Interleukin-6-Related Inflammatory Burden in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence for Elevation with Suboptimal Glycemic Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
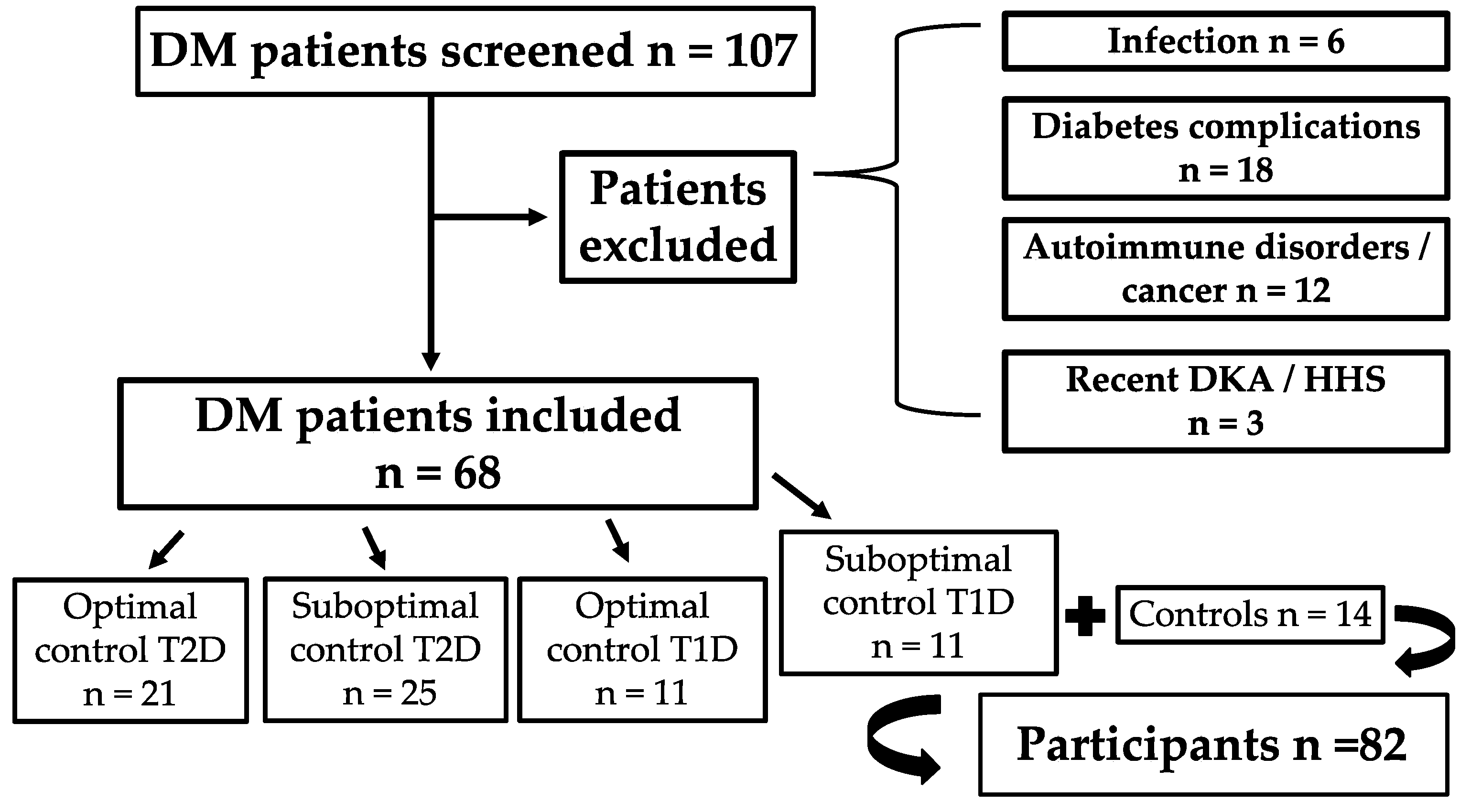
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Interleukin-6 Concentrations Across Groups
3.3. Correlations Between Biomarkers
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aamodt, K.I.; Powers, A.C. The pathophysiology, presentation and classification of Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27 (Suppl. 6), 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Forbes, J.M.; Cooper, M.E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 137–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo, M.J.; Steck, A.K.; Pugliese, A. Genetics of type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 19, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rewers, M.; Ludvigsson, J. Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2016, 387, 2340–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Longendyke, R.; Grundman, J.B.; Majidi, S. Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 53, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Blagov, A.V.; Summerhill, V.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Popov, M.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Type 1 diabetes mellitus: Inflammation, mitophagy, and mitochondrial function. Mitochondrion 2023, 72, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Candia, P.; Prattichizzo, F.; Garavelli, S.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Di Rella, F.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Colamatteo, A.; Fusco, C.; Micillo, T.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes: How Much of an Autoimmune Disease? Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arumugam, S.; Suyambulingam, A. Association Between Serum Ferritin and the Duration of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Chennai. Cureus 2024, 16, e53117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kouroupis, D.; Zografou, I.; Doukelis, P.; Patoulias, D.; Popovic, D.S.; Karakasis, P.; Pyrpasopoulou, A.; Stavropoulos, K.; Papadopoulos, C.; Giouleme, O.; et al. Presepsin: An Emerging Biomarker in the Management of Cardiometabolic Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Jiang, X.Y.; Ren, W.Y.; Lei, S.F.; Deng, F.Y.; Wu, L.F. High sensitivity C-reactive protein and prediabetes progression and regression in middle-aged and older adults: A prospective cohort study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Velikova, T.V.; Kabakchieva, P.P.; Assyov, Y.S.; Georgiev, T.A. Targeting Inflammatory Cytokines to Improve Type 2 Diabetes Control. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7297419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simpson, R.J.; Hammacher, A.; Smith, D.K.; Matthews, J.M.; Ward, L.D. Interleukin-6: Structure-function relationships. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 929–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kristiansen, O.P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Interleukin-6 and diabetes: The good, the bad, or the indifferent? Diabetes 2005, 54 (Suppl. 2), S114–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, P.; Lozano, P.; Ros, G.; Solano, F. Hyperglycemia and Oxidative Stress: An Integral, Updated and Critical Overview of Their Metabolic Interconnections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bahrami, H.S.Z.; Jørgensen, P.G.; Hove, J.D.; Dixen, U.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Rossing, P.; Jensen, M.T. Association between interleukin-6, suPAR, and hsCRP with subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in type 1 diabetes: The Thousand & 1 study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 222, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S27–S49. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wegner, M.; Araszkiewicz, A.; Piorunska-Stolzmann, M.; Wierusz-Wysocka, B.; Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz, D. Association between IL-6 concentration and diabetes-related variables in DM1 patients with and without microvascular complications. Inflammation 2013, 36, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Galassetti, P.R.; Iwanaga, K.; Pontello, A.M.; Zaldivar, F.P.; Flores, R.L.; Larson, J.K. Effect of prior hyperglycemia on IL-6 responses to exercise in children with type 1 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E833–E839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, M.; Rasool, H.F.; Javed, I.; Raza, S.; Abang, L.; Hashim, M.M.A.; Saleem, Z.; Abdullah, R.M.; Faraz, M.A.; Hassan, K.M.; et al. Comparative Roles of IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, IL-18, IL-22, IL-33, and IL-37 in Various Cardiovascular Diseases With Potential Insights for Targeted Immunotherapy. Cureus 2023, 15, e42494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alexandraki, K.I.; Piperi, C.; Ziakas, P.D.; Apostolopoulos, N.V.; Makrilakis, K.; Syriou, V.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Kaltsas, G.; Kalofoutis, A. Cytokine secretion in long-standing diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: Associations with low-grade systemic inflammation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Qiao, Y.C.; Pan, Y.H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Geng, L.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, X.X. Correlation between serum interleukin-6 level and type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2017, 94, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koufakis, T.; Kourti, A.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Makedou, K.; Zografou, I. Divergent Interleukin-6 Responses to Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: Insights From Continuous Glucose Monitoring. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayano-Takahara, S.; Ikeda, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Hamasaki, A.; Harashima, S.; Toyoda, K.; Fujita, Y.; Nagashima, K.; Tanaka, D.; Inagaki, N. Glycemic variability is associated with quality of life and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmot, E.G.; Choudhary, P.; Leelarathna, L.; Baxter, M. Glycaemic variability: The under-recognized therapeutic target in type 1 diabetes care. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, L.; Lalic, N.M.; Rajkovic, N.; Jotic, A.; Lalic, K.; Milicic, T.; Seferovic, J.P.; Macesic, M.; Gajovic, J.S. Hypertension in obese type 2 diabetes patients is associated with increases in insulin resistance and IL-6 cytokine levels: Potential targets for an efficient preventive intervention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3586–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rajkovic, N.; Zamaklar, M.; Lalic, K.; Jotic, A.; Lukic, L.; Milicic, T.; Singh, S.; Stosic, L.; Lalic, N.M. Relationship between obesity, adipocytokines and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Relevance for cardiovascular risk prevention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4049–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bowker, N.; Shah, R.L.; Sharp, S.J.; Luan, J.; Stewart, I.D.; Wheeler, E.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Baras, A.; Wareham, N.J.; Langenberg, C.; et al. Meta-analysis investigating the role of interleukin-6 mediated inflammation in type 2 diabetes. eBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Pirro, M.; Sahebkar, A. A review of the anti-inflammatory properties of antidiabetic agents providing protective effects against vascular complications in diabetes. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 8286–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, E.A.; Joglekar, A.V.; Linnemann, A.K.; Russ, H.A.; Kent, S.C. The beta cell-immune cell interface in type 1 diabetes (T1D). Mol. Metab. 2023, 78, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, S.; Venugopal, S.K.; Singh, U.; Jialal, I. Hyperglycemia induces monocytic release of interleukin-6 via induction of protein kinase C-α and-β. Diabetes 2005, 54, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, R.P.; Dye, A.S.; Huang, H.; Bauer, J.A. Glycemic variability predicts inflammation in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 29, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suh, S.; Kim, J.H. Glycemic Variability: How Do We Measure It and Why Is It Important? Diabetes Metab. J. 2015, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ngwa, D.N.; Pathak, A.; Agrawal, A. IL-6 regulates induction of C-reactive protein gene expression by activating STAT3 isoforms. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 146, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sibianu, M.; Slevin, M. The Pathogenic Role of C-Reactive Protein in Diabetes-Linked Unstable Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Järvisalo, M.J.; Raitakari, M.; Toikka, J.O.; Putto-Laurila, A.; Rontu, R.; Laine, S.; Lehtimäki, T.; Rönnemaa, T.; Viikari, J.; Raitakari, O.T. Endothelial dysfunction and increased arterial intima-media thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Circulation 2004, 109, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremova, I.; Maslennikov, R.; Poluektova, E.; Medvedev, O.; Kudryavtseva, A.; Krasnov, G.; Fedorova, M.; Romanikhin, F.; Zharkova, M.; Zolnikova, O.; et al. Presepsin as a biomarker of bacterial translocation and an indicator for the prescription of probiotics in cirrhosis. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zografou, I.; Kouroupis, D.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Doukelis, P.; Doumas, M.; Koufakis, T. Correlation Between Presepsin Levels and Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Infection-Free Individuals With Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2025, 19, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kouroupis, D.; Zografou, I.; Balaska, A.; Reklou, A.; Varouktsi, A.; Paschala, A.; Pyrpasopoulou, A.; Stavropoulos, K.; Vogiatzis, K.; Sarvani, A.; et al. Presepsin Levels in Infection-Free Subjects with Diabetes Mellitus: An Exploratory Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Greenbaum, C.J.; Serti, E.; Lambert, K.; Weiner, L.J.; Kanaparthi, S.; Lord, S.; Gitelman, S.E.; Wilson, D.M.; Gaglia, J.L.; Griffin, K.J.; et al. IL-6 receptor blockade does not slow β cell loss in new-onset type 1 diabetes. JCI Insight. 2021, 6, e150074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hundhausen, C.; Roth, A.; Whalen, E.; Chen, J.; Schneider, A.; Long, S.A.; Wei, S.; Rawlings, R.; Kinsman, M.; Evanko, S.P.; et al. Enhanced T cell responses to IL-6 in type 1 diabetes are associated with early clinical disease and increased IL-6 receptor expression. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 356ra119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Group | N | Age, Mean (SD), Years | BMI, Mean (SD), kg/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 14 | 54.1 (7.8) | 24.5 (2.5) |
| Type 2 with suboptimal control | 25 | 63.9 (14.1) | 32.3 (7.3) |
| Type 2 with optimal control | 21 | 60.4 (10.4) | 30.1 (4.1) |
| Type 1 with suboptimal control | 11 | 30.7 (11.9) | 25.7 (5.5) |
| Type 1 with optimal control | 11 | 45.8 (10.4) | 28.0 (3.5) |
| Overall | 82 | 52.6 (16.6) | 29.0 (5.9) |
| Group | Adjusted IL-6, pg/mL | Predicted Probability (IL-6 > 1.5 pg/mL) | Fold-Change vs. Control (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.79 | 31% | Reference | – |
| Type 1 with optimal control | 2.72 | 67% | 2.35 (0.91–6.06) | 0.079 |
| Type 1 with suboptimal control | 4.14 | 85% | 4.06 (1.36–12.1) | 0.013 |
| Type 2 with optimal control | 2.08 | 47% | 1.46 (0.60–3.55) | 0.401 |
| Type 2 with suboptimal control | 1.99 | 42% | 1.32 (0.53–3.28) | 0.562 |
| IL-6 | hs-CRP | Ferritin | Presepsin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 1.000 (p = 1.0) | 0.463 (p < 0.001) | –0.227 (p = 0.060) | 0.119 (p = 0.332) |
| hs-CRP | 0.463 (p < 0.001) | 1.000 (p = 1.0) | –0.157 (p = 0.198) | 0.077 (p = 0.522) |
| Ferritin | –0.227 (p = 0.060) | –0.157 (p = 0.198) | 1.000 (p = 1.0) | 0.027 (p = 0.828) |
| Presepsin | 0.119 (p = 0.332) | 0.077 (p = 0.522) | 0.027 (p = 0.828) | 1.000 (p = 1.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koufakis, T.; Kouroupis, D.; Kourti, A.; Thisiadou, K.; Karalazou, P.; Popovic, D.S.; Patoulias, D.; Maltese, G.; Pyrpasopoulou, A.; Doukelis, P.; et al. Interleukin-6-Related Inflammatory Burden in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence for Elevation with Suboptimal Glycemic Control. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186511
Koufakis T, Kouroupis D, Kourti A, Thisiadou K, Karalazou P, Popovic DS, Patoulias D, Maltese G, Pyrpasopoulou A, Doukelis P, et al. Interleukin-6-Related Inflammatory Burden in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence for Elevation with Suboptimal Glycemic Control. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186511
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoufakis, Theocharis, Dimitrios Kouroupis, Areti Kourti, Katerina Thisiadou, Paraskevi Karalazou, Djordje S. Popovic, Dimitrios Patoulias, Giuseppe Maltese, Athina Pyrpasopoulou, Panagiotis Doukelis, and et al. 2025. "Interleukin-6-Related Inflammatory Burden in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence for Elevation with Suboptimal Glycemic Control" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186511
APA StyleKoufakis, T., Kouroupis, D., Kourti, A., Thisiadou, K., Karalazou, P., Popovic, D. S., Patoulias, D., Maltese, G., Pyrpasopoulou, A., Doukelis, P., Zografou, I., Kotsa, K., Doumas, M., & Makedou, K. (2025). Interleukin-6-Related Inflammatory Burden in Type 1 Diabetes: Evidence for Elevation with Suboptimal Glycemic Control. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6511. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186511









