The Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
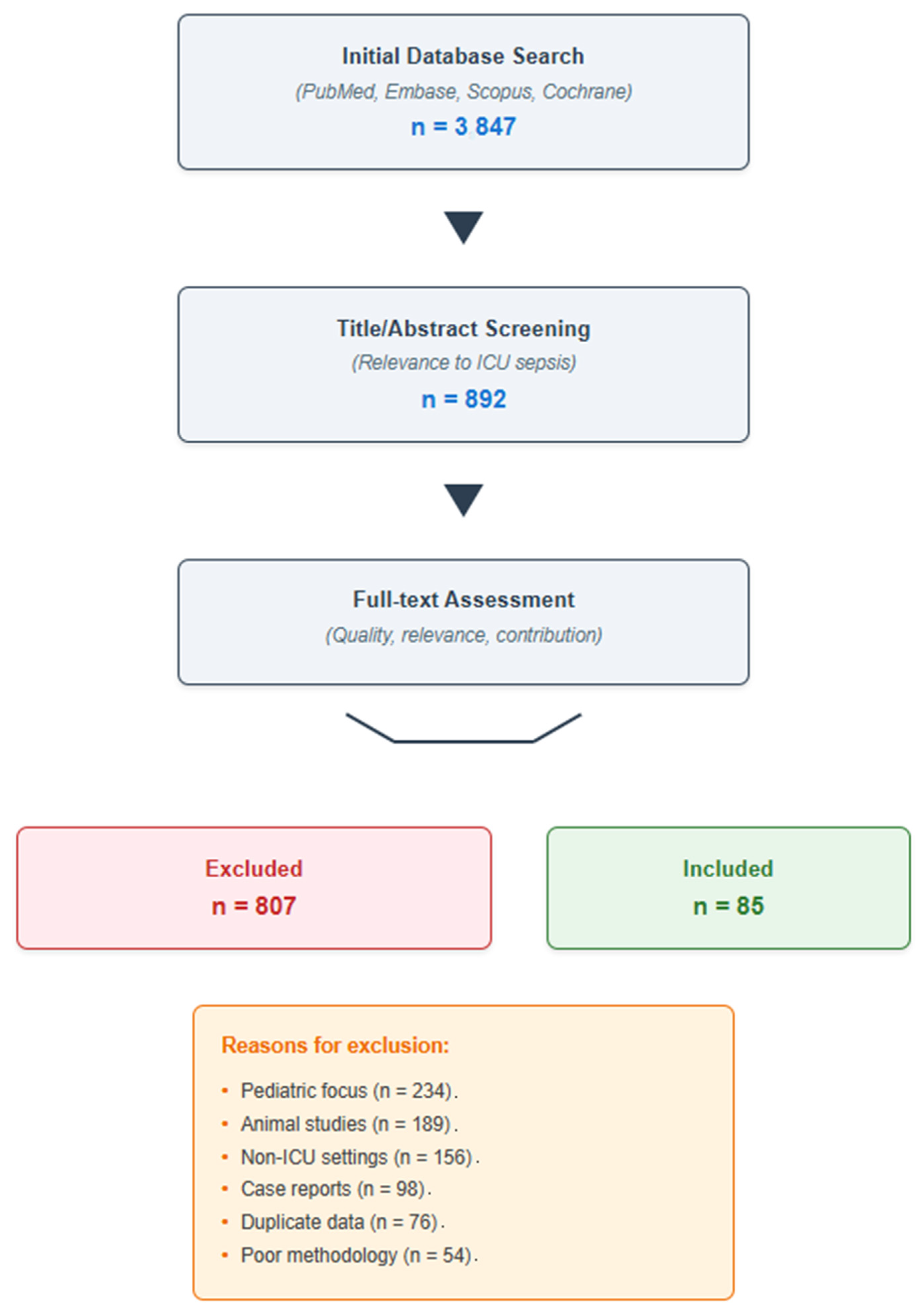
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Literature Selection Process
3. Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock in the ICU: Incidence, Prevalence, and Outcomes
4. Pathophysiology and Clinical Spectrum
5. Diagnostic Challenges and Biomarkers in ICU Sepsis
5.1. Bedside Assessment, Laboratory, and Imaging
5.2. Role of Microbiological Diagnosis and Emerging Biomarkers
5.3. Point-of-Care and AI-Driven Tools
6. Advanced Management Strategies for Sepsis and Septic Shock in the ICU
6.1. Early Resuscitation and Hemodynamic Optimization
6.2. Antimicrobial Therapy: Timing, Spectrum, and Stewardship
6.3. Source Control and Adjunctive Therapies
6.4. Mechanical Ventilation, Organ Support, and Immunomodulation
6.5. Blood Purification and Hemoperfusion Therapies: Evidence and Patient Selection
6.6. Bundled Care and Systems-Level Implementation
7. Long-Term Outcomes and Post-Intensive Care Sequelae in Sepsis Survivors
7.1. Mortality and Physical Sequelae
7.2. Cognitive Impairment and Psychological Impact
7.3. Post-Sepsis Syndrome and Immunological Legacy
7.4. Socioeconomic Burden and Follow-Up Strategies
7.5. Research Gaps and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CU | Intensive Care Unit |
| PICS | Post-Intensive Care Syndrome |
| MR-proADM | Mid-Regional Pro-Adrenomedullin |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| GBD | Global Burden of Disease |
| LMICs | Low- and Middle-Income Countries |
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| MODS | Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| PRRs | Pattern Recognition Receptors |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor κB |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| qSOFA | Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| NEWS | National Early Warning Score |
| MEWS | Modified Early Warning Score |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| PET-CT | Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PCT | Procalcitonin |
| sTREM-1 | Soluble Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 |
| POCT | Point-Of-Care Testing |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| SSC | Surviving Sepsis Campaign |
| MAP | Mean Arterial Pressure |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| RR | Respiratory Rate |
| WBC | White Blood Cell |
| IVIG | Intravenous Immunoglobulin |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| RRT | Renal Replacement Therapy |
| CRRT | Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death-1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 |
| CIP | Critical Illness Polyneuropathy |
| CIM | Critical Illness Myopathy |
| PTSD | Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Mellhammar, L.; Rose, N.; Cassini, A.; Rudd, K.E.; Schlattmann, P.; Allegranzi, B.; Reinhart, K. Incidence and mortality of hospital- and ICU-treated sepsis: Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, K.; Daniels, R.; Kissoon, N.; Machado, F.R.; Schachter, R.D.; Finfer, S. Recognizing Sepsis as a Global Health Priority—A WHO Resolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, C.; Bouadma, L.; Ruckly, S.; Perozziello, A.; Van-Gysel, D.; Mageau, A.; Mourvillier, B.; de Montmollin, E.; Bailly, S.; Papin, G.; et al. Sepsis and septic shock in France: Incidences, outcomes and cost-of-care. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Maniaci, A.; Lentini, M.; Ronsivalle, S.; Nunnari, G.; Cocuzza, S.; Parisi, F.M.; Cacopardo, B.; Lavalle, S.; La Via, L. The Global Burden of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Epidemiologia 2025, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Lower Respiratory Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality burden of non-COVID-19 lower respiratory infections and aetiologies, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 974–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Via, L.; Sangiorgio, G.; Stefani, S.; Marino, A.; Nunnari, G.; Cocuzza, S.; La Mantia, I.; Cacopardo, B.; Stracquadanio, S.; Spampinato, S.; et al. The Global Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K.; International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Jones, G.; David, S.; Olariu, E.; Cadwell, K.K. Frequency and mortality of septic shock in Europe and North America: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y.; Sprung, C.L.; Ranieri, V.M.; Reinhart, K.; Gerlach, H.; Moreno, R.; Carlet, J.; Le Gall, J.R.; Payen, D.; et al. Sepsis in European intensive care units: Results of the SOAP study. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia between 2009 and 2019—Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucelić, V.; Klobučar, I.; Đuras-Cuculić, B.; Gverić Grginić, A.; Prohaska-Potočnik, C.; Jajić, I.; Vučičević, Ž.; Degoricija, V. Sepsis and septic shock—An observational study of the incidence, management, and mortality predictors in a medical intensive care unit. Croat. Med. J. 2020, 61, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, C.J.; Reynolds, M.A.; Sinha, M.; Gitlin, M.; Crouser, E. Epidemiology and Costs of Sepsis in the United States-An Analysis Based on Timing of Diagnosis and Severity Level. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarczak, D.; Kluge, S.; Nierhaus, A. Sepsis—Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Concepts. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis 3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakihana, Y.; Ito, T.; Nakahara, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yasuda, T. Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction: Pathophysiology and therapeutic approaches. J. Intensive Care 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markwart, R.; Saito, H.; Harder, T.; Tomczyk, S.; Cassini, A.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Reichert, F.; Eckmanns, T.; Allegranzi, B. Epidemiology and burden of sepsis acquired in hospitals and intensive care units: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1536–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annane, D.; Bellissant, E.; Cavaillon, J.M. Septic shock. Lancet 2005, 365, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Roberts, D.; Wood, K.E.; Light, B.; Parrillo, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Suppes, R.; Feinstein, D.; Zanotti, S.; Taiberg, L.; et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Liu, V.X.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Rea, T.D.; Scherag, A.; Rubenfeld, G.; Kahn, J.M.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Singer, M.; et al. Assessment of Clinical Criteria for Sepsis: For the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Lemachatti, N.; Krastinova, E.; Van Laer, M.; Claessens, Y.E.; Avondo, A.; Occelli, C.; Feral-Pierssens, A.L.; Truchot, J.; Ortega, M.; et al. Prognostic Accuracy of Sepsis-3 Criteria for In-Hospital Mortality Among Patients with Suspected Infection Presenting to the Emergency Department. JAMA 2017, 317, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.B.; Prytherch, D.R.; Meredith, P.; Schmidt, P.E.; Featherstone, P.I. The ability of the National Early Warning Score (NEWS) to discriminate patients at risk of early cardiac arrest, unanticipated ICU admission, and death. Resuscitation 2013, 84, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povoa, P. C-reactive protein: A valuable marker of sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2002, 28, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, J.A.; Madias, N.E. Lactic Acidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Rello, J.; Marshall, J.; Silva, E.; Anzueto, A.; Martin, C.D.; Moreno, R.; Lipman, J.; Gomersall, C.; Sakr, Y.; et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA 2009, 302, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, S.; Carroll, K.C. Laboratory detection of sepsis: Biomarkers and molecular approaches. Clin. Lab. Med. 2013, 33, 413–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, P.; Beishuizen, A.; Broyles, M.; Ferrer, R.; Gavazzi, G.; Gluck, E.H.; González Del Castillo, J.; Jensen, J.U.; Kanizsai, P.L.; Kwa, A.L.H.; et al. Procalcitonin (PCT)-guided antibiotic stewardship: An international experts consensus on optimized clinical use. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.; van Oers, J.A.; Beishuizen, A.; Vos, P.; Vermeijden, W.J.; Haas, L.E.; Loef, B.G.; Dormans, T.; van Melsen, G.C.; Kluiters, Y.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing antibiotic exposure in intensive care patients with sepsis: A randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, C.; Pang, S. The diagnostic accuracy of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin for sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021, 87, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, G.; Shozushima, T.; Ishikura, H.; Murai, A.; Nishida, T.; Irie, Y.; Miura, M.; Iguchi, H.; et al. Usefulness of presepsin in the diagnosis of sepsis in a multicenter prospective study. J. Infect. Chemother. 2012, 18, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Hur, M.; Yi, A.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.N. Prognostic value of presepsin in adult patients with sepsis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Song, J.; Park, D.W.; Seok, H.; Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Cho, H.J.; Moon, S. Diagnostic and prognostic value of presepsin and procalcitonin in non-infectious organ failure, sepsis, and septic shock: A prospective observational study according to the Sepsis-3 definitions. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, E.A.; O’Kane, C.M.; McAuley, D.F. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults: Diagnosis, outcomes, long-term sequelae, and management. Lancet 2022, 400, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, E.E.; Burnham, K.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Humburg, P.; Hutton, P.; Mills, T.C.; Rautanen, A.; Gordon, A.C.; Garrard, C.; Hill, A.V.S.; et al. Genomic landscape of the individual host response and outcomes in sepsis: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teggert, A.; Datta, H.; Ali, Z. Biomarkers for Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Sepsis. Micromachines 2020, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, S.; Holder, A.; Razmi, F.; Stanley, M.D.; Clifford, G.D.; Buchman, T.G. An Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Accurate Prediction of Sepsis in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wyk, F.; Khojandi, A.; Kamaleswaran, R. How much does it help? Machine learning prediction of sepsis in the ICU does not improve patient outcomes—A randomized controlled trial. J. Crit. Care 2024, 79, 154400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Alsaawi, A.; Alzahrani, M.; Al Khathaami, A.M.; AlHazme, R.H.; Al Mutrafy, A.; Al Qarni, A.; Vishwakarma, R.K.; Al Anazi, R.; Al Qasim, E.; et al. Electronic Sepsis Screening Among Patients Admitted to Hospital Wards: A Stepped-Wedge Cluster Randomized Trial. JAMA 2025, 333, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, K.E.; Hager, D.N.; Pronovost, P.J.; Saria, S. A targeted real-time early warning score (TREWScore) for septic shock. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 299ra122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Henry, K.E.; Sridharan, A.; Soleimani, H.; Zhan, A.; Rawat, N.; Johnson, L.; Hager, D.N.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Markowski, A.; et al. Prospective, multi-site study of patient outcomes after implementation of the TREWS machine learning-based early warning system for sepsis. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisman, D.E.; Harhay, M.O. Imperfect World, Imperfect Trials, and Overestimated Treatment Effects in Sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Lavalle, S.; Gagliano, C.; Lentini, M.; Masiello, E.; Parisi, F.; Iannella, G.; Cilia, N.D.; Salerno, V.; Cusumano, G.; et al. The Integration of Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence in Modern Medicine. Life 2024, 14, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotts, J.E.; Matthay, M.A. Sepsis: Pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ 2016, 353, i1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Prevention and Early Treatment of Acute Lung Injury Clinical Trials Network; Shapiro, N.I.; Douglas, I.S.; Brower, R.G.; Brown, S.M.; Exline, M.C.; Ginde, A.A.; Gong, M.N.; Grissom, C.K.; Hayden, D.; et al. Early Restrictive or Liberal Fluid Management for Sepsis-Induced Hypotension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyhoff, T.S.; Hjortrup, P.B.; Wetterslev, J.; Sivapalan, P.; Laake, J.H.; Cronhjort, M.; Jakob, S.M.; Cecconi, M.; Nalos, M.; Ostermann, M.; et al. Restriction of Intravenous Fluid in ICU Patients with Septic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrain, M.L.N.G.; Van Regenmortel, N.; Saugel, B.; De Tavernier, B.; Van Gaal, P.-J.; Joannes-Boyau, O.; Teboul, J.-L.; Rice, T.W.; Mythen, M.; Monnet, X. Principles of fluid management and stewardship in septic shock: It is time to consider the four D’s and the four phases of fluid therapy. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanfilippo, F.; La Via, L.; Dezio, V.; Santonocito, C.; Amelio, P.; Genoese, G.; Astuto, M.; Noto, A. Assessment of the inferior vena cava collapsibility from subcostal and trans-hepatic imaging using both M-mode or artificial intelligence: A prospective study on healthy volunteers. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2023, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D. FALLS-protocol: Lung ultrasound in hemodynamic assessment of shock. Heart Lung Vessel. 2013, 5, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Semler, M.W.; Self, W.H.; Wanderer, J.P.; SMART Investigators and the Pragmatic Critical Care Research Group. Balanced Crystalloids versus Saline in Critically Ill Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Via, L.; Vasile, F.; Perna, F.; Zawadka, M. Prediction of fluid responsiveness in critical care: Current evidence and future perspective. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 2024, 54, 101–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan, E.; Ospina-Tascón, G.A.; Teboul, J.-L.; Castro, R.; Cecconi, M.; Ferri, G.; Bakker, J.; Hernández, G.; ANDROMEDA-SHOCK Investigators. Systematic assessment of fluid responsiveness during early septic shock resuscitation: Secondary analysis of the ANDROMEDA-SHOCK trial. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon Hidalgo, D.; Patel, J.; Masic, D.; Park, D.; Rech, M.A. Delayed vasopressor initiation is associated with increased mortality in patients with septic shock. J. Crit. Care 2020, 55, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATHOS-3 Investigators; Khanna, A.; English, S.W.; Wang, X.S.; Ham, K.; Tumlin, J.; Szerlip, H.; Busse, L.W.; Altaweel, L.; Albertson, T.E.; et al. Angiotensin II for the Treatment of Vasodilatory Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, S.A.; Miller, W.R.; Pryor, J.; Puskarich, M.A.; Jones, A.E. The impact of timing of antibiotics on outcomes in severe sepsis and septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Augello, E.; Bellanca, C.M.; Cosentino, F.; Stracquadanio, S.; La Via, L.; Maniaci, A.; Spampinato, S.; Fadda, P.; Cantarella, G.; et al. Antibiotic Therapy Duration for Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections: An Evidence-Based Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.; Bechis, C.; Baumstarck, K.; Lefrant, J.-Y.; Albanèse, J.; Jaber, S.; Lepape, A.; Constantin, J.-M.; Papazian, L.; Bruder, N.; et al. De-escalation versus continuation of empirical antimicrobial treatment in severe sepsis: A multicenter non-blinded randomized noninferiority trial. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Waele, J.J.; Girardis, M.; Martin-Loeches, I. Source control in the management of sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annane, D.; Renault, A.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Megarbane, B.; Quenot, J.-P.; Siami, S.; Cariou, A.; Forceville, X.; Schwebel, C.; Martin, C.; et al. Hydrocortisone plus fludrocortisone for adults with septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmelé, T.; Kellum, J.A. Clinical review: Blood purification for sepsis. Crit. Care 2011, 15, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar-Hari, M.; Spencer, J.; Sewell, W.A.; Rowan, K.M.; Singer, M. Bench-to-bedside review: Immunoglobulin therapy for sepsis—Biological plausibility, current evidence and future directions. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, E.; Del Sorbo, L.; Goligher, E.C.; Hodgson, C.L.; Munshi, L.; Walkey, A.J.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Amato, M.B.P.; Branson, R.; Brower, R.G.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Society of Intensive Care Medicine/Society of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline: Mechanical Ventilation in Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, C.; Reignier, J.; Richard, J.-C.; Beuret, P.; Gacouin, A.; Boulain, T.; Mercier, E.; Badet, M.; Mercat, A.; Baudin, O.; et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudry, S.; Hajage, D.; Schortgen, F.; Martin-Lefevre, L.; Pons, B.; Boulet, E.; Boyer, A.; Chevrel, G.; Lerolle, N.; Carpentier, D.; et al. Initiation strategies for renal-replacement therapy in the intensive care unit. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttone, G.; La Via, L.; Misseri, G.; Martucci, G.; Sorbello, M.; Patroniti, N.; Pappalardo, F. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in the Awake or Extubated Patient. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2025, 39, 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, L.A.; Stewart, D.J.; Mei, S.H.; Courtman, D.; Watpool, I.; Granton, J.; Marshall, J.; Dos Santos, C.; Walley, K.R.; Winston, B.W.; et al. Cellular immunotherapy for septic shock: A phase I clinical trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.N.; Antonelli, M.; Fumagalli, R.; Foltran, F.; Brienza, N.; Donati, A.; Malcangi, V.; Petrini, F.; Volta, G.; Bobbio Pallavicini, F.M.; et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: The EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Antonelli, M.; Foster, D.M.; Klein, D.J.; Marshall, J.C.; Palevsky, P.M.; Weisberg, L.S.; Schorr, C.A.; Trzeciak, S.; et al. Effect of Targeted Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion on 28-Day Mortality in Patients with Septic Shock and Elevated Endotoxin Level: The EUPHRATES Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.J.; Foster, D.; Walker, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Mekonnen, H.; Antonelli, M. Polymyxin B hemoperfusion in endotoxemic septic shock patients without extreme endotoxemia: A post hoc analysis of the EUPHRATES trial. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlot, G.; Scamperle, A.; Istrati, T. Kinetics of Cytokines during Septic Shock Patients Treated with LPS Adsorption or CytoSorb. Shock 2023, 59, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schädler, D.; Pausch, C.; Heise, D.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Brederlau, J.; Weiler, N.; Marx, G.; Putensen, C.; Spies, C.; Jörres, A.; et al. The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzu, A.; Schorer, R.; Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Cassina, T.; Landoni, G. Blood Purification and Mortality in Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Gesten, F.C.; Phillips, G.S.; Terry, K.M.; Seymour, C.W.; Prescott, H.C.; Friedrich, M.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Osborn, T.; Lemeshow, S. Mortality changes associated with mandated public reporting for sepsis. JAMA 2018, 320, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Kaukonen, K.M.; Bailey, M.; Suzuki, S.; Pilcher, D.; Bellomo, R. Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000–2012. JAMA 2014, 311, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.E.; Curtis, J.R.; Mulkerin, C.; Campbell, M.; Lustbader, D.R.; Mosenthal, A.C.; Puntillo, K.; Ray, D.E.; Bassett, R.; Boss, R.D.; et al. Choosing and using screening criteria for palliative care consultation in the ICU: A report from the Improving Palliative Care in the ICU (IPAL-ICU) Advisory Board. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.M.; Davidson, J.; Cohen, H.; Hopkins, R.O.; Weinert, C.; Wunsch, H.; Zawistowski, C.; Bemis-Dougherty, A.; Berney, S.C.; Bienvenu, O.J.; et al. Improving long-term outcomes after discharge from intensive care unit: Report from a stakeholders’ conference. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Osterholzer, J.J.; Langa, K.M.; Angus, D.C.; Iwashyna, T.J. Late mortality after sepsis: Propensity matched cohort study. BMJ 2016, 353, i2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.S.; Park, S.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Hyun, I.G. Mortality and Prognostic Prediction in Very Elderly Patients with Severe Pneumonia. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Moldawer, L.L.; Opal, S.M.; Reinhart, K.; Turnbull, I.R.; Vincent, J.L. Sepsis and septic shock. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latronico, N.; Bolton, C.F. Critical illness polyneuropathy and myopathy: A major cause of muscle weakness and paralysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthucheary, Z.A.; Rawal, J.; McPhail, M.; Connolly, B.; Ratnayake, G.; Chan, P.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Phadke, R.; Dew, T.; Sidhu, P.S.; et al. Acute skeletal muscle wasting in critical illness. JAMA 2013, 310, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, M.S.; Tansey, C.M.; Matté, A.; Tomlinson, G.; Diaz-Granados, N.; Cooper, A.; Guest, C.B.; Mazer, C.D.; Mehta, S.; Stewart, T.E.; et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Morandi, A.; Thompson, J.L.; Pun, B.T.; Brummel, N.E.; Hughes, C.G.; Vasilevskis, E.E.; Shintani, A.K.; et al. Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashyna, T.J.; Ely, E.W.; Smith, D.M.; Langa, K.M. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA 2010, 304, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, A.; Widmann, C.N.; Okulla, T.; Urbach, H.; Kaiser, M.; Widman, G.; Mormann, F.; Weide, J.; Fliessbach, K.; Hoeft, A.; et al. Persistent cognitive impairment, hippocampal atrophy and EEG changes in sepsis survivors. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.M.; Sricharoenchai, T.; Raparla, S.; Schneck, K.W.; Bienvenu, O.J.; Needham, D.M. Posttraumatic stress disorder in critical illness survivors: A meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydow, D.S.; Gifford, J.M.; Desai, S.V.; Bienvenu, O.J.; Needham, D.M. Depression in general intensive care unit survivors: A systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venet, F.; Monneret, G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldás, I.; Menéndez, R.; Méndez, R.; España, P.P.; Almirall, J.; Boderías, L.; Rajas, O.; Zalacaín, R.; Vendrell, M.; Mir, I.; et al. Early and Late Cardiovascular Events in Patients Hospitalized for Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.D.; Fowler, R.A.; Pinto, R.; Herridge, M.S.; Cuthbertson, B.H.; Scales, D.C. Long-term outcomes and healthcare utilization following critical illness—A population-based study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, J.I.; Chu, L.M.; Matte, A.; Tomlinson, G.; Chan, L.; Thomas, C.; Friedrich, J.O.; Mehta, S.; Lamontagne, F.; Levasseur, M.; et al. One-year outcomes in caregivers of critically ill patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweickert, W.D.; Pohlman, M.C.; Pohlman, A.S.; Nigos, C.; Pawlik, A.J.; Esbrook, C.L.; Spears, L.; Miller, M.; Franczyk, M.; Deprizio, D.; et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, C.M.; Bloom, S.L.; Jackson, J.C.; Wang, L.; Ely, E.W.; Stollings, J.L. Comprehensive care of ICU survivors: Development and implementation of an ICU recovery center. J. Crit. Care 2018, 46, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.C.; Ely, E.W.; Morey, M.C.; Anderson, V.M.; Denne, L.B.; Clune, J.; Siebert, C.S.; Archer, K.R.; Torres, R.; Janz, D.; et al. Cognitive and physical rehabilitation of ICU survivors: Results of the RETURN randomized trial. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, J.M.; Le, T.Q.; Barnato, A.E.; Hravnak, M.; Kuza, C.C.; Pike, F.; Angus, D.C. ICU telemedicine and critical care mortality: A national effectiveness study. Med. Care 2016, 54, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiser, S.L.; Fatima, A.; Ali, M.; Needham, D.M. Post-intensive care syndrome (PICS): Recent updates. J. Intensive Care 2023, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Criteria | Sepsis-1 (1991) | Sepsis-2 (2001) | Sepsis-3 (2016) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in response to infection | Documented or suspected infection plus systemic inflammatory response | Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection |
| Key Criteria | SIRS criteria, ≥2:
| Same as Sepsis-1 with expanded list of possible signs, including the following:
|
|
| Clinical Tools | SIRS criteria (primary tool) |
|
|
| Limitations |
|
|
|
| Mortality Implications |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Via, L.; Maniaci, A.; Lentini, M.; Cuttone, G.; Ronsivalle, S.; Tutino, S.; Rubulotta, F.M.; Nunnari, G.; Marino, A. The Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Intensive Care Unit. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196691
La Via L, Maniaci A, Lentini M, Cuttone G, Ronsivalle S, Tutino S, Rubulotta FM, Nunnari G, Marino A. The Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Intensive Care Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(19):6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196691
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Via, Luigi, Antonino Maniaci, Mario Lentini, Giuseppe Cuttone, Salvatore Ronsivalle, Simona Tutino, Francesca Maria Rubulotta, Giuseppe Nunnari, and Andrea Marino. 2025. "The Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Intensive Care Unit" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 19: 6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196691
APA StyleLa Via, L., Maniaci, A., Lentini, M., Cuttone, G., Ronsivalle, S., Tutino, S., Rubulotta, F. M., Nunnari, G., & Marino, A. (2025). The Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock in the Intensive Care Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(19), 6691. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14196691









