Lymph Node Ratio as a Risk Factor for Early Recurrence in Older Patients with Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
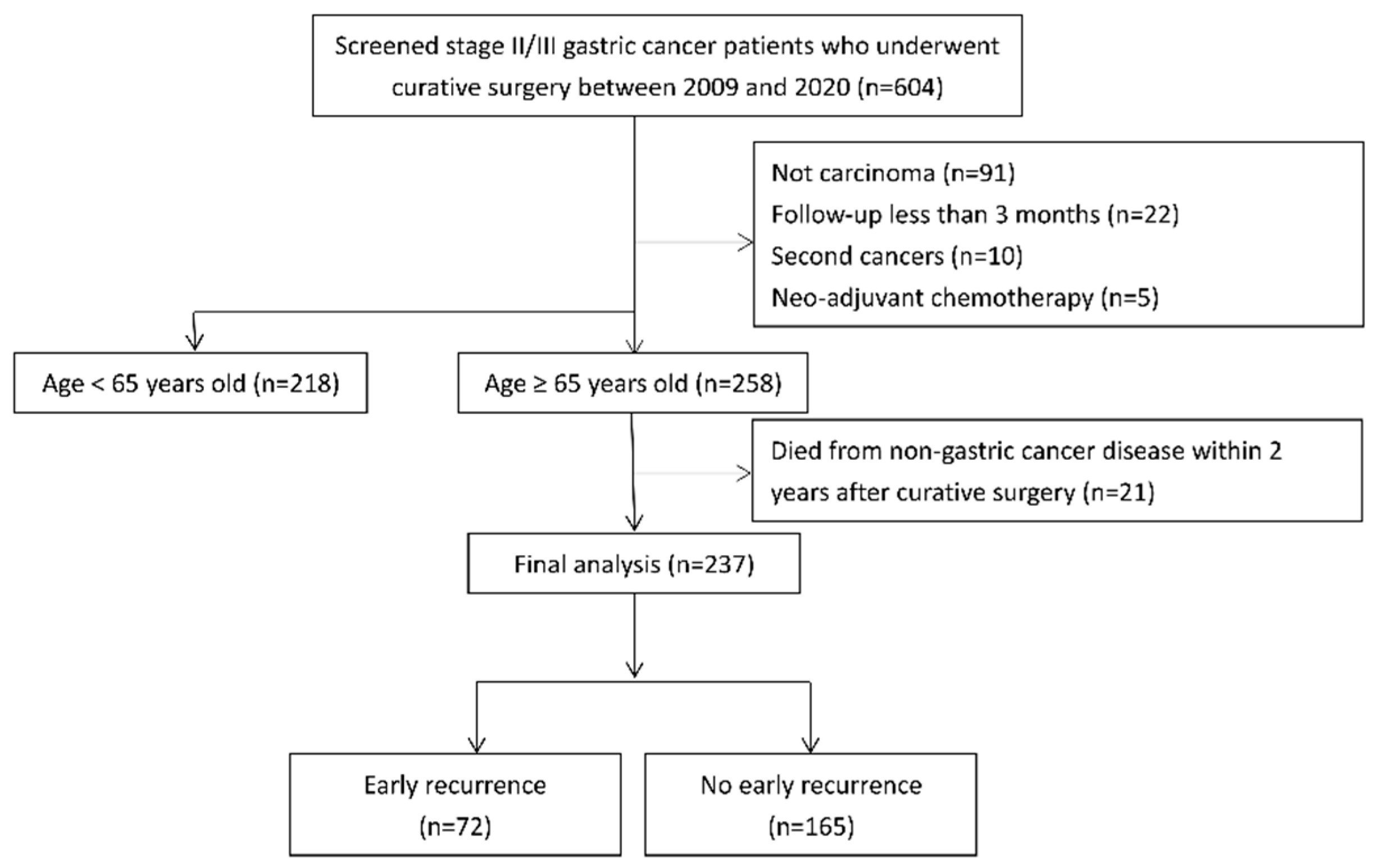
2.1. Patients
2.2. Variables and Outcome Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
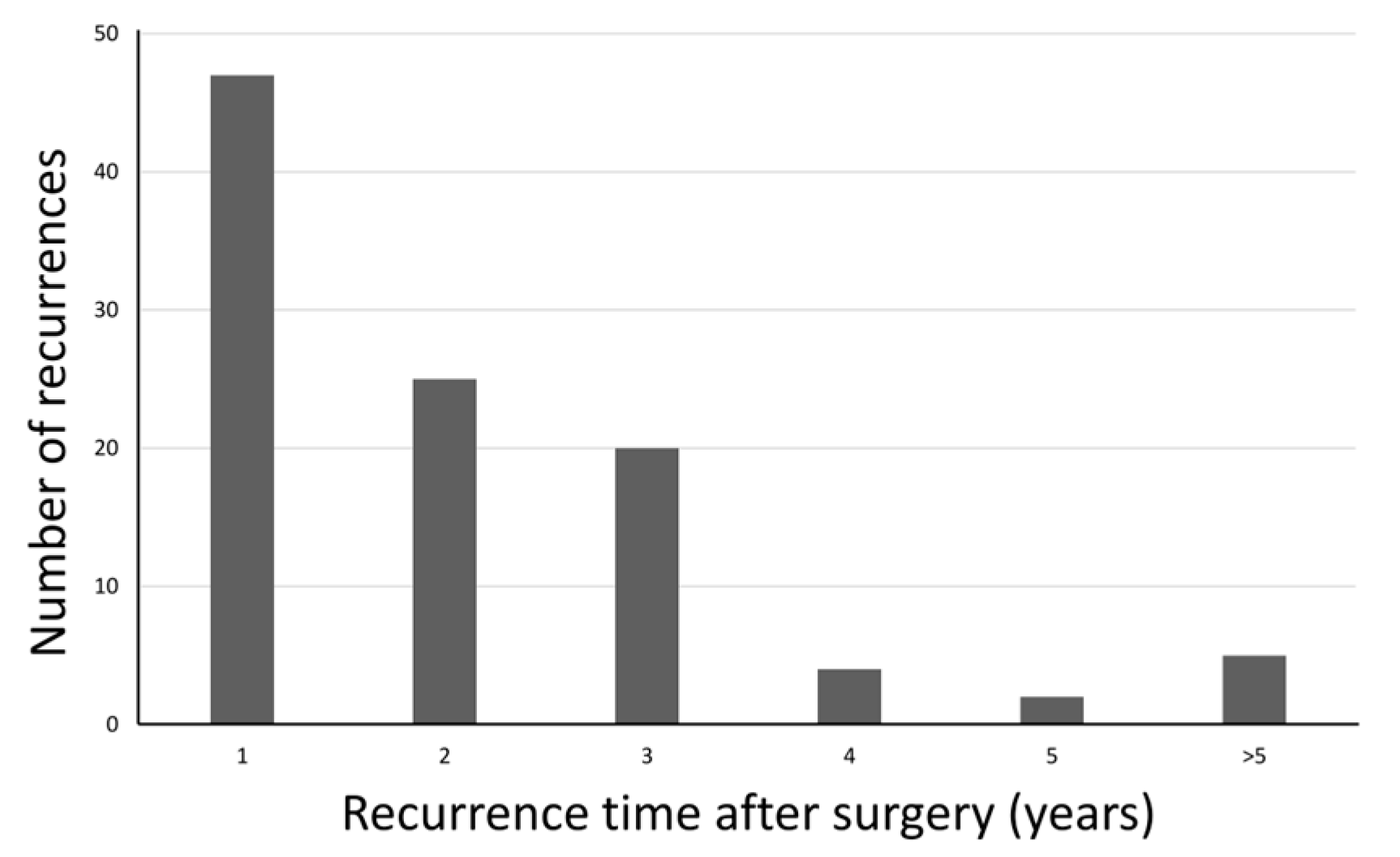
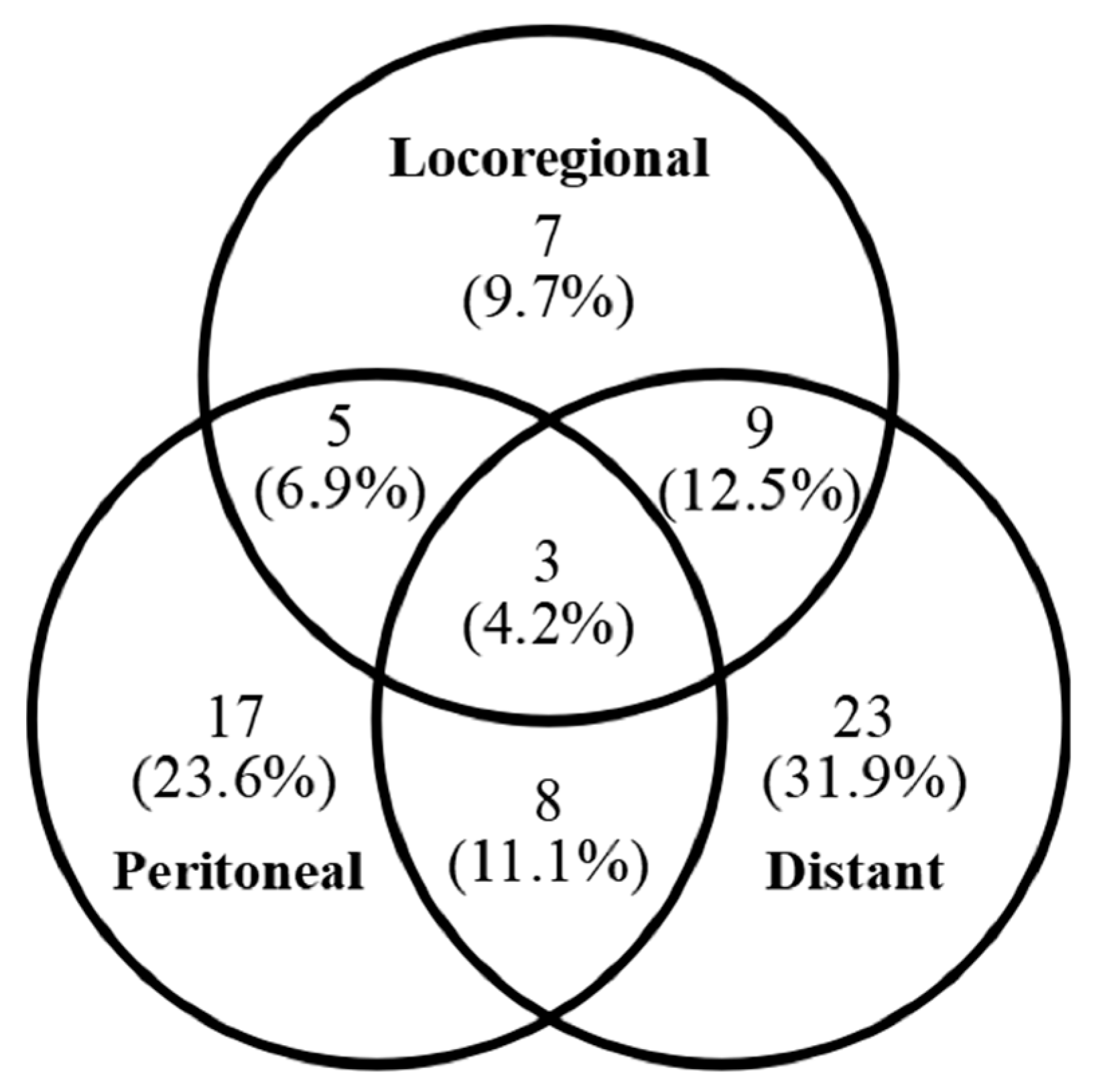
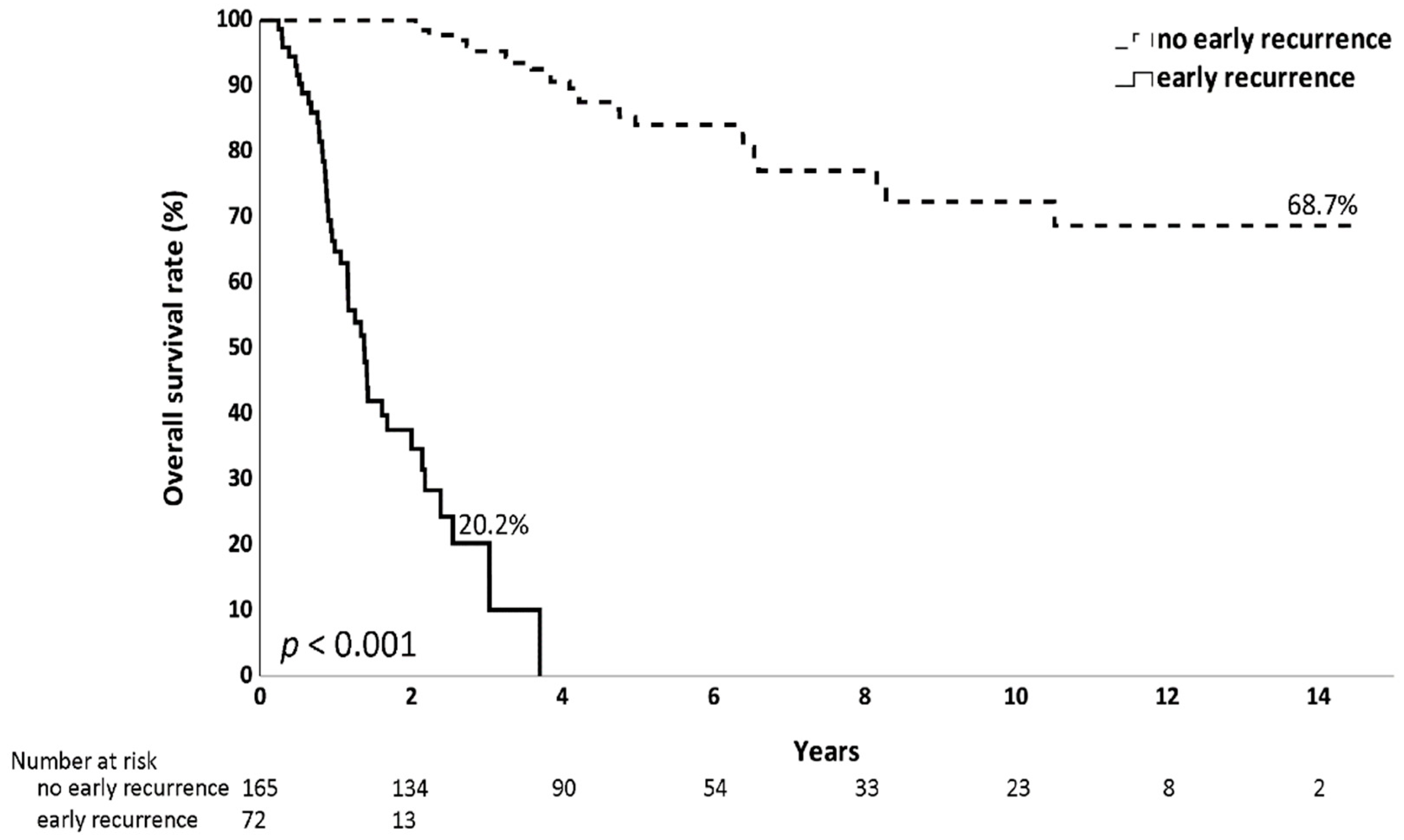
3.1. Recurrence Timing and Early Recurrence Pattern
3.2. Comparison of the Clinical Characteristics Between the Early Recurrence and No Early Recurrence Groups
3.3. Risk Factors for Early Recurrence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.S.; Xie, F.; Chen, B.; Yu, P.; Yu, J.; To, K.F.; Kang, W. Updated Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer in Asia: Decreased Incidence but Still a Big Challenge. Cancers 2023, 15, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Kuo, S.-H.; Chu, P.-Y.; Shan, Y.-S.; Tsai, C.-R.; Tsai, H.-J.; Chen, L.-T. The Epidemiology of Gastric Cancers in the Era of Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Nationwide Cancer Registry-Based Study in Taiwan. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Arco, C.D.; Medina, L.O.; Muñoz, L.E.; Roldán, E.M.; Heras, S.G.G.d.L.; Aceñero, M.J.F. Impact of Age at Diagnosis on Clinicopathological Features, Prognosis, and Management of Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Single-Center Experience from Spain. Cancers 2023, 15, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, M.; Kruszewski, W.J.; Szajewski, M.; Walczak, J.; Spychalska, N.; Szefel, J.; Zieliński, J. Extremely High Mortality Rate after a Successful Gastrectomy for Cancer in Older Adults. J. Gastric Cancer 2019, 19, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese Gastric Cancer Treatment Guidelines 2021 (6th edition). Gastric Cancer 2023, 26, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Fleitas, T.; Kawakami, H.; Curigliano, G.; Narita, Y.; Wang, F.; Wardhani, S.; Basade, M.; Rha, S.; Zamaniah, W.W.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with gastric cancer. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri, A.; Weeden, S.; Fielding, J.; Bancewicz, J.; Craven, J.; Joypaul, V.; Sydes, M.; Fayers, P. Patient survival after D1 and D2 resections for gastric cancer: Long-term results of the MRC randomized surgical trial. Surgical Co-operative Group. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasako, M.; Sakuramoto, S.; Katai, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Furukawa, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nashimoto, A.; Fujii, M.; Nakajima, T.; Ohashi, Y. Five-year outcomes of a randomized phase III trial comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 versus surgery alone in stage II or III gastric cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4387–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lu, M.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, L. The patterns and timing of recurrence after curative resection for gastric cancer in China. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shen, L.; Shui, Y.; Yu, W.; Guo, Q.; Yu, R.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Q. Patterns of recurrence after curative D2 resection for gastric cancer: Implications for postoperative radiotherapy. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4724–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouliaris, K.; Rachiotis, G.; Diamantis, A.; Christodoulidis, G.; Polychronopoulou, E.; Tepetes, K. Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in gastric cancer patients following D1 resection. Comparison with the current TNM staging system. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, P.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ma, B.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z. Can the Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Be Used to Determine Gastric Cancer Treatment Outcomes? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 7862469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yao, X.; Cen, D.; Zhi, Y.; Zhu, N.; Xu, L. The prognostic role of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio on overall survival in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Liu, Q. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in patients with gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 50, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Liu, J.; Meng, C.; Liu, B.; Liao, J. Pan-immune-inflammation value as a novel prognostic biomarker for digestive system cancers: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 22, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xishan, Z.; Ye, Z.; Feiyan, M.; Liang, X.; Shikai, W. The role of prognostic nutritional index for clinical outcomes of gastric cancer after total gastrectomy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.M.; Meng, Q.B.; Yu, J.C.; Ma, Z.Q.; Li, Z.T. Factors associated with early recurrence after curative surgery for gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5934–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.-W.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Zheng, W.-Z.; He, Q.-C.; Huang, Z.-N.; Xie, J.-W.; Wang, J.-B.; Lin, J.-X.; Lu, J.; Cao, L.-L.; et al. Postoperative follow-up for gastric cancer needs to be individualized according to age, tumour recurrence pattern, and recurrence time. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakatsuki, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Migita, K.; Kunishige, T.; Nakade, H.; Miyao, S.; Sho, M. Risk Factors and Risk Scores for Predicting Early Recurrence After Curative Gastrectomy in Patients with Stage III Gastric Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, S.; Kumagai, K.; Nunobe, S.; Ishizuka, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Imai, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Haruta, S.; Fukunaga, H.; Yamada, T.; et al. Risk factors for early recurrence after radical gastrectomy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II or III gastric cancer: A multicenter, retrospective study. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 54, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Yin, X.; Zhou, H.; Quan, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Xiao, H. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for predicting early recurrence after curative resection of stage II/III gastric cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supsamutchai, C.; Wilasrusmee, C.; Jirasiritham, J.; Rakchob, T.; Phosuwan, S.; Chatmongkonwat, T.; Choikrua, P.; Thampongsa, T. Recurrence outcome of lymph node ratio in gastric cancer after underwent curative resection: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 54, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Jeon, C.H.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, H.S.; Song, K.Y.; Lee, H.H. A Novel Approach for Gastric Cancer Staging in Elderly Patients Based on the Lymph Node Ratio. J. Gastric Cancer 2021, 21, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Nishimura, M.; Kosuga, T.; Okamoto, K.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; Fujiwara, H.; Otsuji, E. Evaluation of prognostic value and stage migration effect using positive lymph node ratio in gastric cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Song, X.N.; Liu, N.; Zhang, R.P.; Wang, C.L.; Liang, H. Prognostic value of the lymph node ratio in stage III gastric cancer patients undergoing radical resection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, T.; Komori, K.; Tamagawa, A.; Nakazano, M.; Hara, K.; Hashimoto, I.; Tamagawa, H.; Segami, K.; Maezawa, Y.; Kano, K.; et al. Clinical Influence of the Lymph Node Ratio on Lymph Node Metastasis-positive Gastric Cancer Patients Who Receive Curative Treatment. In Vivo 2022, 36, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergenc, M.; Uprak, T.K.; Akin, M.I.; Hekimoglu, E.E.; Celikel, C.A.; Yegen, C. Prognostic significance of metastatic lymph node ratio in gastric cancer: A Western-center analysis. BMC Surg. 2023, 23, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelen, S.D.; van Steenbergen, L.N.; Dassen, A.E.; van der Wurff, A.A.; Lemmens, V.E.; Bosscha, K. The lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor for gastric cancer. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, C.H.; Lee, H.H. Necessity of D2 lymph node dissection in older patients >/=80years with gastric cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2018, 9, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Hosogi, H.; Kanaya, S. Is D2 laparoscopic gastrectomy essential for elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer? A propensity score matched analysis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degiuli, M.; Reddavid, R.; Tomatis, M.; Ponti, A.; Morino, M.; Sasako, M.; Rebecchi, F.; Garino, M.; Vigano, L.; Scaglione, D.; et al. D2 dissection improves disease-specific survival in advanced gastric cancer patients: 15-year follow-up results of the Italian Gastric Cancer Study Group D1 versus D2 randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 150, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Liao, P.-W.; Chou, C.-W.; Lin, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Teng, C.-L.J.; Wu, F.-H.; Luo, S.-C.; Kao, S.-H. The efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy for older adults with stage II/III gastric cancer: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Chemotherapy treatment decision making by professionals and older patients with cancer: A narrative review of the literature. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2012, 21, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.C. Chemotherapy in Elderly Patients with Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Xia, Y.-Y.; Zhou, C.; Shen, X.-M.; Li, X.-L.; Han, S.-G.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, Z.-Q.; Gong, F.-R.; Wu, M.-Y.; et al. Application of platelet/lymphocyte and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratios in early diagnosis and prognostic prediction in patients with resectable gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2015, 15, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; He, B.; Liu, X.; Yue, J.; Ying, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, T.; et al. Prognostic value of pre-operative inflammatory response biomarkers in gastric cancer patients and the construction of a predictive model. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caglar, R. The relationship of different preoperative inflammatory markers with the prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, W.K.; Chang, H.J.; Suh, J.; Ahn, J.; Shin, J.; Hur, J.-Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S. The Prognostic Nutritional Index Predicts Survival and Identifies Aggressiveness of Gastric Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, P.; Song, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Ma, B.; Wang, Z. The prognostic nutritional index is a predictive indicator of prognosis and postoperative complications in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Wang, C.C.; Yang, W.; Gao, L.L.; Yu, S.Q. Prognostic value of preoperative prognostic nutritional index in stage III gastric cancer after curative resection: A retrospective cohort study. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fest, J.; Ruiter, R.; Ikram, M.A.; Voortman, T.; van Eijck, C.H.J.; Stricker, B.H. Reference Values for White Blood-Cell-Based Inflammatory Markers in the Rotterdam Study: A Population-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, S.S.; Kravchenko, G.; Korycka-Błoch, R.; Kostka, T.; Sołtysik, B.K. How Immunonutritional Markers Are Associated with Age, Sex, Body Mass Index and the Most Common Chronic Diseases in the Hospitalized Geriatric Population—A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, C.; Lo Buglio, A.; Bellanti, F.; Vendemiale, G. Prognostic Nutritional Index and Instant Nutritional Assessment Are Associated with Clinical Outcomes in a Geriatric Cohort of Acutely Inpatients. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lin, H.C.; Hsu, C.Y. 167P The factors associated with early recurrence in older patients with stage II/III gastric cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, S1469–S1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 237) | No Early Recurrence (n = 165) | Early Recurrence (n = 72) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 75.0 | (70–81) | 74.0 | (70–81) | 77.0 | (71–83) | 0.256 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.418 | ||||||
| Female | 78 | (32.9%) | 57 | (34.5%) | 21 | (29.2%) | |
| Male | 159 | (67.1%) | 108 | (65.5%) | 51 | (70.8%) | |
| BMI, n (%) | 0.096 | ||||||
| <18.5 | 19 | (8.0%) | 10 | (6.1%) | 9 | (12.5%) | |
| 18.5–24 | 119 | (50.2%) | 80 | (48.5%) | 39 | (54.2%) | |
| ≥24 | 99 | (41.8%) | 75 | (45.5%) | 24 | (33.3%) | |
| ECOG Performance Status, n (%) | 0.053 | ||||||
| 0–1 | 147 | (62.0%) | 109 | (66.1%) | 38 | (52.8%) | |
| >1 | 90 | (38.0%) | 56 | (33.9%) | 34 | (47.2%) | |
| aCCI, n (%) | 0.341 | ||||||
| 0–3 | 83 | (35.0%) | 61 | (37.0%) | 22 | (30.6%) | |
| >3 | 154 | (65.0%) | 104 | (63.0%) | 50 | (69.4%) | |
| Location, n (%) | 0.917 | ||||||
| Proximal | 57 | (24.1%) | 40 | (24.2%) | 17 | (23.6%) | |
| Non-proximal | 180 | (75.9%) | 125 | (75.8%) | 55 | (76.4%) | |
| Size, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤4 | 98 | (41.4%) | 81 | (49.0%) | 17 | (23.6%) | |
| >4 | 139 | (58.6%) | 84 | (50.9%) | 55 | (76.4%) | |
| Differentiation, n (%) | 0.207 | ||||||
| Well to moderate | 37 | (15.6%) | 29 | (17.6%) | 8 | (11.1%) | |
| Poor differentiation | 200 | (84.4%) | 136 | (82.4%) | 64 | (88.9%) | |
| Helicobacter pylori infection, n/total n (%) | 0.979 | ||||||
| No | 180/219 | (82.2%) | 125/152 | (82.2%) | 55/67 | (82.1%) | |
| Yes | 39/219 | (17.8%) | 27/152 | (17.8%) | 12/67 | (17.9%) | |
| Signet ring feature, n/total n (%) | 0.367 | ||||||
| No | 170/236 | (72.0%) | 121/164 | (73.8%) | 49/72 | (68.1%) | |
| Yes | 66/236 | (28.0%) | 43/164 | (26.2%) | 23/72 | (31.9%) | |
| Gastrectomy type, n (%) | 0.004 | ||||||
| Subtotal gastrectomy | 154 | (65.0%) | 117 | (70.9%) | 37 | (51.4%) | |
| Total gastrectomy | 83 | (35.0%) | 48 | (29.1%) | 35 | (48.6%) | |
| Lymphadenectomy type, n (%) | 0.205 | ||||||
| <D2 dissection | 72 | (30.4%) | 46 | (27.9%) | 26 | (36.1%) | |
| D2 dissection | 165 | (69.6%) | 119 | (72.1%) | 46 | (63.9%) | |
| Stage, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| Stage II | 104 | (43.9%) | 89 | (53.9%) | 15 | (20.8%) | |
| Stage III | 133 | (56.1%) | 76 | (46.1%) | 57 | (79.2%) | |
| T Stage, n (%) | 0.148 | ||||||
| T 1–2 | 35 | (14.8%) | 28 | (17.0%) | 7 | (9.7%) | |
| T 3–4 | 202 | (85.2%) | 137 | (83.0%) | 65 | (90.3%) | |
| N Stage, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| N 0–1 | 102 | (43.0%) | 85 | (51.5%) | 17 | (23.6%) | |
| N 2–3 | 135 | (57.0%) | 80 | (48.5%) | 55 | (76.4%) | |
| Lymph nodes ratio, n (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤0.17 | 149 | (62.9%) | 125 | (75.8%) | 24 | (33.3%) | |
| >0.17 | 88 | (37.1%) | 40 | (24.2%) | 48 | (66.7%) | |
| Lymphovascular invasion, n/total n (%) | 0.007 | ||||||
| No | 56/236 | (23.7%) | 47/164 | (28.7%) | 9/72 | (12.5%) | |
| Yes | 180/236 | (76.3%) | 117/164 | (71.3%) | 63/72 | (87.5%) | |
| Perineural invasion, n/total n (%) | 0.007 | ||||||
| No | 102/234 | (43.6%) | 80/162 | (49.4%) | 22/72 | (30.6%) | |
| Yes | 132/234 | (56.4%) | 82/162 | (50.6%) | 50/72 | (69.4%) | |
| Margin, n (%) | 0.013 | ||||||
| Negative | 223 | (94.1%) | 160 | (97.0%) | 63 | (87.5%) | |
| Positive | 14 | (5.9%) | 5 | (3.0%) | 9 | (12.5%) | |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy, n (%) | 0.048 | ||||||
| No | 68 | (28.7%) | 41 | (24.8%) | 27 | (37.5%) | |
| Yes | 169 | (71.3%) | 124 | (75.2%) | 45 | (62.5%) | |
| CEA level, n/total n (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| Normal | 185/226 | (81.9%) | 139/157 | (88.5%) | 46/69 | (66.7%) | |
| Elevated (≥5 U/mL) | 41/226 | (18.1%) | 18/157 | (11.5%) | 23/69 | (33.3%) | |
| CA19-9 level, n/total n (%) | 0.002 | ||||||
| Normal | 146/188 | (77.7%) | 110/131 | (84.0%) | 36/57 | (63.2%) | |
| Elevated (≥34 U/mL) | 42/188 | (22.3%) | 21/131 | (16.0%) | 21/57 | (36.8%) | |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, n/total n (%) | 0.113 | ||||||
| ≤2.7 | 120/233 | (51.5%) | 89/162 | (54.9%) | 31/71 | (43.7%) | |
| >2.7 | 113/233 | (48.5%) | 73/162 | (45.1%) | 40/71 | (56.3%) | |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, n/total n (%) | 0.341 | ||||||
| ≤164 | 116/233 | (49.8%) | 84/162 | (51.9%) | 32/71 | (45.1%) | |
| >164 | 117/233 | (50.2%) | 78/162 | (48.1%) | 39/71 | (54.9%) | |
| Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, n/total n (%) | 0.137 | ||||||
| ≤3.1 | 124/233 | (53.2%) | 81/162 | (50.0%) | 43/71 | (60.6%) | |
| >3.1 | 109/233 | (46.8%) | 81/162 | (50.0%) | 28/71 | (39.4%) | |
| Prognostic Nutritional index, n (%) | 0.717 | ||||||
| ≤45 | 126 | (53.2%) | 89 | (53.9%) | 37 | (51.4%) | |
| >45 | 111 | (46.8%) | 76 | (46.1%) | 35 | (48.6%) | |
| Pan-immune inflammation value, n/total n (%) | 0.341 | ||||||
| ≤305 | 116/233 | (49.8%) | 84/162 | (51.9%) | 32/71 | (45.1%) | |
| >305 | 117/233 | (50.2%) | 78/162 | (48.1%) | 39/71 | (54.9%) | |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | (95% CI) | p-Value | OR | (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age | ||||||
| ≤75 | 1.00 | |||||
| >75 | 1.45 | (0.83–2.53) | 0.187 | |||
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 1.00 | |||||
| Male | 1.28 | (0.70–2.34) | 0.418 | |||
| BMI | ||||||
| <18.5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 18.5–24 | 0.54 | (0.20–1.44) | 0.219 | 0.89 | (0.24–3.37) | 0.864 |
| ≥24 | 0.36 | (0.13–0.98) | 0.045 | 0.59 | (0.15–2.36) | 0.461 |
| ECOG Performance Status | ||||||
| 0–1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| >1 | 1.74 | (0.99–3.06) | 0.054 | 1.23 | (0.51–2.97) | 0.639 |
| aCCI | ||||||
| 0–3 | 1.00 | |||||
| >3 | 1.33 | (0.74–2.41) | 0.342 | |||
| Location | ||||||
| Proximal | 1.00 | |||||
| Non-proximal | 1.04 | (0.54–1.98) | 0.917 | |||
| Size | ||||||
| ≤4 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| >4 | 3.12 | (1.67–5.82) | <0.001 | 2.04 | (0.84–5.00) | 0.117 |
| Differentiation | ||||||
| Well to moderate | 1.00 | |||||
| Poor differentiation | 1.71 | (0.74–3.94) | 0.211 | |||
| Helicobacter pylori infection | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | |||||
| Yes | 1.01 | (0.48–2.14) | 0.979 | |||
| Signet ring feature | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | |||||
| Yes | 1.32 | (0.72–2.42) | 0.368 | |||
| Gastrectomy type | ||||||
| Subtotal gastrectomy | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Total gastrectomy | 2.31 | (1.30–4.08) | 0.004 | 2.04 | (0.86–4.84) | 0.106 |
| Lymphadenectomy type | ||||||
| <D2 dissection | 1.00 | |||||
| D2 dissection | 0.68 | (0.38–1.23) | 0.206 | |||
| T Stage | ||||||
| T 1–2 | 1.00 | |||||
| T 3–4 | 1.90 | (0.79–4.57) | 0.153 | |||
| N Stage | ||||||
| N 0–1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| N 2–3 | 3.44 | (1.84–6.41) | <0.001 | 1.38 | (0.50–3.84) | 0.534 |
| Lymph nodes ratio | ||||||
| ≤0.17 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| >0.17 | 6.25 | (3.41–11.45) | <0.001 | 5.30 | (2.07–13.53) | <0.001 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 2.81 | (1.29–6.11) | 0.009 | 1.05 | (0.36–3.06) | 0.926 |
| Perineural invasion | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 2.22 | (1.23–3.99) | 0.008 | 1.96 | (0.83–4.62) | 0.122 |
| Margin | ||||||
| Negative | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Positive | 4.57 | (1.47–14.17) | 0.008 | 1.83 | (0.29–11.79) | 0.523 |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 0.55 | (0.30–1.00) | 0.049 | 0.43 | (0.16–1.12) | 0.08 |
| CEA level | ||||||
| Normal | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Elevated (≥5 U/mL) | 3.86 | (1.92–7.78) | <0.001 | 2.02 | (0.78–5.20) | 0.145 |
| CA19–9 level | ||||||
| Normal | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Elevated (≥34 U/mL) | 3.06 | (1.50–6.23) | 0.002 | 2.05 | (0.82–5.08) | 0.123 |
| Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio | ||||||
| ≤2.7 | 1.00 | |||||
| >2.7 | 1.57 | (0.90–2.76) | 0.114 | |||
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | ||||||
| ≤164 | 1.00 | |||||
| >164 | 1.31 | (0.75–2.30) | 0.341 | |||
| Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio | ||||||
| ≤3.1 | 1.00 | |||||
| >3.1 | 0.65 | (0.37–1.15) | 0.138 | |||
| Prognostic Nutritional index | ||||||
| ≤45 | 1.00 | |||||
| >45 | 1.11 | (0.64–1.93) | 0.717 | |||
| Pan-immune inflammation value | ||||||
| ≤305 | 1.00 | |||||
| >305 | 1.31 | (0.75–2.30) | 0.341 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Wu, F.-H.; Luo, S.-C.; Shih, Y.-H. Lymph Node Ratio as a Risk Factor for Early Recurrence in Older Patients with Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186609
Tsai Y-C, Lin H-C, Hsu C-Y, Wu F-H, Luo S-C, Shih Y-H. Lymph Node Ratio as a Risk Factor for Early Recurrence in Older Patients with Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186609
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Yun-Chen, Hsin-Chen Lin, Chiann-Yi Hsu, Feng-Hsu Wu, Shao-Ciao Luo, and Yu-Hsuan Shih. 2025. "Lymph Node Ratio as a Risk Factor for Early Recurrence in Older Patients with Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186609
APA StyleTsai, Y.-C., Lin, H.-C., Hsu, C.-Y., Wu, F.-H., Luo, S.-C., & Shih, Y.-H. (2025). Lymph Node Ratio as a Risk Factor for Early Recurrence in Older Patients with Stage II/III Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6609. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186609







