Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Local Control and Survival After Escalated High-Dose SBRT in Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Inflammatory Markers
2.3. Study Endpoints
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Oncologic Outcomes of the Cohort
3.2. Inflammatory Marker Distribution
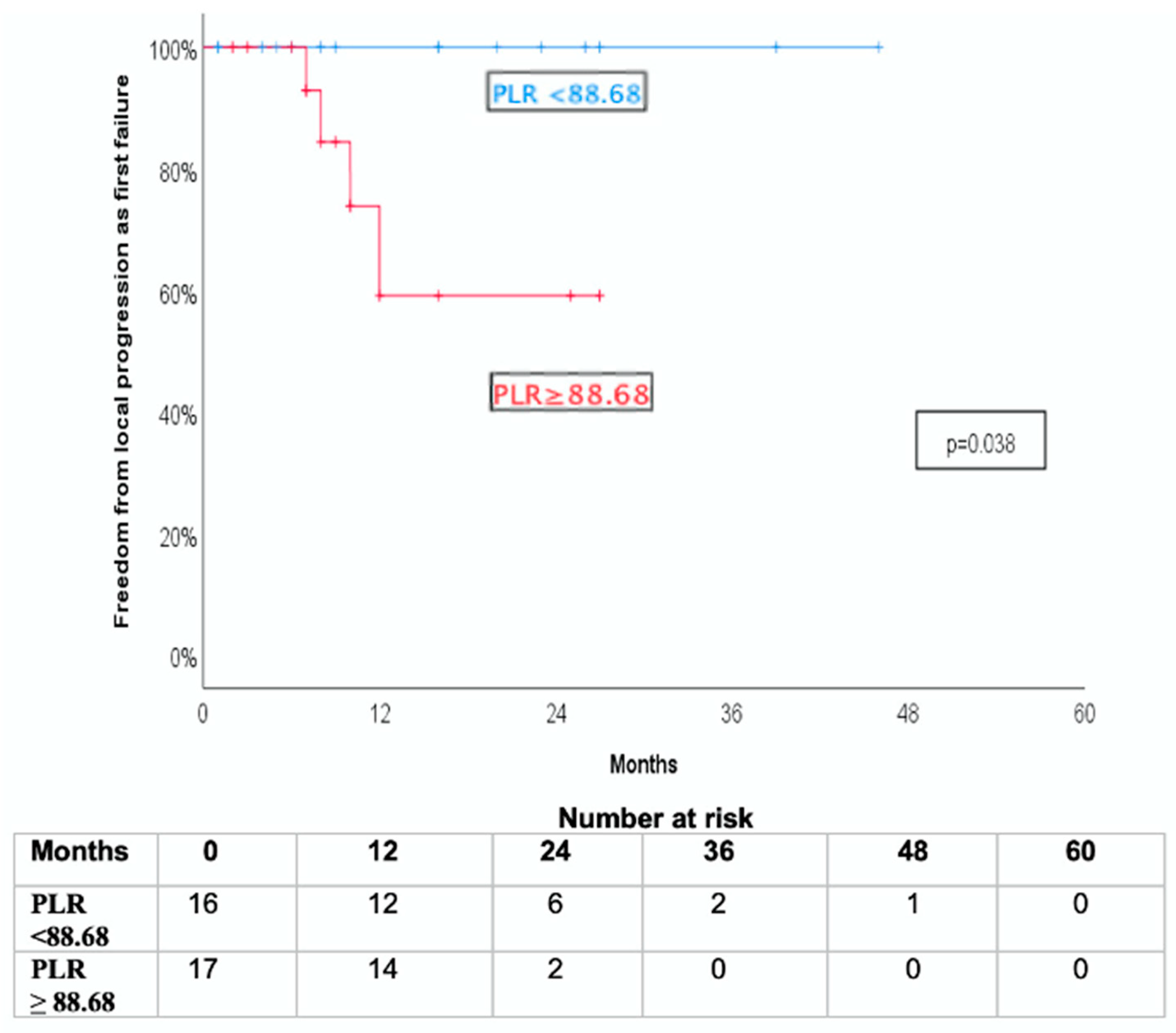
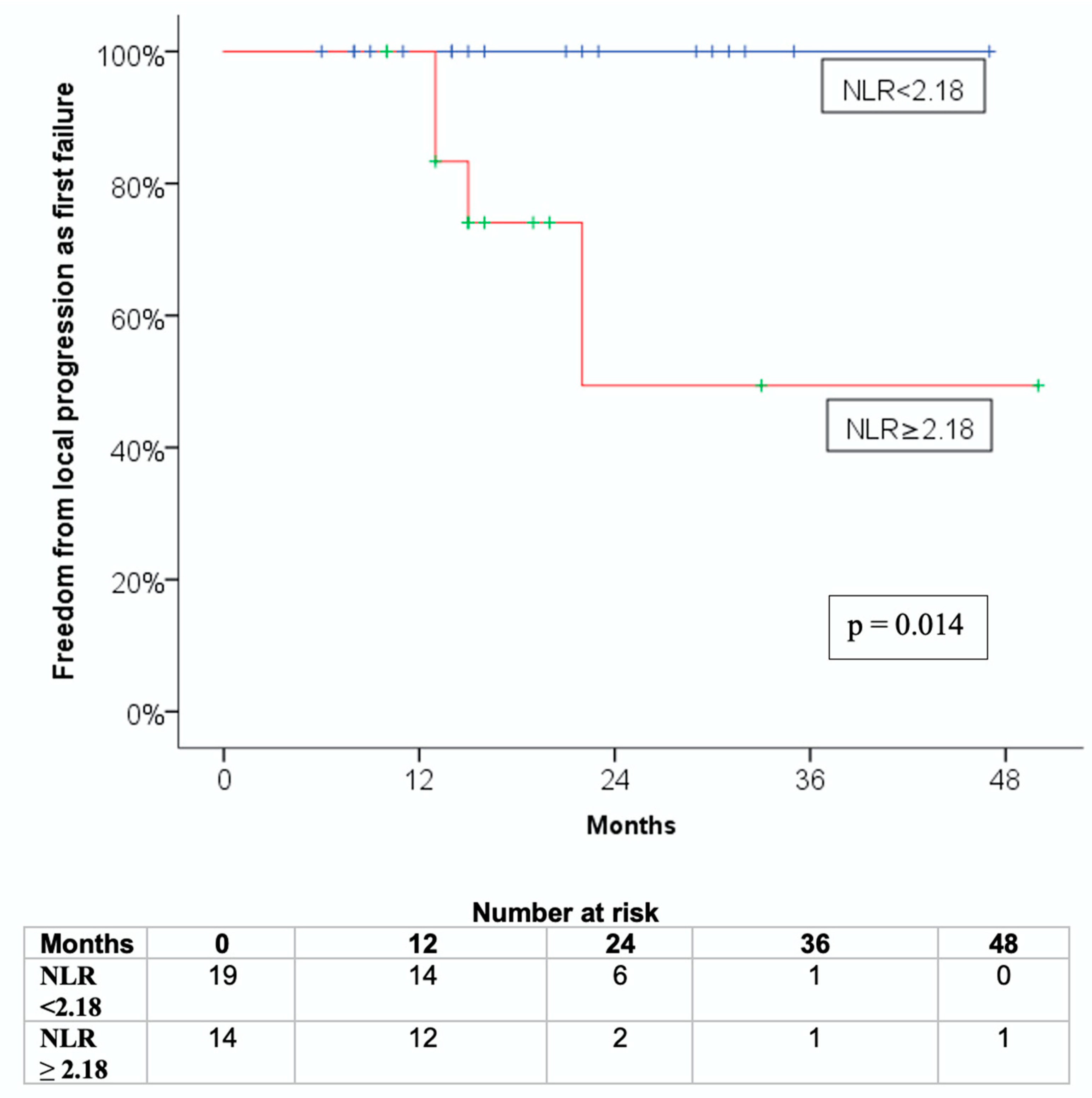
3.3. Association with Freedom from Local Progression as First Failure (FFLP-FF)
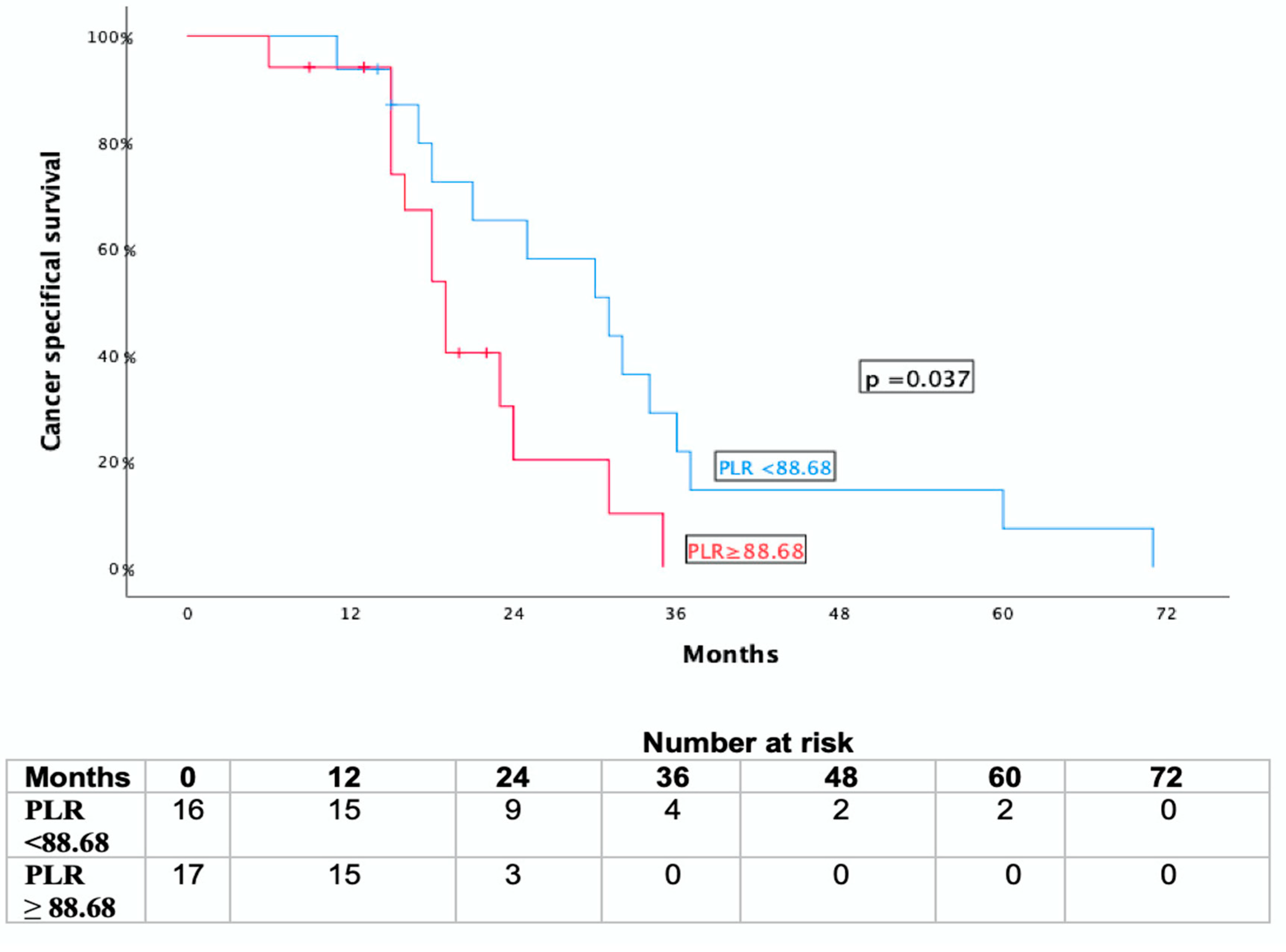
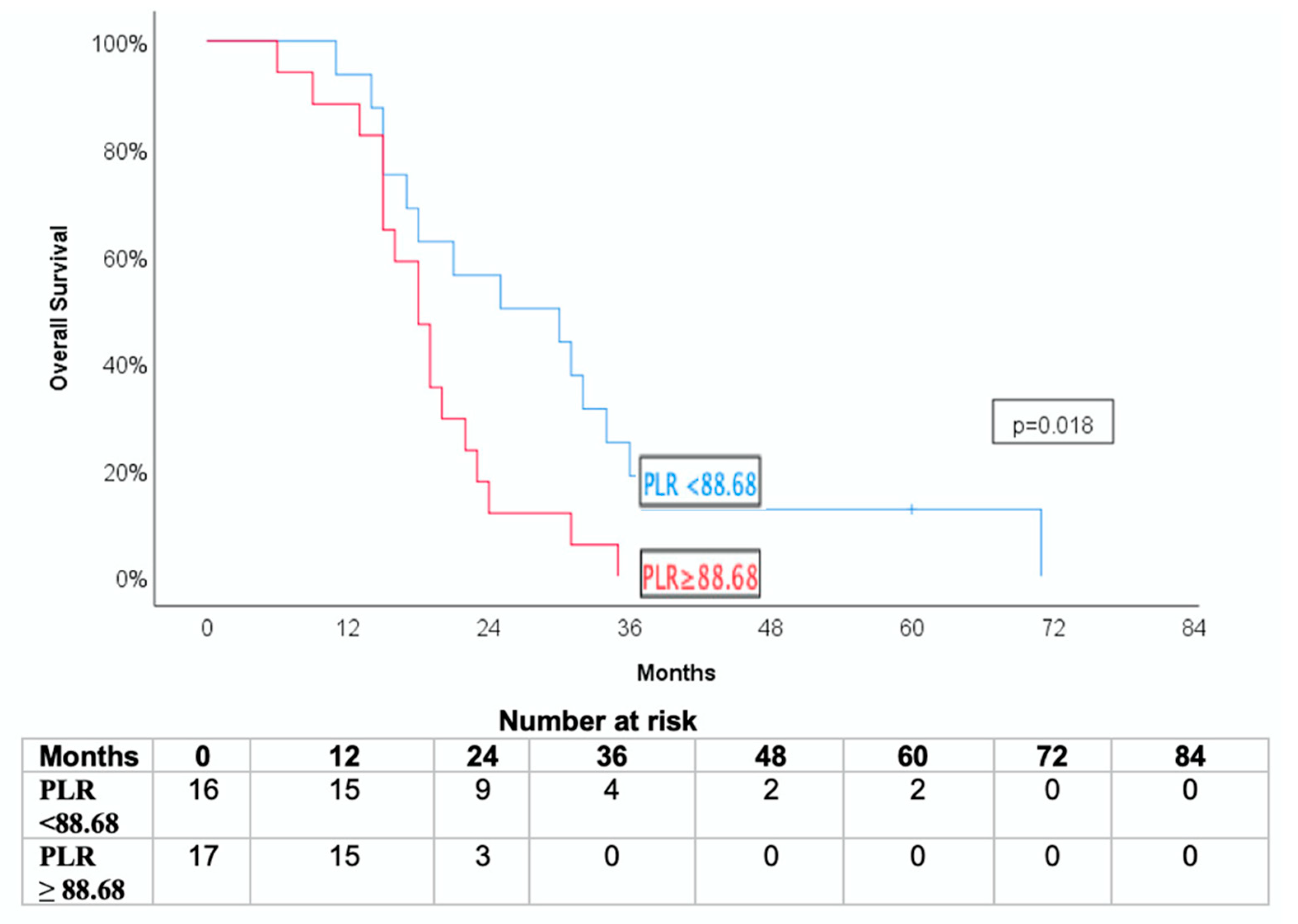
3.4. Association with Overall Survival and Cancer-Specific Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salas, B.; Ferrera-Alayón, L.; Espinosa-López, A.; Vera-Rosas, A.; Salcedo, E.; Kannemann, A.; Alayon, A.; Chicas-Sett, R.; LLoret, M.; Lara, P.C. Dose-Escalated SBRT for Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Feasibility, Safety and Preliminary Clinical Results of a Multicenter Study. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 45, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, I.; Lora, D.; Herradón, N.; de Velasco, G.; Carretero-González, A.; Jiménez-Varas, M.; de Vázquez Parga, P.; Feliu, J. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with or without Radiotherapy versus Upfront Surgery for Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietkau, R.; Grützmann, R.; Wittel, U.A.; Croner, R.S.; Jacobasch, L.; Neumann, U.P.; Reinacher-Schick, A.; Imhoff, D.; Boeck, S.; Keil-holz, L.; et al. R0 Resection Following Chemo (Radio)Therapy Improves Survival of Primary Inoperable Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Interim Results of the German Randomized CONKO-007± Trial. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Comito, T.; Ghidini, A.; Torri, V.; Scorsetti, M.; Barni, S. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis of 19 Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurmuz, P.; Cengiz, M.; Ozyigit, G.; Yuce Sari, S.; Kahvecioglu, A.; Beduk Esen, C.S.; Yalcin, S.; Zorlu, F. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy as an Effective Treatment for Pancreatic Cancer. Cureus 2023, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouman, M.A.; Fuchs, F.; Walter, F.; Corradini, S.; Westphalen, C.B.; Vornhülz, M.; Beyer, G.; Andrade, D.; Belka, C.; Niyazi, M.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer—A Systematic Review of Prospective Data. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 45, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz Ejlsmark, M.; Bahij, R.; Schytte, T.; Rønn Hansen, C.; Bertelsen, A.; Mahmood, F.; Bau Mortensen, M.; Detlefsen, S.; Weber, B.; Bernchou, U.; et al. Adaptive MRI-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer—A Phase II Study. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 197, 110347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarli, N.; Dikmen, K.; Bostanci, H.; Buyukkasap, A.C.; Kerem, M.; Taneri, F. The Prognostic Significance of Preoperative CA 19-9, Neutrophil / Lymphosit And Platelet / Lymphosit Ratio in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Pharmacol. Clin. Res. 2018, 6, 555692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.L.; Ohara, K.; Kiberu, A.; Van Hagen, T.; Davidson, A.; Khattak, M.A.K. Prognostic Value of Systemic Inflammation-Based Markers in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Hu, Z.G.; Shi, W.X.; Deng, T.; He, S.Q.; Yuan, S.G. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2807–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkandera, J.; Stotz, M.; Eisner, F.; Absenger, G.; Stojakovic, T.; Samonigg, H.; Kornprat, P.; Schaberl-Moser, R.; AlZoughbi, W.; Ress, A.L.; et al. External Validation of the Derived Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Marker on a Large Cohort of Pancreatic Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumour-Associated Neutrophils in Patients with Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Nepovimova, E.; Adam, V.; Sivak, L.; Heger, Z.; Valko, M.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Neutrophils in Cancer Immunotherapy: Friends or Foes? Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Fathy, A.H.; Qian, H.; Zhao, Y. Prognostic Value of Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of 17 Cohort Studies. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Herrera, J.S.; Muñoz-Montaño, W.R.; López-Basave, H.N.; Morales-Vásquez, F.; Castillo-Morales, C.; Rivera-Mogollán, L.G.; Hernández-Castañeda, K.F. Combination of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Serum CA 19-9 as a Prognostic Factor in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1805–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D Brierlay, D.; Mary, K.; Gospodarowicz, C.W. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 8th ed.; Union for International Cancer Control: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, D.; Jin, X.; Wu, H. The Prognostic Value of Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score in Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased Survival in Pancreatic Cancer with Nab-Paclitaxel plus Gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouché, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Bécouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardière, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus Gemcitabine for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, A.J.; Mcnamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Sonpavde, G.; Knox, J.J.; Tran, B.; et al. Prognostic Role of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, Q.; Fan, J.; Cheng, S.; Ding, W.; Hua, Z. Prognostic Role of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis Containing 8252 Patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 479, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, D.; Chen, B.; Tang, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, W. The Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Response and Prognostic Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tao, L.; Lu, M.; Xiu, D. Prognostic Role of Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio in Pancreatic Cancers. Medicine 2018, 97, e9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.G.; Bradburn, M.J.; Love, S.B.; Altman, D.G. Survival Analysis Part I: Basic Concepts and First Analyses. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riauka, R.; Ignatavicius, P.; Barauskas, G. Preoperative Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Factor for Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Surg. 2020, 37, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Zhang, F.P.; Zhang, Y.; Ou-Yang, Y.P.; Yu, X.W.; Wang, W.L.; Xu, W.J.; Luo, Z.Q. Prognostic Role of the Pre-Treatment Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio in Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99003–99012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagappan, M.; Pollom, E.L.; Von Eyben, R.; Kozak, M.M.; Aggarwal, S.; Poultsides, G.A.; Koong, A.C.; Chang, D.T. Albumin and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Predict Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Treated with SBRT. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.S.; Fernandes, P.C.; Silva, M.J.B.; Lima, V.C.; Fontes, W.; Freitas, R.; Eterovic, A.K.; Forget, P. The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio: A Narrative Review. Ecancermedicalscience 2016, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.M.; Chung, S.Y.; Chang, J.S.; Lee, K.J.; Seong, J. The Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio Are Prognostic Factors in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Treated with Chemoradiotherapy. Gut Liver 2018, 12, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asari, S.; Matsumoto, I.; Toyama, H.; Shinzeki, M.; Goto, T.; Ishida, J.; Ajiki, T.; Fukumoto, T.; Ku, Y. Preoperative Independent Prognostic Factors in Patients with Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Following Curative Resection: The Neutrophil-Lymphocyte and Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratios. Surg. Today 2015, 46, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshimoto, S.; Hishinuma, S.; Shirakawa, H.; Tomikawa, M.; Ozawa, I.; Ogata, Y. Validation and Clinical Usefulness of Pre- and Postoperative Systemic Inflammatory Parameters as Prognostic Markers in Patients with Potentially Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Shao, Z.; Chen, W.; Xie, H.; Qin, G.; Zhao, N. Neutrophil and Lymphocyte Counts at Diagnosis Are Associated with Overall Survival of Pancreatic Cancer A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Salas, B.; Ferrera-Alayon, L.; Espinosa-Lopez, A.; Perez-Rodriguez, M.L.; Afonso, A.A.; Vera-Rosas, A.; Garcia-Plaza, G.; Chicas-Sett, R.; Martinez-Martin, M.S.; Salcedo, E.; et al. Dose-Escalated SBRT for Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Resectability Rate and Pathological Results of a Multicenter Prospective Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suker, M.; Nuyttens, J.J.; Eskens, F.A.L.M.; Haberkorn, B.C.M.; Coene, P.P.L.O.; van der Harst, E.; Bonsing, B.A.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Mieog, J.S.D.; Jan Swijnenburg, R.; et al. Efficacy and Feasibility of Stereotactic Radiotherapy after Folfirinox in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (LAPC-1 Trial). EClinicalMedicine 2019, 17, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, C.R.; Marchegiani, G.; Hong, T.S.; Ryan, D.P.; Deshpande, V.; McDonnell, E.I.; Sabbatino, F.; Santos, D.D.; Allen, J.N.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; et al. Radiological and Surgical Implications of Neoadjuvant Treatment with FOLFIRINOX for Locally Advanced and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C. The Systemic Inflammation-Based Glasgow Prognostic Score: A Decade of Experience in Patients with Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013, 39, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoi, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamaki, S.; Sakaguchi, T.; Sekimoto, M. Surgical Indication for and Desirable Outcomes of Conversion Surgery in Patients with Initially Unresectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2020, 4, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, S.B.; Jodrell, N.B.; Cooke, S.L.; Valle, J.W.; McKay, C.J.; Biankin, A.V.; Chang, D.K. PRECISION-Panc: The next generation therapeutic development platform for pancreatic cancer. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, S.; Eguchi, H.; Tomokuni, A.; Tomimaru, Y.; Asaoka, T.; Wada, H.; Hama, N.; Kawamoto, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Marubashi, S.; et al. Pre-Treatment Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictive Marker for Pathological Response to Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X. Risk Factors and Prognostic Index Model for Pancreatic Cancer. Gland. Surg. 2022, 11, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.; Kanetsky, P.A.; Egan, K.M. Exploring the Prognostic Value of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Canceritle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 14 (42.4%) |
| Female | 19 (57.6%) |
| Histology | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 33 (100%) |
| Stage T | |
| T2 | 6 (18.2%) |
| T3 | 15 (45.5%) |
| T4 | 12 (36.3%) |
| Stage N | |
| N0 | 25 (75.8%) |
| N1 | 6 (18.1%) |
| N2 | 2 (6.1%) |
| Stage M | |
| M0 | 33 (100%) |
| Tumor classification | |
| Borderline (BRPC) | 13 (39.4%) |
| Locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC) | 20 (60.6%) |
| Freedom from Local Progression as First Failure (FFLP-FF 2 Years) | Cancer-Specific Survival (CSS) (2 Years) | Overall Survival (OS) 2 Years | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLR | |||
| Low (<88.68) | 77.4% ± 9.8% | 63.2% ± 12.6% | 11.8% ± 7.8% |
| High (≥88.68) | 45.2% ± 12.7% | 40.3% ± 12.7% | 47.1% ± 12.1% |
| p = 0.038 | p = 0.037 | p = 0.018 | |
| NLR | |||
| Low (<2.18) | 71.8% ± 13.1% | 45.1% ± 12.5% | 42.1% ± 11.3% |
| High (≥2.18) | 11.1% ± 10.5% | 36.9% ± 13.8% | 21.4% ± 11.0% |
| p = 0.014 | p = 0.886 | p = 0.597 | |
| PLR/NLR | |||
| Low | 100% ± 0.0% | 50.8% ± 10.7% | 44% ± 9.9% |
| High | 50.0% ± 17.1% | 28.6% ± 17.1% | 0.0% ± 0.0% |
| p < 0.001 | p = 0.224 | p = 0.041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrera-Alayon, L.; Alayón Afonso, A.; Salas-Salas, B.; Rodríguez-González, N.; Lara, P.C.; Lloret-Saez-Bravo, M. Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Local Control and Survival After Escalated High-Dose SBRT in Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186573
Ferrera-Alayon L, Alayón Afonso A, Salas-Salas B, Rodríguez-González N, Lara PC, Lloret-Saez-Bravo M. Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Local Control and Survival After Escalated High-Dose SBRT in Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186573
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrera-Alayon, Laura, Antonio Alayón Afonso, Bárbara Salas-Salas, Nereida Rodríguez-González, Pedro C. Lara, and Marta Lloret-Saez-Bravo. 2025. "Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Local Control and Survival After Escalated High-Dose SBRT in Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186573
APA StyleFerrera-Alayon, L., Alayón Afonso, A., Salas-Salas, B., Rodríguez-González, N., Lara, P. C., & Lloret-Saez-Bravo, M. (2025). Inflammatory Biomarkers Predict Local Control and Survival After Escalated High-Dose SBRT in Borderline and Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6573. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186573






