone Results Interpretation in the Background of Variable Analytical Performance. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2019, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Motto, D.G.; Di Paola, J. Diagnostic Approach to von Willebrand Disease. Blood 2015, 125, 2029–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balder, J.W.; de Vries, J.K.; Nolte, I.M.; Lansberg, P.J.; Kuivenhoven, J.A.; Kamphuisen, P.W. Lipid and Lipoprotein Reference Values from 133,450 Dutch Lifelines Participants: Age- and Gender-Specific Baseline Lipid Values and Percentiles. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 1055–1064.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.A.; Rossello, X.; Coughlan, J.J.; Barbato, E.; Berry, C.; Chieffo, A.; Claeys, M.J.; Dan, G.-A.; Dweck, M.R.; Galbraith, M.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3720–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, A.E.; Berezin, A.A. Biomarkers in Heart Failure: From Research to Clinical Practice. Ann. Lab. Med. 2023, 43, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Snider, J.V.; Grenache, D.G. Establishment of Reference Intervals for Soluble ST2 from a United States Population. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1825–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, P.; Kimenai, D.M.; Marioni, R.E.; Hayward, C.; Campbell, A.; Porteous, D.; Mills, N.L.; O’Rahilly, S.; Sattar, N. Reference Ranges for GDF-15, and Risk Factors Associated with GDF-15, in a Large General Population Cohort. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Bellia, C.; Lo Sasso, B.; Pivetti, A.; Muratore, M.; Scazzone, C.; Bivona, G.; Lippi, G.; Ciaccio, M. Establishing the Upper Reference Limit of Galectin-3 in Healthy Blood Donors. Biochem. Med. 2017, 27, 030709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ-Crain, M.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Stolz, D.; Müller, C.; Bingisser, R.; Harbarth, S.; Tamm, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Müller, B. Pro-Adrenomedullin to Predict Severity and Outcome in Community-Acquired Pneumonia [ISRCTN04176397]. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S.E.; Docherty, K.F.; Campbell, R.T.; Jhund, P.S.; Hammarstedt, A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jarolim, P.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; et al. Endothelin-1, Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction, and Effects of Dapagliflozin: Findings from DAPA-HF. Circulation 2023, 147, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostov, K.; Blazhev, A. Circulating Levels of Endothelin-1 and Big Endothelin-1 in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Hirono, K.; Higuma, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Ichida, F.; Origasa, H.; Nishida, N.; Imura, J.; Emoto, N.; et al. Endothelin-1 May Play an Important Role in the Fontan Circulation. Interdiscip. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2018, 26, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.K.; Kam, K.K.; Yan, B.P.; Lam, Y.-Y. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Blockade for Cardiovascular Diseases: Current Status. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1273–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normal Hormone Reference Ranges. In Greenspan’s Basic & Clinical Endocrinology; Gardner, D.G., Shoback, D., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-259-58928-7. [Google Scholar]
- Blandini, F.; Martignoni, E.; Melzi d’Eril, G.V.; Biasio, L.; Sances, G.; Lucarelli, C.; Rizzo, V.; Costa, A.; Nappi, G. Free Plasma Catecholamine Levels in Healthy Subjects: A Basal and Dynamic Study. The Influence of Age. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1992, 52, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, E.A.; Al-Reesi, I.; Al-Shizawi, N.; Jaju, S.; Al-Balushi, M.S.; Koh, C.Y.; Al-Jabri, A.A.; Jeyaseelan, L. Defining IL-6 Levels in Healthy Individuals: A Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3915–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valaperti, A.; Li, Z.; Vonow-Eisenring, M.; Probst-Müller, E. Diagnostic Methods for the Measurement of Human TNF-Alpha in Clinical Laboratory. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 113010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, C.; Domienik-Karłowicz, J.; Tykarski, A.; Filipiak, K.J.; Jaguszewski, M.J.; Narkiewicz, K.; Barylski, M.; Mamcarz, A.; Wolf, J.; Mancia, G. Expert Consensus for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Hyperuricemia and High Cardiovascular Risk: 2023 Update. Cardiol. J. 2024, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
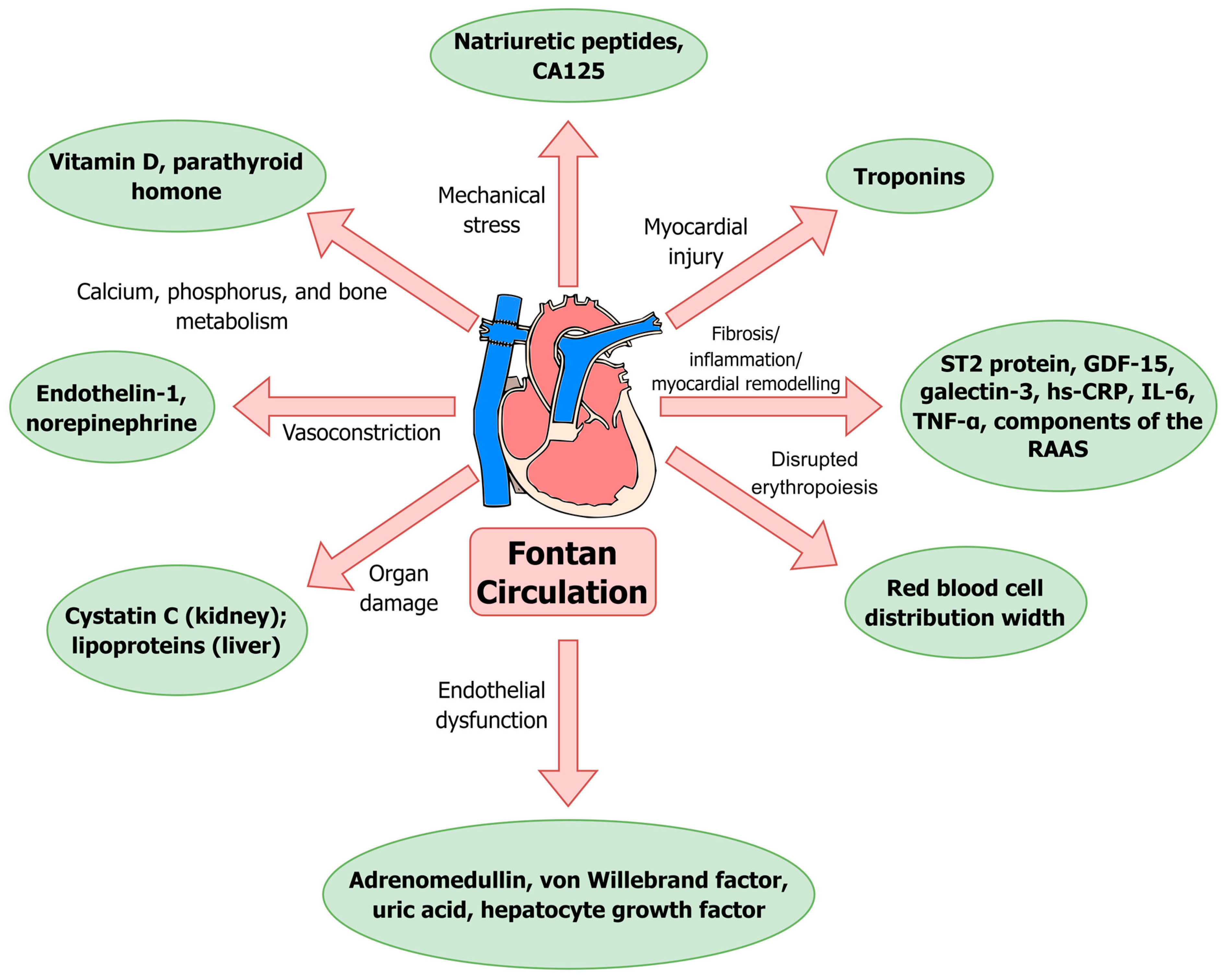
| Biomarker/Biomarkers Group | Correspondence to Pathophysiological Mechanism | Available Cut-Off Value(s) [for Serum/Plasma] * | Studies in the Fontan Circulation | Clinical Use in Fontan Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natriuretic peptides | Mechanical stress (primarily), systemic ischemia and hypoxia, neurohumoral factors [17] |
| [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] |
|
| Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) | Disrupted erythropoiesis [165] | [50,51,52] |
| |
| Cystatin C | Renal insufficiency (estimation of the glomerular filtration rate) [53] |
| [56,57,58,59,60] |
|
| High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) | Inflammation [62] |
| [32,64,66,67] |
|
| Vitamin D | Abnormalities in calcium, phosphorus, and bone metabolism [169] |
| [72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79] |
|
| Parathyroid hormone (PTH) | Overproduction of PTH leads to hypercalcemia [81] |
| [73,74,75,77,83] |
|
| von Willebrand factor | Endothelial dysfunction [85] |
| [37,88,89,90,91,92] |
|
| CA125 | Increased hydrostatic pressures, mechanical stress, and cytokine activation [93] | [52] |
| |
| Lipoproteins | Hypocholesterolemia as a marker of liver dysfunction [98] | [98,99,100,103] |
| |
| Hepatocyte growth factor | Endothelial injury [104] | [105,106,107] |
| |
| Troponins | Myocardial injury [109] |
| [34,38,39,59,110,111,112,113] |
|
| ST2 protein | Extracellular fibrosis and inflammation [174] | [37,38,39,117,118] |
| |
| Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) | Hypoxic, mechanical, oxidative or inflammatory stress [119] |
| [37,39,59,121,122] |
|
| Galectin-3 | Extracellular fibrosis and inflammation [174] |
| [37,127] |
|
| Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) | Endothelial dysfunction; residual tissue congestion [129] |
| [66,130,131,132] |
|
| Endothelin-1 (ET-1) | Vasoconstriction, especially in the pulmonary circulation [179] |
| [29,66,90,131,138,139,140,141,181] |
|
| Components of the RAAS | Myocardial and vascular remodeling: hypertrophy, fibrosis [182] |
| [19,20,30,59,144,145,146,147,148] |
|
| Norepinephrine (NE) | Increased myocardial contraction, peripheral vasoconstriction, heart rate, energy expenditure [150] |
| [19,20,31,147,153] |
|
| Pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) | Inflammation | [32,59,158,159,160,161] |
| |
| Uric acid | Inflammation in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells, intracellular oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction [162] |
| [31,127,164] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wittczak, A.; Mazurek-Kula, A.; Banach, M.; Piotrowski, G.; Bielecka-Dabrowa, A. Blood Biomarkers as a Non-Invasive Method for the Assessment of the State of the Fontan Circulation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020496
Wittczak A, Mazurek-Kula A, Banach M, Piotrowski G, Bielecka-Dabrowa A. Blood Biomarkers as a Non-Invasive Method for the Assessment of the State of the Fontan Circulation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020496
Chicago/Turabian StyleWittczak, Andrzej, Anna Mazurek-Kula, Maciej Banach, Grzegorz Piotrowski, and Agata Bielecka-Dabrowa. 2025. "Blood Biomarkers as a Non-Invasive Method for the Assessment of the State of the Fontan Circulation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020496
APA StyleWittczak, A., Mazurek-Kula, A., Banach, M., Piotrowski, G., & Bielecka-Dabrowa, A. (2025). Blood Biomarkers as a Non-Invasive Method for the Assessment of the State of the Fontan Circulation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020496








