Post-Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum: Heroin Addiction as a Generator of Trauma Sensitisation in Everyday Life: A Perspective Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The bidirectional relationship between PTSD and substance use, including epidemiological links, clinical symptom overlap, and theoretical models.
- From classical PTSD to Opioid-Trauma Syndromes, with an emphasis on neurobiological mechanisms of stress sensitisation.
- Clinical evidence of the post-heroin PTSD spectrum, derived from observational and psychometric data.
- The implications of this model for trauma-informed care, including a discussion on whether opioid agonist treatment (OAT) can reduce PTSD-spectrum symptoms in this population.
- Limitations and Strengths of pH-PTSD/S.
2. The Bidirectional Link Between PTSD and Substance Use
2.1. The Relationship Between PTSD and SUD
2.1.1. Epidemiological Links Between PTSD and SUD
2.1.2. Clinical Overlap and Symptom Interactions
2.1.3. Etiological Frameworks
2.2. The “Addiction-Induced PTSD Vulnerability” Model: SUD as an Independent Risk Factor in Increasing Individual Susceptibility to PTSD
3. From Classical PTSD to Opioid-Trauma Syndromes
3.1. Rethinking PTSD: From Diagnostic Criteria to Trauma Spectrum
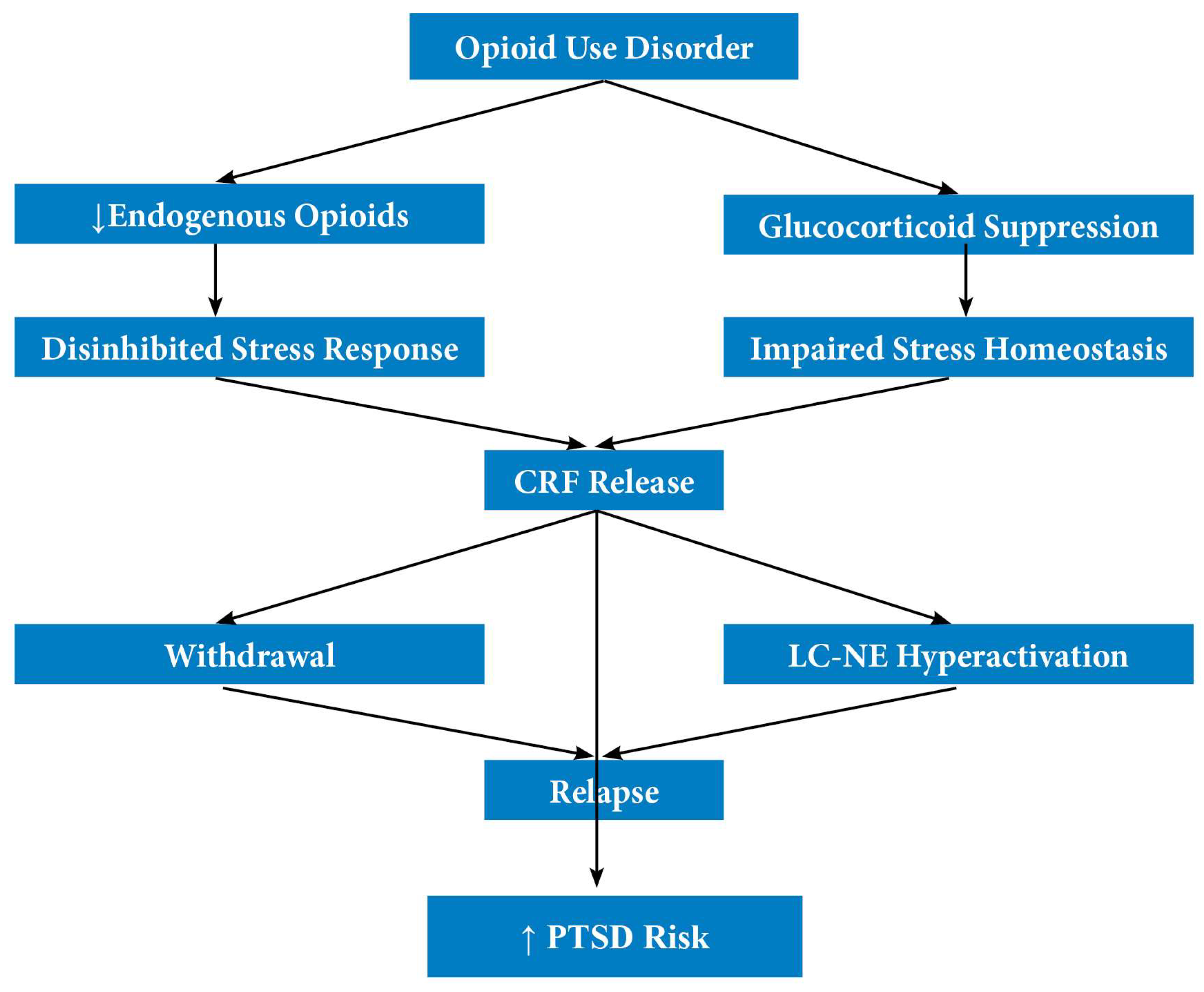
3.2. Opioid-Induced Stress Dysregulation and Neurobiological Trauma
4. Clinical Evidence of the Post-Heroin PTSD Spectrum
4.1. Comparative Analysis of Stress Reactivity Before and After Heroin Addiction Onset
4.2. Converging Trajectories: Towards a Unified Model of PTSD and HUD
4.3. Trauma Without Disaster: PTSD/Symptomatology in Heroin Users Compared to Earthquake Survivors
4.4. Trait Psychopathology and Emotional Reactivity
4.5. Clinical Profiles of PTSD/S Patients
4.6. PTSD/S and Long-Term Outcomes of Continuous Treatment
4.7. Future Directions
5. Implications for Trauma-Informed Care and the Role of Opioid Agonist Treatment
6. Limitations and Strengths of pH-PTSD/S
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swannell, M.; Bradlow, R.C.J.; Pham, D.; Gabriel, J.; Manahan, Y.; Arunogiri, S. Pharmacological treatments for co-occurring PTSD and substance use disorders: A systematic review. J. Subst. Use Addict. Treat. 2025, 169, 209601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, A.A. The experience of chronic illness and post-traumatic stress disorder: The consequences of cumulative adversity. Soc. Sci. Med. 2000, 50, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R. Chronic stress, drug use, and vulnerability to addiction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1141, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, K.T.; Sinha, R. Co-Occurring Mental and Substance Use Disorders: The Neurobiological Effects of Chronic Stress. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.K.; Southwick, S.M.; Kosten, T.R. Substance use disorders in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder: A review of the literature. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.; Mezey, G.; Chapman, M.; Wheeler, M.; Drummond, C.; Baldacchino, A. Co-morbid post-traumatic stress disorder in a substance misusing clinical population. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2005, 77, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.D.; Striley, C.; Cottler, L.B. The association of substance use disorders with trauma exposure and PTSD among African American drug users. Addict. Behav. 2006, 31, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakey, S.M.; Campbell, S.B.; Simpson, T.L. Associations Between Lifetime Panic Attacks, Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, and Substance Use Disorders in a Nationally Representative Sample. J. Dual Diagn. 2022, 18, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler Boden, M.; Kimerling, R.; Kulkarni, M.; Bonn-Miller, M.O.; Weaver, C.; Trafton, J. Coping among military veterans with PTSD in substance use disorder treatment. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2014, 47, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, D.; Cohen, L.; Campbell, A. Is traumatic stress a vulnerability factor for women with substance use disorders? Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2005, 25, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etami, Y.; Lildharrie, C.; Manza, P.; Wang, G.J.; Volkow, N.D. Neuroimaging in Adolescents: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Risk for Substance Use Disorders. Genes 2023, 14, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinckley, J.D.; Adams, Z.W.; Dellucci, T.V.; Berkowitz, S. Co-occurring trauma- and stressor-related and substance-related disorders in youth: A narrative review. Med. Res. Arch. 2024, 12, 10–18103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, M.; Schulte, S.; Luedecke, C.; Schaefer, I.; Sutmann, F.; Ohlmeier, M.; Kemper, U.; Koesters, G.; Chodzinski, C.; Schneider, U.; et al. Trauma and PTSD in patients with alcohol, drug, or dual dependence: A multi-center study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, S.S. Women and addiction: A trauma-informed approach. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2008, 40 (Suppl. S5), 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, J.L.; Killeen, T.; Gros, D.F.; Brady, K.T.; Back, S.E. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Co-Occurring Substance Use Disorders: Advances in Assessment and Treatment. Clin. Psychol. 2012, 19, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.L.; Marel, C.; Darke, S.; Ross, J.; Slade, T.; Teesson, M. The long-term impact of post traumatic stress disorder on recovery from heroin dependence. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2018, 89, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapkin, M.L.; Yusko, D.; Yasinski, C.; Oslin, D.; Hembree, E.A.; Foa, E.B. Baseline functioning among individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder and alcohol dependence. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2011, 41, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Read, J.P.; Brown, P.J.; Kahler, C.W. Substance use and posttraumatic stress disorders: Symptom interplay and effects on outcome. Addict. Behav. 2004, 29, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straus, E.; Haller, M.; Lyons, R.C.; Norman, S.B. Functional and Psychiatric Correlates of Comorbid Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol. Res. 2018, 39, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouimette, P.C.; Brown, P.J.; Najavits, L.M. Course and treatment of patients with both substance use and posttraumatic stress disorders. Addict. Behav. 1998, 23, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.S.; Elmaadawi, A.; Nasr, S.; Haskin, J. Comorbid Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Opioid Dependence. Cureus 2017, 9, e1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareed, A.; Eilender, P.; Haber, M.; Bremner, J.; Whitfield, N.; Drexler, K. Comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder and opiate addiction: A literature review. J. Addict. Dis. 2013, 32, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria-Rios, C.E.; Morrow, J.D. Mechanisms of Shared Vulnerability to Post-traumatic Stress Disorder and Substance Use Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, T.I.; Stone, E.; Singal, S.; Novakovic, V.; Barkin, R.L.; Barkin, S. Brain reward circuitry: The overlapping neurobiology of trauma and substance use disorders. World J. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzimenti, C.L.; Navis, T.M.; Lattal, K.M. Persistent effects of acute stress on fear and drug-seeking in a novel model of the comorbidity between post-traumatic stress disorder and addiction. Learn. Mem. 2017, 24, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najavits, L.M.; Hien, D. Helping vulnerable populations: A comprehensive review of the treatment outcome literature on substance use disorder and PTSD. J. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 69, 433–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, J.S.; Koppenhaver, J.M.; Alterman, A.I.; McKay, J.R. Posttraumatic stress disorder and other psychopathology in substance abusing patients. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2009, 101, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovitch, I. Post-traumatic stress disorder and opioid use disorder: A narrative review of conceptual models. J. Addict. Dis. 2016, 35, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khantzian, E.J. The self-medication hypothesis of substance use disorders: A reconsideration and recent applications. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1997, 4, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerra, G.; Somaini, L.; Manfredini, M.; Raggi, M.A.; Saracino, M.A.; Amore, M.; Leonardi, C.; Cortese, E.; Donnini, C. Dysregulated responses to emotions among abstinent heroin users: Correlation with childhood neglect and addiction severity. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, L.; Vilens, A. Neurobiology of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder; Nova Biomedical: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. viii. 376p. [Google Scholar]
- Vermetten, E. Stress, trauma, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Tijdschr. Psychiatr. 2009, 51, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin, T.M.; Niehaus, C.; Gonçalves, S.F. Stress reactivity and the developmental psychopathology of adolescent substance use. Neurobiol. Stress. 2018, 9, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladin, M.E.; Brady, K.T.; Dansky, B.S.; Kilpatrick, D.G. Understanding comorbidity between PTSD and substance use disorders: Two preliminary investigations. Addict. Behav. 1995, 20, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhart, M.; Wand, G.S. Stress, alcohol and drug interaction: An update of human research. Addict. Biol. 2009, 14, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, L.; Tang, Y.L.; Bradley, B.; Cubells, J.F.; Ressler, K.J. Substance use, childhood traumatic experience, and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in an urban civilian population. Depress. Anxiety 2010, 27, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinckley, J.D.; Danielson, C.K. Elucidating the Neurobiologic Etiology of Comorbid PTSD and Substance Use Disorders. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leconte, C.; Mongeau, R.; Noble, F. Traumatic Stress-Induced Vulnerability to Addiction: Critical Role of the Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid Receptor System. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 856672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerra, G.; Somaini, L.; Leonardi, C.; Cortese, E.; Maremmani, I.; Manfredini, M.; Donnini, C. Association between gene variants and response to buprenorphine maintenance treatment. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 215, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Mueser, K.T.; Rosenberg, S.D.; Jankowski, M.K. Correlates of adverse childhood experiences among adults with severe mood disorders. Psychiatr. Serv. 2008, 59, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, L.A.; Blendy, J.A. Not all stress is equal: CREB is not necessary for restraint stress reinstatement of cocaine-conditioned reward. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 246, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, S.K.; Sinha, R. Alcohol, stress, and glucocorticoids: From risk to dependence and relapse in alcohol use disorders. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F. A role for brain stress systems in addiction. Neuron 2008, 59, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemm, S.E.; Sinha, R. Drug-induced stress responses and addiction risk and relapse. Neurobiol. Stress. 2019, 10, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.B.; Thompson, B.L. Neuroplasticity of the extended amygdala in opioid withdrawal and prolonged opioid abstinence. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1253736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosnocht, A.Q.; Briand, L.A. Substance use modulates stress reactivity: Behavioral and physiological outcomes. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 166, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, T.; Kirschbaum, C.; Heinze, K.; Steudte, S.; Foley, P.; Tietze, A.; Dettenborn, L. Use of hair cortisol analysis to detect hypercortisolism during active drinking phases in alcohol-dependent individuals. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 85, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, A.C.; Sands, H.R.; Jones, L.; Clow, A.; Evans, P.; Downey, L.A.; Stalder, T. Increased cortisol levels in hair of recent Ecstasy/MDMA users. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Wang, T.J.; Yin, G.; Yan, Y.; Xiao, L.H.; Li, Q.; Bi, K.S. Metabonomic Study of Biochemical Changes in Human Hair of Heroin Abusers by Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Ion Trap-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 58, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Pu, Y.; Deng, H. Simultaneous Determination of Cortisol, Cortisone, and Multiple Illicit Drugs in Hair among Female Drug Addicts with LC-MS/MS. Molecules 2021, 26, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottler, L.B.; Compton, W.M., 3rd; Mager, D.; Spitznagel, E.L.; Janca, A. Posttraumatic stress disorder among substance users from the general population. Am. J. Psychiatry 1992, 149, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, D.E.; Debnam, K.J.; Wang, M.Q. Ten-year trends in physical dating violence victimization among U.S. adolescent females. J. Sch. Health 2013, 83, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, S.; Raghavan, C. The relationship of sexual abuse, early initiation of substance use, and adolescent trauma to PTSD. J. Trauma. Stress. 2009, 22, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmel, B.; Kreek, M.J. Neurobiology of addictive behaviors and its relationship to methadone maintenance. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2000, 67, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerra, G.; Zaimovic, A.; Zambelli, U.; Timpano, M.; Reali, N.; Bernasconi, S.; Brambilla, F. Neuroendocrine responses to psychological stress in adolescents with anxiety disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2000, 42, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.; Kreek, M.J. Stress, dysregulation of drug reward pathways, and the transition to drug dependence. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, K.T.; Dansky, B.S.; Sonne, S.C.; Saladin, M.E. Posttraumatic stress disorder and cocaine dependence. Order of onset. Am. J. Addict. 1998, 7, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiger, P.K.; Melville, F.; Hides, L.; Kambouropoulos, N.; Lubman, D.I. Can emotion-focused coping help explain the link between posttraumatic stress disorder severity and triggers for substance use in young adults? J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2009, 36, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Logrip, M.L.; Koob, G.F. Corticotropin releasing factor: A key role in the neurobiology of addiction. Front. Neuroendocr. 2014, 35, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, L.; Dickinson, A.; Wolf, O.T. Stress, habits, and drug addiction: A psychoneuroendocrinological perspective. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 19, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmack, S.A.; Vendruscolo, J.C.M.; Adrienne McGinn, M.; Miranda-Barrientos, J.; Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Bosse, G.D.; Mercatelli, D.; Giorgi, F.M.; Fu, Y.; Hinrich, A.J.; et al. Corticosteroid sensitization drives opioid addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Buck, C.L.; Cohen, A.; Edwards, S.; Park, P.E.; Schlosburg, J.E.; Schmeichel, B.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Wade, C.L.; Whitfield, T.W., Jr. Addiction as a stress surfeit disorder. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt B, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al’Absi, M.; Nakajima, M.; DeAngelis, B.; Grant, J.; King, A.; Grabowski, J.; Hatsukami, D.; Allen, S. Blunted opioid regulation of the HPA stress response during nicotine withdrawal: Therapeutic implications. Stress 2021, 24, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaini, L.; Manfredini, M.; Amore, M.; Zaimovic, A.; Raggi, M.A.; Leonardi, C.; Gerra, M.L.; Donnini, C.; Gerra, G. Psychobiological responses to unpleasant emotions in cannabis users. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 262, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Borgwardt, S.; Gerber, H.; Wiesbeck, G.A.; Schmid, O.; Riecher-Rössler, A.; Smieskova, R.; Lang, U.E.; Walter, M. Acute effects of heroin on negative emotional processing: Relation of amygdala activity and stress-related responses. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetti, L.; Cavagnini, F.; Martino, E.; Ambrogio, A. Effects of cocaine on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2014, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, A.C. Oxytocin, cortisol and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine: Neurohormonal aspects of recreational ‘ecstasy’. Behav. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, S.K.; Nautiyal, N.; Hart, R.; Guarnaccia, J.B.; Sinha, R. Craving, cortisol and behavioral alcohol motivation responses to stress and alcohol cue contexts and discrete cues in binge and non-binge drinkers. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, A.M.; Tassin, J.P.; Blanc, G.; Glowinski, J. Selective activation of mesocortical DA system by stress. Nature 1976, 263, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Chiara, G.; Imperato, A. Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5274–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Duffy, P. Similar effects of daily cocaine and stress on mesocorticolimbic dopamine neurotransmission in the rat. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 25, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R. The role of stress in addiction relapse. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2007, 9, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, L.A.; Vassoler, F.M.; Pierce, R.C.; Valentino, R.J.; Blendy, J.A. Ventral tegmental afferents in stress-induced reinstatement: The role of cAMP response element-binding protein. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16149–16159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cloitre, M.; Garvert, D.W.; Brewin, C.R.; Bryant, R.A.; Maercker, A. Evidence for proposed ICD-11 PTSD and complex PTSD: A latent profile analysis. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol 2013, 4, 20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerde, J.A.; Merrin, G.J.; Le, V.T.; Toumbourou, J.A.-O.; Bailey, J.A.-O. Health of Young Adults Experiencing Social Marginalization and Vulnerability: A Cross-National Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Env. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Nunes, E.V., Jr.; Novo, P.; Bachrach, K.; Bailey, G.L.; Bhatt, S.; Farkas, S.; Fishman, M.; Gauthier, P.; Hodgkins, C.C.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R.L.; Lei, M.K.; Beach, S.R.H.; Barr, A.B.; Simons, L.G.; Gibbons, F.X.; Philibert, R.A. Discrimination, segregation, and chronic inflammation: Testing the weathering explanation for the poor health of Black Americans. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Carter, S.E.; Ressler, K.J.; Fani, N.; Harnett, N.G. The neurophysiological consequences of racism-related stressors in Black Americans. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 161, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.I.; Papageorgiou, C.; Margariti, M. Neurobiological Trajectories Involving Social Isolation in PTSD: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affrunti, N.W.; Suarez, L.; Simpson, D. Community violence and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in urban youth: The moderating influence of friend and parent support. J. Community Psychol. 2018, 46, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, M.H.; Marusak, H.A.; Ely, T.D.; van Rooij, S.J.H.; Stenson, A.F.; Stevens, J.S.; France, J.M.; Tottenham, N.; Jovanovic, T. Community Violence Exposure is Associated with Hippocampus-Insula Resting State Functional Connectivity in Urban Youth. Neuroscience 2021, 468, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, H.K.; Beauchaine, T.P.; Shannon, K.E. Neurobiological adaptations to violence across development. Dev. Psychopathol. 2010, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, L.M.; Wand, G.S. Opioids and alcoholism. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 81, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellbach, S.; Gartner, P.; Deicke, J.; Fischer, D.; Hassan, A.H.; Almeida, O.F. Inherent glucocorticoid response potential of isolated hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singewald, N.; Philippu, A. Release of neurotransmitters in the locus coeruleus. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 237–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, R.J.; Van Bockstaele, E. Opposing regulation of the locus coeruleus by corticotropin-releasing factor and opioids. Potential for reciprocal interactions between stress and opioid sensitivity. Psychopharmacology 2001, 158, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.C.; Schluger, J.; Gunduz, M.; Borg, L.; Perret, G.; Ho, A.; Kreek, M.J. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis response and biotransformation of oral naltrexone: Preliminary examination of relationship to family history of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 26, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volavka, J.; Cho, D.; Mallya, A.; Bauman, J. Naloxone increases ACTH and cortisol levels in man. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979, 300, 1056–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, C.A.; Oswald, L.M.; Weerts, E.M.; McCaul, M.E.; Wand, G.S. Hormone responses to social stress in abstinent alcohol-dependent subjects and social drinkers with no history of alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, G.S.; Schumann, H. Relationship between plasma adrenocorticotropin, hypothalamic opioid tone, and plasma leptin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 2138–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liberzon, I.; Sripada, C.S. The functional neuroanatomy of PTSD: A critical review. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 167, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Grau, J.W.; Hyson, R.L.; Maier, S.F.; Madden, J., IV; Barchas, J.D. Long-term stress-induced analgesia and activation of the opiate system. Science 1981, 213, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, C.; Nemeroff, C.B. Neurobiology of posttraumatic stress disorder. CNS Spectr. 2009, 14 (Suppl. S1), 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Strawn, J.R.; Geracioti, T.D., Jr. Noradrenergic dysfunction and the psychopharmacology of posttraumatic stress disorder. Depress. Anxiety 2008, 25, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, H.; Borgwardt, S.J.; Schmid, O.; Gerhard, U.; Joechle, W.; Riecher-Rossler, A.; Wiesbeck, G.A.; Walter, M. The impact of diacetylmorphine on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and heroin craving in heroin dependence. Eur. Addict. Res. 2012, 18, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.F.; Ren, Y.P.; Sheng, L.X.; Chi, Y.; Du, W.J.; Guo, S.; Jiang, Z.N.; Xiao, L.; Luo, X.N.; Tang, Y. Let al. Dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in opioid dependent subjects: Effects of acute and protracted abstinence. Am. J. Drug Alcohol. Abus. 2008, 34, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, T.L.; Galarneau, M.R.; Dye, J.L.; Quinn, K.; Dougherty, A.L. Morphine Use after Combat Injury in Iraq and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, G.; Stoddard, F.; Courtney, D.; Cunningham, K.; Chawla, N.; Sheridan, R.; King, D.; King, L. Relationship Between Acute Morphine and the Course of PTSD in Children With Burns. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Z.T.; Trott, J.M.; Rajbhandari, A.K.; Li, K.; Walwyn, W.M.; Evans, C.J.; Fanselow, M.S. Chronic opioid pretreatment potentiates the sensitization of fear learning by trauma. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Clark, S.D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.H.; Brucher, F.A.; Zeng, J.; Ly, N.K.; Henriksen, S.J.; et al. Neuropeptide S: A neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects. Neuron 2004, 43, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Veer, A.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Role of kappa-opioid receptors in stress and anxiety-related behavior. Psychopharmacology 2013, 229, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, F.; Caldiroli, E.; Premi, S.; Lucchini, A. Relationship between plasma cortisol levels, withdrawal symptoms and craving in abstinent and treated heroin addicts. J. Addict. Dis. 2006, 25, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, A.; Heberlein, A.; Dürsteler-MacFarland, K.M.; Lenz, B.; Frieling, H.; Gröschl, M.; Wiesbeck, G.A.; Kornhuber, J.; Bönsch, D.; Bleich, S.; et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide, arginine vasopressin peptide and cortisol serum levels in opiate-dependent patients. Neuropsychobiology 2013, 67, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerra, G.; Zaimovic, A.; Moi, G.; Bussandri, M.; Delsignore, R.; Caccavari, R.; Brambilla, F. Neuroendocrine correlates of antisocial personality disorder in abstinent heroin-dependent subjects. Addict. Biol. 2003, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.S.; Carpenter, R.D.; Majumdar, S.; Ma, C.B. Three-dimensional in vivo patellofemoral kinematics and contact area of anterior cruciate ligament-deficient and -reconstructed subjects using magnetic resonance imaging. Arthroscopy 2009, 25, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.S.; Dackis, C.A.; Gold, M.S. The relationship of addiction, tolerance, and dependence to alcohol and drugs: A neurochemical approach. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 1987, 4, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreek, M.J. Tolerance and dependence: Implications for the pharmacological treatment of addiction. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1987, 76, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McDougle, C.J.; Black, J.E.; Malison, R.T.; Zimmermann, R.C.; Kosten, T.R.; Heninger, G.R.; Price, L.H. Noradrenergic dysregulation during discontinuation of cocaine use in addicts. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1994, 51, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, J.C.; Cooper, T.A. Differences in hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical activity in the rat after acute and prolonged treatment with morphine. Neuroendocrinology 1984, 38, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, J.C.; Cooper, T.A. Interrelationships of opioidergic and adrenergic mechanisms controlling the secretion of corticotrophin releasing factor in the rat. Neuroendocrinology 1987, 46, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, G.P.; Akil, H. Role of corticotropin-releasing hormone in the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the behavioral, pain modulatory, and endocrine consequences of opiate withdrawal. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaferi, A.; Lane, D.A.; Pickel, V.M. Subcellular plasticity of the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor in dendrites of the mouse bed nucleus of the stria terminalis following chronic opiate exposure. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Carmona, J.A.; Milanes, M.V.; Laorden, M.L. Brain stress system response after morphine-conditioned place preference. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1999–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaham, Y.; Funk, D.; Erb, S.; Brown, T.J.; Walker, C.D.; Stewart, J. Corticotropin-releasing factor, but not corticosterone, is involved in stress-induced relapse to heroin-seeking in rats. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrichs, S.C.; Menzaghi, F.; Schulteis, G.; Koob, G.F.; Stinus, L. Suppression of corticotropin-releasing factor in the amygdala attenuates aversive consequences of morphine withdrawal. Behav. Pharmacol. 1995, 6, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Wiesbeck, G.A.; Degen, B.; Albrich, J.; Oppel, M.; Schulz, A.; Schachinger, H.; Dursteler-MacFarland, K.M. Heroin reduces startle and cortisol response in opioid-maintained heroin-dependent patients. Addict. Biol. 2011, 16, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountas, A.; Chai, S.T.; Kourkouti, C.; Karavitaki, N. Mechanisms of Endocrinology: Endocrinology of opioids. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, R183–R196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.D. Commentary on the Special Section on Complex PTSD: Still Going Strong After All These Years. J. Trauma. Stress. 2019, 32, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugani, F.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Rovai, L.; Mautone, S.; Perugi, P.; Pani, P.P.; Dell’Osso, L.; Maremmani, I. Life events (loss and traumatic) and emotional responses to them in heroin-dependent patients before and after the dependence age of onset. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2011, 13, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerra, G.; Zaimovic, A.; Mascetti, G.G.; Gardini, S.; Zambelli, U.; Timpano, M.; Raggi, M.A.; Brambilla, F. Neuroendocrine responses to experimentally-induced psychological stress in healthy humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2001, 26, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, S.J.; Maloney, T.; Parvaz, M.A.; Dunning, J.P.; Alia-Klein, N.; Woicik, P.A.; Hajcak, G.; Telang, F.; Wang, G.J.; Volkow, N.D.; et al. Enhanced choice for viewing cocaine pictures in cocaine addiction. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Rugani, F.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Bertoni, S.; Pani, P.P.; Maremmani, I. Towards a unitary perspective between Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Substance Use Disorder. Heroin Use Disord. Case study. Compr. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.W.; Vogt, D.S.; Mozley, S.L.; Kaloupek, D.G.; Keane, T.M. PTSD and substance-related problems: The mediating roles of disconstraint and negative emotionality. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2006, 115, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.B.; Spitzer, R.L.; Gibbon, M.; Gibbon, W.; Janet, B.W. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, Clinician Version (SCID-CV); American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Massimetti, E.; Rugani, F.; Carmassi, C.; Fareed, A.; Stratta, P.; Rossi, A.; Massimetti, G.; Maremmani, I. Life events (loss and traumatic) and emotional responses to them in acute catastrophe survivors and long-lasting heroin use disorder patients never exposed to catastrophic events. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2015, 17, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Geffen, D.B.; Blaustein, A.; Amir, M.C.; Cohen, Y. Post-traumatic stress disorder and quality of life in long-term survivors of Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Israel. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.; Jayson, G.; Tarrier, N. A longitudinal investigation of posttraumatic stress disorder in patients with ovarian cancer. J. Psychosom. Res. 2011, 70, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostacoli, L.; Carletto, S.; Borghi, M.; Cavallo, M.; Rocci, E.; Zuffranieri, M.; Malucchi, S.; Bertolotto, A.; Zennaro, A.; Furlan, P.M.; et al. Prevalence and significant determinants of post-traumatic stress disorder in a large sample of patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Psychol. Med. Settings 2013, 20, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.K.; Zimmerman, S.; Williams, C.S.; Benecha, H.; Abernethy, A.P.; Mayer, D.K.; Edwards, L.J.; Ganz, P.A. Post-traumatic stress symptoms in long-term non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma survivors: Does time heal? J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4526–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.K.; Zimmerman, S.; Williams, C.S.; Preisser, J.S.; Clipp, E.C. Post-traumatic stress outcomes in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, V.S.; Ng, A.; Mauch, P.; Recklitis, C.J. Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in survivors of Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Prevalence of PTSD and partial PTSD compared with sibling controls. Psycho Oncol. 2013, 22, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, L.; Nagra, N.; Kulubya, G.; Catalan, J.; Clucas, C.; Harding, R. HIV infection associated post-traumatic stress disorder and post-traumatic growth—A systematic review. Psychol. Health Med. 2011, 16, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.R.; Cordell, E.; Sobin, S.M.; Neumeister, A. Recent progress in understanding the pathophysiology of post-traumatic stress disorder: Implications for targeted pharmacological treatment. CNS Drugs 2013, 27, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Marsa, M.; Molina, R.; Lozano, M.C.; Carrasco, J.L. Biological basis of posttraumatic stress disorder. Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2000, 28, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert, U.; Wagner, D.; Heinrichs, M.; Heim, C. Psychobiological aspects of posttraumatic stress disorder. Nervenarzt 1999, 70, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graef, F.G. Biological basis of posttraumatic stress disorder. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2003, 25 (Suppl S1), 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hoffman, L.; Burges Watson, P.; Wilson, G.; Montgomery, J. Low plasma beta-endorphin in post-traumatic stress disorder. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 1989, 23, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khozhenko, E.V. Neuronal mechanisms underlying main clinical syndromes of post-traumatic stress disorder. Klin Med. 2009, 87, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Knoll, A.T.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Dynorphin, stress, and depression. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauriyal, D.S.; Jaggi, A.S.; Singh, N. Extending pharmacological spectrum of opioids beyond analgesia: Multifunctional aspects in different pathophysiological states. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Land, B.B.; Chavkin, C. The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, F.I.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Development of κ Opioid Receptor Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2178–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreek, M.J.; Ragunath, J.; Plevy, S.; Hamer, D.; Schneider, B.; Hartman, N. ACTH, cortisol and beta-endorphin response to metyrapone testing during chronic methadone maintenance treatment in humans. Neuropeptides 1984, 5, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluger, J.H.; Borg, L.; Ho, A.; Kreek, M.J. Altered HPA axis responsivity to metyrapone testing in methadone maintained former heroin addicts with ongoing cocaine addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 24, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.A.; Creamer, M.; O’Donnell, M.; Silove, D.; McFarlane, A.C. A study of the protective function of acute morphine administration on subsequent posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, F.J., Jr.; Sorrentino, E.A.; Ceranoglu, T.A.; Saxe, G.; Murphy, J.M.; Drake, J.E.; Ronfeldt, H.; White, G.W.; Kagan, J.; Snidman, N.; et al. Preliminary evidence for the effects of morphine on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms in one- to four-year-olds with burns. J. Burn. Care Res. 2009, 30, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maremmani, I.; Pani, P.P.; Pacini, M.; Bizzarri, J.V.; Trogu, E.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Perugi, G.; Gerra, G.; Dell’Osso, L. Subtyping Patients with Heroin Addiction at Treatment Entry: Factors Derived fron the SCL-90. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maremmani, A.G.I.; Maiello, M.; Carbone, M.G.; Pallucchini, A.; Brizzi, F.; Belcari, I.; Conversano, C.; Perugi, G.; Maremmani, I. Towards a psychopathology specific to Substance Use Disorder: Should emotional responses to life events be included? Compr. Psychiatry 2018, 80, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, P.P.; Trogu, E.; Vigna-Taglianti, F.; Mathis, F.; Diecidue, R.; Kirchmayer, U.; Amato, L.; Ghibaudi, J.; Camposeragna, A.; Saponaro, A.; et al. Psychopathological symptoms of heroin-addicted patients entering opioid agonist or therapeutic community treatment. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2014, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, P.P.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Trogu, E.; Vigna-Taglianti, F.; Mathis, F.; Diecidue, R.; Kirchmayer, U.; Amato, L.; Davoli, M.; Ghibaudi, J.; et al. Psychopathological symptoms in detoxified and non-detoxified heroin-dependent patients entering residential treatment. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2015, 17, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, M.G.; Maiello, M.; Spera, V.; Manni, C.; Pallucchini, A.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Maremmani, I. The SCL90-based psychopathological structure may be applied in Substance Use Disorder patients irrespectively of the involved drug also in heroin, alcohol and cocaine mono-drug users. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2018, 20, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kreek, M.J.; Nielsen, D.A.; Butelman, E.R.; La Forge, K.S. Genetic influences on impulsivity, risk taking, stress responsivity and vulnerability to drug abuse and addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreek, M.J.; Wardlaw, S.L.; Hartman, N.; Raghunath, J.; Friedman, J.; Schneider, B.; Frantz, A.G. Circadian rhythms and levels of beta-endorphin, ACTH, and cortisol during chronic methadone maintenance treatment in humans. Life Sci. 1983, 33 (Suppl. S1), 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreek, M.J.; Zhon, Y.; Schussman, S. Craving in Opiate, Cocaine and Alcohol Addiction. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2004, 6, 5–52. [Google Scholar]
- Maremmani, I.; Cecchini, L.; Avella, M.T.; Novi, M.; Ciapparelli, A.; Maremmani, A.G.I. Prominent psychopathological and clinical characteristics of Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum patients during treatment. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2020, 22, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Maremmani, I.; Castrogiovanni, P. DAH-Q: Drug Addiction History Questionnaire; University Press: Pisa, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Derogatis, L.R.; Lipman, R.S.; Rickels, K.; Uhlenhuth, E.H.; Covi, L. The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL): A self-report symptom inventory. Behav. Sci. 1974, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maremmani, A.G.I.; Rovai, L.; Bacciardi, S.; Massimetti, E.; Gazzarrini, D.; Rugani, F.; Pallucchini, A.; Piz, L.; Maremmani, I. An inventory for assessing the behavioural covariates of craving in heroin substance use disorder. Development, theoretical description, reliability, exploratory factor analysis and preliminary construct validity. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2015, 17, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Carmassi, C.; Rucci, P.; Conversano, C.; Shear, M.K.; Calugi, S.; Maser, J.D.; Endicott, J.; Fagiolini, A.; Cassano, G.B. A multidimensional spectrum approach to post-traumatic stress disorder: Comparison between the Structured Clinical Interview for Trauma and Loss Spectrum (SCI-TALS) and the Self-Report instrument (TALS-SR). Compr. Psychiatry 2009, 50, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guina, J.; Nahhas, R.W.; Mata, N.; Farnsworth, S. Which Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms, Trauma Types, and Substances Correlate With Suicide Attempts in Trauma Survivors? Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2017, 19, 26158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamanna, F.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Maremmani, I. Nearly thirty years of experience of real-world long-term treatment with Opioid Agonists. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2020, 22, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rovai, L.; Maremmani, A.G.; Pacini, M.; Pani, P.P.; Rugani, F.; Lamanna, F.; Schiavi, E.; Mautone, S.; Dell’Osso, L.; Maremmani, I. Negative dimension in psychiatry. Amotivational syndrome as a paradigm of negative symptoms in substance abuse. Riv. Psichiatr. 2013, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maremmani, A.G.I.; Rovai, L.; Bacciardi, S.; Rugani, F.; Pacini, M.; Pani, P.P.; Dell’Osso, L.; Akiskal, H.S.; Maremmani, I. The long-term outcomes of heroin dependent-treatment-resistant patients with bipolar 1 comorbidity after admission to enhanced methadone maintenance. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 151, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, P.P.; Maremmani, I.; Pacini, M.; Lamanna, F.; Maremmani, A.G.I.; Dell’ Osso, L. Effect of psychiatric severity on the outcome of methadone maintenance treatment. Eur. Addict. Res. 2011, 17, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Shear, M.K.; Carmassi, C.; Rucci, P.; Maser, J.D.; Frank, E.; Endicott, J.; Lorettu, L.; Altamura, C.A.; Carpiniello, B.; et al. Validity and reliability of the Structured Clinical Interview for the Trauma and Loss Spectrum (SCI-TALS). Clin. Pr. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2008, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maremmani, I.; Miccoli, M. The TALS—Reduced form: An inventory for assessing the Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum (H/PTSD-S). Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2020, 22, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Maremmani, I.; Della Rocca, F.; Carbone, M.G.; Miccoli, M.; Maremmani, A.G.I. Assessing Subjective Wellness in Heroin Use Disorder. Part III: Convergent and Discriminant Validity of the DM-SWS. Correlations with demographics, Symptom Scales and Behavioural Questionnaires. Heroin Addict. Relat. Clin. Probl. 2025, 27, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maremmani, I.; Della Rocca, F.; Carbone, M.G.; Maremmani, A.G.I. Post-Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum: Heroin Addiction as a Generator of Trauma Sensitisation in Everyday Life: A Perspective Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186662
Maremmani I, Della Rocca F, Carbone MG, Maremmani AGI. Post-Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum: Heroin Addiction as a Generator of Trauma Sensitisation in Everyday Life: A Perspective Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186662
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaremmani, Icro, Filippo Della Rocca, Manuel Glauco Carbone, and Angelo Giovanni Icro Maremmani. 2025. "Post-Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum: Heroin Addiction as a Generator of Trauma Sensitisation in Everyday Life: A Perspective Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186662
APA StyleMaremmani, I., Della Rocca, F., Carbone, M. G., & Maremmani, A. G. I. (2025). Post-Heroin Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Spectrum: Heroin Addiction as a Generator of Trauma Sensitisation in Everyday Life: A Perspective Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186662







