Retrospective Observational Study of Nintedanib in Managing Idiopathic and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Routine Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Radiological Assessment
2.2. Respiratory Functional Assessment
2.3. Assessment of Comorbidities
2.4. Stage Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.2. Radiological Pattern
3.2.1. Histological Pattern
3.2.2. BAL Cellularity
3.2.3. Comorbidities
3.2.4. Stage Assessment
3.3. Treatment with Nintedanib in the Two Populations
3.3.1. Subgroup Analysis: IPF
3.3.2. Subgroup Analysis: PPF
3.4. Survival Assessment
3.5. Impact of Nintedanib on Lung Function
3.6. Potential Predictors of Mortality in ILDs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ILD | Interstitial Lung Disease |
| IPF | Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| PPF | Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| PF | Pulmonary Fibrosis |
| UIP | Usual Interstitial Pneumonia |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal Reflux |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CTD-ILD | Connective Tissue Disease-related Interstitial Lung Disease |
| iNSIP | Idiopathic Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia |
| UC-ILD | Unclassifiable Interstitial Lung Disease |
| fHP | Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis |
| IPAF | Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features |
| OP | Organizing Pneumonia |
| PAP | Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis |
| SSc-ILD | Systemic Sclerosis-related Interstitial Lung Disease |
| RA-ILD | Rheumatoid Arthritis-related Interstitial Lung Disease |
References
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Cottin, V. Spectrum of Fibrotic Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasakova, M.; Poletti, V. Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases Involve Different Pathogenic Pathways with Similar Outcomes. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2015, 32, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Koudstaal, T.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Kreuter, M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to clinical decision-making. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.K.; Cottin, V.; Dhar, R.; Danoff, S.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Mohan, A.; Renzoni, E.; Mohan, M.; Udwadia, Z.; et al. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis: An expert group consensus statement. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchemann, B.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; de Naurois, C.J.; Sanyal, S.; Brillet, P.-Y.; Brauner, M.; Kambouchner, M.; Huynh, S.; Naccache, J.M.; Borie, R.; et al. Prevalence and incidence of interstitial lung diseases in a multi-ethnic county of Greater Paris. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1602419. [Google Scholar]
- Monteleone, G.; Passantino, L.; Simonetti, J.; Iovene, B.; Varone, F.; Cameli, P.; Sgalla, G.; Richeldi, L. A Simple Ratio in a Complex Disease: Exploring the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. JCM 2025, 14, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 18–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Inoue, Y.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Suda, T.; Baldwin, M.; Mueller, H.; Rohr, K.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; et al. Effects of nintedanib on symptoms in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2300752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.W.; Ryerson, C.J.; Guler, S.A. Progression of fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, P.; Alonzi, V.; D’alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Pordon, E.; Guerrieri, M.; Refini, R.M.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. The Effectiveness of Nintedanib in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis and Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Real-World Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, G.; Hague, S.; Mulholland, S.; Adamali, H.; Khin, A.M.N.; Thould, H.; Connon, R.; Minnis, P.; Murtagh, E.; Khan, F.; et al. Real-world experience of nintedanib for progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease in the UK. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10, 00529-02023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Chen, S.Y.; Hou, Q.; Yeh, W.S.; Collard, H.R. Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US adults 18–64 years old. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, A.L.; Gifford, A.H.; Inase, N.; Fernández Pérez, E.R.; Suda, T. The epidemiology of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial lung diseases at risk of a progressive-fibrosing phenotype. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, M.; Larrieu, S.; Boussel, L.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Bazin, F.; Marque, S.; Massol, J.; Thivolet-Bejui, F.; Chalabreysse, L.; Maucort-Boulch, D.; et al. Estimates of epidemiology, mortality and disease burden associated with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease in France (the PROGRESS study). Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Hino, T.; Hwang, J.; Franks, T.J.; Han, J.; Im, Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Chung, M.P.; Hatabu, H.; Lee, K.S. Connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD) and interstitial lung abnormality (ILA): Evolving concept of CT findings, pathology and management. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2022, 9, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A.; Sverzellati, N.; Travis, W.D.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Galvin, J.R.; Goldin, J.G.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A Fleischner Society White Paper. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, T.M.; Leong, M.C.H.; Montesi, S.B.; Ryerson, C.J.; Khor, Y.H. Comorbidities in the idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and progressive pulmonary fibrosis trial population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2025, 34, 240238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Pozzan, R.; Confalonieri, P.; Tavano, S.; Hughes, M.; Cerinic, M.M.; Baratella, E.; Zanatta, E.; Lerda, S.; Geri, P.; et al. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Viewer or Actor? To Treat or Not to Treat? Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Ogura, T.; Azuma, A.; Kondoh, Y.; Homma, S.; Muraishi, K.; Ikeda, R.; Ochiai, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nukiwa, T. Real-World Safety, Tolerability and Effectiveness of Nintedanib in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Final Report of Post-marketing Surveillance in Japan. Adv. Ther. 2025, 42, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefániková, M.; Doubková, M.; Ovesná, P.; Šterclová, M.; Lacina, L.; Žurková, M.; Plačková, M.; Bartoš, V.; Janíčková, I.; Bittenglová, R.; et al. The effect of nintedanib on lung functions and survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Real-life analysis of the Czech EMPIRE registry. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; Castelli, G.; Franco, G.; Bocchino, M.; Carroccio, L.; Lalla, F.; Cefaloni, F.; Deidda, S.; Chimera, D.; di Liberti, R.; et al. Perception of the role of Telemedicine in Interstitial Lung Diseases: Findings from Società Italiana di Pneumologia/Italian Respiratory-Society (SIP-IRS) survey. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2025, 20, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazipura, M.; Mammen, M.J.; Herman, D.D.; Hon, S.M.; Bissell, B.D.; Macrea, M.; Kheir, F.; Khor, Y.H.; Knight, S.L.; Raghu, G.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, L.; Stewart, I.; Barratt, S.L.; Chua, F.; Chaudhuri, N.; Crawshaw, A.; Gibbons, M.; Hogben, C.; Hoyles, R.; Kouranos, V.; et al. Nintedanib for non-IPF progressive pulmonary fibrosis: 12-month outcome data from a real-world multicentre observational study. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00423-02022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Hara, Y.; Saigusa, Y.; Tagami, Y.; Murohashi, K.; Nagasawa, R.; Aoki, A.; Izawa, A.; Seki, K.; Watanabe, K.; et al. ILD-GAP Combined with the Charlson Comorbidity Index Score (ILD-GAPC) as a Prognostic Prediction Model in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Can. Respir. J. 2023, 2023, 5088207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Ley, B.; Lee, J.S.; Mooney, J.J.; Jones, K.D.; Elicker, B.M.; Wolters, P.J.; Koth, L.L.; King, T.E.; et al. Predicting Survival Across Chronic Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2014, 145, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platenburg, M.G.J.P.; Nakshbandi, G.; Moor, C.C.; van Batenburg, A.A.; Mostard, R.L.M.; Voortman, M.; Moonen, L.A.; Hekelaar, N.; Overbeek, M.J.; Bogaarts, B.A.; et al. Lung Function Course of Patients With Pulmonary Fibrosis After Initiation of Anti-Fibrotic Treatment: Real-World Data From the Dutch National Registry. Respirology 2025, 30, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Hara, Y.; Fujii, H.; Murohashi, K.; Saigusa, Y.; Zhao, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Nagasawa, R.; Tagami, Y.; Izawa, A.; et al. ILD-GAP combined with the monocyte ratio could be a better prognostic prediction model than ILD-GAP in patients with interstitial lung diseases. BMC Pulm Med. 2024, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Ryerson, C.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Ryu, J.H.; Tomassetti, S.; Lee, J.S.; Poletti, V.; Buccioli, M.; Elicker, B.M.; Jones, K.D.; et al. A Multidimensional Index and Staging System for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggisano, M.; Mondini, L.; Chernovsky, M.; Confalonieri, P.; Salton, F.; Reccardini, N.; Kodric, M.; Geri, P.; Confalonieri, M.; Hughes, M.; et al. Safety of Nintedanib in a Patient with Chronic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Kidney Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, A.; Pastre, J.; Valery, S.; King, C.S.; Nathan, S.D. Derivation and validation of a simple multidimensional index incorporating exercise capacity parameters for survival prediction in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2023, 78, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khateeb, J.; Fuchs, E.; Khamaisi, M. Diabetes and Lung Disease: An Underestimated Relationship. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2019, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.; Viggiani, G.; Chen, Y.W.; Coulis, G.; Castaldi, A. MicroRNA and ROS Crosstalk in Cardiac and Pulmonary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, L.; Gauldie, J.; Voelkel, N.F.; Kolb, M. Pulmonary Hypertension and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Tale of Angiogenesis, Apoptosis, and Growth Factors. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisa, M.; Marinelli, C.; Savarino, V.; Savarino, E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and GERD: Links and risks. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagyu, H.; Murohashi, K.; Hara, Y.; Saigusa, Y.; Aoki, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Kaneko, T. Clinical utility of a composite scoring system including Charlson Comorbidity Index score in patients with interstitial lung disease. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 5774–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murohashi, K.; Hara, Y.; Saigusa, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Sato, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kudo, M.; Kaneko, T. Clinical significance of Charlson comorbidity index as a prognostic parameter for patients with acute or subacute idiopathic interstitial pneumonias and acute exacerbation of collagen vascular diseases-related interstitial pneumonia. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Calandriello, L.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N. Deep learning for classifying fibrotic lung disease on high-resolution computed tomography: A case-cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. 2018, 6, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Baratella, E.; Caforio, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Wade, B.; Marrocchio, C.; Geri, P.; Pozzan, R.; Andrisano, A.G.; Cova, M.A.; et al. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: An Update. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; Cameli, P.; Bonella, F. The role of heat shock protein 90 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: State of the art. Eur Respir Rev. 2025, 34, 240147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfei, M.; Schmitt, S.; Ruppert, C.; Henneke, I.; Markart, P.; Loeh, B.; Mahavadi, P.; Wygrecka, M.; Klepetko, W.; Fink, L.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of lung tissue from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and lung transplant donor lungs. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 2185–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaro, B.; Gandin, I.; Pozzan, R.; Tavano, S.; Bozzi, C.; Hughes, M.; Kodric, M.; Cifaldi, R.; Lerda, S.; Confalonieri, M.; et al. Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Tolerability and Safety in a Real Life Experience in a Single Centre in Patients also Treated with Oral Anticoagulant Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salotti, A.; Chianese, M.; Romallo, A.; De Nes, A.; Angoni, D.; Galantino, A.; Chernovsky, M.; Mondini, L.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; et al. Comorbidities’ Effect on IPF: Pathogenesis and Management. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, G.; ILDs Study Group Sip/Irs; Bergantini, L.; D’Alessandro, M.; Pianigiani, T.; Simonetti, J.; Iovene, B.; Varone, F.; Sgalla, G.; Richeldi, L.; et al. The management of Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis in different medical settings: Where does that leave us? An Italian nationwide survey. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2024, 41, e2024047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, M.; Screm, G.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Trotta, L.; Barbieri, M.; Ruggero, L.; Mari, M.; Reccardini, N.; Geri, P.; et al. Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Lights and Shadows. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kette, S.; Reccardini, N.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Andrisano, A.; Chianese, M.; De Nes, A.; Maggisano, M.; Galantino, A.; Nicolosi, S.; et al. The Impact of Comorbidities on the Discontinuation of Antifibrotic Therapy in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Brown, K.K.; Flaherty, K.R.; Kolb, M.; Thannickal, V.J. What’s in a name? That which we call IPF, by any other name would act the same. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1800692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Salotti, A.; Reccardini, N.; Kette, S.; Da Re, B.; Nicolosi, S.; Zuccon, U.; Confalonieri, M.; Mondini, L.; Pozzan, R.; et al. Functional Progression after Dose Suspension or Discontinuation of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Real-Life Multicentre Study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Vonk, M.C.; Distler, O.; Azuma, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Gahlemann, M.; James, A.; Kohlbrenner, V.; Alves, M.; Khanna, D.; et al. Continued treatment with nintedanib in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: Data from SENSCIS-ON. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibold, J.R.; Maher, T.M.; Highland, K.B.; Assassi, S.; Azuma, A.; Hummers, L.K.; Costabel, U.; von Wangenheim, U.; Kohlbrenner, V.; Gahlemann, M.; et al. Safety and tolerability of nintedanib in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: Data from the SENSCIS trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, A.U.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Inoue, Y.; Devaraj, A.; Richeldi, L.; Moua, T.; Crestani, B.; Wuyts, W.A.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases-subgroup analyses by interstitial lung disease diagnosis in the INBUILD trial: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, E.L.; Kelly, C.; Distler, J.H.W.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Seibold, J.R.; Mittoo, S.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Aringer, M.; Pope, J.; Distler, O.; et al. Nintedanib in Patients With Autoimmune Disease-Related Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases: Subgroup Analysis of the INBUILD Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, C.; De Luca, G.; Lazzaroni, M.G.; Armentaro, G.; Spinella, A.; Vigone, B.; Ruaro, B.; Stanziola, A.; Benfaremo, D.; De Lorenzis, E.; et al. Real-life efficacy and safety of nintedanib in systemic sclerosis-interstitial lung disease: Data from an Italian multicentre study. RMD Open 2023, 9, e002850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

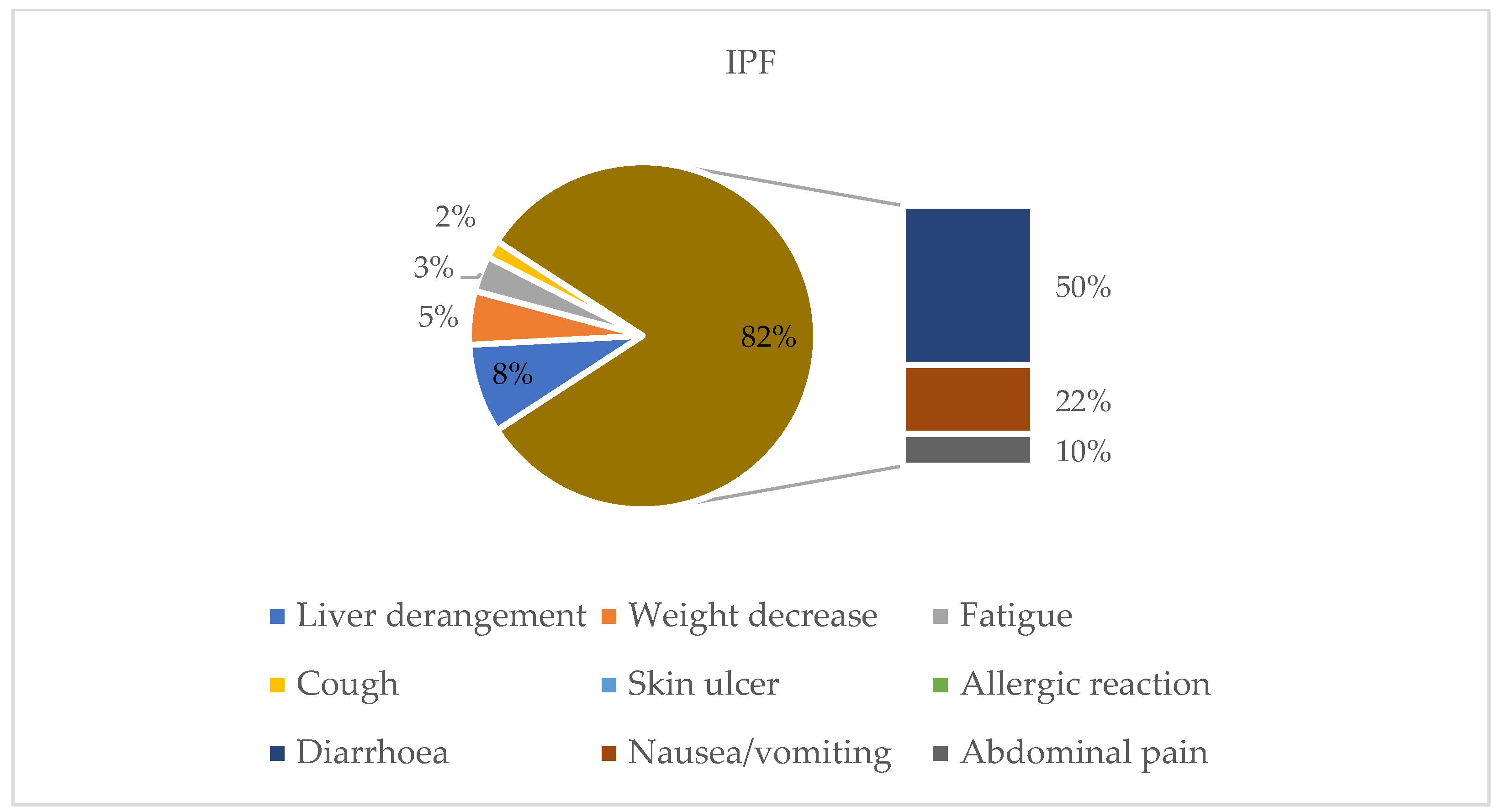
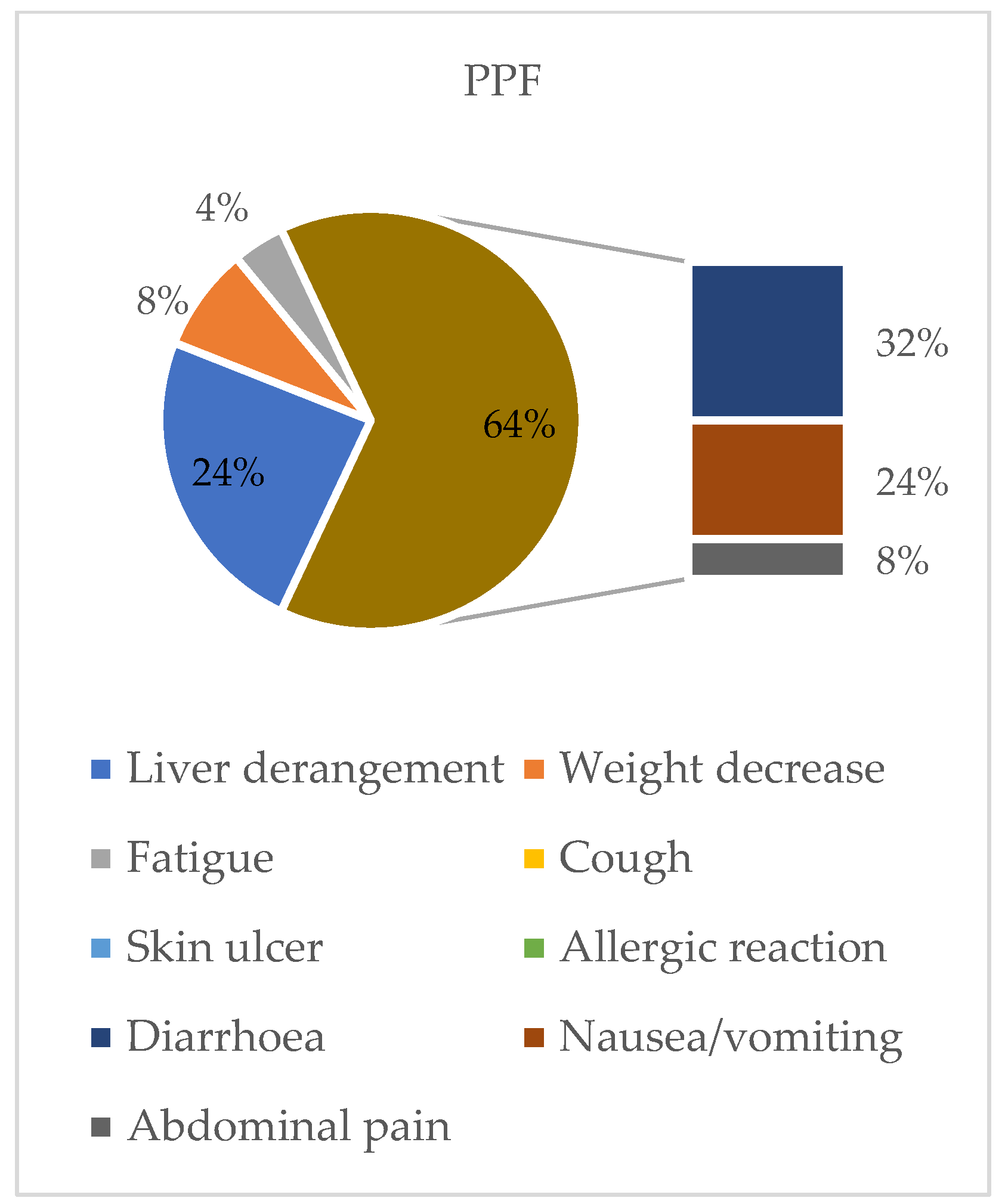
| n = 97 | IPF = 64 | PPF = 33 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (F/M) n, % | 65/32 | 48 (75%)/16 (25%) | 17 (51%)/16 (49%) |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 70.74 ± 10.7 | 72.27 ± 10.5 | 67.79 ± 10.4 |
| Smoking status (never/ex, current) n, % | 28 (28.9%)/69 (71.1%) | 50 (77%) | 19 (37.25) |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) n, % | 31 (31.9%) | 17 (26.5%) | 14 (42.4%) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) n, % | 12 (12.4%) | 8 (12.5%) | 4 (12.1%) |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 12 (12.4%) | 7 (11%) | 5 (15.1%) |
| Lung cancer | 8 (8.2%) | 6 (9.3%) | 2 (6%) |
| Exposure to pneumotoxic agents (drugs; asbestos; molds; wood dusts) n, % | 16 (16.5%) | 11 (17.1%) | 5 (15.1%) |
| HRCT pattern | |||
| UIP (definite, probable) n, % | 72 (74.2%) | 57 (89%) | 15 (45.4%) |
| Indeterminate or inconsistent for UIP n, % | 7 (7.2%) | 7 (10.9%) | - |
| NSIP n, % | 12 (12.3%) | - | 12 (36.3%) |
| fHP n, % | 3 (3%) | - | 3 (9%) |
| OP n, % | 1 (1%) | - | 1 (3%) |
| PAP n, % | 1 (1%) | - | 1 (3%) |
| u-ILD n, % | 1 (1%) | - | 1 (3%) |
| PFT at baseline (mean ± SD) | 1 (1.96) | ||
| FVC %pred | - | 80.2 ± 20.8 | 71.4 ± 21.5 |
| DLCO %pred | - | 47.6 ± 18.5 | 53.4 ± 30.1 |
| ILD-GAP Model Score | ILD-GAPC Model Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ILD diagnosis | IPF/UC-ILD 1 | 0 | 0 |
| CVD-IP 2 ± iNSIP 3 ± CHP 4 | −2 | −2 | |
| Gender | Female | 0 | 0 |
| Male | 1 | 1 | |
| Age | ≤60 | 0 | 0 |
| 61–65 | 1 | 1 | |
| >65 | 2 | 2 | |
| % FVC 5 | >75 | 0 | 0 |
| 50–75 | 1 | 1 | |
| <50 | 2 | 2 | |
| %DLCO 6 | >55 | 0 | 0 |
| 36–55 | 1 | 1 | |
| ≥35 | 2 | 2 | |
| Cannot perform | 3 | 3 | |
| CCIS 7 | 0–1 | 0 | |
| 2–3 | 1 | ||
| ≥4 | 2 |
| IPF | PPF | |
|---|---|---|
| ILD-GAP score | ||
| Stage I | 26 | 16 |
| Stage II | 31 | 15 |
| Stage III | 7 | 2 |
| ILD-GAPC score | ||
| Stage I | 5 | 7 |
| Stage II | 32 | 13 |
| Stage III | 27 | 13 |
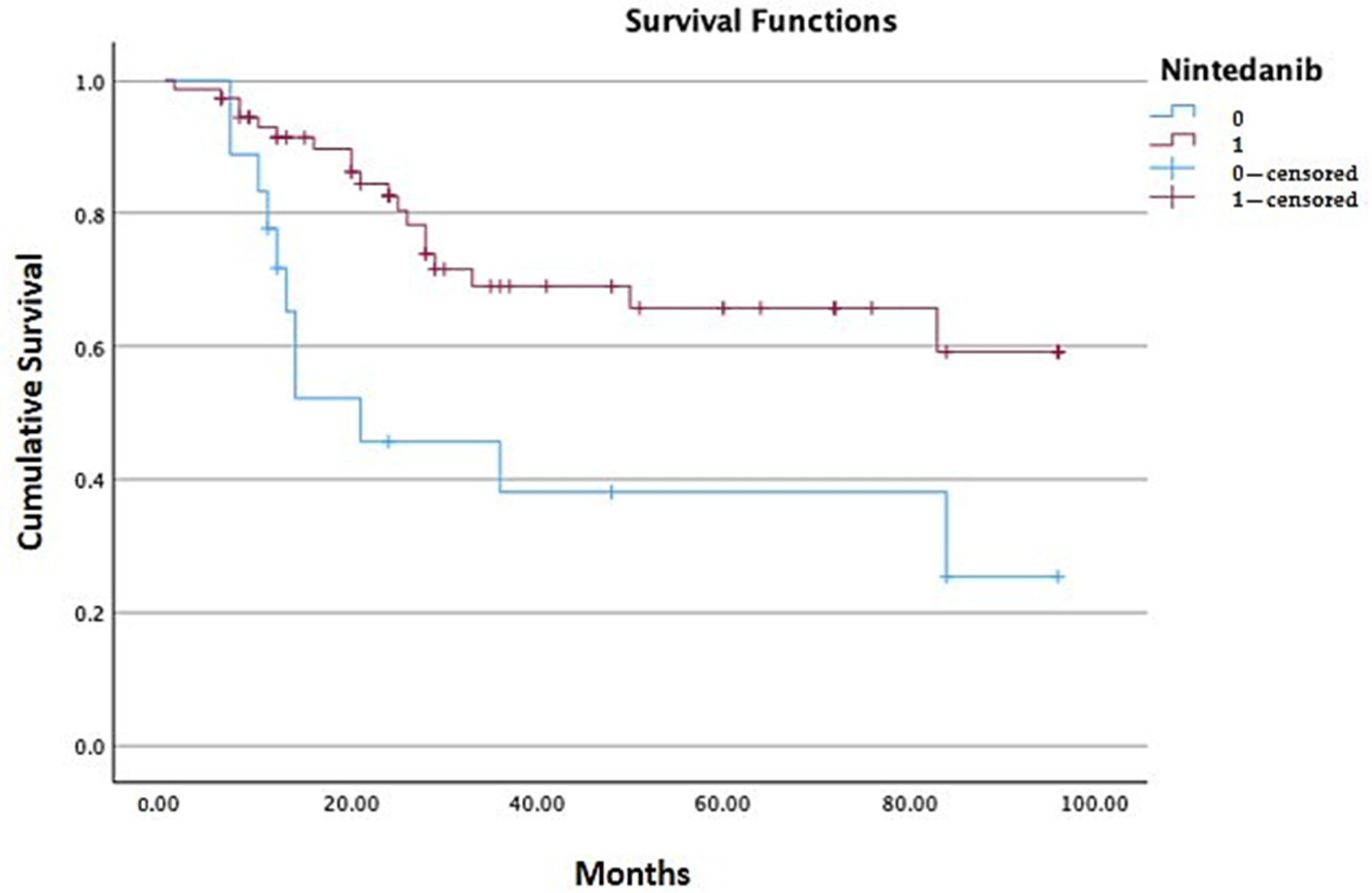
| Nintedanib | N Patients | N Deaths | Mean Estimated Survival 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 = suspended | 18 | 11 | 44.477 (CI 25.56–63.39) |
| 1 = ongoing | 76 | 19 | 70.228 (CI 60.63–79.82) |
| Total population 1 | 94 | 30 | 64.588 (CI 55.72–73.45) |
| Overall Comparisons | Chi-Square | Df | Sig. |
| Log Rank (Mantel–Cox) 3 | 8.260 | 1 | 0.004 |
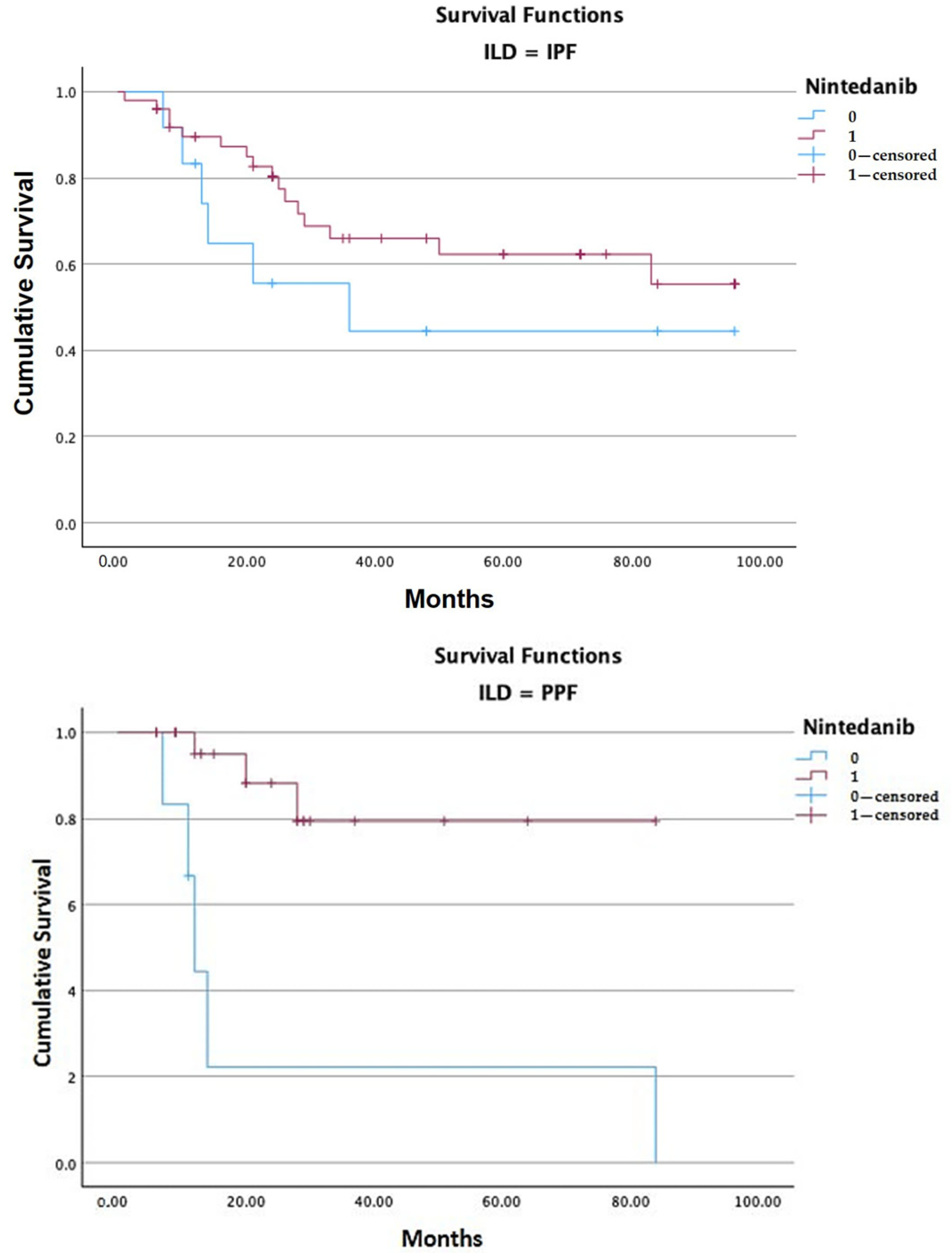
| Nintedanib | N Patients | N Deaths | Mean Estimated Survival 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPF | 0 = suspended | 12 | 6 | 52.520 (CI 28.72–76.33) |
| 1 = ongoing | 50 | 16 | 67.355 (CI 56.08–78.63) | |
| total IPF | 62 | 22 | 64.267 (CI 53.92–74.62) | |
| PPF | 0 = suspended | 6 | 5 | 27.444 (CI 0.00–58.02) |
| 1 = ongoing | 26 | 3 | 71.117 (CI 57.86–84.37) | |
| total PPF | 32 | 8 | 62.054 (CI 47.33–76.78) | |
| Overall Comparisons | Chi-Square | Df | Sig. | |
| IPF | Log Rank (Mantel–Cox) 2 | 1.532 | 1 | 0.216 |
| PPF | Log Rank (Mantel–Cox) | 12.174 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Nintedanib After 1 Year of Observation | N Patients | Mean Difference (FVC % at Baseline—FVC % at 1 Year) | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0 = suspended | 17 | −4.41 ± 9.4% | t 1.606, df 46 p = 0.115 |
| 1 = ongoing | 80 | 0.51 ± 18.4% | ||
| IPF | 53 | 0.32 ± 20.5%, | t −0.357, df 71 p = 0.722 | |
| PPF | 26 | 1.69 ± 13.3% |
| Nintedanib After 1 Year of Observation | N Patients | Mean Difference (DLCO % at Baseline—DLCO % at 1 Year) | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0 = suspended | 78 | −7.44 ± 15.7% | t 0.309, df 21 p = 0.760 |
| 1 = ongoing | 16 | −6.10 ± 15.7% | ||
| IPF | 64 | −5.62 ± 15.8% | t −0.654, df 57 p = 0.516 | |
| PPF | 30 | −7.87 ± 15.5% |
| Predictors * | IPF | PPF | All ILDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced age at diagnosis | X 2 | ||
| Male gender | |||
| UIP pattern HRCT | |||
| FVC % decline 1 year after nintedanib introduction | |||
| Stage III pulmonary fibrosis according to ILD-GAP score | |||
| Stage III pulmonary fibrosis according to ILD-GAPC score | X 1 | X 4 | |
| Nintedanib suspension | X 3 | X 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrisano, A.G.; Castaldo, N.; Giuliana, F.; Femia, D.; Morana, G.; Patruno, V.; Monteleone, G.; Reccardini, N.; Cifaldi, R.; Hughes, M.; et al. Retrospective Observational Study of Nintedanib in Managing Idiopathic and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Routine Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186665
Andrisano AG, Castaldo N, Giuliana F, Femia D, Morana G, Patruno V, Monteleone G, Reccardini N, Cifaldi R, Hughes M, et al. Retrospective Observational Study of Nintedanib in Managing Idiopathic and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Routine Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186665
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrisano, Alessia Giovanna, Nadia Castaldo, Francesco Giuliana, Davide Femia, Giuseppe Morana, Vincenzo Patruno, Giorgio Monteleone, Nicolò Reccardini, Rossella Cifaldi, Michael Hughes, and et al. 2025. "Retrospective Observational Study of Nintedanib in Managing Idiopathic and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Routine Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186665
APA StyleAndrisano, A. G., Castaldo, N., Giuliana, F., Femia, D., Morana, G., Patruno, V., Monteleone, G., Reccardini, N., Cifaldi, R., Hughes, M., Wang, Y., Confalonieri, P., Salton, F., Geri, P., Confalonieri, M., & Ruaro, B. (2025). Retrospective Observational Study of Nintedanib in Managing Idiopathic and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Routine Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6665. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186665










