Clinical and Geriatric Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality in Older Adults Admitted to Internal Medicine Wards: A Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez-Valencia, M.; Izquierdo, M.; Cesari, M.; Casas-Herrero, Á.; Inzitari, M.; Martínez-Velilla, N. The relationship between frailty and polypharmacy in older people: A systematic review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y. Multimorbidity and polypharmacy in hospitalized older patients: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, J.; Lindley, R.I.; Byth, K.; John, R.; Ferguson, C. Frailty in older adults admitted to hospital: Outcomes from the Western Sydney Clinical Frailty Registry. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.C.; Chen, L.K.; Hsiao, F.Y. Predicting mortality and hospitalization of older adults by the multimorbidity frailty index. PLoS ONE. 2017, 12, e0187825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcantonio, E.R. Delirium in Hospitalized Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keeffe, S.; Lavan, J. The prognostic significance of delirium in older hospital patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1997, 45, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ros, P.; Plaza-Ortega, N.; Martínez-Arnau, F.M. Mortality Risk Following Delirium in Older Inpatients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Worldviews Evid. Based Nurs. 2025, 22, e70027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, J.M.; Duggan, M.C.; Wilson, J.E. Why We Must Prevent and Appropriately Manage Delirium. AMA J. Ethics 2023, 25, E751–E757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellelli, G.; Morandi, A.; Davis, D.H.; Mazzola, P.; Turco, R.; Gentile, S.; Ryan, T.; Cash, H.; Guerini, F.; Torpilliesi, T.; et al. Validation of the 4AT, a new instrument for rapid delirium screening: A study in 234 hospitalised older people. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meagher, D. Motor subtypes of delirium: Past, present and future. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2009, 21, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Cella, A.; Pilotto, A.; Daragjati, J.; Veronese, N.; Musacchio, C.; Mello, A.M.; Logroscino, G.; Padovani, A.; Prete, C.; et al. Three Decades of Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment: Evidence Coming From Different Healthcare Settings and Specific Clinical Conditions. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 192.e1–192.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, E.; Veitch, M.; Saripella, A.; Alhamdah, Y.; Butris, N.; Tang-Wai, D.F.; Tartaglia, M.C.; Nagappa, M.; Englesakis, M.; He, D.; et al. Association between postoperative delirium and adverse outcomes in older surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2023, 90, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung Thein, M.Z.; Pereira, J.V.; Nitchingham, A.; Caplan, G.A. A call to action for delirium research: Meta-analysis and regression of delirium associated mortality. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, N.; Eichlseder, M.; Orlob, S.; Klivinyi, C.; Zoidl, P.; Pichler, A.; Eichinger, M.; Fandler-Höfler, S.; Scholz, L.; Baumgartner, J.; et al. Sex specific differences in short-term mortality after ICU-delirium. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallazzi, R.; Saad, M.; Marik, P.E. Delirium in the ICU: An overview. Ann. Intensive Care 2012, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.W.; Chang, C.C.; Chou, R.H.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, L.K.; Huang, P.H.; Lin, S.J. Sex differences in the frailty phenotype and mortality in the I-Lan longitudinal aging study cohort. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penfold, R.S.; Squires, C.; Angus, A.; Shenkin, S.D.; Ibitoye, T.; Tieges, Z.; Neufeld, K.J.; Avelino-Silva, T.J.; Davis, D.; Anand, A.; et al. Delirium detection tools show varying completion rates and positive score rates when used at scale in routine practice in general hospital settings: A systematic review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2024, 72, 1508–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadzadeh, D.; Karlson, B.W.; Alfredsson, J.; Ekerstad, E.; Hellberg, J.; Herlitz, J.; Ekerstad, N. Clinical Frailty Scale score is a predictor of short-, mid- and long-term mortality in critically ill older adults (≥70 years) admitted to the emergency department: An observational study. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Aprile, P.L.; Veronese, N.; Lacorte, E.; Morganti, W.; Custodero, C.; Piscopo, P.; Fabrizi, E.; Gatta, F.D.; Merlo, A.; et al. The Italian guideline on comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA) for the older persons: A collaborative work of 25 Italian Scientific Societies and the National Institute of Health. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
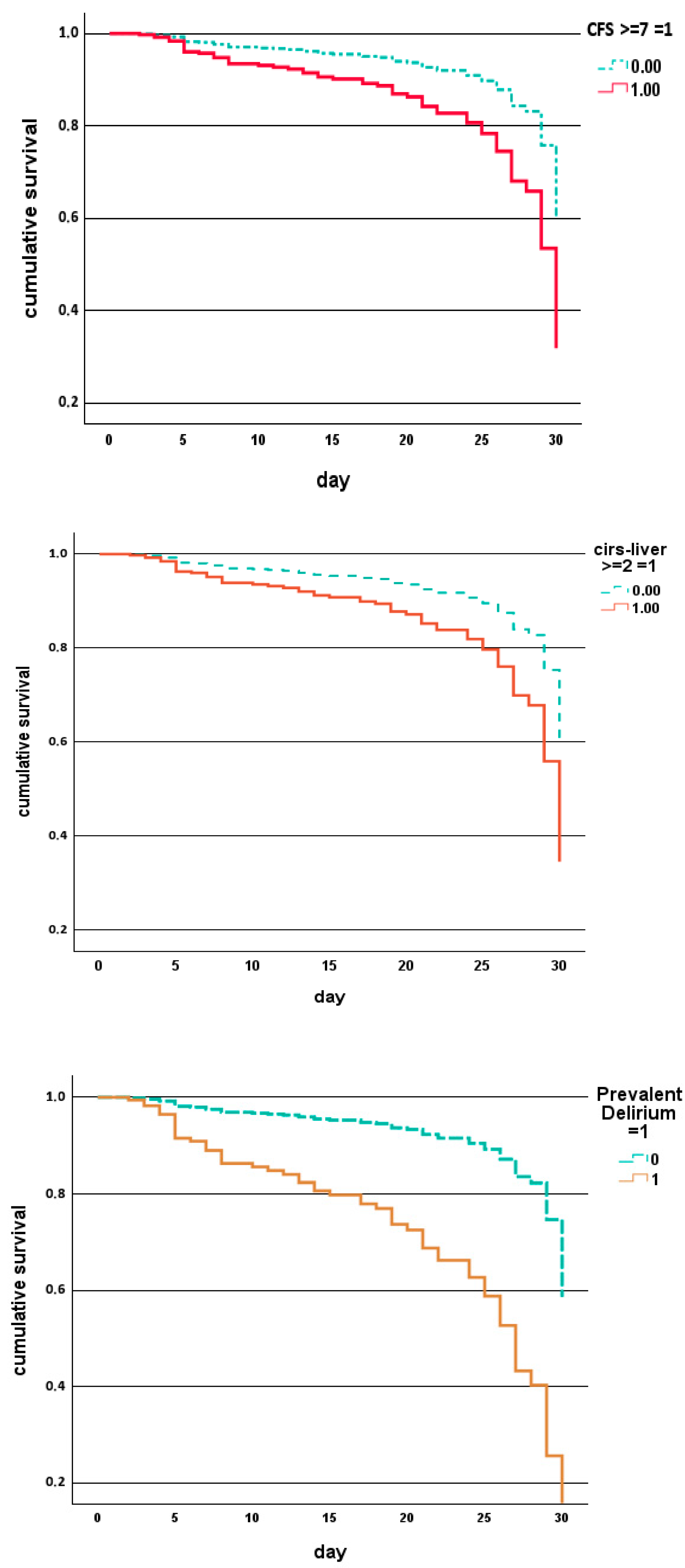
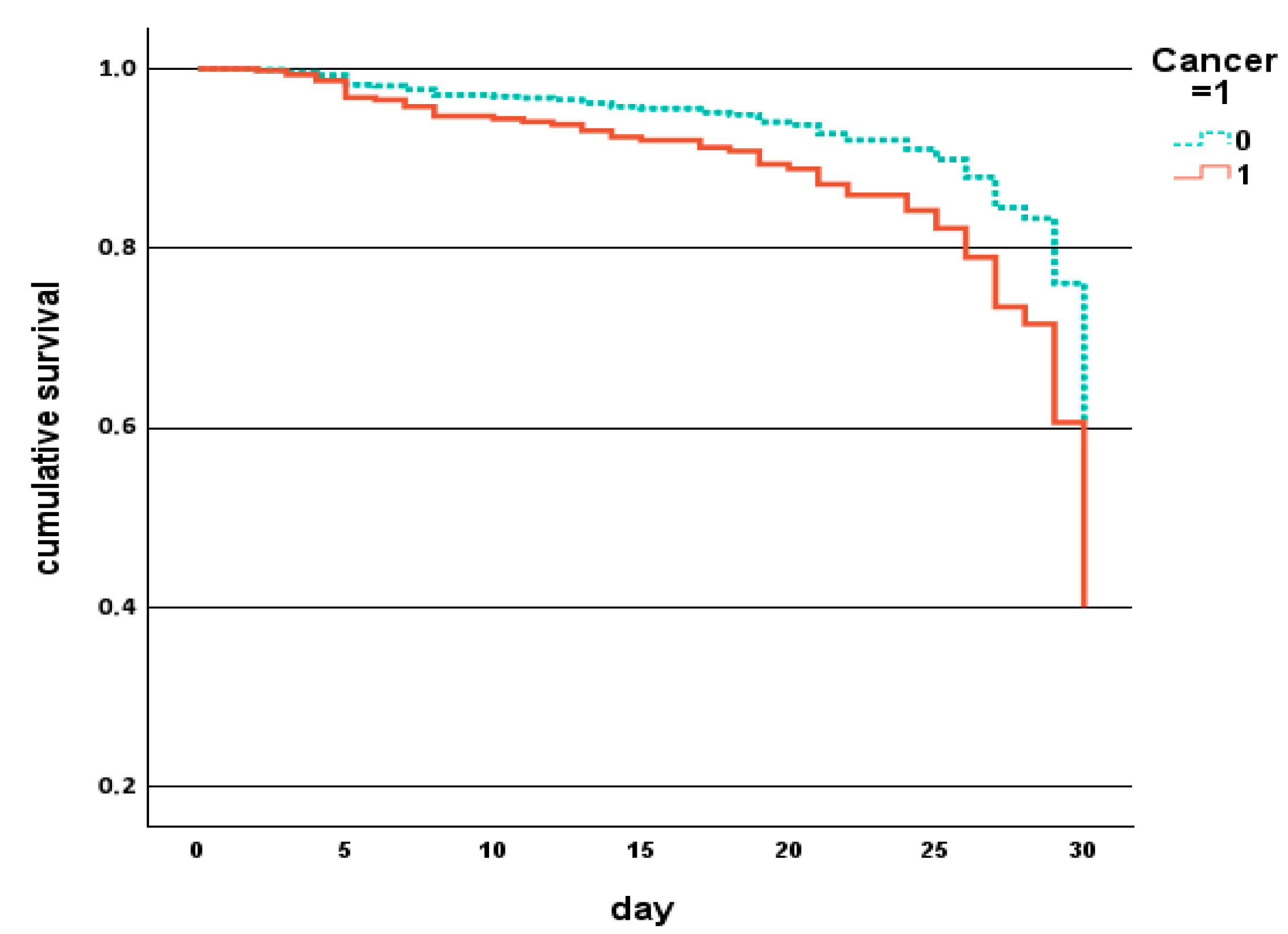
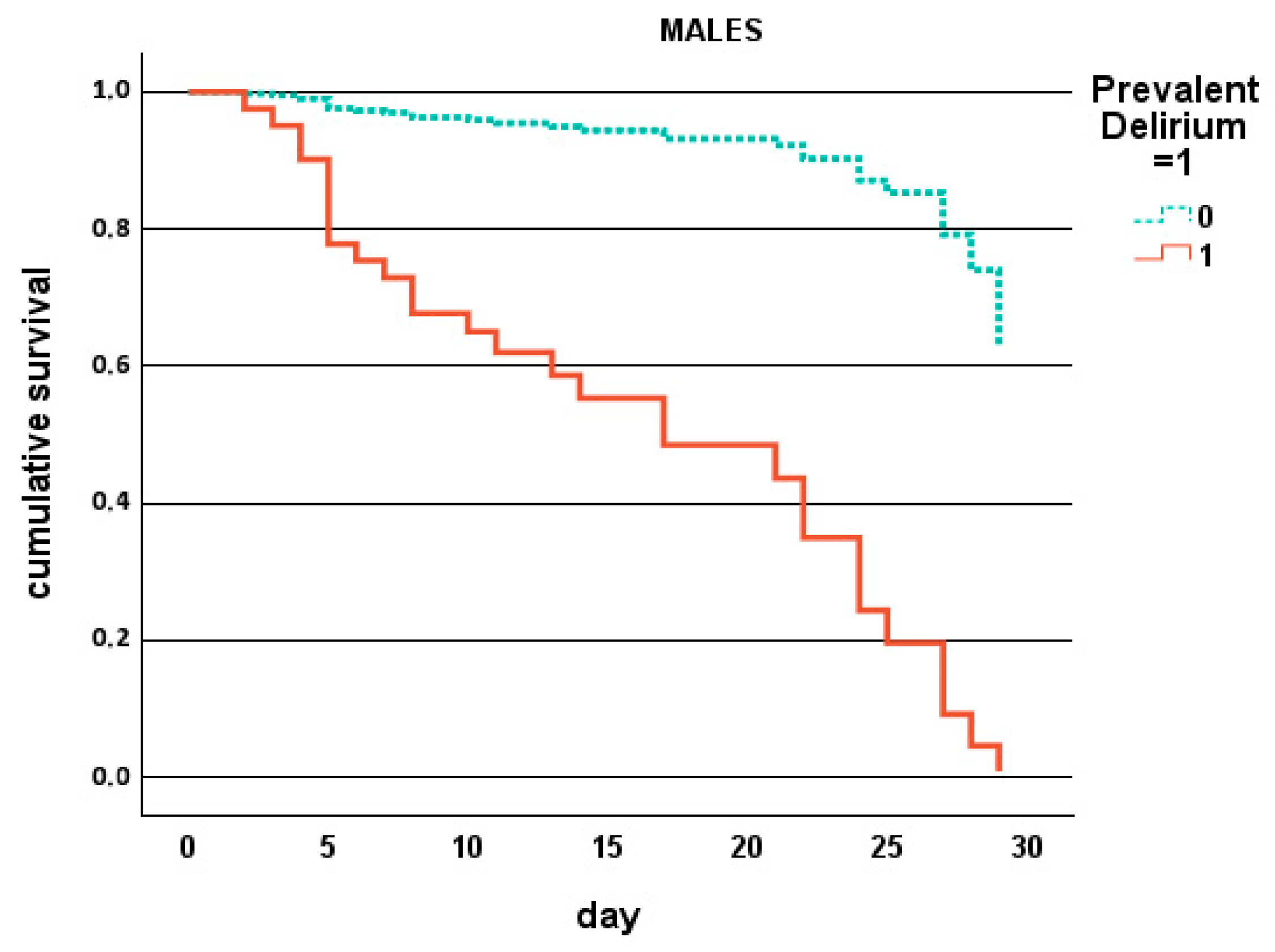
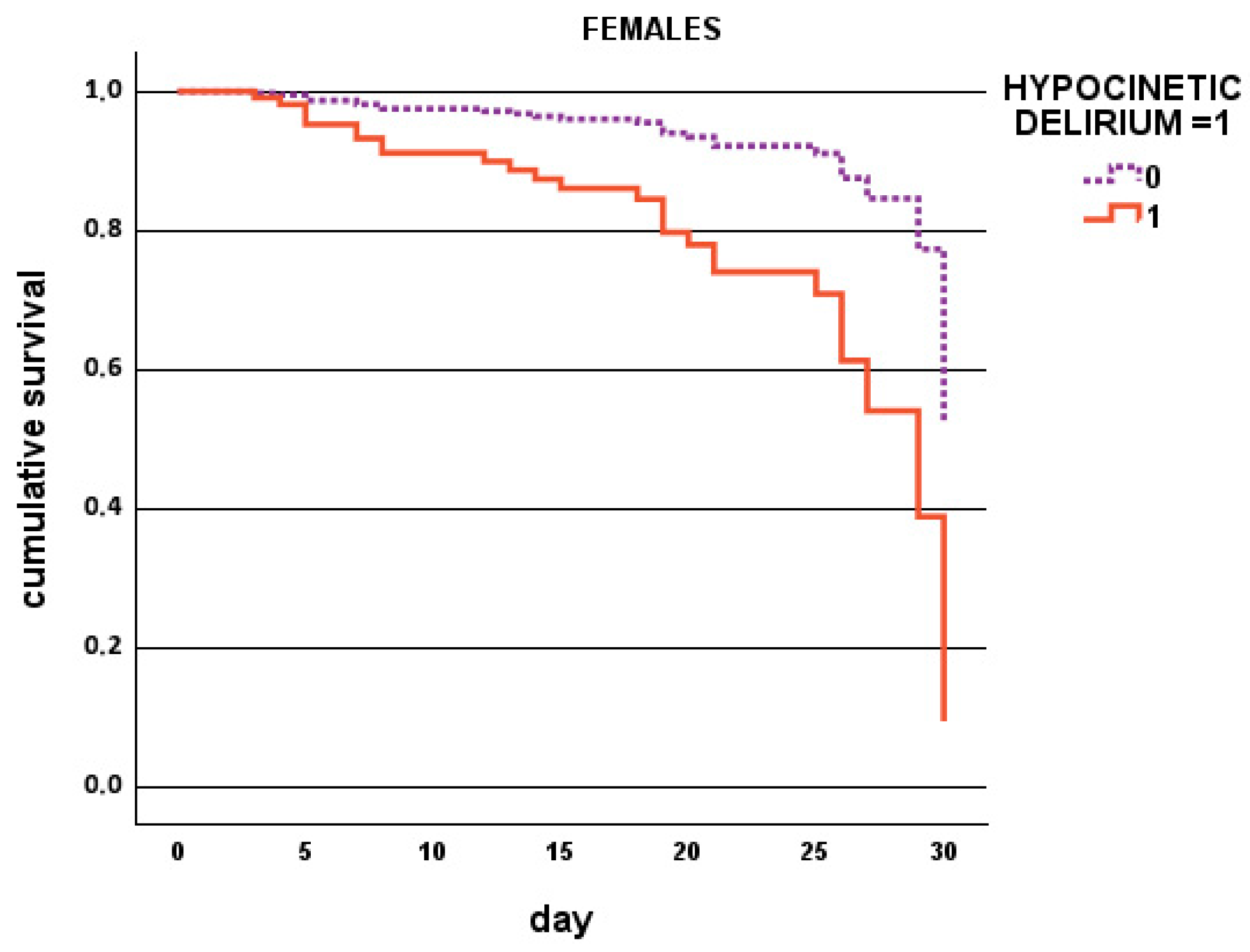
| Parameter | Overall Population N. 556 | Males N. 231 (42%) | Females N. 325 (58%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 85 (80–89) | 83 (78–88) | 86 (80–90) | 0.001 |
| Chronic illnesses, number | 5 (4–7) | 5 (4–7) | 5 (3–7) | 0.195 |
| Drugs, number | 6 (5–9) | 6 (4–8) | 6 (5–9) | 0.696 |
| CFS | 5 (4–6) | 5 (4–6) | 5 (4–6) | 0.285 |
| CFS ≥ 7, % | 19 | 17 | 19 | 0.536 |
| Chronic illnesses | ||||
| Hypertension, % | 70 | 66 | 73 | 0.106 |
| Cardiomyopathy, % | 48 | 49 | 46 | 0.502 |
| Arrythmia, % | 37 | 39 | 35 | 0.266 |
| Anemia, % | 26 | 26 | 26 | 0.871 |
| COPD, % | 30 | 36 | 26 | 0.010 |
| Diabetes, % | 28 | 35 | 22 | <0.001 |
| Obesity, % | 7 | 9 | 6 | 0.201 |
| Dyslipidemia, % | 21 | 24 | 18 | 0.066 |
| Parkinsonism, % | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0.816 |
| Previous stroke, % | 15 | 13 | 16 | 0.251 |
| CKD, % | 16 | 20 | 13 | 0.025 |
| Cancer, % | 26 | 33 | 21 | 0.001 |
| Dementia, % | 30 | 26 | 34 | 0.036 |
| Psychiatric disease, % | 18 | 15 | 20 | 0.168 |
| Peripheral artery disease, % | 30 | 35 | 26 | 0.024 |
| Liver disease, % | 13 | 16 | 10 | 0.015 |
| Gastrointestinal disease, % | 25 | 27 | 24 | 0.383 |
| Osteoporosis, % | 10 | 3 | 15 | <0.001 |
| Arthrosis, % | 25 | 16 | 32 | <0.001 |
| Admission diagnosis | ||||
| Pneumonia, % | 13 | 13 | 13 | 0.781 |
| Infections (urinary, sepsis, other acute infections), % | 9 | 10 | 8 | 0.529 |
| Heart failure, % | 14 | 13 | 15 | 0.728 |
| Syncope, tachyarrhythmia, coronary syndrome, stroke, % | 7 | 7 | 7 | 0.899 |
| COPD, % | 4 | 3 | 5 | 0.166 |
| CKD, % | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.615 |
| Cirrhosis, pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, cholecystitis, diverticulitis, % | 8 | 8 | 7 | 0.858 |
| DVT or lower limb ischemia, % | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.340 |
| Falls with or without fractures, % | 6 | 4 | 7 | 0.146 |
| Overall decay, % | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0.107 |
| Other, % | 36 | 38 | 34 | 0.439 |
| Delirium, % | 21 | 18 | 23 | 0.108 |
| Prevalent delirium, % | 6 | 7 | 5 | 0.318 |
| Delirium incident, % | 18 | 14 | 21 | 0.032 |
| Hyperkinetic delirium, % | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0.995 |
| Mixed delirium | 5 | 3 | 6 | 0.092 |
| Hypokinetic delirium, % | 7 | 5 | 8 | 0.245 |
| Length of hospital stay, day | 15 (8–23) | 15 (7–22) | 16 (8–23) | 0.264 |
| Death, % | 11 | 13 | 10 | 0.305 |
| Survivors N. 495 (89%) | Non-Survivors N. 61 (11%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 85 (79–89) | 86 (80–89) | 0.303 |
| Females, % | 59 | 52 | 0.306 |
| Chronic illnesses, number | 5 (3–7) | 5 (4–7) | 0.708 |
| Drugs, number | 7 (5–9) | 6 (4–8) | 0.027 |
| CFS | 5 (4–6) | 6 (5–7) | <0.001 |
| CFS ≥ 7, % | 16 | 39 | <0.001 |
| CIRS-SI ≥ 3, % | 31 | 55 | <0.001 |
| Chronic illnesses | |||
| Hypertension, % | 71 | 59 | 0.049 |
| Cardiomyopathy, % | 49 | 41 | 0.263 |
| Arrythmia, % | 36 | 41 | 0.469 |
| Anemia, % | 25 | 36 | 0.056 |
| COPD, % | 30 | 31 | 0.900 |
| Diabetes, % | 28 | 21 | 0.260 |
| Obesity, % | 7 | 5 | 0.495 |
| Dyslipidemia, % | 21 | 13 | 0.129 |
| Parkinsonism, % | 9 | 8 | 0.854 |
| Previous stroke, % | 14 | 20 | 0.237 |
| CKD, % | 16 | 16 | 0.968 |
| Cancer, % | 24 | 44 | <0.001 |
| Dementia, % | 29 | 43 | 0.026 |
| Psychiatric disease, % | 18 | 13 | 0.308 |
| Peripheral artery disease, % | 30 | 33 | 0.604 |
| Liver disease, % | 11 | 23 | 0.008 |
| Gastrointestinal disease, % | 25 | 26 | 0.876 |
| Osteoporosis, % | 11 | 7 | 0.332 |
| Arthrosis, % | 26 | 20 | 0.276 |
| Admission diagnosis | |||
| Pneumonia, % | 13 | 11 | 0.745 |
| Infections (urinary, sepsis, other acute infections), % | 9 | 10 | 0.727 |
| Heart failure, % | 15 | 7 | 0.074 |
| Syncope, tachyarrhythmia, coronary syndrome, stroke, % | 7 | 10 | 0.427 |
| COPD, % | 4 | 2 | 0.495 |
| CKD, % | 1 | 3 | 0.259 |
| Cirrhosis, pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, cholecystitis, diverticulitis, % | 8 | 7 | 1.000 |
| DVT or lower limb ischemia, % | 1 | 2 | 1.000 |
| Falls with or without fractures, % | 6 | 0 | 0.038 |
| Overall decay, % | 1 | 3 | 0.174 |
| Other, % | 35 | 46 | 0.083 |
| Delirium, % | 19 | 36 | 0.002 |
| Prevalent delirium, % | 4 | 20 | <0.001 |
| Delirium incident, % | 17 | 28 | 0.034 |
| Hyperkinetic delirium, % | 9 | 8 | 0.780 |
| Hypokinetic delirium, % | 5 | 20 | <0.001 |
| Mixed delirium, % | 4 | 8 | 0.200 |
| Length of hospital stay, day | 15 (8–23) | 15 (7–25) | 0.739 |
| Males N. 230 | Females N. 325 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivors N. 201 (87%) | Non-Survivors N. 29 (13%) | p | Survivors N. 293 (90%) | Non-Survivors N. 32 (10%) | p | |
| Age, years | 83 (78–88) | 85 (81–89) | 0.081 | 86 (80–90) | 86 (80–90) | 0.869 |
| Chronic illnesses, number | 5 (4–7) | 5 (4–7) | 0.667 | 5 (3–7) | 5 (4–7) | 0.847 |
| Drugs, number | 7 (5–9) | 5 (4–6) | 0.020 | 7 (5–9) | 6 (4–8) | 0.365 |
| CFS | 5 (4–6) | 6 (5–7) | <0.001 | 5 (4–6) | 6 (4–7) | 0.026 |
| CFS ≥ 7, % | 13 | 45 | <0.001 | 18 | 34 | 0.024 |
| Anemia, % | 23 | 45 | 0.011 | 26 | 28 | 0.790 |
| Cancer, % | 29 | 59 | 0.002 | 20 | 31 | 0.145 |
| Dementia, % | 22 | 45 | 0.009 | 33 | 41 | 0.395 |
| Liver disease, % | 16 | 21 | 0.520 | 8 | 25 | 0.002 |
| CIRS-LIVER ≥ 2, % | 21 | 38 | 0.036 | 11 | 35 | <0.001 |
| Delirium, % | 16 | 31 | 0.047 | 22 | 41 | 0.015 |
| Prevalent delirium, % | 4 | 28 | <0.001 | 4 | 13 | 0.037 |
| Delirium incident, % | 13 | 17 | 0.582 | 19 | 38 | 0.015 |
| Hypokinetic delirium, % | 3 | 17 | 0.002 | 6 | 22 | 0.001 |
| Delirium Incident N. 85 (73%) | Prevalent Delirium N. 32 (27%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 88 (84–92) | 84 (79–89) | 0.037 |
| Females, % | 71 | 50 | 0.062 |
| CFS | 6 (5–7) | 7 (6–7) | 0.020 |
| CFS ≥ 7, % | 29 | 50 | 0.062 |
| Hyperkinetic delirium, % | 51 | 31 | 0.096 |
| Mixed delirium, % | 21 | 28 | 0.583 |
| Hypokinetic delirium, % | 28 | 41 | 0.288 |
| Death, % | 12 | 38 | 0.004 |
| Death in males, % | 4 | 50 | <0.001 |
| Death in females, % | 15 | 25 | 0.454 |
| Death in patients without hypokinetic delirium, % | 7 | 32 | 0.010 |
| Death in patients with hypokinetic delirium, % | 25 | 46 | 0.200 |
| p | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI for Hazard Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFS ≥ 7, % | 0.003 | 2.258 | 1.319–3.868 |
| Prevalent delirium, % | <0.001 | 4.660 | 2.424–8.957 |
| CIRS-LIVER ≥ 2, % | 0.010 | 2.052 | 1.184–3.555 |
| Cancer, % | 0.026 | 1.835 | 1.073–3.136 |
| p | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI for Hazard Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | |||
| Prevalent delirium, % | <0.001 | 10.227 | 4.253–24.588 |
| Cancer, % | 0.017 | 2.486 | 1.176–5.254 |
| Females | |||
| Hypokinetic delirium, % | 0.003 | 3.672 | 1.556–8.668 |
| CIRS-LIVER ≥ 2, % | 0.008 | 2.745 | 1.302–5.786 |
| p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI for Odds Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFS | 0.003 | 1.350 | 1.107–1.646 |
| Prevalent delirium, % | <0.001 | 5.254 | 2.267–12.177 |
| CIRS-LIVER | 0.007 | 1.337 | 1.082–1.652 |
| CIRS-SI ≥ 3, % | 0.034 | 1.904 | 1.049–3.458 |
| Cancer, % | 0.048 | 1.886 | 1.006–3.536 |
| p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI for Odds Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | |||
| CFS ≥ 7, % | 0.003 | 4.393 | 1.655–11.663 |
| Prevalent delirium, % | 0.003 | 7.073 | 1.968–25.421 |
| Cancer, % | 0.007 | 3.435 | 1.404–8.403 |
| Anemia, % | 0.015 | 3.162 | 1.255–7.966 |
| Females | |||
| CIRS-LIVER | <0.001 | 1.640 | 1.231–2.185 |
| CIRS-SI ≥ 3, % | 0.021 | 2.558 | 1.155–5.667 |
| Hypokinetic delirium, % | 0.001 | 5.328 | 1.921–14.777 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siniscalchi, C.; Di Micco, P.; Guerra, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Cerundolo, N.; Parise, A.; Meschi, T. Clinical and Geriatric Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality in Older Adults Admitted to Internal Medicine Wards: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196726
Siniscalchi C, Di Micco P, Guerra A, Nouvenne A, Cerundolo N, Parise A, Meschi T. Clinical and Geriatric Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality in Older Adults Admitted to Internal Medicine Wards: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196726
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiniscalchi, Carmine, Pierpaolo Di Micco, Angela Guerra, Antonio Nouvenne, Nicoletta Cerundolo, Alberto Parise, and Tiziana Meschi. 2025. "Clinical and Geriatric Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality in Older Adults Admitted to Internal Medicine Wards: A Retrospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196726
APA StyleSiniscalchi, C., Di Micco, P., Guerra, A., Nouvenne, A., Cerundolo, N., Parise, A., & Meschi, T. (2025). Clinical and Geriatric Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality in Older Adults Admitted to Internal Medicine Wards: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196726







