Evidence of Multifidus Changes Post-Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation: A Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
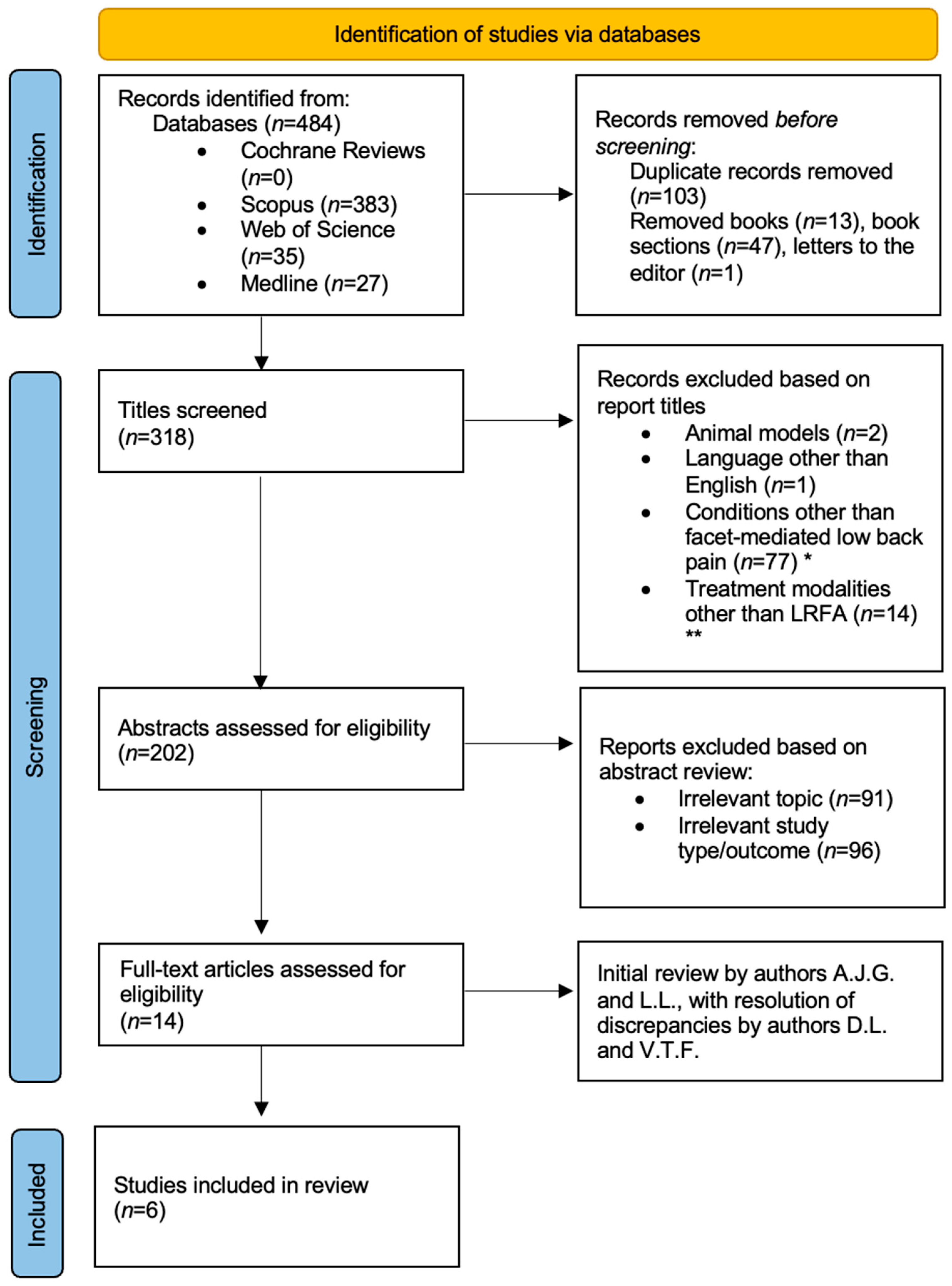
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Multifidus Atrophy Following LRFA
4.2. Clinical Implications
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CLBP | Chronic low back pain |
| LMBN | Lumbar medial branch nerves |
| LRFA | Lumbar medial branch radiofrequency ablation |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| FCSA | Functional cross-sectional area |
| PNS | Peripheral nerve stimulation |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| ASPN | American Society of Pain and Neuroscience |
| ISASS | International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery |
References
- The Lancet Rheumatology. The global epidemic of low back pain. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, M.V.; Manchikanti, L.; Kaye, A.D.; Bakshi, S.; Gharibo, C.G.; Gupta, S.; Jha, S.S.; Nampiaparampil, D.E.; Simopoulos, T.T.; Hirsch, J.A. A Best-Evidence Systematic Appraisal of the Diagnostic Accuracy and Utility of Facet (Zygapophysial) Joint Injections in Chronic Spinal Pain. Pain Physician 2015, 18, E497–E533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, L.; Dua, A.; Shah, N.; Padalia, D. Facet Joint Disease. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Petersburg, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541049/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Van den Heuvel, S.A.S.; Cohen, S.P.C.; de Andrès Ares, J.; Van Boxem, K.; Kallewaard, J.W.; Van Zundert, J. 3. Pain originating from the lumbar facet joints. Pain Pract. 2024, 24, 160–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.; Peng, P.; Loh, E. Anatomical study of the medial branches of the lumbar dorsal rami: Implications for image-guided intervention. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2022, 47, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanakis, S.; Gkantsinikoudis, N. Anatomy of lumbar facet joint: A comprehensive review. Folia Morphol. 2021, 80, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogduk, N.; Long, D.M. Percutaneous Lumbar Medial Branch Neurotomy: A Modification of Facet Denervation. Spine 1980, 5, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Pritzlaff, S.; Jung, M.J.; Ghosh, P.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Tate, J.; Scarfo, K.; Strand, N.; Chakravarthy, K.; Sayed, D.; et al. Latest Evidence-Based Application for Radiofrequency Neurotomy (LEARN): Best Practice Guidelines from the American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN). J. Pain Res. 2021, ume 14, 2807–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L.; Hirsch, J.A.; Pampati, V.; Boswell, M.V. Utilization of Facet Joint and Sacroiliac Joint Interventions in Medicare Population from 2000 to 2014: Explosive Growth Continues! Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2016, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oosterwyck, W.; Vander Cruyssen, P.; Castille, F.; Van De Kelft, E.; Decaigny, V. Lumbar Facet Joint Disease: What, Why, and When? Life 2024, 14, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, D.A.; Holt, B.; Danko, M.; Atallah, J.; Iqbal, M.; Shah, B.; Singh, A.; Sachdeva, H.; Donck, E.V.; Shaw, E.; et al. Assessment of real-world, prospective outcomes in patients treated with lumbar radiofrequency ablation for chronic pain (RAPID). Interv. Pain Med. 2025, 4, 100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rachdi, O.; Stephens, A.; Cooper, A.N.; Martin, B.; Burnham, R.; Conger, A.M.; McCormick, Z.L.; Burnham, T.R. A retrospective single arm cohort study evaluating the efficacy of lumbar medial branch radiofrequency ablation using a multi-tined probe and perpendicular approach. Interv. Pain Med. 2025, 4, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juch, J.N.S.; Maas, E.T.; Ostelo, R.W.J.G.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Kallewaard, J.-W.; Koes, B.W.; Verhagen, A.P.; van Dongen, J.M.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; van Tulder, M.W. Effect of Radiofrequency Denervation on Pain Intensity Among Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain: The Mint Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA 2017, 318, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henschke, N.; Kuijpers, T.; Rubinstein, S.M.; van Middelkoop, M.; Ostelo, R.; Verhagen, A.; Koes, B.W.; van Tulder, M.W. Injection therapy and denervation procedures for chronic low-back pain: A systematic review. Eur. Spine J. 2010, 19, 1425–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.T.; Ostelo, R.W.J.G.; Niemisto, L.; Jousimaa, J.; Hurri, H.; Malmivaara, A.; van Tulder, M.W. Radiofrequency denervation for chronic low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 10, CD008572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieppo Francio, V.; Glicksman, M.; Leavitt, L.; Gill, B.; Shah, A.; Westerhaus, B.D.; Lam, C.M.; D’SOuza, R.S. Multifidus atrophy and/or dysfunction following lumbar radiofrequency ablation: A systematic review. PM&R 2024, 16, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.R.; Tomiya, A.; Regev, G.J.; Thacker, B.E.; Benzl, R.C.; Kim, C.W.; Lieber, R.L. Passive mechanical properties of the lumbar multifidus muscle support its role as a stabilizer. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Gottschalk, L.; Eng, C.; Ward, S.; Lieber, R. 160. The Multifidus Muscle is the Strongest Stabilizer of the Lumbar Spine. Spine J. 2007, 7, 76S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieppo Francio, V.; Westerhaus, B.D.; Carayannopoulos, A.G.; Sayed, D. Multifidus dysfunction and restorative neurostimulation: A scoping review. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiner, D.S.; Matz, P.; Bono, C.M.; Cho, C.H.; Easa, J.E.; Ghiselli, G.; Ghogawala, Z.; Reitman, C.A.; Resnick, D.K.; Watters, W.C.; et al. Guideline summary review: An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. Spine J. 2020, 20, 998–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biely, S.; Smith, S.; Silfies, S. Clinical instability of the lumbar spine: Diagnosis and intervention. Orthop. Pract. 2006, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Beazell, J.R.; Mullins, M.; Grindstaff, T.L. Lumbar instability: An evolving and challenging concept. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2010, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhera, J. Narrative Reviews in Medical Education: Key Steps for Researchers. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, A.E.; Evangelisti, G.; Burkhard, M.D.; Köhli, P.; Hambrecht, J.; Zhu, J.; Chiapparelli, E.; Kelly, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Amoroso, K.; et al. Asymmetrical atrophy of the paraspinal muscles in patients undergoing unilateral lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy. Pain 2024, 165, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, K.A.C.; Ekengele, V.; Hoppe, S.; Streitberger, K.; Harnik, M.; Albers, C.E. Radiofrequency Neurotomy Does Not Cause Fatty Degeneration of the Lumbar Paraspinal Musculature in Patients with Chronic Lumbar Pain—A Retrospective 3D-Computer-Assisted MRI Analysis Using iSix Software. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böning, G.; Hartwig, T.; Freyhardt, P.; De Bucourt, M.; Teichgräber, U.; Streitparth, F. MR-guided lumbar facet radiofrequency denervation for treatment of patients with chronic low back pain in an open 1.0 Tesla MRI system. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Bible, J.E.; Cortes, D.H. Quantifying Dysfunction of the Lumbar Multifidus Muscle After Radiofrequency Neurotomy and Fusion Surgery: A Preliminary Study. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 3, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuck, M.; Crisostomo, R.A.; Demirjian, R.; Fitch, D.S.; Kennedy, D.J.; Geisser, M.E. Morphologic changes in the lumbar spine after lumbar medial branch radiofrequency neurotomy: A quantitative radiological study. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, P.; Stout, A.; Aprill, C.; Pollei, S.; Johnson, B.; Bogduk, N. The Significance of Multifidus Atrophy After Successful Radiofrequency Neurotomy for Low Back Pain. PM&R 2009, 1, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieppo Francio, V.; Leavitt, L.; Radlicz, C.; Gill, B.; Sayed, D. Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation (LRFA)–Myths and Facts: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2025, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, A.; Dobruch-Sobczak, K. Introduction to ultrasound elastography. J. Ultrason. 2016, 16, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kanchiku, T.; Imajo, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Nishida, N.; Taguchi, T. Percutaneous radiofrequency facet joint denervation with monitoring of compound muscle action potential of the multifidus muscle group for treating chronic low back pain: A preliminary report. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2014, 27, E262–E267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottlors, M.; Glocker, F.X. Polysegmental innervation of the medial paraspinal lumbar muscles. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, P.B.; Date, E.S.; Kingery, W.S. The lumbar multifidus muscle in polysegmentally innervated. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 40, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vas, L.; Khandagale, N.; Pai, R. Report of an unusual complication of radiofrequency neurotomy of medial branches of dorsal rami. Pain Physician 2014, 17, E654–E657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, H.S.; Chapman, A.W. Dropped head syndrome: Report of a rare complication after multilevel bilateral cervical radiofrequency neurotomy. Pain Rep. 2022, 7, e1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, F.A.; Cortes, D.H. Multifidus Denervation After Radiofrequency Ablation of the Medial Nerve Alters the Biomechanics of the Spine—A Computational Study. J. Appl. Biomech. 2023, 39, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.D.; Woodham, M.A.; Woodham, A.W. The Role of the Lumbar Multifidus in Chronic Low Back Pain: A Review. PM&R 2010, 2, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.R.; Kim, C.W.; Eng, C.M.; Gottschalk, L.J.; Tomiya, A.; Garfin, S.R.; Lieber, R.L. Architectural Analysis and Intraoperative Measurements Demonstrate the Unique Design of the Multifidus Muscle for Lumbar Spine Stability. J. Bone Jt. Surg Am. Vol. 2009, 91, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaty, E.M.; Shendy, S.; Lotfy, O.; Hassan, K.A. The difference in multifidus muscle morphology and motor control in non-specific low back pain with clinical lumbar instability and healthy subjects: A case-control study. Physiother. Res. Int. 2024, 29, e2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, A.E.; Schönnagel, L.; Camino-Willhuber, G.; Chiapparelli, E.; Amoroso, K.; Zhu, J.; Tani, S.; Caffard, T.; Arzani, A.; Zadeh, A.T.; et al. Relationship between facet joint osteoarthritis and lumbar paraspinal muscle atrophy: A cross-sectional study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2024, 41, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkaya, S.; Sağlam Akkaya, G. Magnetic Resonance Imaging- Defined Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Morphometry and Lumbopelvic Parameters in Patients with Lumbar Isthmic Spondylolisthesis. J. Acad. Res. Med. 2025, 14, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S. Links among MRI features in paraspinal muscles, inflammatory processes, and related back pain in patients with lumbar disc herniation. JOR Spine 2024, 7, e1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Ahern, B.; Goodwin, W.; Goss, B.; Hodges, P. Structural changes of muscle spindles in the multifidus muscle after intervertebral disk injury are resolved by targeted activation of the muscle. Eur. Spine J. 2025, 34, 1600–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieppo Francio, V.; Westerhaus, B.D.; Rupp, A.; Sayed, D. Non-Spinal Neuromodulation of the Lumbar Medial Branch Nerve for Chronic Axial Low Back Pain: A Narrative Review. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 835519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deer, T.R.; Eldabe, S.; Falowski, S.M.; A Huntoon, M.; Staats, P.S.; Cassar, I.R.; Crosby, N.D.; Boggs, J.W. Peripherally Induced Reconditioning of the Central Nervous System: A Proposed Mechanistic Theory for Sustained Relief of Chronic Pain with Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, C.; Volschenk, W.; Russo, M.; Green, M.; Gilmore, C.; Mehta, V.M.; Deckers, K.; De Smedt, K.; Latif, U.M.; Georgius, P.; et al. An implantable restorative-neurostimulator for refractory mechanical chronic low back pain: A randomized sham-controlled clinical trial. Pain 2021, 162, 2486–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, C.; Volschenk, W.; Russo, M.; Green, M.; Gilmore, C.; Mehta, V.; Deckers, K.; De Smedt, K.; Latif, U.; Georgius, P.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Restorative Neurostimulation in Patients With Refractory Chronic Low Back Pain Secondary to Multifidus Dysfunction: Two-Year Results of the ReActiv8-B Pivotal Trial. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural Interface 2023, 26, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, C.; Volschenk, W.; Russo, M.; Green, M.; Gilmore, C.; Mehta, V.; Deckers, K.; De Smedt, K.; Latif, U.; Sayed, D.; et al. Three-Year Durability of Restorative Neurostimulation Effectiveness in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain and Multifidus Muscle Dysfunction. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural Interface 2023, 26, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, C.; Volschenk, W.; Russo, M.; Green, M.; Gilmore, C.; Mehta, V.; Deckers, K.; De Smedt, K.; Latif, U.; Sayed, D.; et al. Five-Year Longitudinal Follow-Up of Restorative Neurostimulation Shows Durability of Effectiveness in Patients with Refractory Chronic Low Back Pain Associated with Multifidus Muscle Dysfunction. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural Interface 2024, 27, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardeshiri, A.; Amann, M.; Thomson, S.; Gilligan, C.J. Application of restorative neurostimulation for chronic mechanical low back pain in an older population with 2-year follow up. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2025, 50, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, F.; Mekhail, N.; Patel, K.V.; Langhorst, M.; Heros, R.D.; Gentile, J.; Costandi, S.; Moore, G.; Gilmore, C.; Manion, S.; et al. Restorative Neurostimulation Therapy Compared to Optimal Medical Management: A Randomized Evaluation (RESTORE) for the Treatment of Chronic Mechanical Low Back Pain due to Multifidus Dysfunction. Pain Ther. 2025, 14, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, D.; Grider, J.; Strand, N.; Hagedorn, J.M.; Falowski, S.; Lam, C.M.; Francio, V.T.; Beall, D.P.; Tomycz, N.D.; Davanzo, J.R.; et al. The American Society of Pain and Neuroscience (ASPN) Evidence-Based Clinical Guideline of Interventional Treatments for Low Back Pain. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 3729–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorio, M.; Lewandrowski, K.U.; Coric, D.; Phillips, F.; Shaffrey, C.I. International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery Statement: Restorative Neurostimulation for Chronic Mechanical Low Back Pain Resulting From Neuromuscular Instability. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2023, 17, 728–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, S.; Williams, A.; Vajramani, G.; Sharma, M.; Love-Jones, S.; Chawla, R.; Eldabe, S. 5-year longitudinal follow-up of patients treated for chronic mechanical low back pain using restorative neurostimulation. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2025; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Original peer-reviewed research | Book chapters, letters to the editor, conference abstracts |
| English language | Manuscripts in languages other than English |
| Human studies | Non-human studies |
| Study designs: randomized controlled trials, prospective/retrospective observational cohorts, case series, case reports | Duplicate data |
| Outcomes assessing multifidus morphology or function post-LRFA |
| Author | Study Design | Number of Subjects | Outcome Tool Measurement (Multifidus Measurement Method) | Measurement Timing | Follow-Up Intervals After LRFA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guven [26] | Retrospective longitudinal case series with paired analysis | 24 patients (51 spinal levels) | Custom software analysis of multifidus fat area based on T2w MRIs | Pre- and post-LRFA | Over 2 years |
| Oswald [27] | Retrospective, longitudinal cohort study | 20 | Semi-automatic analysis of standard T2w MRI of L-spine | Pre- and post-LRFA | 16.8 months (median) |
| Böning [28] | Prospective, longitudinal cohort study | 17 | Manual measurement of axial T2w MRI of L-spine | Pre- and post-LRFA | 1 week and 6 months |
| Sadeghi [29] | Prospective, cross-sectional cohort study | 46 | Customized supersonic ultrasound SWE of multifidus at the middle level | Post-LRFA | 11.42 months (mean) |
| Smuck [30] | Retrospective, longitudinal, cohort study | 27 | Fat-subtracted multifidus CSA with gray-scale cutoff values of axial T2w MRI of L-spine | Pre- and post-LRFA | 7.5 months (mean) |
| Dreyfuss [31] | Prospective, cross-sectional cohort study | 5 | T2w sagittal and T1w axial MRI images of L-spine and EMG | Post-LRFA | 21 months (mean) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, A.J.; Lee, D.W.; Leavitt, L.; Tieppo Francio, V. Evidence of Multifidus Changes Post-Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation: A Narrative Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186462
Garcia AJ, Lee DW, Leavitt L, Tieppo Francio V. Evidence of Multifidus Changes Post-Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation: A Narrative Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186462
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Abigail Joy, David W. Lee, Logan Leavitt, and Vinicius Tieppo Francio. 2025. "Evidence of Multifidus Changes Post-Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation: A Narrative Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186462
APA StyleGarcia, A. J., Lee, D. W., Leavitt, L., & Tieppo Francio, V. (2025). Evidence of Multifidus Changes Post-Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation: A Narrative Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186462







