Thyromental Height Test as a Method for Predicting Difficult Intubation in Patients with Obesity: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- MMT: The oropharyngeal view was assessed using the modified Mallampati classification. Patients sat with their mouths maximally opened, tongue protruding, and without phonation.
- TMD was measured between the thyroid prominence and the most anterior part of the mental prominence of the mandible using a tape measure (Standard, Hoechstmas, Sulzbach, Germany), with distance in millimeters, with the patient in a supine position, head fully extended, and mouth closed.
- SMD was measured between the superior border of the manubrium sterni and the most anterior part of the mental prominence of the mandible with a tape measure (Standard, Sulzbach, Germany), with distance in millimeters, with the patient in a supine position, head fully extended, and mouth closed.
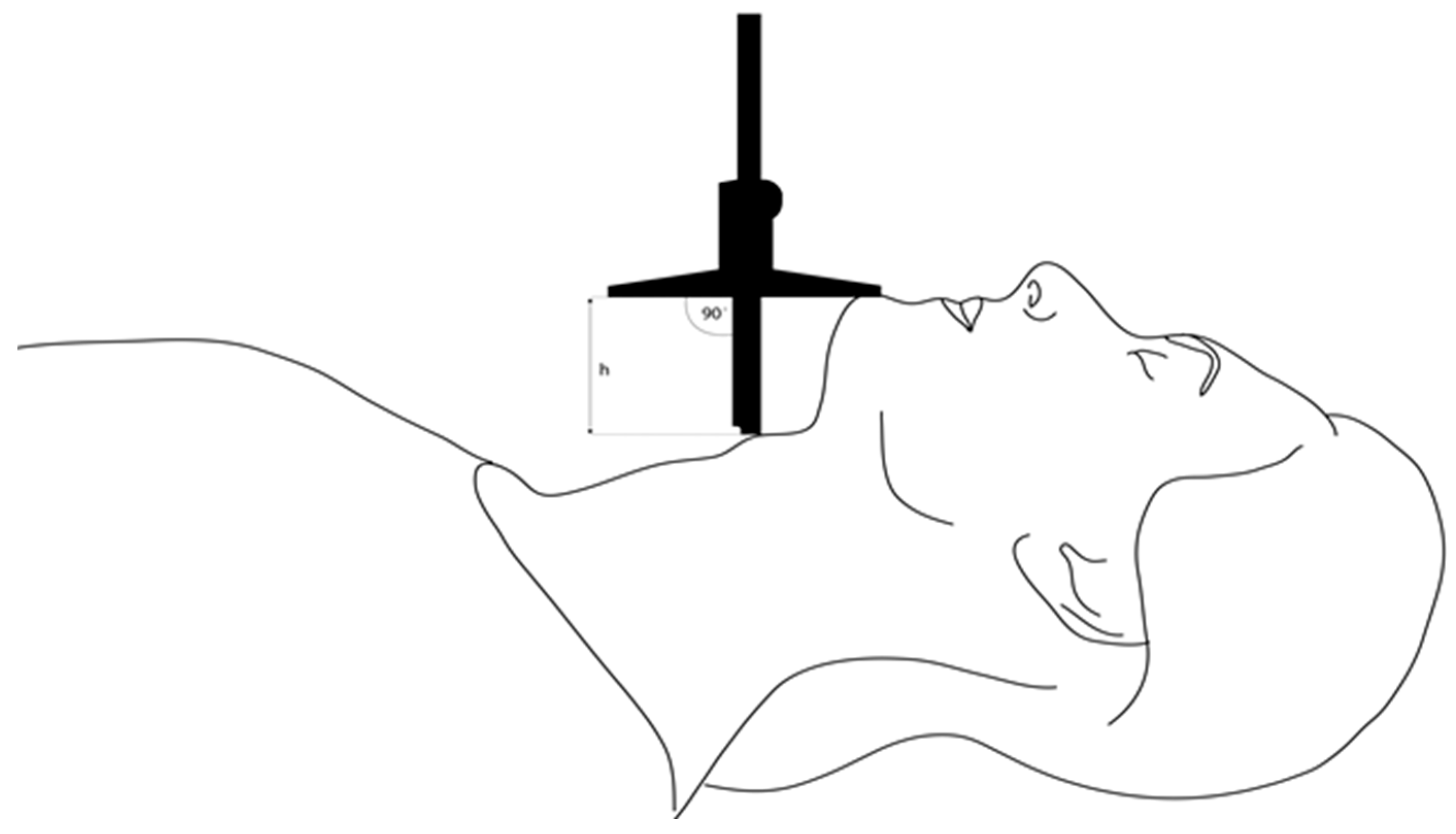
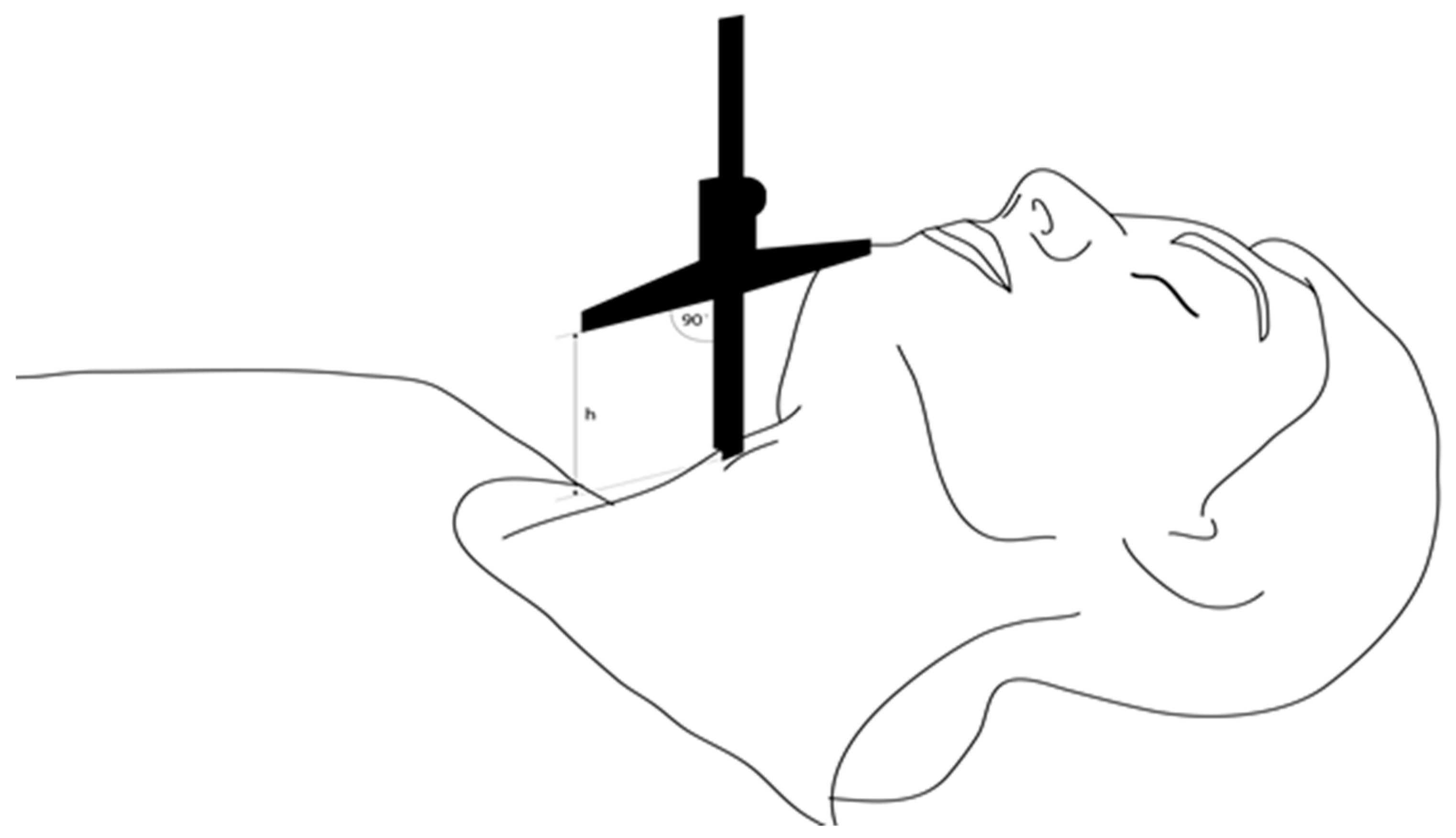
- TMH was measured as the height between the anterior border of the thyroid cartilage (on the thyroid notch just between the second thyroid laminae) and the anterior border of the mentum (on the mental protuberance of the mandible) with a depth gauge (Limit, Alingsås, Sweden), in millimeters, with the patient in a supine position with their mouth closed, as presented in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
- NC was measured at the level of the cricoid cartilage horizontally with a tape measure (Standard, Sulzbach, Germany) as a circumference in millimeters, with patients in the sitting position.
- MO was measured as the distance between the lower and upper incisors with a tape measure (Standard, Sulzbach, Germany), with distance in millimeters. Patients sat with their mouths maximally opened, tongues retracted, and without phonation.
- More than two attempts were required to achieve successful intubation using a conventional Macintosh laryngoscope.
- Two failed intubation attempts were made by two experienced anesthesiologists.
- A change in technique was necessary (e.g., the use of an alternative airway device, different laryngoscope, or bougie stylet).
- Total duration of intubation attempts exceeded three minutes.
Statistical Analysis
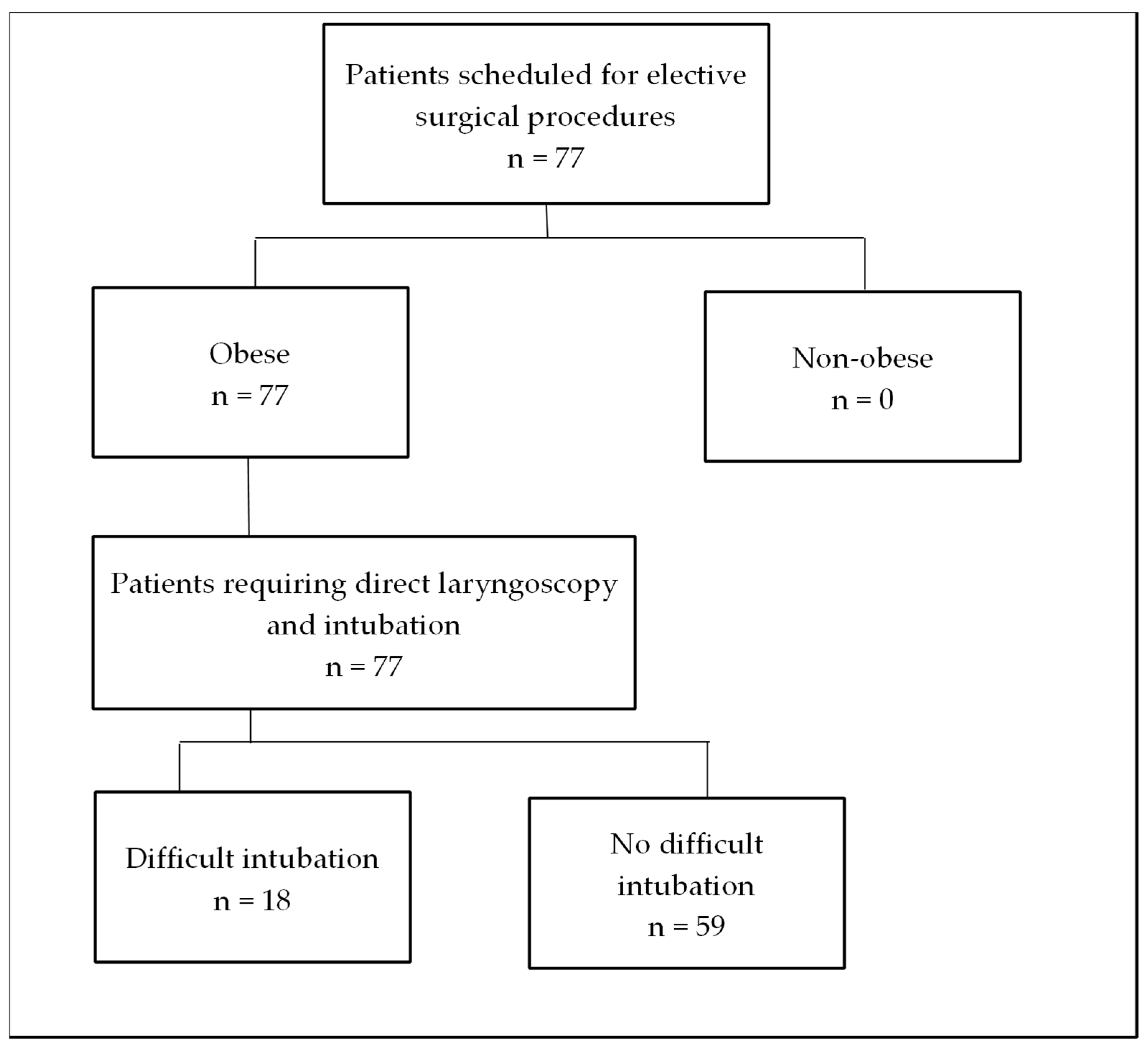
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TMHT | Thyromental Height Test |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| MMT | Modified Mallampati Test |
| TMD | Thyromental Distance |
| SMD | Sternomental Distance |
| NC | Neck Circumference |
| MO | Mouth Opening |
| TOF | Train of Four |
| OSAS | Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the ROC Curve |
| SE | Standard Error |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| ULBT | Upper Lip Bite Test |
References
- Enterlein, G.; Byhahn, C. Practice Guidelines for Management of the Difficult Airway, Update der American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force. Der Anaesthesist 2013, 62, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, A.C. Emergency airway management in the UK. J. R. Soc. Med. 2005, 98, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.; Pace, N.L.; Lee, A.; Hovhannisyan, K.; Warenits, A.-M.; Arrich, J.; Herkner, H. Airway physical examination tests for detection of difficult airway management in apparently normal adult patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018, 15, CD008874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, E.J.; Carrier-Boucher, A.; Provencher, S.; Tanoubi, I.; Marceau, S.; Bussières, J.S. Effect of reverse Trendelenburg position and positive pressure ventilation on safe non-hypoxic apnea period in obese, a randomized-control trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Alkhouri, H.; Badge, H.; Long, E.; Chan, T.; Vassiliadis, J.; Fogg, T. Bed tilt and ramp positions are associated with increased first-pass success of adult endotracheal intubation in the emergency department: A registry study. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2023, 35, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachshon, A.; Firman, S.; Batzofin, B.M.; Miklosh, B.; van Heerden, P.V. Can’t intubate, can’t oxygenate? What is the preferred surgical strategy? A retrospective analysis. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2024, 56, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hung, K.C.; Chuang, M.H.; Kang, F.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Lin, C.M.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, I.W.; Sun, C.K. Prevalence and risk factors of difficult mask ventilation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2023, 90, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.S.; Fox, P.E.; Somasundaram, A.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gonzales, M.X.; Pak, T.J.; Ogunnaike, B. The influence of morbid obesity on difficult intubation and difficult mask ventilation. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.S.; Viknaswaran, N.; Lau, J.; Cheong, C.; Wang, C. Effectiveness of preoxygenation during endotracheal intubation in a head-elevated position: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2022, 54, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheterpal, S.; Healy, D.; Aziz, M.F.; Shanks, A.M.; Freundich, R.E.; Linton, F.; Martin, L.D.; Linton, J.; Epps, J.L.; Fernandez-Bustamante, A.; et al. Incidence, predictors, and outcome of difficult mask ventilation combined with difficult laryngoscopy: A report from the multicenter perioperative outcomes group. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy and safety of Cook staged Extubation Set in patients with difficult airway: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, S.; Bhar Kundu, S.; Nivetha, C. Evaluation of neck-circumference- thyromental- distance ratio as a predictor of difficult intubation: A prospective, observational study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2023, 67, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriussawakul, A.; Rattanaarpa, S.; Jirachaipitak, S.; Chatsiriphattana, A.; Nimmannit, A.; Wong-in, N. The Performance of the Neck Circumference for a Difficult Laryngoscopy in Obese Patients. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2016, 99, 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Prathep, S.; Jitpakdee, W.; Woraathasin, W.; Oofuvong, M. Predicting difficult laryngoscopy in morbidly obese Thai patients by ultrasound measurement of distance from skin to epiglottis: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKechnie, A.; Iliff, H.A.; Black, R.; Ahmad, I.; Chesworth, A.; Chesworth, P.; Davis, N.; Griffiths, C. Airway management in patients living with obesity: Best practice recommendations from the Society for Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia: Endorsed by the All Wales Airway Group, Scottish Airway Group and Difficult Airway Society. Anaesthesia 2025, 80, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thota, B.; Jan, K.M.; Oh, M.W.; Moon, T.S. Airway management in patients with obesity. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2022, 16, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamperti, M.; Romero, C.S.; Guarracino, F.; Cammarota, G.; Vetrugno, L.; Tufegdzic, B.; Lozsan, F.; Frias, J.J.M.; Duma, A.; Bock, M.; et al. Preoperative assessment of adults undergoing elective noncardiac surgery: Updated guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2024, 42, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, D.; Šurbatović, M.; Milisavljević, D.; Marjanović, V.; Kovačević, T.; Stanković, M. Addition of flexible laryngoscopy to anesthesiological parameters improves prediction of difficult intubation in laryngeal surgery. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2024, 56, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Etezadi, F.; Ahangari, A.; Shokri, H.; Najafi, A.; Khajavi, M.R.; Daghigh, M.; Moharari, R.S. Thyromental height: A new clinical test for prediction of difficult laryngoscopy. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Schindler, E. Ideal endotracheal intubation depth at the vocal-cord level to avoid single-lung intubation using the percentage ratio of the tracheal length to body height. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2023, 55, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carvalho, C.C.; Santos Neto, J.M.; Orange, F.A. Predictive performance of thyromental height for difficult laryngoscopies in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2021, 73, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajmohamed, S.; Patel, D.; Apruzzese, P.; Kendall, M.C.; De Oliveira, G. Early Postoperative Outcomes of Super Morbid Obese Compared to Morbid Obese Patients After Ambulatory Surgery Under General Anesthesia: A Propensity-Matched Analysis of a National Database. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 133, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetzler, K.; Rivas, E.; Cohen, B.; Mosteller, L.; Martin, A.; Keebler, A.; Maheshwari, K.; Steckner, K.; Wang, M.; Praveen, C.; et al. McGrath Video Laryngoscope Versus Macintosh Direct Laryngoscopy for Intubation of Morbidly Obese Patients: A Randomized Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, C.J.; Shin, B.S.; Ko, J.S.; Choi, S.J.; Ryu, S.A. Neck circumference to thyromental distance ratio: A new predictor of difficult intubation in obese patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 106, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjiar, P.; Kochhar, A.; Bhat, K.M.; Bhat, M.A. Comparison of thyromental height test with ratio of height to thyromental distance, thyromental distance, and modified Mallampati test in predicting difficult laryngoscopy: A prospective study. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 35, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.N.; Dhatchinamoorthi, D.; Nandhakumar, A.; Selvarajan, N.; Akula, H.R.; Thiruvenkatarajan, V. Validity of thyromental height test as a predictor of difficult laryngoscopy: A prospective evaluation comparing modified Mallampati score, interincisor gap, thyromental distance, neck circumference, and neck extension. Indian J. Anaesth. 2018, 62, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Das, S.; Kanchi, M. Thyromental height test for prediction of difficult laryngoscopy in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgical procedure. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2017, 20, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.; Saeed, M.; Hasanin, A.; Badawy, S.; Khaled, D. Accuracy of thyromental height test for predicting difficult intubation in elderly. J. Anesth. 2020, 34, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, P.; Shrestha, S.M. The Evaluation of Thyromental Height Test as a Single, Accurate Predictor of Difficult Laryngoscopy. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2020, 18, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; Mullick, P.; Singh, R. Evaluation of thyromental height as a predictor of difficult laryngoscopy and difficult intubation: A cross-sectional observational study. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2021, 72, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuki, S.; Iwaoka, S.; Murakami, M.; Miura, H. Reliability of the thyromental height test for prediction of difficult visualization of the larynx: A prospective external validation. Indian J. Anaesth. 2019, 63, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tian, T.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.; Xue, F. Use of the Thyromental Height Test for Prediction of Difficult Laryngoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, E.; Oliveira Marques, F.; Sousa Govêia, C.; Araújo Ladeira, L.C.; Lagares, J. Use of simple clinical predictors on preoperative diagnosis of difficult endotracheal intubation in obese patients. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2013, 63, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriussawakul, A.; Maboonyanon, P.; Kueprakone, S.; Samankatiwat, S.; Komoltri, C.; Thanakiattiwibun, C. Predictive performance of a multivariable difficult intubation model for obese patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emik, E.; Gümüs-Özcan, F.; Demirgan, S.; Selcan, A. Evaluation of the correlation between preoperative airway assessment tests, anthropometric measurements, and endotracheal intubation difficulty in obesity class III patients undergoing bariatric surgery. Medicine 2021, 100, e27188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshniwal, G.; McKelvey, G.M.; Wang, H. STOP-Bang and prediction of difficult airway in obese patients. J. Clin. Anesth. 2014, 26, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, H.; Minville, V.; Delanoue, K.; Mazerolles, M.; Concina, D.; Fourcade, O. The importance of increased neck circumference to intubation difficulties in obese patients. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiamcharoenwit, J.; Itthisompaiboon, N.; Limpawattana, P.; Suwanpratheep, A.; Siriussawakul, A. The performance of neck circumference and other airway assessment tests to predict difficult intubation in obese parturients undergoing cesarean delivery. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2017, 31, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palczynski, P.; Bialka, S.; Misiolek, H.; Copik, M.; Smelik, A.; Szarpak, L.; Ruetzler, K. Thyromental height test as a new method for prediction of difficult intubation with double lumen tube. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Zaky, M.N.; El-Mekawy, N.M.; Ollaek, M.A.; Sami, W.M.; Mohamed, D.M. Evaluation of thyromental height test in prediction of difficult airway in obese surgical patients: An observational study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2021, 65, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, A.; Ozayar, E.; Turksal, E.; Kurtay, A.; Kucuk, O. Can chin-nape circumference and the ratio of neck circumference to chin-nape circumference predict difficult mask ventilation or difficult intubation in obese patients? Medicine 2023, 102, e36614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirabadi, D.; Honarmand, A.; Rasouli, M.R.; Safavi, M.R.; Maracy, M.R. Comparison of airway assessment tests for prediction of difficult intubation in obese patients: Importance of thyromental height and upper lip bite test. Minerva Anestesiol. 2022, 88, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Yadav, H.P.; Prakash, A.; Yadav, N.; Kumar, M.; Abbas, H. Assessment of Different Indices as Predictors of Difficult Airway in Obese Patients. Cureus 2024, 16, e55005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.; Chason, H.; Schick, A.; Asselin, N.; Lindquist, D.; Musisca, N. Assessment of the Thyromental Height Test as an Effective Airway Evaluation Tool. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2021, 77, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giacinto, I.; Guarnera, M.; Esposito, C.; Falcetta, S.; Cortese, G.; Pascarella, G.; Sorbello, M.; Cataldo, R. Emergencies in obese patients: A narrative review. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care 2021, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Petrini, F.; Di Giacinto, I.; Cataldo, R.; Esposito, C.; Pavoni, V.; Donato, P.; Trolio, A.; Merli, G.; Sorbello, M.; Pelosi, P. Obesity Task Force for the SIAARTI Airway Management Study Group. Perioperative and periprocedural airway management and respiratory safety for the obese patient: 2016 SIAARTI Consensus. Minerva Anestesiol. 2016, 82, 1314–1335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Members of the Working Party; Nightingale, C.E.; Margarson, M.P.; Shearer, E.; Redman, J.W.; Lucas, D.N.; Cousins, J.M.; Fox, W.T.A.; Kennedy, N.J.; Venn, P.J.; et al. Peri-operative management of the obese surgical patient 2015: Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland Society for Obesity and Bariatric Anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moura, E.C.R.; Filho, A.S.M.; de Oliveira, E.J.S.G.; Freire, T.T.; Leal, P.d.C.; Gomes, L.M.R.d.S.; Servin, E.T.N.; de Oliveira, C.M.B. Comparative Study of Clinical and Ultrasound Parameters for Defining a Difficult Airway in Patients with Obesity. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 4118–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, G.; Alessandri, F.; Zulian, A.; Bilotta, F.; Pugliese, F. Pre-operative ultrasound prediction of difficult airway management in adult patients: A systematic review of clinical evidence. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2023, 40, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, S.; Yildirim, M.; Artaş, H.; Bolat, E. Predicting difficult airway in morbidly obese patients using ultrasound. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 54, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prathep, S.; Geater, A.F.; Sriplung, H.; Kumwichar, P.; Chongsuvivatwong, V. Failed/difficult Intubation comparing between pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19 pandemic period using a national insurance claims database and information system of a university hospital. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024, 24, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Feng, J.; Sun, J. Evaluation of preoperative difficult airway prediction methods for adult patients without obvious airway abnormalities: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024, 24, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Apfelbaum, J.L.; Hagberg, C.A.; Connis, R.T.; Abdelmalak, B.B.; Agarkar, M.; Dutton, R.P.; Fiadjoe, J.E.; Greif, R.; Klock, P.A.; Mercier, D.; et al. 2022 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Management of the Difficult Airway. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 31–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, Z.J.; Ang, A.; Ang, S.N.; See, S.; Zhang, J.; Venkatesan, K.; Chiew, W.A. Videolaryngoscopy vs. direct laryngoscopy in class 2 and 3 obesity: A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised controlled trials. Anaesthesia 2025, 80, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Number (%), Mean ± SD or Median (Q1–Q3) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43.21 ± 9.3 | |
| Gender | male | 21 (27.3) |
| female | 56 (72.7) | |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 37.18 (34.6–42.8) | |
| ASA | I | 1 (1.3) |
| II | 34 (44.2) | |
| III | 42 (54.5) | |
| Condition of the dentition | 1 | 63 (81.8) |
| 2 | 8 (10.4) | |
| 3 | 3 (3.9) | |
| 4 | 3 (3.9) | |
| OSAS | no | 54 (70.1) |
| yes | 23 (29.9) | |
| Variable | Easy Laryngoscopy (n = 59) | Difficult Laryngoscopy (n = 18) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43.0 (34.0–48.0) | 45.0 (42.0–48.0) | 0.124 | |
| Gender | male | 13 (22.0) | 8 (44.4) | 0.061 # |
| female | 46 (78.0) | 10 (55.6) | ||
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 38.1 (34.6–43.0) | 36.4 (33.9–41.2) | 0.329 | |
| ASA scale | I | 1 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.749 |
| II | 25 (42.4) | 9 (50.0) | ||
| III | 33 (55.9) | 9 (50.0) | ||
| Condition of dentition | 1 | 48 (81.4) | 15 (83.3) | 0.621 |
| 2 | 6 (10.2) | 2 (11.1) | ||
| 3 | 3 (5.1) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| 4 | 2 (3.4) | 1 (5.6) | ||
| Sleep apnea | no | 45 (76.3) | 9 (50.0) | 0.033 * |
| yes | 14 (23.7) | 9 (50.0) | ||
| Thyromental height test (TMHT) [mm] | 53.0 (48.0–70.0) | 57.0 (45.0–66.0) | 0.823 | |
| Thyromental distance (TMD) [mm] | 90.0 (80.0–105.0) | 90.0 (80.0–100.0) | 0.805 | |
| Chin–sternum distance [mm] | 180.0 (170.0–190.0) | 170.0 (150.0–180.0) | 0.030 * | |
| Mallampati scale | I | 18 (30.5) | 3 (16.7) | 0.248 |
| II | 25 (42.4) | 8 (44.4) | ||
| III | 12 (20.3) | 7 (38.9) | ||
| IV | 4 (6.8) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Neck circumference [mm] | 400.0 (380.0–440.0) | 410.0 (390.0–460.0) | 0.150 | |
| Mouth opening [mm] | 60.0 (50.0–70.0) | 50.0 (50.0–60.0) | 0.070 # | |
| Intubation time [sec] | 13.0 (10.0–19.0) | 29.5 (19.0–66.0) | <0.0001 * | |
| Number of intubation attempts | 1 | 58 (98.3) | 13 (72.2) | 0.0013 * |
| 2 | 1 (1.7) | 4 (22.2) | ||
| 5 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.6) | ||
| Use of bougie stylet | no | 59 (100.0) | 13 (72.2) | <0.0001 * |
| yes | 0 (0.0) | 5 (27.8) | ||
| Cormack–Lehane grade | I | 50 (84.8) | 0 (0.0) | <0.0001 * |
| II | 7 (11.9) | 9 (50.0) | ||
| III | 2 (3.4) | 4 (22.2) | ||
| IV | 0 (0.0) | 5 (27.8) | ||
| Modification of intubation technique or bougie use | no | 59 (100.0) | 10 (55.6) | <0.0001 * |
| yes | 0 (0.0) | 8 (44.4) | ||
| Variable | Modification-No (n = 69) | Modification-Yes (n = 8) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43.00 (36.00–48.00) | 43.50 (42.00–47.50) | 0.287 | |
| Gender | male | 54 (78.26) | 2 (25.00) | 0.004 * |
| female | 15 (21.74) | 6 (75.00) | ||
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 37.10 (34.54–42.77) | 40.20 (36.31–43.57) | 0.300 | |
| ASA scale | I | 1 (1.45) | 0 (0.00) | 0.462 |
| II | 32 (46.38) | 2 (25.00) | ||
| III | 36 (52.17) | 6 (75.00) | ||
| Condition of dentition | 1 | 57 (82.61) | 6 (75.00) | 0.461 |
| 2 | 6 (8.70) | 2 (25.00) | ||
| 3 | 3 (4.35) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| 4 | 3 (4.35) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| OSAS | no | 52 (75.36) | 2 (25.00) | 0.007 * |
| yes | 17 (24.64) | 6 (75.00) | ||
| TMH [mm] | 56.00 (49.00–70.00) | 47.5 (42.50–57.50) | 0.163 | |
| TMD [mm] | 90.00 (80.00–100.00) | 85.00 (77.50–100.00) | 0.713 | |
| SMD [mm] | 180.00 (170.00–190.00) | 170.00 (160.00–180.00) | 0.118 | |
| MMT | I | 18 (26.09) | 3 (37.50) | 0.558 |
| II | 31 (44.93) | 2 (25.00) | ||
| III | 16 (23.19) | 3 (37.50) | ||
| IV | 4 (5.80) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| NC [mm] | 400.00 (380.00–440.00) | 450.00 (425.00–500.00) | 0.011 * | |
| MO [mm] | 55.00 (50.00–70.00) | 52.50 (50.00–57.50) | 0.478 | |
| Neck circumference and TMH ratio | 7.20 (6.00–9.16) | 9.00 (8.29–10.85) | 0.037 * | |
| Independent Variable | Univariable Logistic Regression | Multivariable Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (±95%CI) | p-Value | OR (±95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Male gender | 0.35 (0.11–1.09) | 0.067 | 0.13 (0.02–0.65) | 0.012 * |
| Sleep apnea | 3.21 (1.05–9.84) | 0.038 | 2.21 (0.61–7.94) | 0.216 |
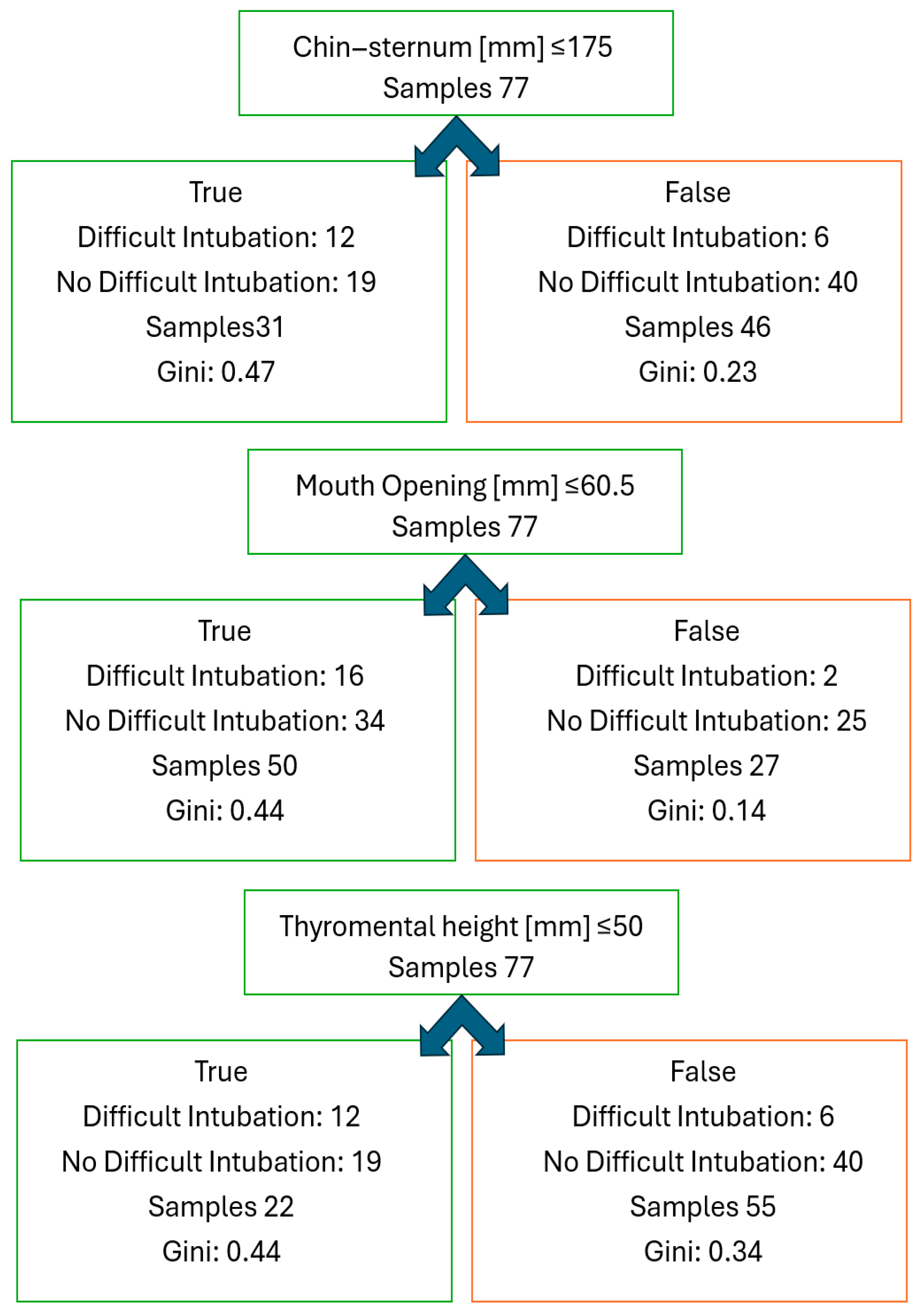
| Chin–sternum distance ≤ 175 mm | 3.90 (1.25–12.15) | 0.017 | 6.78 (1.42–32.38) | 0.014 * |
| Mouth opening ≤ 60.5 mm | 5.88 (1.21–28.66) | 0.026 | 7.35 (1.18–45.87) | 0.029 * |
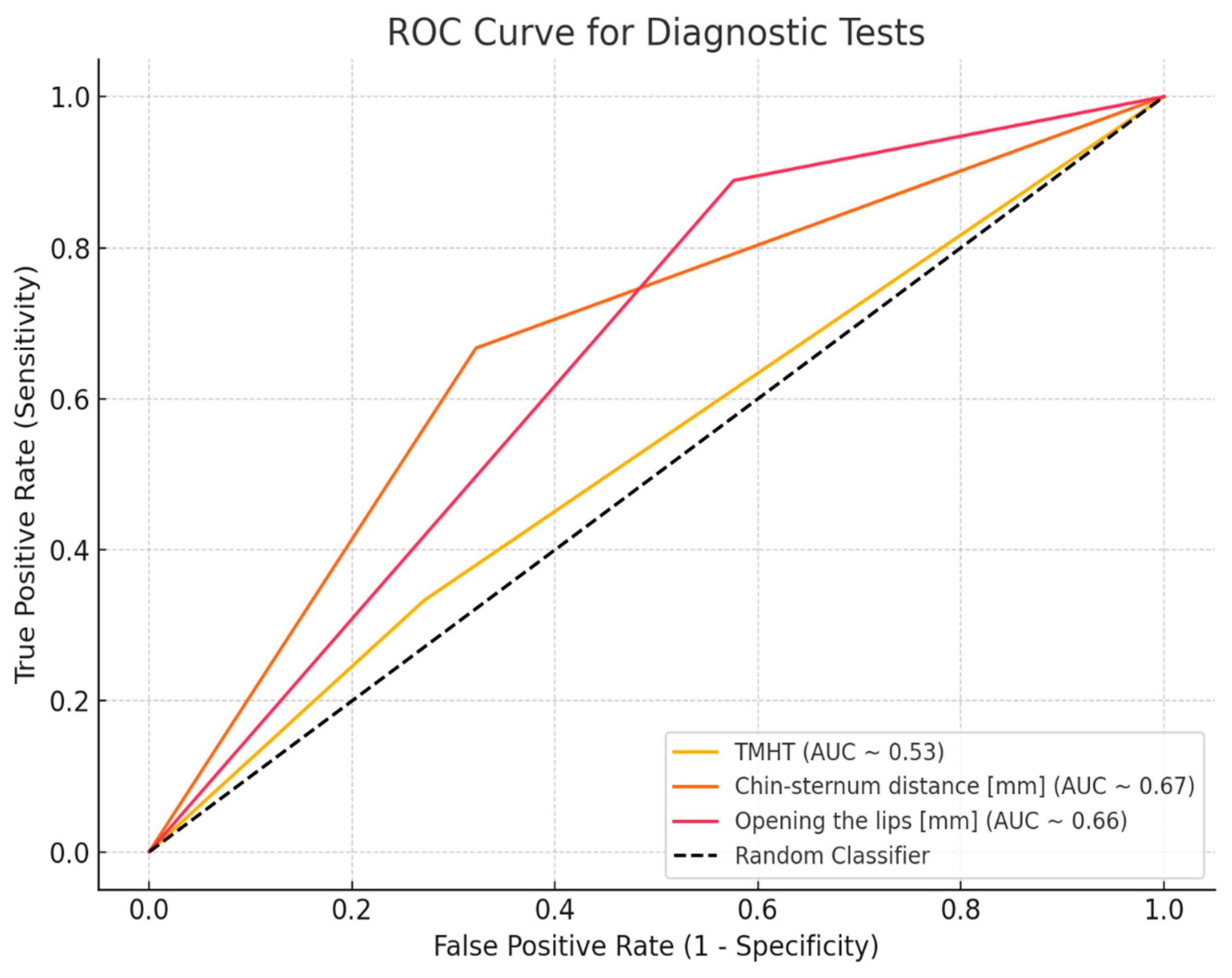
| Male Gender | Chin–Sternum Distance [mm] | Opening of the Lips [mm] | Thyromental Height [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.612 [0.457–0.768] | 0.67 [0.544–0.825] | 0.66 [0.510–0.775] | 0.53 [0.24–0.64] |
| p-value | 0.158 | 0.010 * | 0.035 * | >0.05 |
| SE | 0.079 | 0.072 | 0.068 | 0.080 |
| Sensitivity (95% CI) | 0.780 | 0.678 | 0.424 | 0.333 [0.133, 0.59] |
| Specificity (95% CI) | 0.444 | 0.667 | 0.889 | 0.729 [0.597, 0.836] |
| Accuracy (95% CI) | 0.701 | 0.675 | 0.532 | 0.636 [0.519, 0.743] |
| PPV (95% CI) | - | 0.387 [0.218, 0.578] | 0.320 [0.195, 0.47] | 0.273 [0.107, 0.502] |
| NPV (95% CI) | - | 0.87 [0.737, 0.951] | 0.926 [0.757, 0.991] | 0.782 [0.650, 0.882] |
| OPERA Score | Mallampati Score III/IV | Opening of the Lips [<35 mm] | Thyromental Height [<50 mm] | Neck Circumference [>430 mm] | History of OSA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | 0.81 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.6 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| p-value | 0.01 * | >0.05 | 0.035 * | >0.05 | 0.04 * | >0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palaczyński, P.; Smereka, J.; Zawadzka-Kaczmarek, K.; Kukliński, J.; Misiolek, H.; Domka, J.; Danel, J.; Bialka, S. Thyromental Height Test as a Method for Predicting Difficult Intubation in Patients with Obesity: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186352
Palaczyński P, Smereka J, Zawadzka-Kaczmarek K, Kukliński J, Misiolek H, Domka J, Danel J, Bialka S. Thyromental Height Test as a Method for Predicting Difficult Intubation in Patients with Obesity: A Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(18):6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186352
Chicago/Turabian StylePalaczyński, Piotr, Jacek Smereka, Katarzyna Zawadzka-Kaczmarek, Jakub Kukliński, Hanna Misiolek, Justyna Domka, Justyna Danel, and Szymon Bialka. 2025. "Thyromental Height Test as a Method for Predicting Difficult Intubation in Patients with Obesity: A Prospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 18: 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186352
APA StylePalaczyński, P., Smereka, J., Zawadzka-Kaczmarek, K., Kukliński, J., Misiolek, H., Domka, J., Danel, J., & Bialka, S. (2025). Thyromental Height Test as a Method for Predicting Difficult Intubation in Patients with Obesity: A Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18), 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14186352







