A Nationwide Study on the Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Greece—The PRENEDIG Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Clinical and Demographic Data
2.4. Study Objectives
2.5. Assessment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
2.5.1. Νeuropathy Scores
2.5.2. Monofilament Testing
2.5.3. Biothesiometer Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
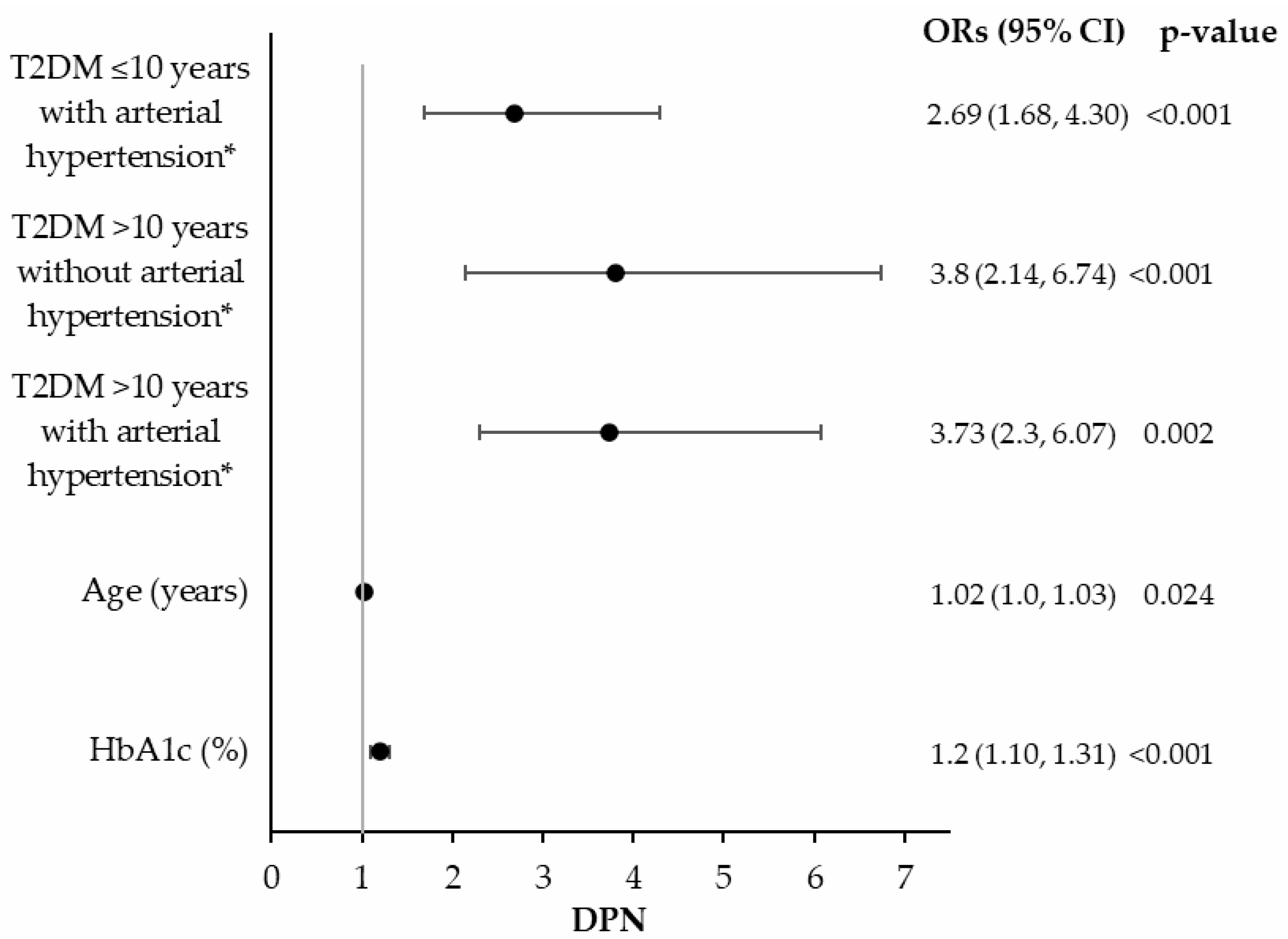
3.2. DPN Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors
3.3. Assessment of Sensory Function
3.3.1. Semmes–Weinstein 5.07 Monofilament Test
3.3.2. Biothesiometer Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PN | Peripheral neuropathy |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| DPN | Diabetic peripheral neuropathy |
| NSS | Neuropathy Symptom Score |
| NDS | Neuropathy Disability Score |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| HES | Health Examination Survey |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| ACR | Albumin-to-creatinine ratio |
| GFR | Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
| Hct | Hematocrit |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| PLT | Platelet count |
| VPT | Vibration perception threshold |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| PAD | Peripheral artery disease |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| MNSI | Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument |
References
- Makrilakis, K.; Kalpourtzi, N.; Ioannidis, I.; Iraklianou, S.; Raptis, A.; Sotiropoulos, A.; Gavana, M.; Vantarakis, A.; Kantzanou, M.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; et al. Prevalence of Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes in Greece. Results of the First National Survey of Morbidity and Risk Factors (EMENO) Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 172, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liatis, S.; Dafoulas, G.E.; Kani, C.; Politi, A.; Litsa, P.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Makrilakis, K. The Prevalence and Treatment Patterns of Diabetes in the Greek Population Based on Real-World Data from the Nation-Wide Prescription Database. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 118, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faka, A.; Ntafla, L.-M.; Chalkias, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Geographical Variation in Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence Rates in Greece. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2023, 19, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 2025, 11th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025.
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) GBD Foresight Visualization; IHME, University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2024.
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) GBD Compare Data Visualization; IHME, University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2024.
- Vollset, S.E.; Ababneh, H.S.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Abbasian, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Magied, A.H.A.A.A.; ElHafeez, S.A.; Abdelkader, A.; et al. Burden of Disease Scenarios for 204 Countries and Territories, 2022–2050: A Forecasting Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2204–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.-S.; Gu, M.-Z.; Zhu, J.-W.; Hu, H.-C.; Yin, L.-P. Current Views of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Comorbid Depression-a Review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10663–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, K.; Fang, M.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Selvin, E.; Hicks, C.W. Etiology, Epidemiology, and Disparities in the Burden of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Lan, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Cao, P. Diabetic Neuropathy: Cutting-Edge Research and Future Directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happich, M.; John, J.; Stamenitis, S.; Clouth, J.; Polnau, D. The Quality of Life and Economic Burden of Neuropathy in Diabetic Patients in Germany in 2002--Results from the Diabetic Microvascular Complications (DIMICO) Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 81, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic Neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, R.; Pan, L. Mechanism of Schwann Cells in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Review. Medicine 2023, 102, e32653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elafros, M.A.; Andersen, H.; Bennett, D.L.; Savelieff, M.G.; Viswanathan, V.; Callaghan, B.C.; Feldman, E.L. Towards Prevention of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Clinical Presentation, Pathogenesis, and New Treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrinelli, F.; Briani, C.; Romano, M.; Ruggero, S.; Toffanin, E.; Triolo, G.; Peter, G.C.; Praitano, M.; Lauriola, M.F.; Zanette, G.; et al. The Association between Serum Cytokines and Damage to Large and Small Nerve Fibers in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 547834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Du, X.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Peng, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1265372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Nave, K.-A.; Jensen, T.S. New Horizons in Diabetic Neuropathy: Mechanisms, Bioenergetics, and Pain. Neuron 2017, 93, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, A.; Giovino, A.; Benny, J.; Martinelli, F. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs): Biochemistry, Signaling, Analytical Methods, and Epigenetic Effects. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3818196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braffett, B.H.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Albers, J.W.; Feldman, E.L.; Martin, C.L.; White, N.H.; Orchard, T.J.; Lopes-Virella, M.; Lachin, J.M.; Pop-Busui, R.; et al. Risk Factors for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, M.E.; Angulo, J.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Diabetes and Ageing-Induced Vascular Inflammation. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2125–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.G.; Estevez, J.J.; Liu, E.; Craig, J.E.; Finnie, J.W. Pericytes, Inflammation, and Diabetic Retinopathy. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Ye, H.; Xiong, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Proinflammatory Cytokines Predict the Incidence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy over 5 Years in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 31, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Past, Present and Future Perspectives. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2021, 122, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Bai, T.; Jia, L. Relationship Between Chronic Inflammatory Indicators and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Hospitalized Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. DMSO 2025, 18, 3075–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.W.; Wang, D.; Daya, N.; Juraschek, S.P.; Matsushita, K.; Windham, B.G.; Selvin, E. The Association of Peripheral Neuropathy Detected by Monofilament Testing with Risk of Falls and Fractures in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2023, 71, 1902–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.M.; Armstrong, D.G.; Kirsner, R.S.; Attinger, C.E.; Lavery, L.A.; Lipsky, B.A.; Mills, J.L.; Steinberg, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Complications; ADA Clinical Compendia Series; American Diabetes Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lazzarini, P.A.; McPhail, S.M.; van Netten, J.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Pacella, R.E. Global Disability Burdens of Diabetes-Related Lower-Extremity Complications in 1990 and 2016. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bönhof, G.J.; Herder, C.; Strom, A.; Papanas, N.; Roden, M.; Ziegler, D. Emerging Biomarkers, Tools, and Treatments for Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 153–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanjee, S.; Das, S.; Das, A.K.; Bhattacharjee, N.; Dihingia, A.; Dua, T.K.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Molecular Mechanism of Diabetic Neuropathy and Its Pharmacotherapeutic Targets. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 833, 472–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.A.; Rumora, A.E.; Beirowski, B.; Bennett, D.L.; Hur, J.; Savelieff, M.G.; Feldman, E.L. New Perspectives in Diabetic Neuropathy. Neuron 2023, 111, 2623–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, M.; Vinik, A.; Simpson, D.M. Pathways in the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2015, 15, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.M. Diabetic Neuropathy and Foot Complications. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 126, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, G.M.; Cavanagh, P.R.; Ulbrecht, J.S.; Gibbons, G.W.; Karchmer, A.W. Assessment and Management of Foot Disease in Patients with Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostev, K.; Jockwig, A.; Hallwachs, A.; Rathmann, W. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Neuropathy in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care Practices: A Retrospective Database Analysis in Germany and U.K. Prim. Care Diabetes 2014, 8, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.P.; Medina, J.L.; Ramos, E.P.; Barros, H.P. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Clinical Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Portuguese Primary Health Care Population. Diabetes Metab. 2001, 27, 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Gregg, E.W.; Gu, Q.; Williams, D.; de Rekeneire, N.; Cheng, Y.J.; Geiss, L.; Engelgau, M. Prevalence of Lower Extremity Diseases Associated with Normal Glucose Levels, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Diabetes among U.S. Adults Aged 40 or Older. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärvestedt, L.; Mårtensson, E.; Grill, V.; Elofsson, S.; von Wendt, G.; Hamsten, A.; Brismar, K. The Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in a Population-Based Study of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Sweden. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2011, 25, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Stevens, L.K.; Stephenson, J.M.; Fuller, J.H.; Plater, M.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Nuber, A.; Pozza, G.; Ward, J.D. Prevalence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Its Relation to Glycaemic Control and Potential Risk Factors: The EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study. Diabetologia 1996, 39, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cerrato, J. The Prevalence of Clinical Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Spain: A Study in Primary Care and Hospital Clinic Groups. Neuropathy Spanish Study Group of the Spanish Diabetes Society (SDS). Diabetologia 1998, 41, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.W.; Selvin, E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; He, H. Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.J.; Boulton, A.J.; MacLeod, A.F.; Williams, D.R.; Sonksen, P.H. A Multicentre Study of the Prevalence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in the United Kingdom Hospital Clinic Population. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Schlösser, F.J.; Sumpio, B.E. The Semmes Weinstein Monofilament Examination as a Screening Tool for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 675–682.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieff, M.G.; Elafros, M.A.; Viswanathan, V.; Jensen, T.S.; Bennett, D.L.; Feldman, E.L. The Global and Regional Burden of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2025, 21, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.S.; Määttä, L.L.; Andersen, S.T.; Charles, M.H. The Epidemiology of Diabetic Neuropathy. In Diabetic Neuropathy: Advances in Pathophysiology and Clinical Management; Tesfaye, S., Gibbons, C.H., Malik, R.A., Veves, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 5–36. ISBN 978-3-031-15612-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pfannkuche, A.; Alhajjar, A.; Ming, A.; Walter, I.; Piehler, C.; Mertens, P.R. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in a Diabetics Cohort: Register Initiative “Diabetes and Nerves”. Endocr. Metab. Sci. 2020, 1, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ashe, H.A.; Parnell, L.N.; Fernando, D.J.; Tsigos, C.; Young, R.J.; Ward, J.D.; Boulton, A.J. The Prevalence of Foot Ulceration and Its Correlates in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Study. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, K.; Bouhassira, D.; De Bacquer, D.; Weiss, S.; Matthys, K.; Raemen, H.; Mathieu, C.; Colin, I.M. Prevalence and Impact on Quality of Life of Peripheral Neuropathy with or without Neuropathic Pain in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetic Patients Attending Hospital Outpatients Clinics. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Brophy, S.; Williams, R.; Taylor, A. The Prevalence, Severity, and Impact of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y. Gold Standard for Diagnosis of DPN. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 719356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovi, J.; Svanborg, E.; Nilsson, B.Y.; Engfeldt, P. Diabetic Neuropathy in Elderly Type 2 Diabetic Patients: Effects of Insulin Treatment. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1998, 98, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; Qiao, X.; Zheng, H.; Lu, B.; Li, Y. Age as an Independent Risk Factor for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, S.; Timar, B.; Baderca, F.; Simu, M.; Diaconu, L.; Velea, I.; Timar, R. Age as an Independent Factor for the Development of Neuropathy in Diabetic Patients. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE. Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: Management (NG28); NICE Guideline; NICE: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-P.; Lin, C.-C.; Li, C.-I.; Liu, C.-S.; Lin, W.-Y.; Hwang, K.-L.; Yang, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Li, T.-C. Cardiovascular Risk Factors Increase the Risks of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Taiwan Diabetes Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Niu, Z.; Hu, F. Study on Risk Factors of Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Establishment of Prediction Model. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, F.; Chen, T.; Wang, X. HbA1c Variability and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, Y.-W.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, I.-T.; Chang, M.-H. Prevalence and Biochemical Risk Factors of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy with or without Neuropathic Pain in Taiwanese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.R.L.; Moran, C.B.M.; Marinho, F.S.; Ferreira, M.T.; Salles, G.F. Increased Aortic Stiffness Predicts Future Development and Progression of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The Rio de Janeiro Type 2 Diabetes Cohort Study. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Yan, S. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Is Associated With Higher Systolic Blood Pressure in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes With and Without Hypertension in the Chinese Han Population. Can. J. Diabetes 2020, 44, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, G.A. Abstract 407: The Association Between Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Peripheral Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, A407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, R.; Pillai, G.S.; Kumar, H.; Shajan, A.T.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Ravindran, G.C. Relationship between Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy-Neurodegenerative and Microvascular Changes. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 3370–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabrdalik, K.; Kwiendacz, H.; Moos, J.; Moos, Ł.; Kulpa, J.; Brzoza, Z.; Stompór, T.; Gumprecht, J.; Lip, G.Y.H. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Is Associated With Diabetic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: The Silesia Diabetes-Heart Project. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdalis, I.N.; Papanas, N.; Raptis, A.E.; Ioannidis, I.M.; Sotiropoulos, A.E.; Dimitriadis, G.D.; Hellenic Diabetic Nephropathy Study (HDNS) Group. The Prevalence of Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease in Adult Greek Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Series from Hospital-Based Diabetes Clinics. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 166, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Chen, B.-X.; Chen, Z.; Wan, Q. Correlation Study of Renal Function Indices with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Diabetic Retinopathy in T2DM Patients with Normal Renal Function. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1302615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, C.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-M.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-L.; Wang, I.-J. Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: Development and Progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, R.; Pianta, T.J.; Issar, T.; Kirby, A.; Scales, C.M.K.; Kwai, N.C.G.; Endre, Z.; Krishnan, A.V. Peripheral Neuropathy: An Important Contributor to Physical Limitation and Morbidity in Stages 3 and 4 Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ji, Q.; Ran, X.; Li, C.; Kuang, H.; Yu, X.; Fang, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study in China. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2023, 39, e3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Phoon, R.K.S.; Pussell, B.A.; Charlesworth, J.A.; Bostock, H.; Kiernan, M.C. Altered Motor Nerve Excitability in End-Stage Kidney Disease. Brain 2005, 128, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.; Pussell, B.A.; Howells, J.; Grinius, V.; Kiernan, M.C.; Lin, C.S.-Y.; Krishnan, A.V. Evidence for a Causal Relationship between Hyperkalaemia and Axonal Dysfunction in End-Stage Kidney Disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, R.; Pianta, T.J.; Pussell, B.A.; Kirby, A.; O’Brien, K.; Sullivan, K.; Holyday, M.; Cormack, C.; Kiernan, M.C.; Krishnan, A.V. Randomized, Controlled Trial of the Effect of Dietary Potassium Restriction on Nerve Function in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalliedde, J.; Gnudi, L. Diabetes Mellitus, a Complex and Heterogeneous Disease, and the Role of Insulin Resistance as a Determinant of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Armstrong, D.G.; Harvey, C.; Harkless, L.B.; Giurini, J.M.; Veves, A. Screening Techniques to Identify People at High Risk for Diabetic Foot Ulceration: A Prospective Multicenter Trial. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, E.J.; Ahroni, J.H.; Stensel, V.; Forsberg, R.C.; Davignon, D.R.; Smith, D.G. A Prospective Study of Risk Factors for Diabetic Foot Ulcer. The Seattle Diabetic Foot Study. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Lavery, L.A.; Pham, H.; Harvey, C.; Harkless, L.; Veves, A. Role of Neuropathy and High Foot Pressures in Diabetic Foot Ulceration. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, M.; Sierra, O.R.; Saavedra, G.; Moreno, S. Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Diabetic Neuropathy in Patients Taking Metformin: A Cross-Sectional Study. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, R.C.; Goodbred, A.J. Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Recognition and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- NHS. NHS-Guidelines for the Investigation & Management of Vitamin B12 Deficiency; NHS: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher, E.; Didangelos, T.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Cegan, A.; Peter, A.; Kantartzis, K. Clinical Pathobiochemistry of Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Improving Our Understanding by Exploring Novel Mechanisms with a Focus on Diabetic Neuropathy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didangelos, T.; Karlafti, E.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Margariti, E.; Giannoulaki, P.; Batanis, G.; Tesfaye, S.; Kantartzis, K. Vitamin B12 Supplementation in Diabetic Neuropathy: A 1-Year, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwak, L.; Goh, S.-Y.; Hussein, Z.; Malek, R.; Prusty, V.; Khamseh, M.E. Prevalence of Diabetes Complications in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Association with Baseline Characteristics in the Multinational A1chieve Study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.; Reid, K.; Duclos, C.; Mai, A.; Odoi, A. Investigation of Predictors of Severity of Diabetes Complications among Hospitalized Patients with Diabetes in Florida, 2016–2019. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masupe, T.; De Man, J.; Onagbiye, S.; Puoane, T.; Delobelle, P. Prevalence of Disease Complications and Risk Factor Monitoring amongst Diabetes and Hypertension Patients Attending Chronic Disease Management Programmes in a South African Township. Afr. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med. 2021, 13, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Class | Total, n = 1807 | T2DM Patients with DPN, n = 341 | T2DM Patients Without DPN, n = 1466 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | (males), n (%) | 1001 (55.40%) | 194 (56.89%) | 807 (55.05%) |
| (females), n (%) | 806 (44.60%) | 147 (43.11%) | 659 (44.95%) | |
| Age * | (years) mean (SD) | 65.26 (10.390) | 68.02 (10.304) | 64.62 (10.308) |
| (years), n (%) | ||||
| <50 | 131 (7.25%) | 18 (5.28%) | 113 (7.71%) | |
| 50–59 | 379 (20.97%) | 54 (15.84%) | 325 (22.17%) | |
| 60–69 | 659 (36.47%) | 121 (35.48%) | 538 (36.70%) | |
| 70–79 | 507 (28.06%) | 104 (30.50%) | 403 (27.49%) | |
| ≥80 | 131 (7.25%) | 44 (12.90%) | 87 (5.93%) | |
| Anthropometric characteristics | Weight (kg) | 86.67 (19.133) | 85.98 (19.341) | 86.83 (19.088) |
| BMI (kg/m2) mean (SD) | 30.67 (6.088) | 30.45 (5.617) | 30.72 (6.194) | |
| Overweight (BMI:25–29,9), n (%) | 681 (37.69%) | 125 (36.66%) | 556 (37.95%) | |
| Obese (BMI ≥ 30), n (%) | 866 (47.92%) | 163 (47.80%) | 703 (47.99%) | |
| Smoking, n (%) | Never | 986 (54.57%) | 183 (53.67%) | 803 (54.77%) |
| Former | 485 (26.84%) | 98 (28.74%) | 387 (26.40%) | |
| Current | 336 (18.59%) | 60 (17.60%) | 276 (18.83%) | |
| Diabetes duration, n (%) * | <5 years | 585 (32.37%) | 61 (17.89%) | 524 (35.74%) |
| 5–10 years | 516 (28.56%) | 93 (27.27%) | 423 (28.85%) | |
| >10 years | 706 (39.07%) | 187 (54.84%) | 519 (35.40%) | |
| Comorbidities | Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 1545 (85.50%) | 297 (87.87%) | 1248 (85.36%) |
| Heart failure, n (%) * | 115 (6.36%) | 37 (11.49%) | 78 (5.62%) | |
| Foot ulcers, n (%) * | 78 (4.32%) | 48 (14.08%) | 30 (2.05%) | |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) * | 1292 (71.50%) | 279 (81.82%) | 1013 (69.72%) | |
| Macrovascular complications | Coronary artery disease, n (%) * | 350 (19.37%) | 79 (24.09%) | 271 (18.90%) |
| Peripheral arterial disease, n (%) * | 115 (6.36%) | 52 (16.94%) | 63 (4.73%) | |
| Cerebrovascular events, n (%) | 94 (5.20%) | 21 (6.23%) | 73 (5.00%) | |
| Microvascular complications | Retinopathy, n (%) * | 164 (9.08%) | 76 (30.52%) | 88 (7.18%) |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) * | 268 (14.83%) | 90 (26.87%) | 178 (12.43%) | |
| Laboratory test results | Total cholesterol (mg/dL) mean (SD) | 157.91 (40.368) | 157.08 (43.256) | 158.10 (39.680) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) mean (SD) | 140.01 (73.296) | 142.21 (74.900) | 139.50 (72.938) | |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) mean (SD) | 83.69 (34.975) | 83.95 (38.612) | 83.62 (34.089) | |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) mean (SD) | 46.59 (11.938) | 45.90 (11.397) | 46.75 (12.058) | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) mean (SD) | 132.94 (43.149) | 137.57 (54.812) | 131.84 (39.849) | |
| HbA1c (%) mean (SD) * | 6.95 (1.340) | 7.26 (1.607) | 6.87 (1.258) | |
| Urea (mg/dL) mean (SD)* | 39.82 (16.027) | 43.80 (19.273) | 38.88 (15.008) | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) mean (SD) * | 0.92 (0.349) | 0.98 (0.427) | 0.91 (0.326) | |
| WBC (103/L) mean (SD) | 7663.68 (1958.057) | 7718.39 (2023.456) | 7650.63 (1942.643) | |
| WBC differential count (%) mean (SD) * | 51.53 (20.028) | 49.08 (22.658) | 52.11 (19.315) | |
| Hct (%) mean (SD) * | 41.90 (4.268) | 41.05 (4.602) | 42.11 (4.160) | |
| Hb (g/dL) mean (SD) * | 13.75 (1.556) | 13.50 (1.787) | 13.82 (1.488) | |
| PLT (103/L) mean (SD) | 247,337.30 (63,784.816) | 249,642.86 (67,737.075) | 246,794.22 (62,831.376) | |
| Vitamin B12 (pg/mL) mean (SD) * | 365.56 (149.275) | 387.68 (164.229) | 360.55 (145.282) | |
| ACR (mg/g) mean (SD) * | 65.12 (246.191) | 140.02 (434.844) | 48.09 (173.094) |
| Total, n = 1700 | T2DM < 5 Years, n = 552 | T2DM 5–10 Years, n = 489 | T2DM > 10 Years, n = 659 | T2DM Patients with DPN, n = 318 | T2DM Patients Without DPN, n = 1382 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of protective sensation, n (%) | ||||||
| Yes | 260 (15.29%) | 48 (8.70%) | 69 (14.11%) | 143 (21.70%) | 176 (55.35%) | 84 (6.08%) |
| No | 1440 (84.71%) | 504 (91.30%) | 420 (85.89%) | 516 (78.30%) | 142 (44.65%) | 1298 (93.92%) |
| Total, n = 629 | T2DM < 5 Years, n = 183 | T2DM 5–10 Years, n = 171 | T2DM > 10 years, n = 275 | T2DM Patients with DPN, n = 125 | T2DM Patients Without DPN, n = 504 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPT (volts) mean (SD) | ||||||
| Right toe | 16.72 (10.613) | 13.63 (7.595) | 17.38 (12.011) | 18.36 (11.001) | 26.59 (13.744) | 14.27 (7.990) |
| Left toe | 16.92 (10.693) | 14.33 (8.392) | 17.59 (12.369) | 18.24 (10.672) | 26.93 (13.760) | 14.44 (8.066) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Migdalis, I.N.; Tentolouris, N.K.; Didangelos, T.P.; Papanas, N.; Bristianou, M.X.; Mavrogiannaki, A.N.; on behalf of the PRENEDIG Study. A Nationwide Study on the Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Greece—The PRENEDIG Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196723
Migdalis IN, Tentolouris NK, Didangelos TP, Papanas N, Bristianou MX, Mavrogiannaki AN, on behalf of the PRENEDIG Study. A Nationwide Study on the Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Greece—The PRENEDIG Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196723
Chicago/Turabian StyleMigdalis, Ilias N., Nikolaos K. Tentolouris, Triantafyllos P. Didangelos, Nikolaos Papanas, Magdalini X. Bristianou, Anastasia N. Mavrogiannaki, and on behalf of the PRENEDIG Study. 2025. "A Nationwide Study on the Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Greece—The PRENEDIG Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196723
APA StyleMigdalis, I. N., Tentolouris, N. K., Didangelos, T. P., Papanas, N., Bristianou, M. X., Mavrogiannaki, A. N., & on behalf of the PRENEDIG Study. (2025). A Nationwide Study on the Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Greece—The PRENEDIG Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6723. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196723








