Appraisal of Clinical Explanatory Variables in Subtyping of Type 2 Diabetes Using Machine Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
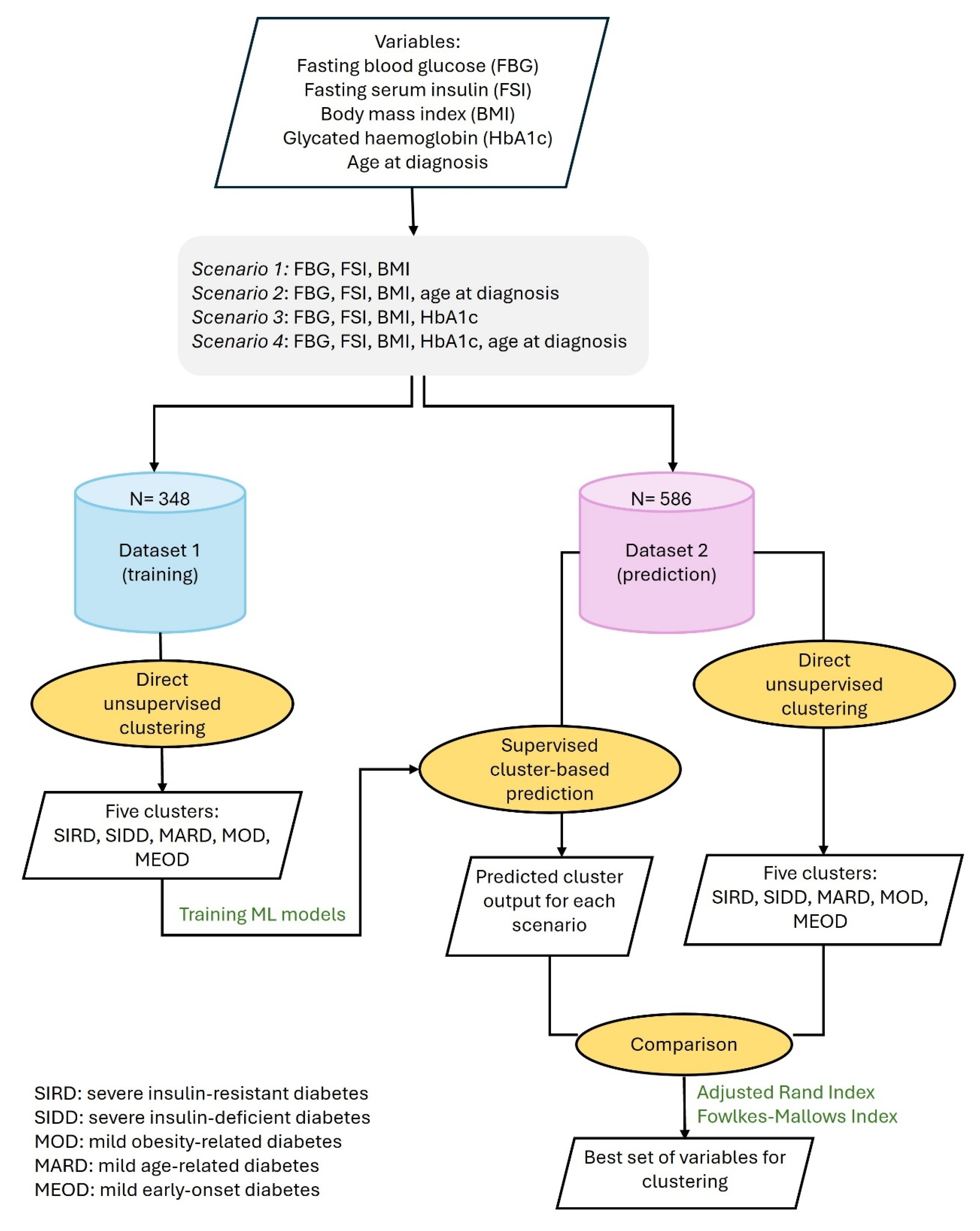
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Clustering Techniques
Validation of Explanatory Variables
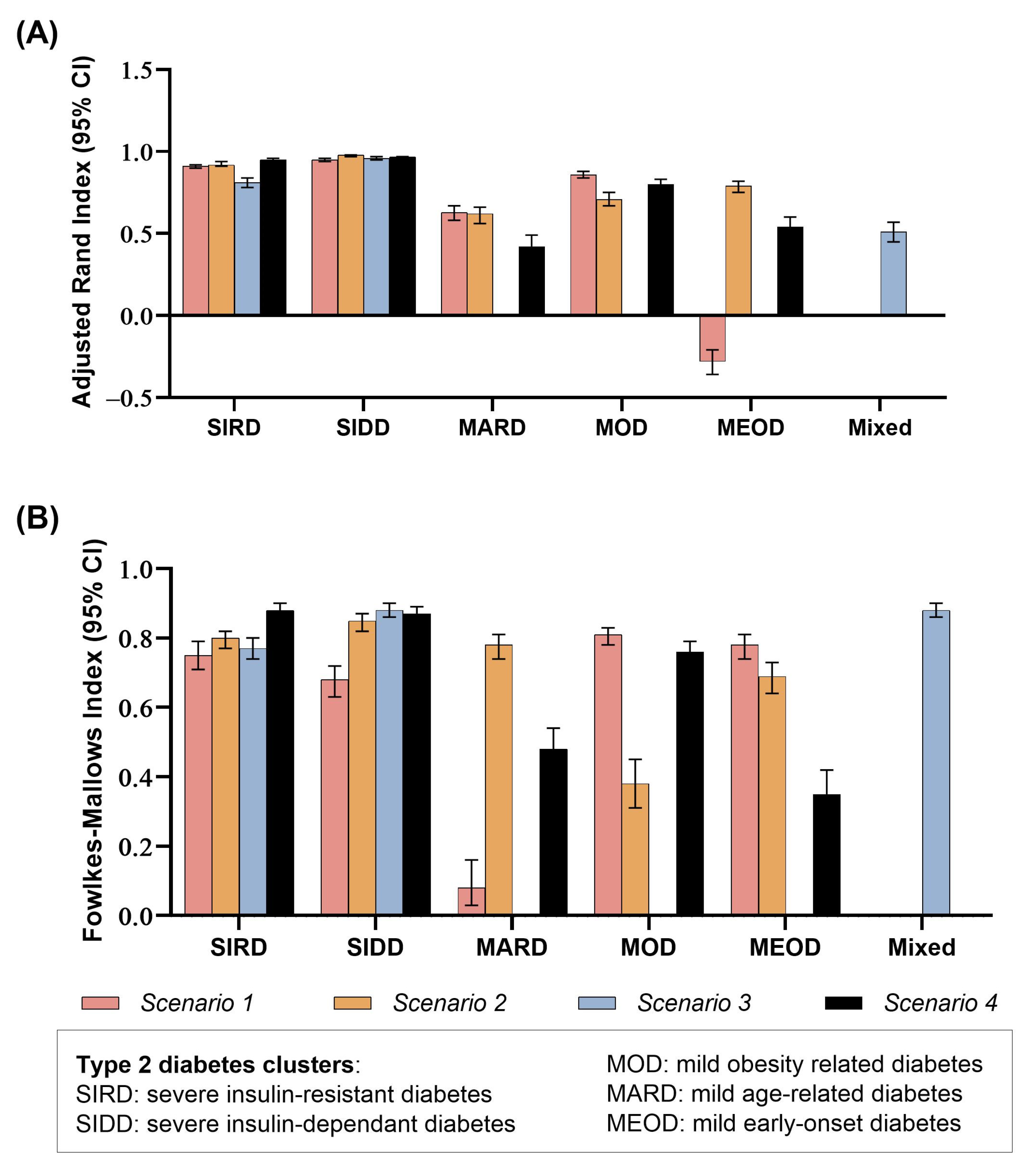
2.4. Testing Similarity Between Clusters
2.4.1. The Adjusted Rand Index (ARI)
2.4.2. The Fowlkes–Mallows Index (FMI)
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 11th ed.; The International Diabetes Federation (IDF): Brussels, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlqvist, E.; Storm, P.; Käräjämäki, A.; Martinell, M.; Dorkhan, M.; Carlsson, A.; Vikman, P.; Prasad, R.B.; Aly, D.M.; Almgren, P.; et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: A data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlqvist, E.; Prasad, R.B.; Groop, L. Subtypes of type 2 diabetes determined from clinical parameters. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.M.; Shields, B.M.; Henley, W.E.; Jones, A.G.; Hattersley, A.T. Disease progression and treatment response in data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes compared with models based on simple clinical features: An analysis using clinical trial data. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herder, C.; Maalmi, H.; Strassburger, K.; Zaharia, O.P.; Ratter, J.M.; Karusheva, Y.; Elhadad, M.A.; Bódis, K.; Bongaerts, B.W.; Rathmann, W.; et al. Differences in biomarkers of inflammation between novel subgroups of recent-onset diabetes. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, O.P.; Strassburger, K.; Strom, A.; Bönhof, G.J.; Karusheva, Y.; Antoniou, S.; Bódis, K.; Markgraf, D.F.; Burkart, V.; Müssig, K.; et al. Risk of diabetes-associated diseases in subgroups of patients with recent-onset diabetes: A 5-year follow-up study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello-Chavolla, O.Y.; Bahena-López, J.P.; Vargas-Vázquez, A.; Antonio-Villa, N.E.; Márquez-Salinas, A.; Fermín-Martínez, C.A.; Rojas, R.; Mehta, R.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Hernández-Jiménez, S.; et al. Clinical characterization of data-driven diabetes subgroups in Mexicans using a reproducible machine learning approach. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dragan, I.; Tran, V.D.T.; Fung, C.H.; Kuznetsov, D.; Hansen, M.K.; Beulens, J.W.; Hart, L.M.T.; Slieker, R.C.; Donnelly, L.A.; et al. Multi-omics subgroups associated with glycaemic deterioration in type 2 diabetes: An IMI-RHAPSODY Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1350796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lv, Y.; Huang, N.; Sun, J.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Inpatients with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in Eastern China: Based on Novel Clustering Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 927661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, S.; Cao, C.; Yan, X.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, L.; Da, J.; Tang, X.; Ji, L.; Yang, X.; et al. Validation of the Swedish diabetes re-grouping scheme in adult-onset diabetes in China. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3519–e3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Peng, F.; Liang, Q.; Dai, X.; Ren, J.; Wu, H.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhao, S. Clinical Characteristics and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Data-Driven Clusters Among Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 617628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, H.; Saito, H.; Kudo, A.; Machii, N.; Hirai, H.; Maimaituxun, G.; Tanaka, K.; Masuzaki, H.; Watanabe, T.; Asahi, K.; et al. Factors associated with risk of diabetic complications in novel cluster-based diabetes subgroups: A Japanese retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, R.M.; Baskar, V.; Nair, A.T.N.; Jebarani, S.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Pradeepa, R.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Palmer, C.; Pearson, E.; Mohan, V. Novel subgroups of type 2 diabetes and their association with microvascular outcomes in an Asian Indian population: A data-driven cluster analysis: The INSPIRED study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Wagner, R.; Ozkan, B.; Schön, M.; Sevilla-Gonzalez, M.; Prystupa, K.; Wang, C.C.; Kreienkamp, R.J.; Cromer, S.J.; Rooney, M.R.; et al. Precision subclassification of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghlool, S.B.; Halama, A.; Stephan, N.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Gudnason, V.; Jennings, L.L.; Thangam, M.; Ahlqvist, E.; Malik, R.A.; Albagha, O.M.; et al. Metabolic and proteomic signatures of type 2 diabetes subtypes in an Arab population. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thani, N.M.; Zaghlool, S.B.; Toor, S.M.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Suhre, K.; Albagha, O.M.E. Subtyping of type 2 diabetes from a large Middle Eastern biobank: Implications for precision medicine. Mol. Metab. 2025, 99, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, R.; Farooqi, M.; Alawadi, F.; Hassanein, M.; Osama, A.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Abdul, F.; Sulaiman, F.; Dsouza, S.; Mulla, F.; et al. Etiologies underlying subtypes of longstanding type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Hatzikotoulas, K.; Southam, L.; Taylor, H.J.; Yin, X.; Lorenz, K.M.; Mandla, R.; Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Melloni, G.E.; Kanoni, S.; et al. Genetic drivers of heterogeneity in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. Nature 2024, 627, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udler, M.S.; Kim, J.; von Grotthuss, M.; Bonàs-Guarch, S.; Cole, J.B.; Chiou, J.; Anderson, C.D.; Boehnke, M.; Laakso, M.; Atzmon, G.; et al. Type 2 diabetes genetic loci informed by multi-trait associations point to disease mechanisms and subtypes: A soft clustering analysis. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Deutsch, A.J.; McGrail, C.; Kim, H.; Hsu, S.; Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Mandla, R.; Schroeder, P.H.; Westerman, K.E.; Szczerbinski, L.; et al. Multi-ancestry polygenic mechanisms of type 2 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Xi, Y.; Brandmaier, S.; Fuchs, M.; Huemer, M.T.; Waldenberger, M.; Niu, J.; Herder, C.; Rathmann, W.; Roden, M.; et al. Subphenotypes of adult-onset diabetes: Data-driven clustering in the population-based KORA cohort. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slieker, R.C.; Donnelly, L.A.; Fitipaldi, H.; Bouland, G.A.; Giordano, G.N.; Åkerlund, M.; Gerl, M.J.; Ahlqvist, E.; Ali, A.; Dragan, I.; et al. Replication and cross-validation of type 2 diabetes subtypes based on clinical variables: An IMI-RHAPSODY study. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Westerman, K.E.; Smith, K.; Chiou, J.; Cole, J.B.; Majarian, T.; von Grotthuss, M.; Kwak, S.H.; Kim, J.; Mercader, J.M.; et al. High-throughput genetic clustering of type 2 diabetes loci reveals heterogeneous mechanistic pathways of metabolic disease. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.H.; Nicolaisen, S.K.; Ahlqvist, E.; Stidsen, J.V.; Nielsen, J.S.; Hojlund, K.; Olsen, M.H.; García-Calzón, S.; Ling, C.; Rungby, J.; et al. Type 2 diabetes classification: A data-driven cluster study of the Danish Centre for Strategic Research in Type 2 Diabetes (DD2) cohort. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowska-Andersen, A.; Brorsson, C.A.; Bizzotto, R.; Mari, A.; Tura, A.; Koivula, R.; Mahajan, A.; Vinuela, A.; Tajes, J.F.; Sharma, S.; et al. Four groups of type 2 diabetes contribute to the etiological and clinical heterogeneity in newly diagnosed individuals: An IMI DIRECT study. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez-Guillen, N.E.; Gonzalez-Compean, J.L.L.; Lopez-Arevalo, I.; Contreras-Murillo, M.; Aldana-Bobadilla, E. Machine learning based study for the classification of Type 2 diabetes mellitus subtypes. BioData Min. 2023, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azit, N.A.; Sahran, S.; Leow, V.M.; Subramaniam, M.; Mokhtar, S.; Nawi, A.M. Prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in patients with type-2 diabetes using supervised machine learning classification model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamis, A.; Abdul, F.; Dsouza, S.; Sulaiman, F.; Farooqi, M.; Al Awadi, F.; Hassanein, M.; Ahmed, F.S.; Alsharhan, M.; AlOlama, A.; et al. Risk of Microvascular Complications in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Patients Using Automated Machine Learning Prediction Models. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, F.; Nasiri, M.; Safdari, R.; Arji, G.; Hashemi, Z.; Sharifian, R. Myocardial infarction prediction and estimating the importance of its risk factors using prediction models. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karajizadeh, M.; Nasiri, M.; Yadollahi, M.; Zolfaghari, A.H.; Pakdam, A. Mortality prediction from hospital-acquired infections in trauma patients using an unbalanced dataset. Heal. Inform. Res. 2020, 26, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hou, J.; Shi, Y.; Tan, Q.; Peng, L.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z. Influence of lifestyles on mild cognitive impairment: A decision tree model study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.A.M.; Mohamed, W.M.A.; Lau, A.C.C.; Chatanga, E.; Qiu, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Naguib, D.; Sato, K.; Takano, A.; Matsuno, K.; et al. R A language and environment for statistical computing, R Foundation for Statistical. Computing 2020, 20, 1979–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, S.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Del Prato, S. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on the past, present, and future. Lancet 2014, 383, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Manson, J.E.; Stamfer, M.J.; Hu, F.B.; Giovannucci, E.; Colditz, G.A.; Hennekens, C.H.; Willett, W.C. A prospective study of whole-grain intake and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in US women. Am. J. Public Health 2000, 90, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, S.I.; Khan, H.A.; Ekhzaimy, A.; Masood, A.; Sakharkar, M.K. Significance of HbA1c test in diagnosis and prognosis of diabetic patients. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, S.A.; Karter, A.J.; Corbie-Smith, G.; Seligman, H.K.; Ackroyd, S.A.; Barnard, L.S.; Atlas, S.J.; Wexler, D.J. Food insecurity, food “deserts,” and glycemic control in patients with diabetes: A longitudinal analysis. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, R.M. A caution regarding rules of thumb for variance inflation factors. Qual. Quant. 2007, 41, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Neter, J.; Li, W. Introduction to the design of experimental and observational studies. In Applied Linear Statistical Models; McGraw-Hill/Irwin: Colombus, OH, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, M.; Dutta, M.; Mahalle, N. Study of beta-cell function (by HOMA model) in metabolic syndrome. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 15, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slieker, R.C.; Donnelly, L.A.; Fitipaldi, H.; Bouland, G.A.; Giordano, G.N.; Åkerlund, M.; Gerl, M.J.; Ahlqvist, E.; Ali, A.; Dragan, I.; et al. Distinct Molecular Signatures of Clinical Clusters in People With Type 2 Diabetes: An IMI-RHAPSODY Study. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Q. The transcriptomic and epigenetic alterations in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients of Chinese Tibetan and Han populations. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1122047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, K. Proteomics, metabolomics and metagenomics for type 2 diabetes and its complications. Life Sci. 2018, 212, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yong, H.; He, X.-D. Multi-omics: Opportunities for research on mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ji, L. Novel subgroups of patients with adult-onset diabetes in Chinese and US populations. Lancet Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, S.; Yan, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, W. Clinical characteristics of patients with early-onset diabetes mellitus: A single-center retrospective study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, L.A.; Ward, M.S.; Fotheringham, A.K.; Zhuang, A.; Borg, D.J.; Flemming, N.B.; Harvie, B.M.; Kinneally, T.L.; Yeh, S.M.; McCarthy, D.A.; et al. Once daily administration of the SGLT2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, attenuates markers of renal fibrosis without improving albuminuria in diabetic db/db mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veelen, A.; Erazo-Tapia, E.; Oscarsson, J.; Schrauwen, P. Type 2 diabetes subgroups and potential medication strategies in relation to effects on insulin resistance and beta-cell function: A step toward personalised diabetes treatment? Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenchula, S.; Sharma, P.; Ghanta, M.K.; Amerneni, K.C.; Rajakarunakaran, P.; Saggurthi, P.; Chandra, M.B.; Gupta, R.; Chavan, M. Association and Mechanisms of Proton Pump Inhibitors Use with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Incidence in Adults: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2024, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, S.; Perfilyev, A.; Ahlqvist, E.; Groop, L.; Vaag, A.; Martinell, M.; García-Calzón, S.; Ling, C. Novel Subgroups of Type 2 Diabetes Display Different Epigenetic Patterns That Associate with Future Diabetic Complications. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geer, E.B.; Shen, W. Gender differences in insulin resistance, body composition, and energy balance. Gend. Med. 2009, 6, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, P.; Viguerie, N.; Massier, L.; Rydén, M.; Astrup, A.; Blaak, E.; Langin, D.; Andersson, D.P. Sex differences in adipose insulin resistance are linked to obesity, lipolysis and insulin receptor substrate 1. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandla, R.; Lorenz, K.; Yin, X.; Bocher, O.; Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Arruda, A.L.; Piron, A.; Horn, S.; Suzuki, K.; Hatzikotoulas, K.; et al. Multi-omics characterization of type 2 diabetes associated genetic variation. MedRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancks, M.P.; Chen, H.; Balasubramanyam, A.; Bertoni, A.G.; Espeland, M.A.; Kahn, S.E.; Pilla, S.; Vaughan, E.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Look AHEAD Research Group. Type 2 Diabetes Subgroups, Risk for Complications, and Differential Effects Due to an Intensive Lifestyle Intervention. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzini, E.; Vlacho, B.; Franch-Nadal, J.; Escudero, J.; Génova, A.; Reixach, E.; Andrés, E.; Pizarro, I.; Portero, J.L.; Mauricio, D.; et al. Longitudinal deep learning clustering of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus trajectories using routinely collected health records. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 135, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Training Dataset (N = 348) | Prediction Dataset (N = 586) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 41.92 (10.65) | 46.32 (9.27) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 31.27 (5.7) | 31.54 (6.04) | 0.247 |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 146.86 (52.47) | 133 (44.16) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.63 (1.72) | 7 (1.33) | <0.001 |
| Fasting serum insulin (µIU/nmol) | 14.04 (10.67) | 18.04 (10.74) | <0.001 |
| Duration of type 2 diabetes (years) | 14.42 (8.14) | 3.67 (2.9) | <0.001 |
| Supervised Cluster-Based Classification Using ML Predictive Models | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIRD | SIDD | MARD | MOD | MEOD | Total | ||
| Direct unsupervised clustering | Scenario 1: FSI, FBG, and BMI | ||||||
| SIRD | 46 | 2 | 28 | 5 | 0 | 81 | |
| SIDD | 0 | 17 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 18 | |
| MARD | 0 | 15 | 8 | 0 | 38 | 61 | |
| MOD | 0 | 1 | 36 | 96 | 6 | 139 | |
| MEOD | 0 | 0 | 78 | 0 | 209 | 287 | |
| Total | 46 | 35 | 150 | 102 | 253 | 586 | |
| Scenario 2: FSI, FBG, and BMI and age at diagnosis | |||||||
| SIRD | 56 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 58 | |
| SIDD | 3 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 33 | |
| MARD | 1 | 3 | 185 | 0 | 21 | 210 | |
| MOD | 20 | 0 | 66 | 39 | 0 | 125 | |
| MEOD | 5 | 1 | 17 | 43 | 94 | 160 | |
| Total | 85 | 32 | 269 | 85 | 115 | 586 | |
| Scenario 4: FSI, FBG, and BMI, HbA1c and age at diagnosis | |||||||
| SIRD | 62 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 64 | |
| SIDD | 4 | 38 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 45 | |
| MARD | 4 | 1 | 104 | 30 | 94 | 233 | |
| MOD | 7 | 1 | 4 | 79 | 0 | 91 | |
| MEOD | 0 | 2 | 90 | 9 | 52 | 153 | |
| Total | 77 | 42 | 201 | 119 | 147 | 586 | |
| Supervised Cluster-Based Classification Using ML Predictive Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct unsupervised clustering | SIRD | SIDD | Mixed | Total | |
| SIDD | 6 | 51 | 1 | 58 | |
| SIRD | 136 | 1 | 81 | 218 | |
| Mixed | 0 | 6 | 304 | 310 | |
| Total | 142 | 58 | 386 | 586 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khamis, A.H.; Abdul, F.; Dsouza, S.; Sulaiman, F.; Khyreim, C.; Siddig, M.E.; Bayoumi, R. Appraisal of Clinical Explanatory Variables in Subtyping of Type 2 Diabetes Using Machine Learning Models. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186548
Khamis AH, Abdul F, Dsouza S, Sulaiman F, Khyreim C, Siddig ME, Bayoumi R. Appraisal of Clinical Explanatory Variables in Subtyping of Type 2 Diabetes Using Machine Learning Models. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186548
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhamis, Amar H., Fatima Abdul, Stafny Dsouza, Fatima Sulaiman, Costerwell Khyreim, Mohammed E. Siddig, and Riad Bayoumi. 2025. "Appraisal of Clinical Explanatory Variables in Subtyping of Type 2 Diabetes Using Machine Learning Models" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186548
APA StyleKhamis, A. H., Abdul, F., Dsouza, S., Sulaiman, F., Khyreim, C., Siddig, M. E., & Bayoumi, R. (2025). Appraisal of Clinical Explanatory Variables in Subtyping of Type 2 Diabetes Using Machine Learning Models. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186548






