Association of Scene Time Interval and Field Arrival to Epinephrine Administration Time with Outcomes in Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Setting
2.3. Data Source
2.4. Selection of Participants
2.5. Variables and Measurements
2.6. Outcome
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variables | South Korea | Singapore | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 89,081 | N = 5084 | ||||
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Age | median (IQR) | 72 (58, 82) | 72 (59, 84) | ||
| Gender | male | 56,187 | 63.1 | 3120 | 61.4% |
| female | 32,894 | 36.9 | 1964 | 38.6% | |
| Year | 2018 | - | - | 1450 | 28.5% |
| 2019 | 10,214 | 11.5 | 1659 | 32.6% | |
| 2020 | 24,626 | 27.6 | 1975 | 38.8% | |
| 2021 | 26,349 | 29.6 | - | - | |
| 2022 | 27,892 | 31.3 | - | - | |
| Witnessed arrest | yes | 42,323 | 47.5 | 2463 | 48.4% |
| no | 46,758 | 52.5 | 2621 | 51.6% | |
| Location of arrest | private | 55,247 | 62.0 | 4346 | 85.5% |
| public | 33,834 | 38.0 | 738 | 14.5% | |
| Bystander CPR | yes | 43,944 | 49.3 | 2879 | 56.6% |
| no | 45,137 | 50.7 | 2205 | 43.4% | |
| Initial shockable rhythm | yes | 9669 | 10.9 | 730 | 14.4% |
| no | 79,412 | 89.1 | 4354 | 85.6% | |
| Prehospital defibrillation | yes | 13,389 | 15.0 | 898 | 17.7% |
| no | 75,692 | 85.0 | 4186 | 82.3% | |
| PCI (yes) | yes | 5027 | 5.6 | 229 | 5.1% |
| TTM (yes) | yes | 3138 | 3.5 | 250 | 5.5% |
| ECMO (yes) | yes | 897 | 1.0 | 10 | 0.2% |
| Any ROSC (yes) | yes | 29,579 | 33.2 | 1396 | 30.9% |
| Survival to discharge | yes | 7180 | 8.1 | 403 | 7.9% |
| Good neurologic recovery | CPC 1, 2 | 4769 | 5.4 | 322 | 6.3% |
| CPC 3, 4, 5 | 84,312 | 94.6 | 4759 | 93.7% | |
| Survival to Discharge | Good Neurologic Recovery | Total | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | p-Value | No | Yes | p-Value | |||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |||
| South Korea | 17,760 | 94.1 | 1107 | 5.9 | 18,341 | 97.2 | 526 | 2.8 | 18,867 | |||
| scene time interval and field arrival to epinephrine time categorized by median value | ||||||||||||
| short stay and early epinephrine | 5621 | 92.4 | 460 | 7.6 | <0.01 | 5852 | 96.2 | 229 | 3.8 | <0.01 | 6081 | 32.2 |
| short stay and late epinephrine | 2588 | 94.9 | 140 | 5.1 | <0.01 | 2666 | 97.7 | 62 | 2.3 | <0.01 | 2728 | 14.5 |
| long stay and early epinephrine | 2644 | 93.4 | 186 | 6.6 | 0.14 | 2731 | 96.5 | 99 | 3.5 | 0.02 | 2830 | 15.0 |
| long stay and late epinephrine | 6907 | 95.6 | 321 | 4.4 | <0.01 | 7092 | 98.1 | 136 | 1.9 | <0.01 | 7228 | 38.3 |
| scene time interval categorized by median value and field arrival to epinephrine time categorized by 10 min | ||||||||||||
| short stay and early epinephrine | 4772 | 92.3 | 399 | 7.7 | <0.01 | 4973 | 96.2 | 198 | 3.8 | <0.01 | 5171 | 27.4 |
| short stay and late epinephrine | 3437 | 94.5 | 201 | 5.5 | 3545 | 97.4 | 93 | 2.6 | 3638 | 19.3 | ||
| long stay and early epinephrine | 1851 | 93.1 | 137 | 6.9 | 1919 | 96.5 | 69 | 3.5 | 1988 | 10.5 | ||
| long stay and late epinephrine | 7700 | 95.4 | 370 | 4.6 | 7904 | 97.9 | 166 | 2.1 | 8070 | 42.8 | ||
| Singapore | 4079 | 97.5 | 105 | 2.5 | 4131 | 98.7 | 53 | 1.3 | 4177 | |||
| scene time interval and field arrival to epinephrine time categorized by median value | ||||||||||||
| short stay and early epinephrine | 1163 | 96.5 | 42 | 3.5 | <0.001 | 1187 | 98.5 | 18 | 1.5 | 0.006 | 1205 | 28.8 |
| short stay and late epinephrine | 702 | 98.2 | 13 | 1.8 | 709 | 99.2 | 6 | 0.8 | 715 | 17.1 | ||
| long stay and early epinephrine | 725 | 96.2 | 29 | 3.8 | 736 | 97.6 | 18 | 2.4 | 754 | 18 | ||
| long stay and late epinephrine | 1489 | 98.6 | 21 | 1.4 | 1499 | 99.3 | 11 | 0.7 | 1510 | 36.1 | ||
| scene time interval categorized by median value and field arrival to epinephrine time categorized by 10 min | ||||||||||||
| short stay and early epinephrine | 466 | 95.7 | 21 | 4.3 | <0.01 | 479 | 98.4 | 8 | 1.6 | <0.01 | 487 | 11.6 |
| short stay and late epinephrine | 1399 | 97.6 | 34 | 2.4 | 1417 | 98.9 | 16 | 1.1 | 1433 | 34.2 | ||
| long stay and early epinephrine | 140 | 92.7 | 11 | 7.3 | 143 | 94.7 | 8 | 5.3 | 151 | 3.6 | ||
| long stay and late epinephrine | 2074 | 98.2 | 39 | 1.8 | 2092 | 99.0 | 21 | 1.0 | 2113 | 50.5 | ||
| Total | Outcome | Unadjusted | Adjusted * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | OR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | |||||
| South Korea | ||||||||||
| Survival to discharge | 18,867 | 1107 | 5.9 | |||||||
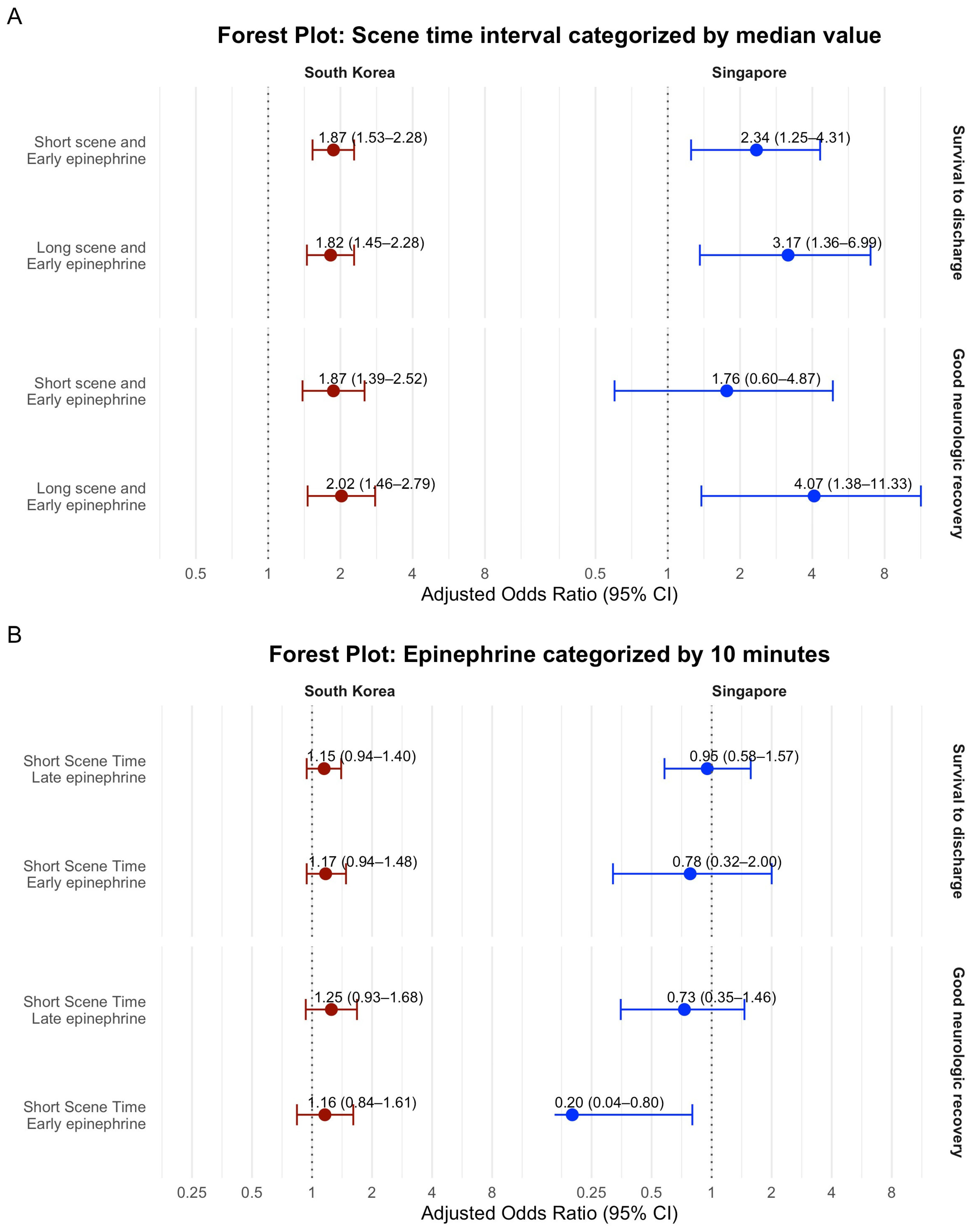
| Median STI and Median FEI | short stay early epinephrine | 5621 | 460 | 7.6 | 1.76 | 1.52 | 2.04 | 2.12 | 1.80 | 2.50 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 2588 | 140 | 5.1 | 1.16 | 0.95 | 1.43 | 1.06 | 0.85 | 1.33 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 2644 | 186 | 6.6 | 1.51 | 1.26 | 1.82 | 1.72 | 1.40 | 2.12 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 6907 | 321 | 4.4 | reference | reference | |||||
| Good neurologic recovery | 18,867 | 526 | 2.8 | |||||||
| Median STI and Median FEI | short stay early epinephrine | 5852 | 229 | 3.8 | 2.04 | 1.65 | 2.53 | 2.49 | 1.95 | 3.20 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 2666 | 62 | 2.3 | 1.21 | 0.90 | 1.64 | 1.20 | 0.85 | 1.69 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 2731 | 99 | 3.5 | 1.89 | 1.45 | 2.46 | 2.18 | 1.62 | 2.94 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 7092 | 136 | 1.9 | reference | reference | |||||
| Singapore | ||||||||||
| Survival to discharge | 4184 | 105 | 2.5 | |||||||
| Median STI and Median FEI | short stay early epinephrine | 1205 | 42 | 3.5 | 2.56 | 1.53 | 4.43 | 2.48 | 1.42 | 4.46 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 715 | 13 | 1.8 | 1.31 | 0.64 | 2.61 | 0.78 | 0.37 | 1.6 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 754 | 29 | 3.8 | 2.84 | 1.61 | 5.07 | 3.00 | 1.63 | 5.63 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 1510 | 21 | 1.4 | reference | reference | |||||
| Good neurologic recovery | 4184 | 53 | 1.3 | |||||||
| Median STI and Median FEI | short stay early epinephrine | 1205 | 18 | 1.5 | 2.07 | 0.99 | 4.53 | 1.73 | 0.77 | 4.07 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 715 | 6 | 0.8 | 1.15 | 0.4 | 3.04 | 0.58 | 0.19 | 1.62 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 754 | 18 | 2.4 | 3.33 | 1.59 | 7.32 | 2.89 | 1.26 | 6.89 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 1510 | 11 | 0.7 | reference | reference | |||||
| Country | Outcome | Scene Time Interval Categorized by Median Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short Scene Time Interval | Long Scene Time Interval | |||||||
| AOR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | |||||
| South Korea | Survival to discharge | early epinephrine by median value | 2.00 | 1.60 | 2.49 | 1.72 | 1.40 | 2.12 |
| late epinephrine by median value | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | early epinephrine by median value | 2.09 | 1.50 | 2.91 | 2.18 | 1.62 | 2.94 | |
| late epinephrine by median value | reference | reference | ||||||
| Singapore | Survival to discharge | early epinephrine by median value | 3.37 | 1.73 | 6.94 | 2.92 | 1.54 | 5.62 |
| late epinephrine by median value | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | early epinephrine by median value | 2.96 | 1.1 | 8.93 | 3.46 | 1.45 | 8.62 | |
| late epinephrine by median value | reference | reference | ||||||
| Epinephrine categorized by median value | ||||||||
| Early epinephrine | Late epinephrine | |||||||
| South Korea | Survival to discharge | short scene time interval | 1.23 | 1.01 | 1.50 | 1.06 | 0.85 | 1.33 |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | short scene time interval | 1.14 | 0.86 | 1.52 | 1.20 | 0.85 | 1.69 | |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
| Singapore | Survival to discharge | short scene time interval | 0.90 | 0.53 | 1.56 | 0.77 | 0.35 | 1.65 |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | short scene time interval | 0.62 | 0.28 | 1.34 | 0.54 | 0.17 | 1.59 | |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
References
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, G.D.; Graesner, J.T.; Semeraro, F.; Olasveengen, T.; Soar, J.; Lott, C.; Van de Voorde, P.; Madar, J.; Zideman, D.; Mentzelopoulos, S.; et al. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021: Executive summary. Resuscitation 2021, 161, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.T.; Teoh, W.Y. The Effect of Prehospital Epinephrine in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prehosp. Disaster. Med. 2019, 34, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Schmicker, R.H.; Newgard, C.D.; Grunau, B.; Scheuermeyer, F.; Cheskes, S.; Vithalani, V.; Alnaji, F.; Rea, T.; Idris, A.H.; et al. Time to Epinephrine Administration and Survival from Nonshockable Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Among Children and Adults. Circulation 2018, 137, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Bae, H.S.; Moon, H.J.; Kim, G.W.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, D.W.; Jeong, D.K.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J. Evaluation of optimal scene time interval for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest using a deep neural network. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 63, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, M.; Komukai, S.; Callaway, C.W.; Izawa, J. Association of Timing of Epinephrine Administration with Outcomes in Adults With Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2120176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzan, N.; Hiasa, K.I.; Ichimura, K.; Nishihara, M.; Iyonaga, T.; Shono, Y.; Tohyama, T.; Funakoshi, K.; Kitazono, T.; Tsutsui, H. Delayed administration of epinephrine is associated with worse neurological outcomes in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and initial pulseless electrical activity: Insight from the nationwide multicentre observational JAAM-OHCA (Japan Association for Acute Medicine) registry. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2022, 11, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Lim, D.; Kim, S.C.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, B.; Kim, S.H. Effect of Prehospital Epinephrine Use on Survival from Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest and on Emergency Medical Services. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, M.E.; Cho, J.; Ma, M.H.; Tanaka, H.; Nishiuchi, T.; Al Sakaf, O.; Karim, S.A.; Khunkhlai, N.; Atilla, R.; Lin, C.-H.; et al. Comparison of emergency medical services systems in the pan-Asian resuscitation outcomes study countries: Report from a literature review and survey. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2013, 25, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, M.E.; Tan, E.H.; Ng, F.S.; Panchalingham, A.; Lim, S.H.; Manning, P.G.; Ong, V.Y.K.; Lim, S.H.C.; Yap, S.; Tham, L.P.; et al. Survival outcomes with the introduction of intravenous epinephrine in the management of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2007, 50, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Ro, Y.S.; Song, K.J.; Shin, S.D. Establishing the Korean Out-of-Hospital cardiac arrest registry (KOHCAR). Resusc. Plus. 2024, 17, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, M.E.; Shin, S.D.; Tanaka, H.; Ma, M.H.; Khruekarnchana, P.; Hisamuddin, N.; Atilla, R.; Middleton, P.; Kajino, K.; Leong, B.S.-H.; et al. Pan-Asian Resuscitation Outcomes Study (PAROS): Rationale, methodology, and implementation. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2011, 18, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.E.; Ho, A.F.; Shahidah, N.; Asyikin, N.; Liew, L.X.; Pek, P.P.; Kua, J.P.; Chia, M.Y.; Ng, Y.Y.; Arulanandam, S.; et al. An essential review of Singapore’s response to out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: Improvements over a ten-year period. Singap. Med. J. 2021, 62, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Ohashi-Fukuda, N.; Inokuchi, R.; Kondo, Y.; Taira, T.; Kukita, I. Timing of Intravenous Epinephrine Administration During Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. Shock 2021, 56, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Kondo, Y.; Hayashida, K.; Sekiguchi, H.; Kukita, I. Time to epinephrine and survival after paediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2018, 4, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako, J.; Komukai, S.; Izawa, J.; Callaway, C.W.; Okubo, M. Evaluation of Use of Epinephrine and Time to First Dose and Outcomes in Pediatric Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e235187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristagno, G.; Tang, W.; Huang, L.; Fymat, A.; Chang, Y.T.; Sun, S.; Castillo, C.; Weil, M.H. Epinephrine reduces cerebral perfusion during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburn, N.P.; Beaver, B.P.; Snavely, A.C.; Nazir, N.; Winslow, J.T.; Nelson, R.D.; Shaw, A.; Camp, S.; Gorman, E.F.; Tran, Q.K. One and Done Epinephrine in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest? Outcomes in a Multiagency United States Study. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2023, 27, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liao, X. Intravenous vs intraosseous adrenaline administration in cardiac arrest: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e23917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.Y.; Bulger, N.; Chocron, R.; Counts, C.R.; Drucker, C.; Yin, L.; Parayil, M.; Johnson, N.J.; Sotoodehenia, N.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; et al. Analysis of Epinephrine Dose, Targeted Temperature Management, and Neurologic and Survival Outcomes Among Adults with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2226191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, L.; Hutton, J.; Yap, J.; Dodek, P.; Scheuermeyer, F.; Asamoah-Boaheng, M.; Heidet, M.; Wall, N.; Fordyce, C.B.; van Diepen, S.; et al. The association of the post-resuscitation on-scene interval and patient outcomes after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2023, 188, 109753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.A.; Ordoobadi, A.J.; Panchal, A.R.; Cash, R.E. Differences in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Management and Outcomes across Urban, Suburban, and Rural Settings. Prehosp. Emerg. Care 2023, 27, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rob, D.; Farkasovska, K.; Kreckova, M.; Smid, O.; Kavalkova, P.; Macoun, J.; Huptych, M.; Havrankova, P.; Gallo, J.; Pudil, J.; et al. Effect of intra-arrest transport, extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation and immediate invasive assessment in refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A long-term follow-up of the Prague OHCA trial. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyher, C.; Karst, S.R.; Muellenbach, R.M.; Lotz, C.; Peivandi, A.A.; Boersch, V.; Weber, K.; Gradaus, R.; Rolfes, C. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (eCPR) for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA): Retrospective analysis of a load and go strategy under the aspect of golden hour of eCPR. Anaesthesist 2021, 70, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes, end-tidal carbon dioxide and extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation eligibility: New South Wales pilot data. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2022, 34, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | South Korea | Singapore | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 18,867 | N = 4184 | ||||
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Age | median (IQR) | 71.4 (58.7, 81.3) | 71.0 (59.0, 82.0) | ||
| Gender | male | 12,679 | 67.2 | 2800 | 66.9 |
| female | 6188 | 32.8 | 1384 | 33.1 | |
| Year | 2018 | - | - | 1417 | 33.9 |
| 2019 | 742 | 3.93 | 1430 | 34.2 | |
| 2020 | 6036 | 31.99 | 1337 | 32.0 | |
| 2021 | 5976 | 31.67 | - | - | |
| 2022 | 6113 | 32.4 | - | - | |
| Witnessed arrest | yes | 8335 | 44.2 | 2152 | 51.4 |
| no | 10,532 | 55.8 | 2032 | 48.6 | |
| Location of arrest | private | 11,754 | 62.3 | 3483 | 83.2 |
| public | 7113 | 37.7 | 701 | 16.8 | |
| Bystander CPR | yes | 12,110 | 64.2 | 2612 | 62.4 |
| no | 6757 | 35.8 | 1572 | 37.6 | |
| Initial shockable rhythm | yes | 2724 | 14.4 | 719 | 17.2 |
| no | 16,143 | 85.6 | |||
| Prehospital defibrillation | yes | 4309 | 22.8 | 1104 | 26.4 |
| no | 14,558 | 77.2 | 3080 | 73.6 | |
| Advanced airway management | yes | 18,684 | 99.0 | 4075 | 97.4 |
| no | 183 | 1.0 | 109 | 2.6 | |
| PCI | yes | 1040 | 5.5 | 109 | 2.6 |
| no | 17,827 | 94.5 | 4074 | 97.4 | |
| TTM | yes | 921 | 4.9 | 234 | 5.6 |
| no | 17,946 | 95.1 | 3949 | 94.4 | |
| ECMO | yes | 277 | 1.5 | 12 | 0.3 |
| no | 18,590 | 98.5 | 4171 | 99.7 | |
| Any ROSC | yes | 7066 | 37.5 | 1315 | 31.4 |
| no | 11,801 | 62.6 | 2868 | 68.6 | |
| Survival to discharge | yes | 1107 | 5.9 | 105 | 2.5 |
| no | 17,760 | 94.1 | 4079 | 97.5 | |
| Good neurologic recovery | CPC 1, 2 | 526 | 2.8 | 53 | 1.3 |
| CPC 3, 4, 5 | 18,341 | 97.2 | 4131 | 98.7 | |
| South Korea (N = 18,867) | Singapore (N = 4184) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | p-Value | No | Yes | p-Value | |||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | |||||
| Survival to discharge | 17,760 | 94.1 | 1107 | 5.9 | 4079 | 97.5 | 105 | 2.5 | ||||
| number of prehospital epinephrine injection | 1 | 2864 | 87.5 | 409 | 12.5 | <0.01 | 933 | 95.0 | 49 | 5.0 | <0.01 | |
| 2 | 4139 | 92.6 | 330 | 7.4 | 1261 | 97.9 | 27 | 0.1 | ||||
| ≥3 | 10,757 | 96.7 | 368 | 3.3 | 1885 | 98.5 | 29 | 1.0 | ||||
| response time (min) | median, IQR | 9 | 7–12 | 8 | 6–10 | <0.01 | 9 | 7–11 | 8 | 7.10 | 0.15 | |
| scene time interval (STI) (min) | median, IQR | 18 | 15–23 | 17 | 14–21 | <0.01 | 24 | 21–28 | 23 | 19.27 | 0.04 | |
| transport time (min) | median, IQR | 7 | 4–11 | 7 | 5–12 | 0.14 | 6 | 4–9 | 6 | 4.8 | 0.6 | |
| field arrival to epinephrine time (FET) (min) | median, IQR | 11 | 8–14 | 10 | 7–13 | <0.01 | 14 | 11–20 | 11 | 9.16 | <0.01 | |
| STI categorized by median value and FET categorized by 10 min | short stay and early epinephrine | 4772 | 92.3 | 399 | 7.7 | <0.01 | 466 | 95.7 | 21 | 4.3 | <0.01 | |
| short stay and late epinephrine | 3437 | 94.5 | 201 | 5.5 | 1399 | 97.6 | 34 | 2.4 | ||||
| long stay and early epinephrine | 1851 | 93.1 | 137 | 6.9 | 140 | 92.7 | 11 | 7.3 | ||||
| long stay and late epinephrine | 7700 | 95.4 | 370 | 4.6 | 2074 | 98.2 | 39 | 1.8 | ||||
| Good neurologic recovery | 18,341 | 97.2 | 526 | 2.8 | 4131 | 98.7 | 53 | 1.3 | ||||
| number of prehospital epinephrine injection | 1 | 3045 | 93.0 | 228 | 7.0 | <0.01 | 954 | 97.1 | 28 | 2.9 | <0.01 | |
| 2 | 4323 | 96.7 | 146 | 3.3 | 1275 | 99.0 | 13 | 1.0 | ||||
| ≥3 | 10,973 | 98.6 | 152 | 1.4 | 1902 | 99.4 | 12 | 0.6 | ||||
| response time (min) | median, IQR | 9 | 6–12 | 8 | 6–10 | <0.01 | 9 | 7–11 | 8 | 7.10 | 0.14 | |
| scene time interval (min) | median, IQR | 18 | 15–23 | 17 | 13–20 | <0.01 | 24 | 21–28 | 24 | 21.29 | 0.8 | |
| transport time (min) | median, IQR | 7 | 4–11 | 7 | 5–13 | 0.02 | 6 | 4–9 | 6 | 5.8 | 0.9 | |
| field arrival to epinephrine time (min) | median, IQR | 11 | 8–14 | 9 | 7–12 | <0.01 | 14 | 11–19 | 11 | 9.16 | <0.01 | |
| STI categorized by median value and FET categorized by 10 min | short stay and early epinephrine | 4973 | 96.2 | 198 | 3.8 | <0.01 | 479 | 98.4 | 8 | 1.6 | <0.01 | |
| short stay and late epinephrine | 3545 | 97.4 | 93 | 2.6 | 1417 | 98.9 | 16 | 1.1 | ||||
| long stay and early epinephrine | 1919 | 96.5 | 69 | 3.5 | 143 | 94.7 | 8 | 5.3 | ||||
| long stay and late epinephrine | 7904 | 97.9 | 166 | 2.1 | 2092 | 99.0 | 21 | 1.0 | ||||
| Total | Outcome | Unadjusted | Adjusted * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | OR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | |||||
| South Korea | ||||||||||
| Survival to discharge | 18,867 | 1107 | 5.9 | |||||||
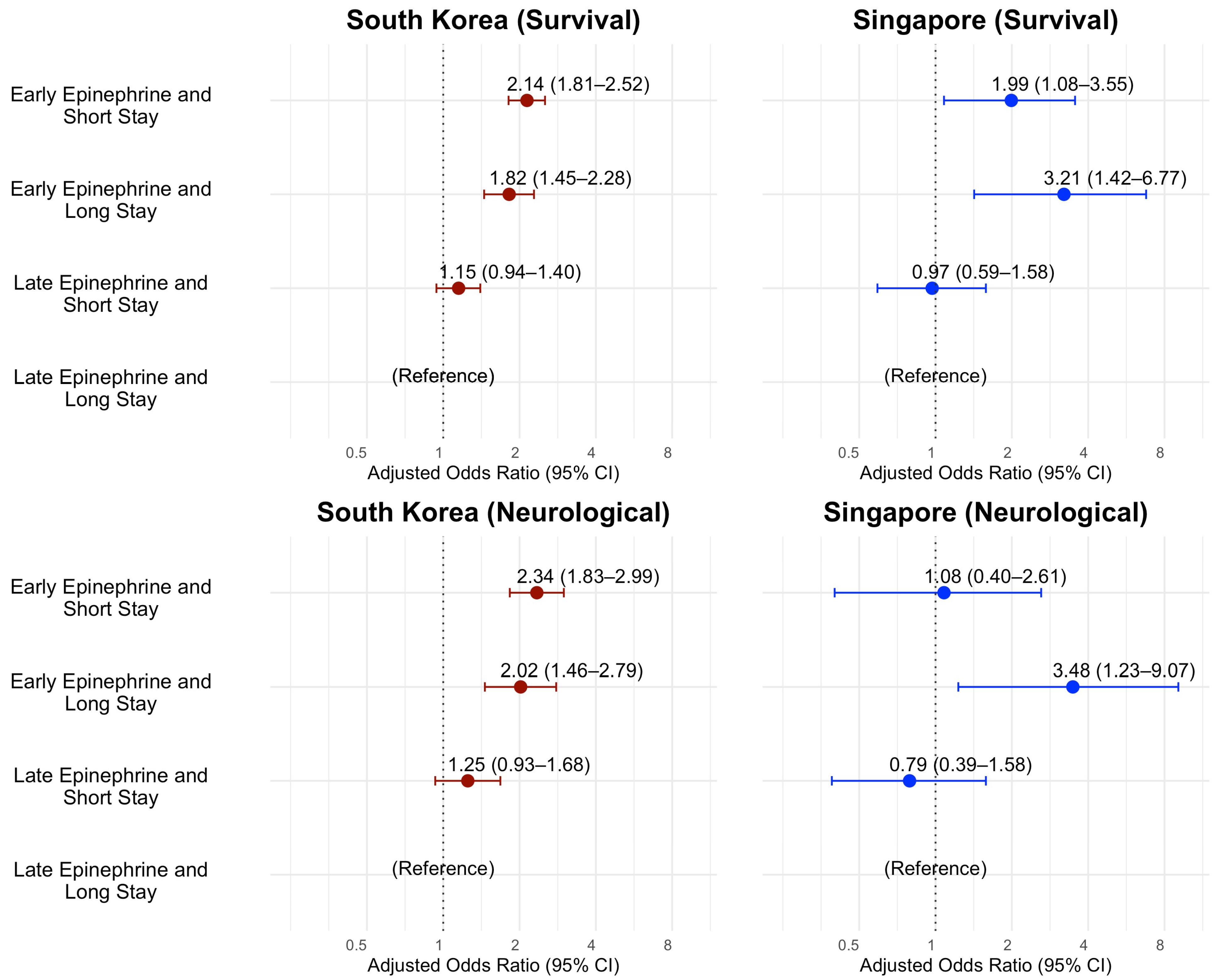
| Median STI and FET by 10 min | short stay early epinephrine | 5171 | 399 | 7.7 | 1.74 | 1.50 | 2.01 | 2.14 | 1.81 | 2.52 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 3638 | 201 | 5.5 | 1.22 | 1.02 | 1.45 | 1.15 | 0.94 | 1.40 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 1988 | 137 | 6.9 | 1.54 | 1.26 | 1.89 | 1.82 | 1.45 | 2.28 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 8070 | 370 | 4.6 | reference | reference | |||||
| Good neurologic recovery | 18,867 | 526 | 2.8 | |||||||
| Median STI and FET by 10 min | short stay early epinephrine | 5171 | 198 | 3.8 | 1.90 | 1.54 | 2.34 | 2.34 | 1.83 | 2.99 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 3638 | 93 | 2.6 | 1.25 | 0.97 | 1.62 | 1.25 | 0.93 | 1.68 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 1988 | 69 | 3.5 | 1.71 | 1.29 | 2.28 | 2.02 | 1.46 | 2.79 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 8070 | 166 | 2.1 | reference | reference | |||||
| Singapore | ||||||||||
| Survival to discharge | 4184 | 105 | 2.5 | |||||||
| Median STI and FET by 10 min | short stay early epinephrine | 487 | 21 | 4.3 | 2.4 | 1.37 | 4.07 | 1.99 | 1.08 | 3.55 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 1433 | 34 | 2.4 | 1.29 | 0.81 | 2.06 | 0.97 | 0.59 | 1.58 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 151 | 11 | 7.3 | 4.18 | 2.00 | 8.07 | 3.21 | 1.42 | 6.77 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 2113 | 39 | 1.8 | reference | reference | |||||
| Good neurologic recovery | 4184 | 53 | 1.3 | |||||||
| Median STI and FET by 10 min | short stay early epinephrine | 487 | 8 | 1.6 | 1.66 | 0.69 | 3.64 | 1.08 | 0.40 | 2.61 |
| short stay late epinephrine | 1433 | 16 | 1.1 | 1.12 | 0.58 | 2.15 | 0.79 | 0.39 | 1.58 | |
| long stay early epinephrine | 151 | 8 | 5.3 | 5.57 | 2.28 | 12.34 | 3.48 | 1.23 | 9.07 | |
| long stay late epinephrine | 2113 | 21 | 1.0 | reference | reference | |||||
| Country | Outcome | Scene Time Interval Categorized by Median Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short Scene Time Interval | Long Scene Time Interval | |||||||
| AOR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI | |||||
| South Korea | Survival to discharge | early epinephrine by 10 min | 1.87 | 1.53 | 2.28 | 1.82 | 1.45 | 2.28 |
| late epinephrine by 10 min | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | early epinephrine by 10 min | 1.87 | 1.39 | 2.52 | 2.02 | 1.46 | 2.79 | |
| late epinephrine by 10 min | reference | reference | ||||||
| Singapore | Survival to discharge | early epinephrine by 10 min | 2.34 | 1.25 | 4.31 | 3.17 | 1.36 | 6.99 |
| late epinephrine by 10 min | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | early epinephrine by 10 min | 1.76 | 0.60 | 4.87 | 4.07 | 1.38 | 11.33 | |
| late epinephrine by 10 min | reference | reference | ||||||
| Epinephrine categorized by 10 min | ||||||||
| Early epinephrine | Late epinephrine | |||||||
| South Korea | Survival to discharge | short scene time interval | 1.17 | 0.94 | 1.48 | 1.15 | 0.94 | 1.40 |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | short scene time interval | 1.16 | 0.84 | 1.61 | 1.25 | 0.93 | 1.68 | |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
| Singapore | Survival to discharge | short scene time interval | 0.78 | 0.32 | 2.00 | 0.95 | 0.58 | 1.57 |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
| Good neurologic recovery | short scene time interval | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.35 | 1.46 | |
| long scene time interval | reference | reference | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okada, Y.; Hong, K.J.; Ong, M.E.H.; Shin, S.D.; Song, K.J.; Park, J.H.; Ro, Y.S.; Shahidah, N.; Lim, S.L.; Siddiqui, F.J. Association of Scene Time Interval and Field Arrival to Epinephrine Administration Time with Outcomes in Cardiac Arrest. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6645. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186645
Okada Y, Hong KJ, Ong MEH, Shin SD, Song KJ, Park JH, Ro YS, Shahidah N, Lim SL, Siddiqui FJ. Association of Scene Time Interval and Field Arrival to Epinephrine Administration Time with Outcomes in Cardiac Arrest. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6645. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186645
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkada, Yohei, Ki Jeong Hong, Marcus Eng Hock Ong, Sang Do Shin, Kyoung Jun Song, Jeong Ho Park, Young Sun Ro, Nur Shahidah, Shir Lynn Lim, and Fahad Javaid Siddiqui. 2025. "Association of Scene Time Interval and Field Arrival to Epinephrine Administration Time with Outcomes in Cardiac Arrest" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6645. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186645
APA StyleOkada, Y., Hong, K. J., Ong, M. E. H., Shin, S. D., Song, K. J., Park, J. H., Ro, Y. S., Shahidah, N., Lim, S. L., & Siddiqui, F. J. (2025). Association of Scene Time Interval and Field Arrival to Epinephrine Administration Time with Outcomes in Cardiac Arrest. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6645. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186645








