Empowering CKD and Hemodialysis Patients with mHealth: Implementation of the NephroGo App in Europe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Application Development
2.2. Technical Implementation
2.3. User Testing and Evaluation
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
2.6. Use of Generative AI
3. Results
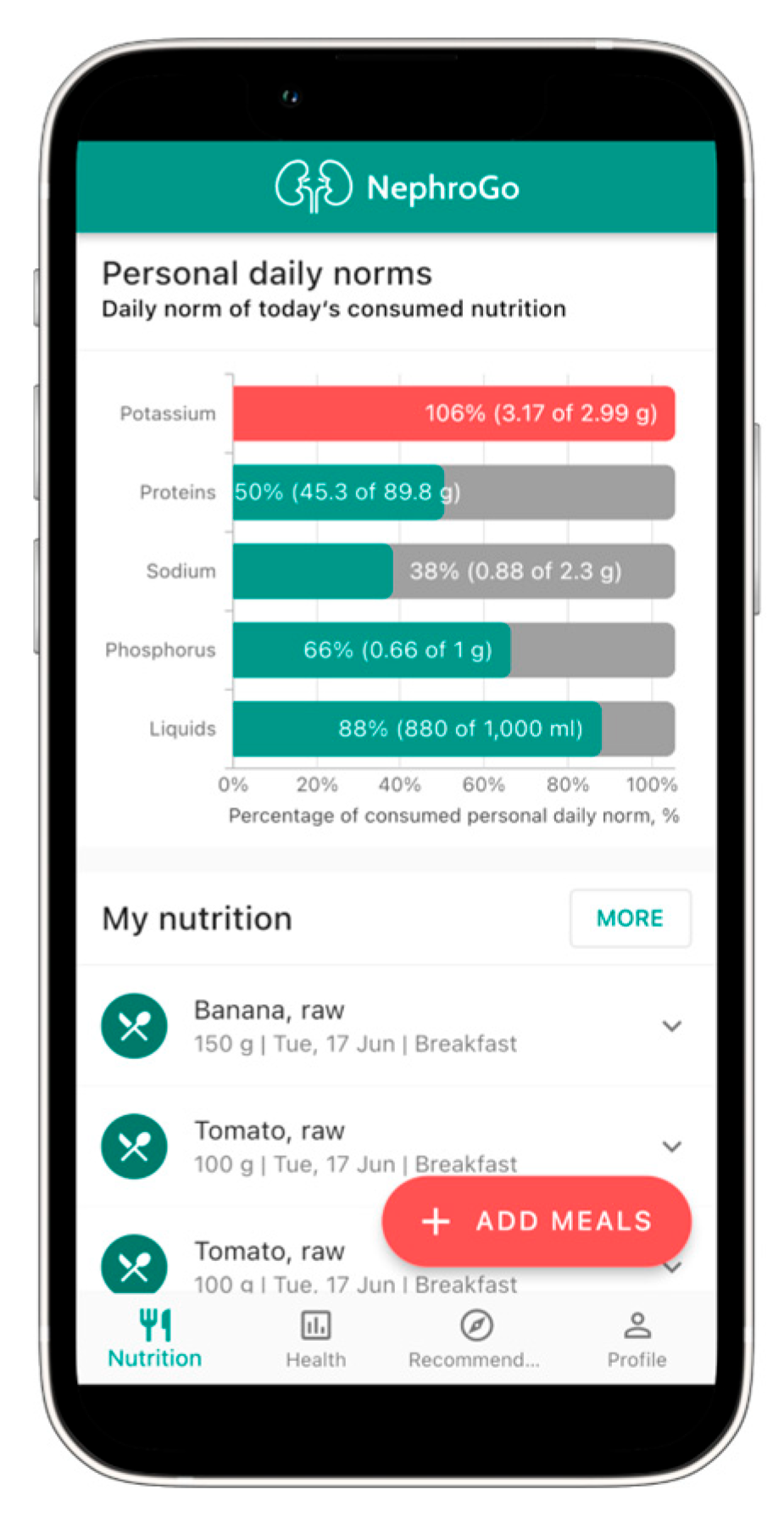
3.1. Nutrition Calculator
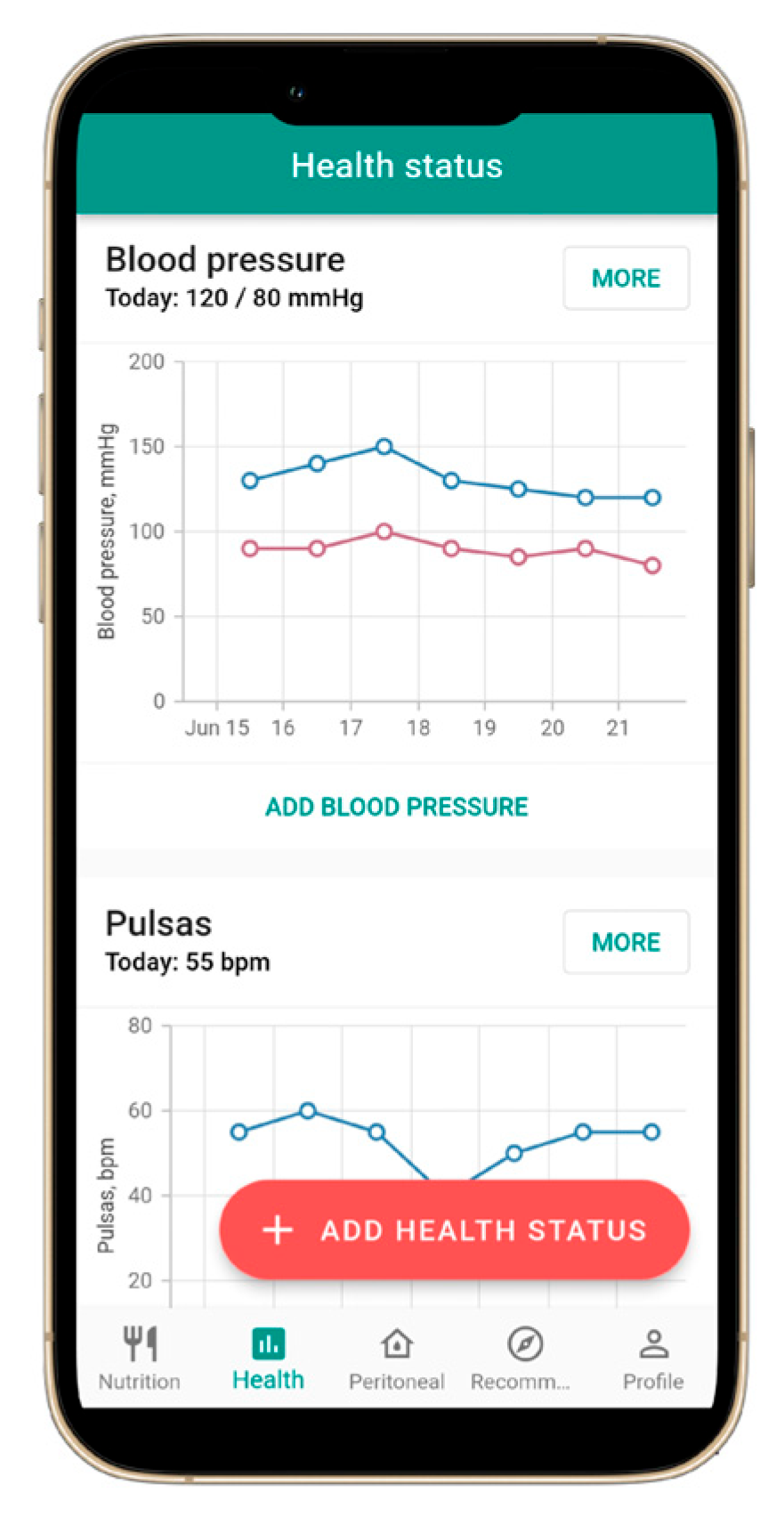
3.2. Health Indicator Tracking
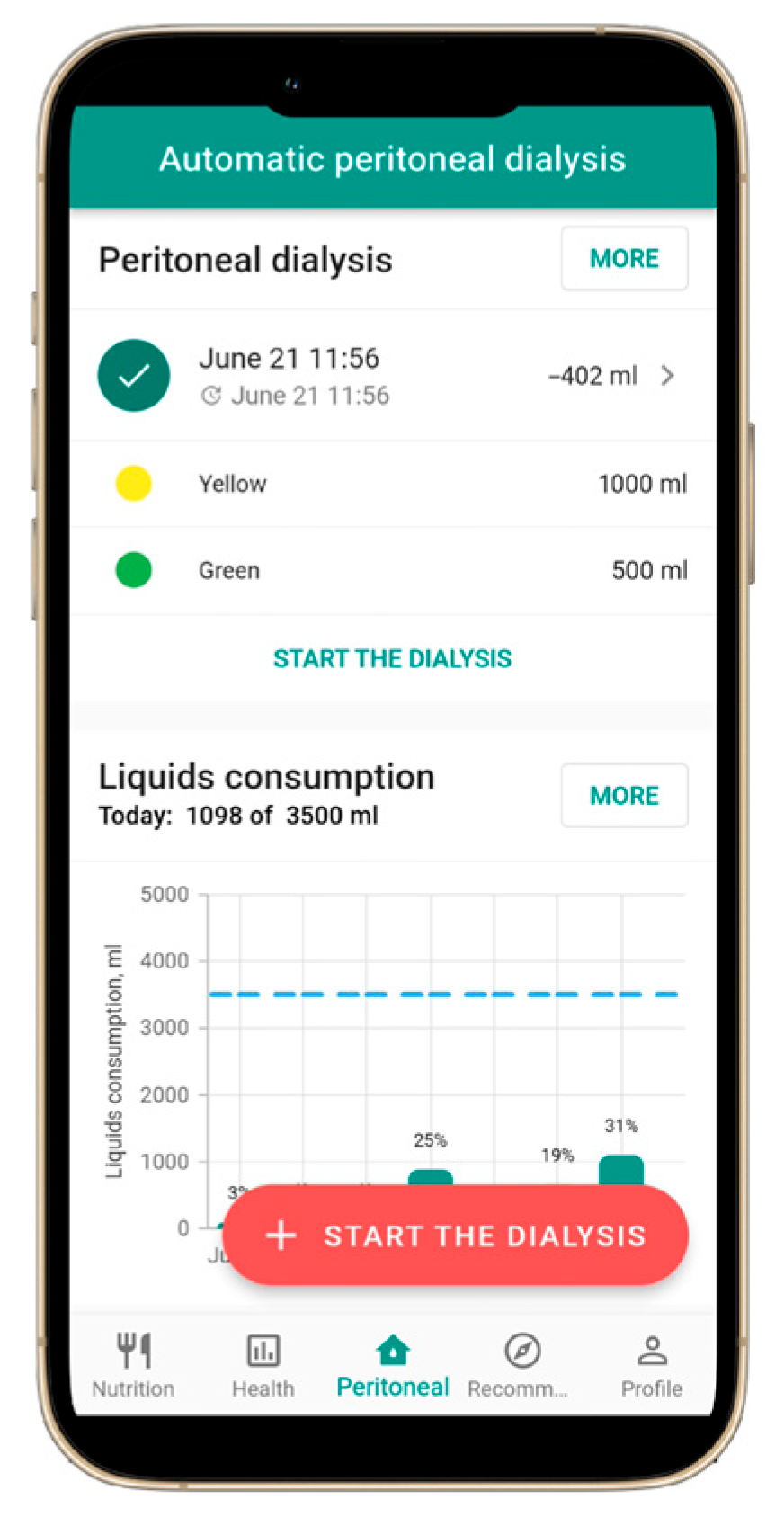
3.3. Peritoneal Dialysis Support
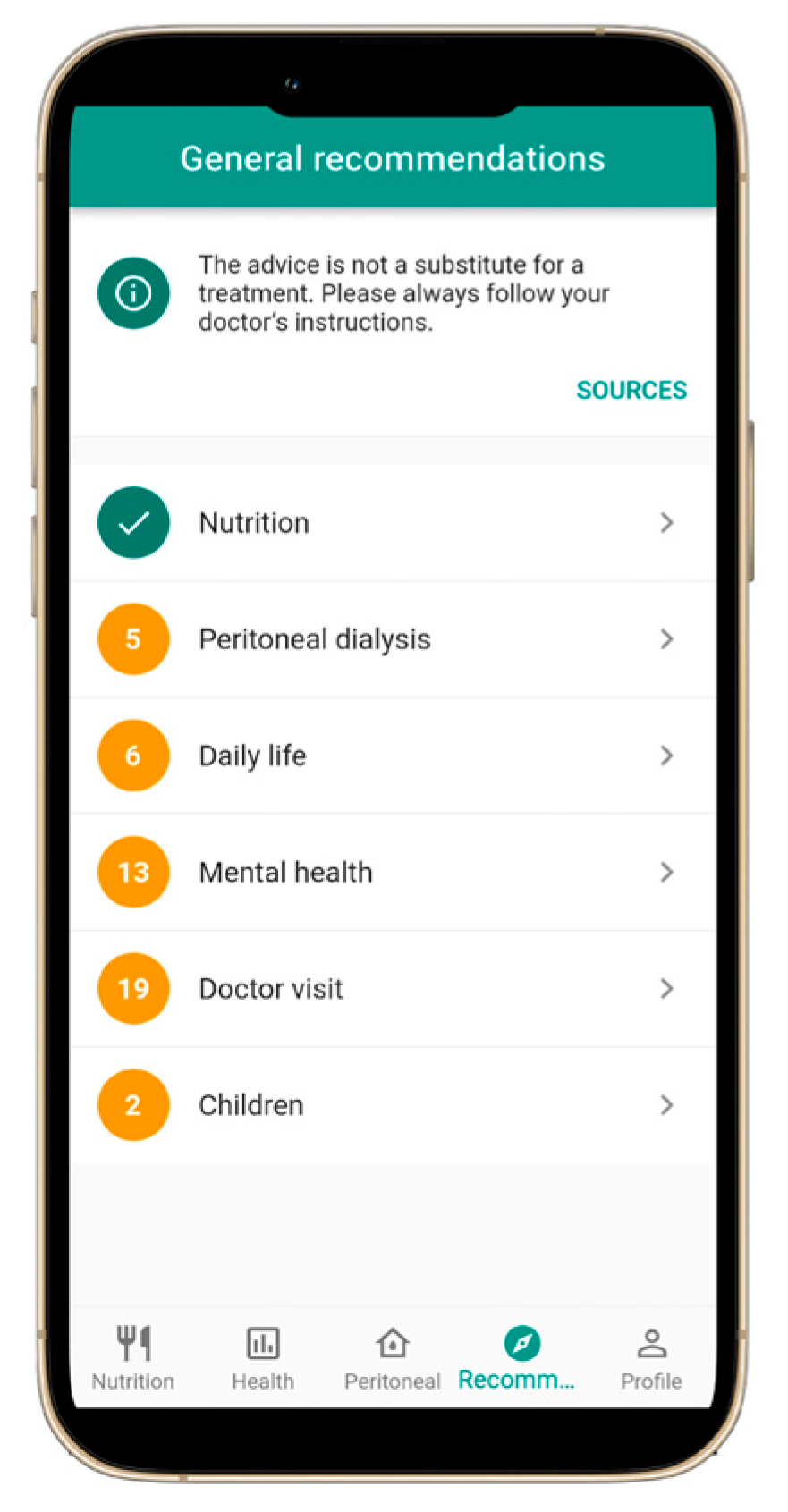
3.4. Educational and Support Section
3.5. User Characteristics and Early App Performance Feedback
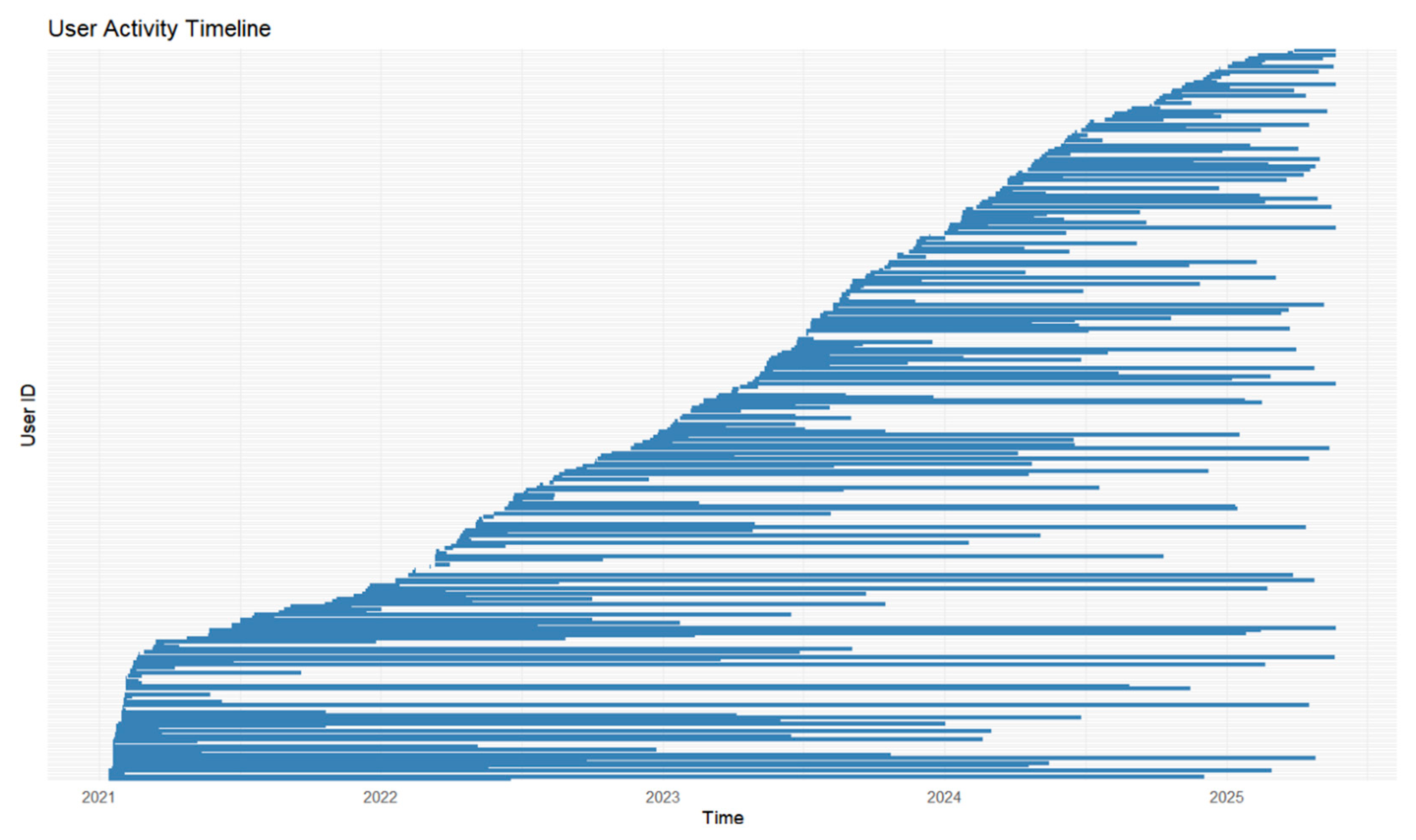
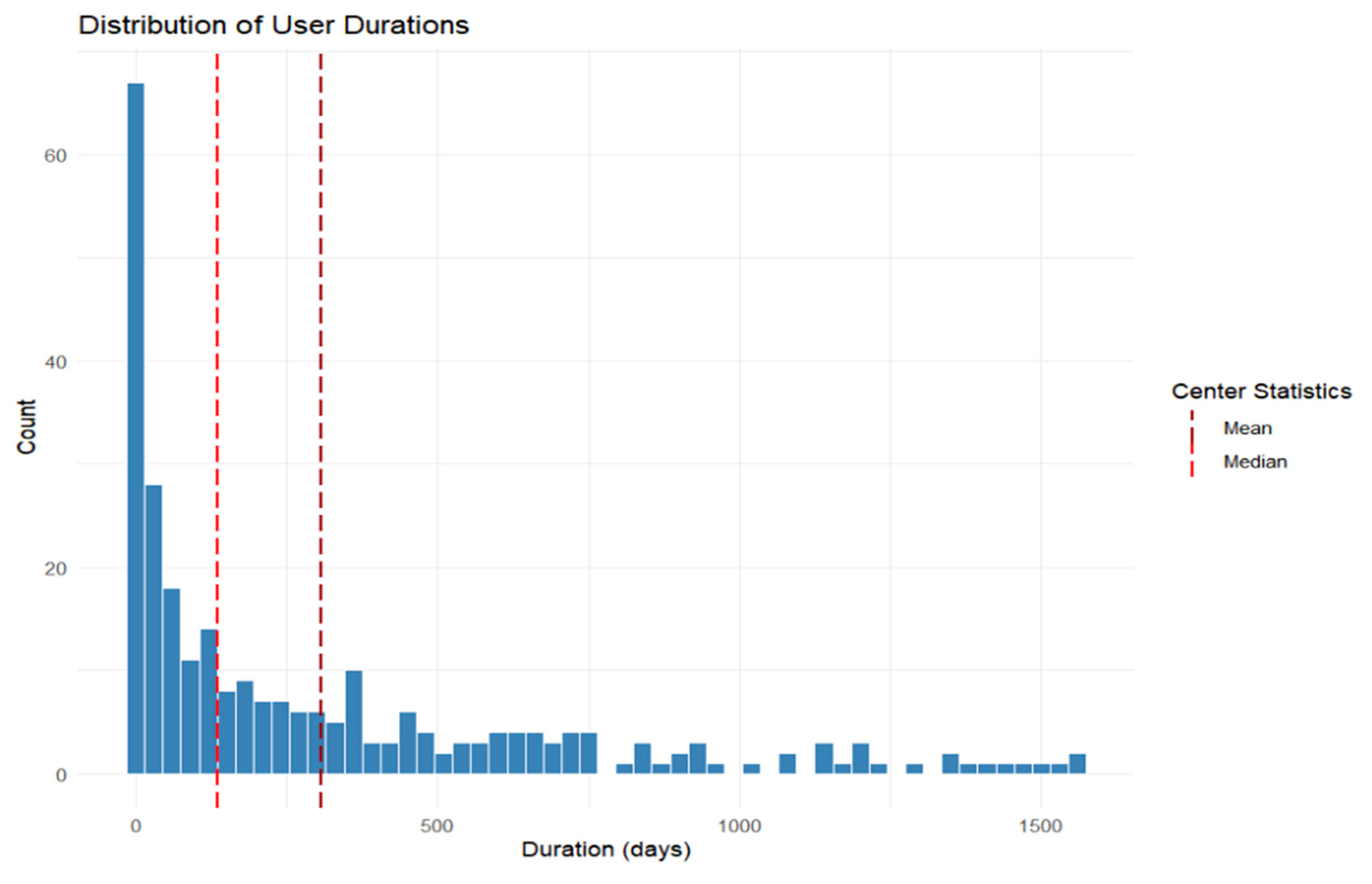
3.6. Long-Term User Characteristics and Feature Engagement
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Utility and Feature Engagement
4.2. User Characteristics and Behavior Patterns
4.2.1. CKD Stage
4.2.2. Source of Recommendation
4.2.3. Sex
4.2.4. Age
4.2.5. Strengths and Limitations
4.2.6. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, V.A.; Tonelli, M.; Stanifer, J.W. The Global Burden of Kidney Disease and the Sustainable Development Goals. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 414–422D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease Statistics for the United States—NIDDK. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/kidney-disease (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Diamantidis, C.J.; Becker, S. Health Information Technology (IT) to Improve the Care of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self-Management Interventions for Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Scoping Review|BMJ Open. Available online: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/8/3/e019814 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Nunes, J.A.W.; Wallston, K.A.; Eden, S.K.; Shintani, A.K.; Ikizler, T.A.; Cavanaugh, K.L. Associations among Perceived and Objective Disease Knowledge and Satisfaction with Physician Communication in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.B.; Krebs, M.; Alvarez, S.; Greenspan, I.; Patel, A.; Kinsolving, J.; Koizumi, N. Mobile Apps for the Care Management of Chronic Kidney and End-Stage Renal Diseases: Systematic Search in App Stores and Evaluation. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2019, 7, e12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, L.E.; Le Leu, R.K.; Matricciani, L.A.; Xu, Q.; Britton, A.; Jesudason, S.; Bennett, P.N. Patient Activation in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Zimmerman, L.; Welch, J.L.; Hertzog, M.; Pozehl, B.; Plumb, T. Patient Activation with Knowledge, Self-Management and Confidence in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Care 2016, 42, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Ebrahim, Z.; Glorieux, G.; Moosa, M.R.; Blaauw, R. Effect of Simplified Dietary Advice on Nutritional Status and Uremic Toxins in Chronic Kidney Disease Participants. S. Afr. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 35, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosa, S.D.; Monize, J.; D’Souza, M.; Joshi, A.; Philip, K.; Reza, S.; Samra, S.; Serrago, B.; Thabane, L.; Gafni, A.; et al. Nutritional Mobile Applications for CKD Patients: Systematic Review. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 4, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.A.; Dhaun, N. Salt Sensitivity: Causes, Consequences, and Recent Advances. Hypertens. Dallas Tex 1979 2024, 81, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, D.; Harasemiw, O.; Curtis, S.; Iman, Y.; Buenafe, J.; DaCosta, J.; Mollard, R.C.; Tangri, N.; Protudjer, J.L.P.; Mackay, D. Dietary Patterns and Perceptions in Older Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease in the Canadian Frailty Observation and Interventions Trial (CanFIT): A Mixed-Methods Study. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2022, 9, 20543581221140633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Choi, S. The Effects of a Tailored Dietary Education Program for Older Adult Patients on Hemodialysis: A Preliminary Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, W.F.; Bennett, P.N.; Abra, G.; Watson, E.; Schiller, B. Integrating Patient Activation Into Dialysis Care. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, R.N.; Ummate, I.; Ohieku, J.D.; Yakubu, S.I.; Adibe, M.O.; Okonta, M.J. Evaluation of Medication Adherence and Predictors of Sub-Optimal Adherence among Pre-Dialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Med. Access Point Care 2020, 4, 2399202620954089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo Catapan, S.; Taylor, M.L.; Scuffham, P.; Smith, A.C.; Kelly, J.T. Improving Consumer Trust in Digital Health: A Mixed Methods Study Involving People Living with Chronic Kidney Disease. Digit. Health 2025, 11, 20552076241312440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinshella, M.-L.W.; Boene, H.; Sevene, E.; Valá, A.; Sharma, S.; Vidler, M.; Magee, L.A.; von Dadelszen, P.; Munguambe, K.; Payne, B.A. How Gender Influenced the Experience of Using a mHealth Intervention in Rural Mozambique: Secondary Qualitative Analysis of Community Health Worker Survey Data. Front. Glob. Womens Health 2022, 3, 661000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, S.L.; Hazzard, V.M.; Loth, K.A.; Larson, N.; Klein, L.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Using Apps to Self-Monitor Diet and Physical Activity Is Linked to Greater Use of Disordered Eating Behaviors among Emerging Adults. Prev. Med. 2022, 155, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, W.F.; Bennett, P.N.; Sun, S.J.; Reiterman, M.; Watson, E.; Farwell, I.M.; Schiller, B. Patient Activation Among Prevalent Hemodialysis Patients: An Observational Cross-Sectional Study. J. Patient Exp. 2022, 9, 23743735221112220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Yuan, J.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Oliveira, A. Current Status of Older People with Chronic Diseases Adopting Digital Health Technologies: A Scoping Review. Digit. Health 2025, 11, 20552076251348578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Ju, M.; Kang, M.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.; Oh, J. Preparedness, Challenges, and Opportunities for Digital Intervention for Chronic Disease Management: A Qualitative Study in Rural Areas of South Korea. Health Syst. Reform 2024, 10, 2378503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouri, A.; Gupta, S.; Straus, S.E.; Sale, J.E.M. Exploring the Perspectives and Experiences of Older Adults with Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Toward Mobile Health: Qualitative Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e45955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Subcategory | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Total initial downloads | 204 | |
| Active users | 191 (93.6%) | |
| Sex | Female | 138 (67.6%) |
| Male | 66 (32.4%) | |
| CKD | CKD > 10 years | 111 (54.4%) |
| Stage 5 CKD | 52 (25.5%) | |
| Renal replacement therapy | No therapy | 81 (39.7%) |
| Hemodialysis | 59 (28.9%) | |
| Peritoneal dialysis | 13 (6.4%) | |
| Nutrition | Daily use of nutrition calculator | 135 (66.2%) |
| Avg. food items added/day | 7 ± 1 | |
| Exceed daily sodium norm | 58 (30.2%) | |
| Exceed daily calorie norm | 12 (6.3%) |
| (1) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Survey Item | Value | |
| Number of respondents | 32 | |
| Source of awareness about NephroGo | Healthcare professionals | 14 (43.8%) |
| Social media | 11 (34.4%) | |
| Patients’ communities and dialysis centers | 7 (21.8%) | |
| Residence | Urban | 26 (81.3%) |
| Rural | 6 (18.7%) | |
| Educational Background | Higher education | 18 (56.3%) |
| Overall MARS score | 4.09 ± 0.66 | |
| (2) | ||
| Survey Item | Value | |
| MARS scores | Overall MARS score | 4.09 ± 0.66 |
| Functionality score | 4.27 ± 0.74 | |
| Engagement score | 3.81 ± 0.80 | |
| Highest rated function | Peritoneal dialysis | 5.00 ± 0.00 (p = 0.0089) |
| Highest rated by | Stage 5 CKD patients | 4.52 ± 0.52 (p = 0.0016) |
| Highest rated if | Recommended by a doctor | 4.50 ± 0.68 (p = 0.039) |
| Category | Subcategory | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Total downloads | 1670 | |
| Sex | Female | 873 (52.3%) |
| Male | 797 (47.7%) | |
| Age groups | 0–10 | 19 (1.1%) |
| 11–20 | 26 (1.6%) | |
| 21–30 | 91 (5.5%) | |
| 31–40 | 277 (16.6%) | |
| 41–50 | 199 (11.9%) | |
| 51–60 | 239 (14.3%) | |
| 61–70 | 201 (12%) | |
| 71–80 | 102 (6.1%) | |
| 81+ | 58 (3.5%) | |
| Unknown * | 458 (27.4%) | |
| CKD | Stage 1 | 142 (8.5%) |
| Stage 2 | 130 (7.8%) | |
| Stage 3 | 257 (14.7%) | |
| Stage 4 | 245 (14.7%) | |
| Stage 5 | 455 (27.2%) | |
| Unknown stage * | 441 (26.4%) | |
| Duration of CKD, years | <1 | 465 (27.8%) |
| 1–5 | 457 (27.4%) | |
| 6–10 | 229 (13.7%) | |
| >10 | 519 (31.1%) | |
| Renal replacement therapy | No therapy | 952 (57.0%) |
| Hemodialysis | 398 (23.8%) | |
| Peritoneal dialysis (automatic) | 67 (4.0%) | |
| Peritoneal dialysis (manual) | 149 (8.9%) | |
| Post-transplant | 104 (6.2%) | |
| Diabetes | No | 1383 (82.8%) |
| Type 1 | 123 (7.4%) | |
| Type 2 | 159 (9.5%) | |
| Unknown | 5 (0.3%) |
| Category | Subcategory | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 39 (59.1%) |
| Male | 27 (40.9%) | |
| CKD stage | Stage 1 | 5 (7.6%) |
| Stage 2 | 3 (4.5%) | |
| Stage 3 | 5 (7.6%) | |
| Stage 4 | 7 (10.6%) | |
| Stage 5 | 26 (39.4%) | |
| Unknown | 20 (30.3%) |
| Category | Subcategory | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 9 (32.1%) |
| Male | 19 (67.9%) | |
| Age categories | 21–40 | 7 (25%) |
| 41–60 | 13 (46.5%) | |
| 61–80 | 3 (10.7%) | |
| Unknown | 5 (17.8%) |
| Category | Subcategory | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 119 (%) |
| Male | 97 (%) | |
| CKD stage | Stage 1 | 9.1% |
| Stages 2–4 | 36.3% | |
| Stage 5 | 45.5% | |
| Unknown | 9.1% | |
| Age categories | 0–20 | 6 (2.8%) |
| 21–40 | 55 (25.5%) | |
| 41–60 | 77 (35.6%) | |
| 61–80 | 46 (21.3%) | |
| 81+ | 5 (2.3%) | |
| Unknown | 27 (12.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Žulpaitė, G.; Vyčius, K.; Deinoravičiūtė, U.; Saukaitytė-Butvilė, E.; Rimševičius, L.; Miglinas, M. Empowering CKD and Hemodialysis Patients with mHealth: Implementation of the NephroGo App in Europe. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176219
Žulpaitė G, Vyčius K, Deinoravičiūtė U, Saukaitytė-Butvilė E, Rimševičius L, Miglinas M. Empowering CKD and Hemodialysis Patients with mHealth: Implementation of the NephroGo App in Europe. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176219
Chicago/Turabian StyleŽulpaitė, Giedrė, Karolis Vyčius, Urtė Deinoravičiūtė, Edita Saukaitytė-Butvilė, Laurynas Rimševičius, and Marius Miglinas. 2025. "Empowering CKD and Hemodialysis Patients with mHealth: Implementation of the NephroGo App in Europe" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176219
APA StyleŽulpaitė, G., Vyčius, K., Deinoravičiūtė, U., Saukaitytė-Butvilė, E., Rimševičius, L., & Miglinas, M. (2025). Empowering CKD and Hemodialysis Patients with mHealth: Implementation of the NephroGo App in Europe. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176219







