The Impact of Ramadan Fasting on Endothelial Function, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
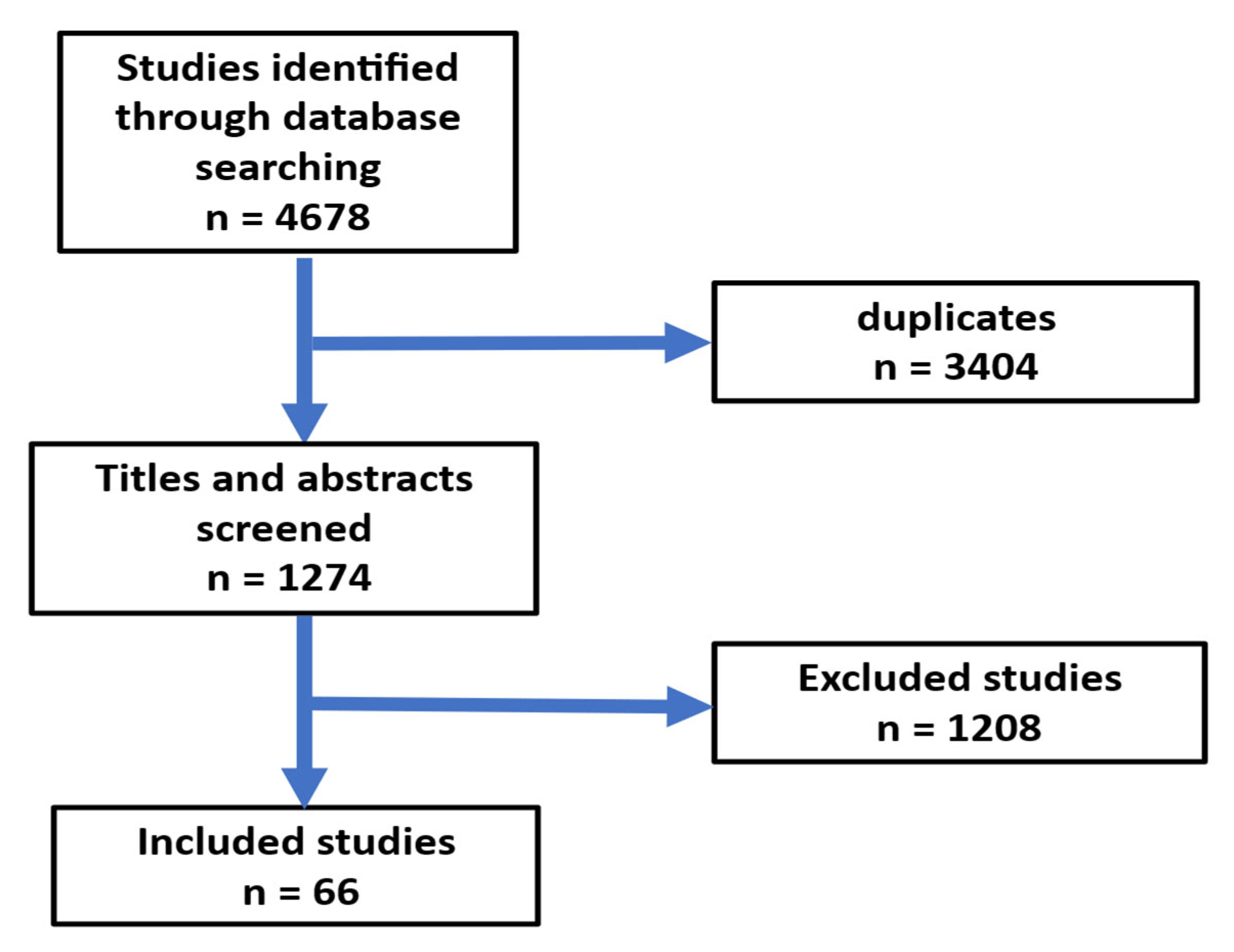
2. Methods
3. Pathophysiology of Endothelial Dysfunction
4. Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction
5. Risk Factors of Endothelial Dysfunction
6. Gut Microbiota and Diseases
6.1. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Diseases
6.2. Gut Microbiota and Hypertension
6.3. Gut Microbiota and Atherosclerosis
6.4. Gut Microbiota and Heart Failure
6.5. Gut Microbiota and Obesity
6.6. Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
7. Ramadan Fasting and Endothelial Dysfunction
7.1. Ramadan Fasting and Hypertension
7.2. Ramadan Fasting and Atherosclerosis
7.3. Ramadan Fasting and Diabetes Mellitus
7.4. Ramadan Fasting and Obesity
7.5. Ramadan Fasting and Heart Failure
7.6. Ramadan and Stroke
7.7. Ramadan Fasting and Gut Microbiota
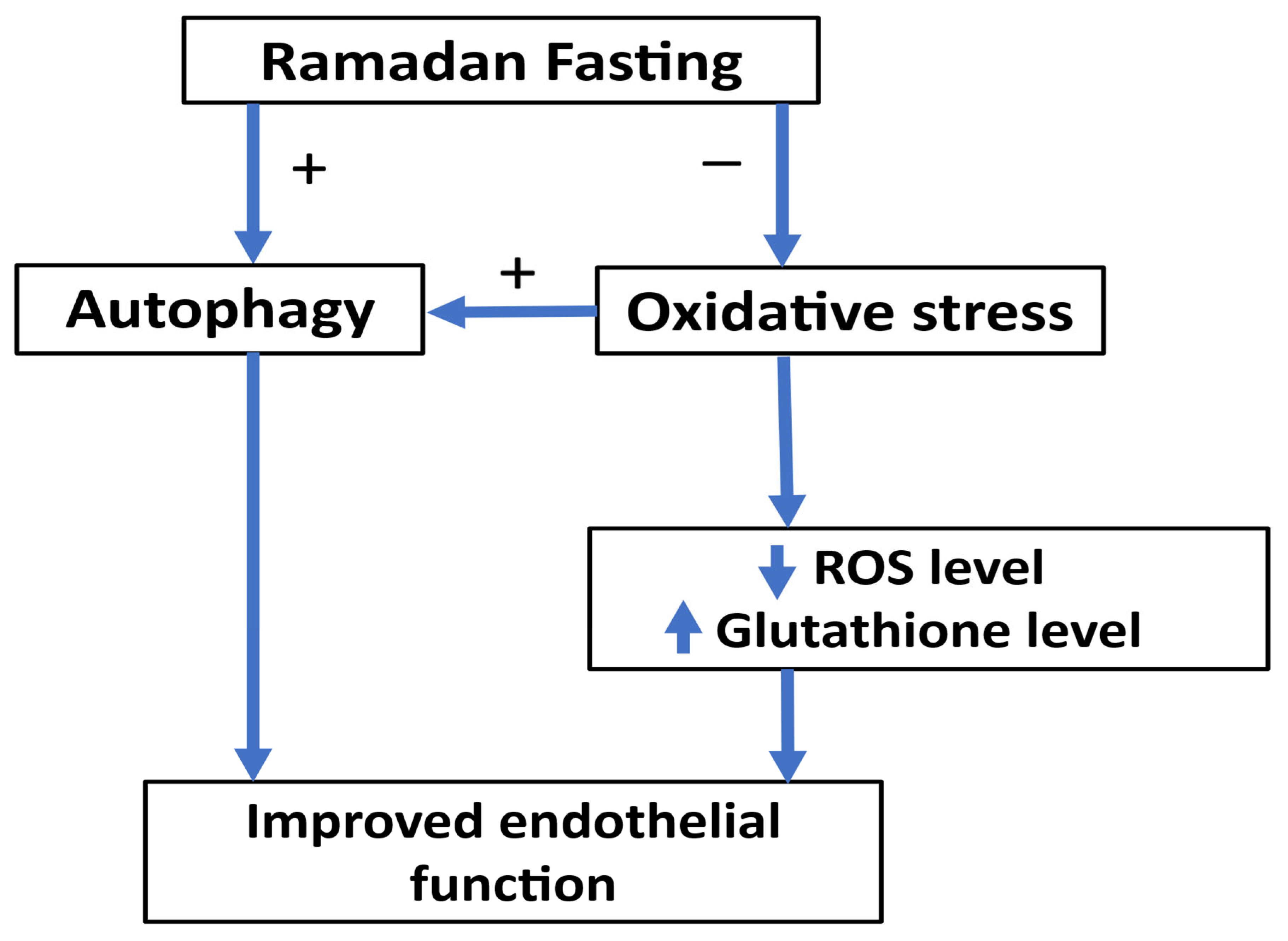
7.8. Ramadan Fasting and Autophagy
7.9. Ramadan Fasting and Oxidative Stress
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallo, G.; Savoia, C. New Insights into Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiometabolic Diseases: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deanfield, J.E.; Halcox, J.P.; Rabelink, T.J. Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical relevance. Circulation 2007, 115, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Garcia-Cardena, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyter, A.C.; Armengaud, J.B.; Guillot, E.; Yzydorczyk, C. Endothelial Progenitor Cells Dysfunctions and Cardiometabolic Disorders: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, L.; Stancu, C.S.; Sima, A.V. Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Is Aggravated by Glycated Lipoproteins; Novel Molecular Therapies. Biomedicines 2020, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drera, A.; Rodella, L.; Brangi, E.; Riccardi, M.; Vizzardi, E. Endothelial Dysfunction in Heart Failure: What Is Its Role? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ahmed, M.H. Ramadan Fasting in Individuals with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, Liver Transplant, and Bariatric Surgery: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ilyas, I.; Little, P.J.; Li, H.; Kamato, D.; Zheng, X.; Luo, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Han, J.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases and Beyond: From Mechanism to Pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 924–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endemann, D.H.; Schiffrin, E.L. Endothelial dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Kumari, N.; Mirgani, Z.; Saeed, A.; Ramadan, A.; Ahmed, M.H.; Almobarak, A.O. Metabolic syndrome; Definition, Pathogenesis, Elements, and the Effects of medicinal plants on it’s elements. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfanti, P.; Gavriilaki, E.; Nikolaidou, B.; Yiannaki, E.; Lazaridis, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Douma, S.; Doumas, M.; Gkaliagkousi, E. Patients with autoimmune chronic inflammatory diseases present increased biomarkers of thromboinflammation and endothelial dysfunction in the absence of flares and cardiovascular comorbidities. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 53, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyers, C.M., 3rd; Miller, F.J., Jr. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11324–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaito, A.; Aramouni, K.; Assaf, R.; Parenti, A.; Orekhov, A.; Yazbi, A.E.; Pintus, G.; Eid, A.H. Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2022, 27, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Carresi, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Mollace, R.; Scarano, F.; Scicchitano, M.; Macri, R.; Nucera, S.; Bosco, F.; Oppedisano, F.; et al. The Contribution of Gut Microbiota and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Development of Arterial Hypertension in Animal Models and in Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Sharrett, A.R.; Smith, L.C.; Davis, C.E.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Boerwinkle, E. Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin in carotid atherosclerosis and incident coronary heart disease cases: The Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation 1997, 96, 4219–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraba, A.; Iurciuc, S.; Nicolin, M.; Iurciuc, M. Endothelial Dysfunction in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome: Correlation with Serum Biomarkers of Disease Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffolo, F.; Monticone, S.; Camussi, G.; Aikawa, E. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Vascular Damage. Hypertension 2022, 79, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibal, L.; Agarwal, S.C.; Home, P.D.; Boger, R.H. The Role of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) in Endothelial Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2010, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horio, E.; Kadomatsu, T.; Miyata, K.; Arai, Y.; Hosokawa, K.; Doi, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Horiguchi, H.; Endo, M.; Tabata, M.; et al. Role of endothelial cell-derived angptl2 in vascular inflammation leading to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis progression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Farooq, M.A.; Gaertner, S.; Bruckert, C.; Qureshi, A.W.; Lee, H.H.; Benrahla, D.; Pollet, B.; Stephan, D.; Ohlmann, P.; et al. Empagliflozin improved systolic blood pressure, endothelial dysfunction and heart remodeling in the metabolic syndrome ZSF1 rat. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y. Smoking cessation and vascular endothelial function. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Riva, P.; Marta-Enguita, J.; Rodriguez-Antiguedad, J.; Bergareche, A.; de Munain, A.L. Understanding Endothelial Dysfunction and Its Role in Ischemic Stroke After the Outbreak of Recanalization Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Carding, S.R. Inflammatory bowel disease: Cause and immunobiology. Lancet 2007, 369, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; An, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, W.; Ji, H.; Lian, F. The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1149239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, S.; Fonseca, L.; Ribeiro, L.; Ramos, H.; Oliveira, J.C.; Palma, I. Novel and traditional lipid profiles in Metabolic Syndrome reveal a high atherogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Tu, X.; Wu, R. Vascular endothelial dysfunction, a major mediator in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayaraa, O.; Inman, C.K.; Thomas, S.A.; Al Jallaf, F.; Alshaikh, M.; Idaghdour, Y.; Ashall, L. Hyperglycemic conditions induce rapid cell dysfunction-promoting transcriptional alterations in human aortic endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; MacFadyen, R.J.; Lip, G.Y. Diabetes mellitus, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and the heart. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.P.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Heng, Y.P.; Kalaiselvan, M.; Teh, Y.W.; Cheong, K.M.; Hadi, M.; Othman, R.B. Renin angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers usage among type II diabetes mellitus patients-A Retrospective Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.Y.; Ustinova, E.E.; Wu, M.H.; Tinsley, J.H.; Xu, W.; Korompai, F.L.; Taulman, A.C. Protein kinase C activation contributes to microvascular barrier dysfunction in the heart at early stages of diabetes. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzaffar, S.; Shukla, N.; Bond, M.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Newby, A.C.; Angelini, G.D.; Jeremy, J.Y. Superoxide from NADPH oxidase upregulates type 5 phosphodiesterase in human vascular smooth muscle cells: Inhibition with iloprost and NONOate. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittleson, M.M.; Panjrath, G.S.; Amancherla, K.; Davis, L.L.; Deswal, A.; Dixon, D.L.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Yancy, C.W. 2023 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Management of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1835–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Weeks, T.L.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Ou, J.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Chronic Diseases: Interactions, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santisteban, M.M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, T.; Shenoy, V.; Cole-Jeffrey, C.T.; Lobaton, G.O.; Stewart, D.C.; Rubiano, A.; et al. Hypertension-Linked Pathophysiological Alterations in the Gut. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Yu, H.R.; Lin, I.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Huang, L.T.; Hou, C.Y.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Sodium butyrate modulates blood pressure and gut microbiota in maternal tryptophan-free diet-induced hypertension rat offspring. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 108, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Zheng, T.; Meric, G.; Marques, F.Z. The gut microbiome and hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lin, L.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Lin, Y. Gut microbiota changes in patients with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2023, 25, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Samarraie, A.; Pichette, M.; Rousseau, G. Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Development of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Z.; Xia, H.; Zhong, S.L.; Feng, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canyelles, M.; Borras, C.; Rotllan, N.; Tondo, M.; Escola-Gil, J.C.; Blanco-Vaca, F. Gut Microbiota-Derived TMAO: A Causal Factor Promoting Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; Buffa, J.A.; Gupta, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Mehrabian, M.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seldin, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hazen, S.L.; Lusis, A.J.; Shih, D.M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Inflammation Through Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-kappaB. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Hou, T.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Wang, T.; Zheng, J.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; et al. Causal relationships between the gut microbiome, blood lipids, and heart failure: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Ye, L.; Li, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Bao, M.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Geng, B.; et al. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses unveil dysbiosis of gut microbiota in chronic heart failure patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The critical role of gut microbiota in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Flay, K.J.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, F.; Li, C.; Yang, D.A. Polysaccharides from Platycodon grandiflorus attenuates high-fat diet induced obesity in mice through targeting gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Nakatani, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Irie, J.; Ozawa, K.; Tsujimoto, G.; Suganami, T.; Itoh, H.; Kimura, I. The short chain fatty acid receptor GPR43 regulates inflammatory signals in adipose tissue M2-type macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Ozawa, K.; Inoue, D.; Imamura, T.; Kimura, K.; Maeda, T.; Terasawa, K.; Kashihara, D.; Hirano, K.; Tani, T.; et al. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, N.; Zahir, A.; Hashmat, A.J.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sikander, M.; Zakir, S.; Ahmad, S.; Awan, S.K.; Raza, S.S.; et al. Gut Microbiota as a Key Modulator of Chronic Disease: Implications for Diabetes, Autoimmunity, and Cancer. Cureus 2025, 17, e84687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, T.; Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Ran, L.; Yan, Y.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.; et al. The polysaccharides from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. confer anti-diabetic effect by regulating gut microbiota and intestinal barrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandaliya, D.K.; Seshadri, S. Short Chain Fatty Acids, pancreatic dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baars, D.P.; Fondevila, M.F.; Meijnikman, A.S.; Nieuwdorp, M. The central role of the gut microbiota in the pathophysiology and management of type 2 diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1280–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, M.H.; Soliman, H.; Said, E.M.; Elbatae, H.; Elazab, M.; Elhefnawy, S.; Zaher, T.I.; Abdel-Razik, A.; Elnadry, M. Intermittent fasting and the liver: Focus on the Ramadan model. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Badi, S.; Elidrisi, A.; Husain, N.E.; Zainudin, S.B.; Mahmood, A.; Abubaker, N.E.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Ahmed, M.H. Safety and effectiveness of newer antidiabetic medications during Ramadan fasting and safety of Ramadan fasting after bariatric surgery. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1991–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.K.; Alutol, M.T.; FadAllah, F.S.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Osman, S.A.; Badi, S.; Fathelrahman, A.I.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmed, M.H. Risk factors associated with fasting during Ramadan among individuals with diabetes according to IDF-DAR risk score in Atbara city, Sudan: Cross-sectional hospital-based study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2023, 17, 102743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, M.; Afandi, B.; Yakoob Ahmedani, M.; Mohammad Alamoudi, R.; Alawadi, F.; Bajaj, H.S.; Basit, A.; Bennakhi, A.; El Sayed, A.A.; Hamdy, O.; et al. Diabetes and Ramadan: Practical guidelines 2021. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 185, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. Ramadan Fasting and Complications of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Impacts on Liver Cirrhosis and Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraj, N.E.; Harouna Malam Brah, N.A.; Elaziz, S.; Chadli, A. Evaluation of Glycemic Control in Patients With Diabetes by a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System During the Month of Ramadan. Cureus 2024, 16, e72710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, G.; Huang, J. The impacts of Ramadan fasting for patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1315408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, B.; Faghfoori, Z.; Samadi, N.; Karami, H.; Ahmadi, Y.; Badalzadeh, R.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V.; Majidinia, M.; Ghavimi, H.; Jabbarpour, M. The effects of Ramadan fasting on endothelial function in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahapary, D.L.; Rizqa, T.; Syarira, C.V.; Lusiani, L.; Rizka, A.; Wafa, S.; Wisnu, W.; Edi Tarigan, T.J.; Harbuwono, D.S. Differential effect of ramadan fasting on intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in diabetes mellitus and non-diabetes mellitus patients. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, E.; Ozkan, E. Improvement in endothelial function in hypertensive patients after Ramadan fasting: Effects of cortisol. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 53, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocer, H.; Gunday, M.; Abusharekh, M.; Unal, M. To show the effect of intermittent fasting during ramadan on endothelial dysfunction via TIMI frame count. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 24, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jafar, R.; Zografou Themeli, M.; Zaman, S.; Akbar, S.; Lhoste, V.; Khamliche, A.; Elliott, P.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Dehghan, A. Effect of Religious Fasting in Ramadan on Blood Pressure: Results From LORANS (London Ramadan Study) and a Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Riza Demir, A.; Kahraman, S.; Memic, K.; Avci, Y.; Gurbak, I.; Karabulut, E.; Erturk, M. The effect of Ramadan fasting on ambulatory blood pressure in treated hypertensive patients using diuretics. Blood Press. Monit. 2020, 25, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, H.A.M.; Baqi, H.R.; Qadir, S.A.; El Bilbeisi, A.H.; Hamafarj, K.K.; Taleb, M.; El Afifi, A. Effects of Ramadan fasting on anthropometric measures, blood pressure, and lipid profile among hypertensive patients in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120965780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, F.; Qazi, F.; Pervaiz, M.B.; Kella, D.K.; Mansoor, M.; Osmani, B.Z.; Mir, F.; Kadir, M.M. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Blood Pressure in Normotensive Males. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2015, 27, 338–342. [Google Scholar]
- Bener, A.; AOA, A.A.-H.; Ozturk, M.; Catan, F.; Haris, P.I.; Rajput, K.U.; Omer, A. Effect of ramadan fasting on glycemic control and other essential variables in diabetic patients. Ann. Afr. Med. 2018, 17, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, I.; Kardi, A.; Boukhayatia, F.; Hammami, B.; Cheikh, M.; Romdhane, N.B.; Feki, M.; Yazidi, M.; Chihaoui, M. Impact of Ramadan intermittent fasting on metabolic and inflammatory profiles in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematy, M.; Alinezhad-Namaghi, M.; Rashed, M.M.; Mozhdehifard, M.; Sajjadi, S.S.; Akhlaghi, S.; Sabery, M.; Mohajeri, S.A.; Shalaey, N.; Moohebati, M.; et al. Effects of Ramadan fasting on cardiovascular risk factors: A prospective observational study. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzy, A.; Hasanzade Daloee, M.; Khoshnasab, A.H.; Khoshnasab, A.; Farrokhi, J.; Nematy, M.; Safarian, M.; Nezafati, P.; Alinezhad-Namaghi, M. Trend of blood pressure in hypertensive and normotensive volunteers during Ramadan fasting. Blood Press. Monit. 2017, 22, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zairi, I.; Bejar, M.A.; Ben Mrad, I.; Mzoughi, K.; Kraiem, S. Effects of Ramadan fasting on blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Tunis. Med. 2021, 99, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Malinowski, B.; Zalewska, K.; Wesierska, A.; Sokolowska, M.M.; Socha, M.; Liczner, G.; Pawlak-Osinska, K.; Wicinski, M. Intermittent Fasting in Cardiovascular Disorders-An Overview. Nutrients 2019, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Fezai, M.; Uzcategui, N.L.; Hosseinzadeh, Z.; Lang, F. SGK3 Sensitivity of Voltage Gated K+ Channel Kv1.5 (KCNA5). Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Almilaji, A.; Munoz, C.; Elvira, B.; Shumilina, E.; Bock, C.T.; Kandolf, R.; Lang, F. Down-regulation of K(+) channels by human parvovirus B19 capsid protein VP1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, B.; Simonsen, U.; Rivera, L. Effects of obesity on vascular potassium channels. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarraf-Zadegan, N.; Atashi, M.; Naderi, G.A.; Baghai, A.M.; Asgary, S.; Fatehifar, M.R.; Samarian, H.; Zarei, M. The effect of fasting in Ramadan on the values and interrelations between biochemical, coagulation and hematological factors. Ann. Saudi Med. 2000, 20, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindikoglu, A.L.; Park, J.; Opekun, A.R.; Abdulsada, M.M.; Wilhelm, Z.R.; Jalal, P.K.; Devaraj, S.; Jung, S.Y. Dawn-to-dusk dry fasting induces anti-atherosclerotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic proteome in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Metabol. Open 2022, 16, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, S.A.; El-Kemery, T.A.; Farrag, K.A.; Badawy, M.R.; Sarkis, N.N.; Soliman, F.S.; Mangoud, H. Ramadan fasting: Relation to atherogenic risk among obese Muslims. J. Egypt. Public. Health Assoc. 2004, 79, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al Hayek, A.; Al Zahrani, W.M.; Al Dawish, M.A. Glucometric parameter changes in patients with type 2 diabetes during ramadan fasting: A prospective comparative real-world study. Metabol. Open 2024, 23, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljahdali, A.; Al-Maiman, R.; Al-Orf, S.; Bawazeer, N. Impact of Ramadan Fasting on Cardiometabolic and InflammatoryBiomarkers among Saudi Adults with Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2024, 20, e080124225329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ahmed, H.; Allouche, E.; Bouzid, K.; Zrelli, S.; Hmaidi, W.; Molahedh, Y.; Ouechtati, W.; Bezdah, L. Impact of Ramadan fasting on lipid profile and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Ann. Cardiol. Angeiol. 2022, 71, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, A.; Roshanravan, N.; Mesri Alamdari, N.; Safaiyan, A.; Mosharkesh, E.; Hadi, A.; Barati, M.; Ostadrahimi, A. The interplay between fasting, gut microbiota, and lipid profile. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.; Khalil, M.; Farella, I.; JohnBritto, J.S.; Lanza, E.; Santoro, S.; Garruti, G.; Portincasa, P.; Di Ciaula, A.; Bonfrate, L. Ramadan intermittent fasting reduces visceral fat and improves gastrointestinal motility. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 53, e14029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetya, G.; Sapwarobol, S. Intermittent Fasting During Ramadan Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Anthropometric Parameters in Healthy Young Muslim Men. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2021, 15, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selen, H.; Kusumler, A.S.; Karakan, T.; Moral, K. Effect of Ramadan Fasting on Intestinal Microbiota and Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in Overweight and Obese Individuals. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2024, 33, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, N.; Henriksen, M.; Soderhamn, N.; Stallknecht, B.; Ploug, T.; Schjerling, P.; Dela, F. Effect of intermittent fasting and refeeding on insulin action in healthy men. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2005, 99, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Abdallah, H.; Jaber, N.; Garruti, G.; Di Ciaula, A.; Portincasa, P. Distinct biophysiological effects of Ramadan fasting and traditional intermittent fasting on markers of body fat storage. A real-life study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 129, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nommsen-Rivers, L.A. Does Insulin Explain the Relation between Maternal Obesity and Poor Lactation Outcomes? An Overview of the Literature. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Rashid, M.; Basher, S.; Sultana, S.; Nomani, M.Z. Improved serum HDL cholesterol profile among Bangladeshi male students during Ramadan fasting. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2004, 10, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, M.I.; El-Serafi, A.T.; Jahrami, H.A.; Sherif, N.M.; Hassan, R.E.; Awadallah, S.; Faris, M.A.E. Ramadan diurnal intermittent fasting modulates SOD2, TFAM, Nrf2, and sirtuins (SIRT1, SIRT3) gene expressions in subjects with overweight and obesity. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 155, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiya, A.; Ahmed, S.; Siddieg, H.H.; Babas, I.J.; Carlsson, M. Effect of Ramadan fasting on metabolic markers, body composition, and dietary intake in Emiratis of Ajman (UAE) with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2011, 4, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouhal, H.; Bagheri, R.; Triki, R.; Saeidi, A.; Wong, A.; Hackney, A.C.; Laher, I.; Suzuki, K.; Ben Abderrahman, A. Effects of Ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Gut Hormones and Body Composition in Males with Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, M.I.; Islam, M.T.; Tippetts, T.S.; Chowdhury, K.H.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Summers, S.A.; Zeb, F.; Abdelrahim, D.N.; AlKurd, R.; Khraiwesh, H.M.; et al. Ramadan intermittent fasting is associated with ameliorated inflammatory markers and improved plasma sphingolipids/ceramides in subjects with obesity: Lipidomics analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaloul, R.; Marzougui, H.; Ben Dhia, I.; Ghroubi, S.; Tagougui, S.; Kallel, C.; Driss, T.; Elleuch, M.H.; Ayadi, F.; Turki, M.; et al. Effectiveness of Ramadan diurnal intermittent fasting and concurrent training in the management of obesity: Is the combination worth the weight? Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengi Celik, O.; Kocak, T.; Koksal, E. Effects of Diurnal Ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Sleep Quality in Healthy Turkish Adults. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2022, 61, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.M.; Sulaiman, K.; Alsheikh-Ali, A.A.; Singh, R.; Asaad, N.; Al-Qahtani, A.; Salim, I.; AlHabib, K.F.; Al-Zakwani, I.; Al-Jarallah, M.; et al. Acute heart failure presentations and outcomes during the fasting month of Ramadan: An observational report from seven Middle Eastern countries. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazid, R.M.; Khalaf, H.H.; Sakr, H.I.; Altorbak, N.A.; Alenzi, H.S.; Awad, Z.M.; Smettei, O.A.; Elsanan, M.A.; Widyan, A.M.; Azazy, A.S.; et al. Effects of Ramadan fasting on the symptoms of chronic heart failure. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Hussain, S.; Abbas, J.; Raza, M.H.; Rasool, W.A.; Alsubai, A.K.; Al-Mousawi, R.; Aldhaheri, K.S.O.; Malik, J.; Almas, T. Clinical outcomes of fasting in patients with chronic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A prospective analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Suwaidi, J.; Bener, A.; Hajar, H.A.; Numan, M.T. Does hospitalization for congestive heart failure occur more frequently in Ramadan: A population-based study (1991–2001). Int. J. Cardiol. 2004, 96, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Suwaidi, J.; Zubaid, M.; Al-Mahmeed, W.A.; Al-Rashdan, I.; Amin, H.; Bener, A.; Hadi, H.R.; Helmy, A.; Hanifah, M.; Al-Binali, H.A. Impact of fasting in Ramadan in patients with cardiac disease. Saudi Med. J. 2005, 26, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Chamsi-Pasha, H.; Ahmed, W.H. The effect of fasting in Ramadan on patients with heart disease. Saudi Med. J. 2004, 25, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Alaarag, A.F.; Elkhalek Abou-Omar, M.A.; Amin, O.A. The Safety of Ramadan Fasting in Chronic Heart Failure Patients With Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2025, 37, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assy, M.H.; Awd, M.; Elshabrawy, A.M.; Gharieb, M. Effect of Ramadan fasting on incidence of cerebrovascular stroke in Egyptian patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 151, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimhony, N.; Abu-Salameh, I.; Sagy, I.; Dizitzer, Y.; Oxman, L.; Yitshak-Sade, M.; Novack, V.; Horev, A.; Ifergane, G. Increase in Ischemic Stroke Incident Hospitalizations Among Bedouin Arabs During Ramadan Month. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnia, M.; Zare, M.; Fatehi, F.; Ahmadi, A. The effect of fasting on cerebral venous and dural sinus thrombosis. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mitwalli, A.; Zaher, A.A.; El Menshawi, E. Circadian rhythm of stroke onset during the month of Ramadan. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, N.; Aldriweesh, M.A.; Alhasson, M.A.; Albdah, B.A.; Aldbas, A.A.; Alluhidan, W.A.; Alsaif, S.A.; Almutairi, F.M.; Alskaini, M.A.; Al Khathaami, A.M. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of ischemic stroke patients during Ramadan vs. non-Ramadan months: Is there a difference? Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 925764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkul, C.; Yalinay, M.; Karakan, T. Islamic fasting leads to an increased abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila and Bacteroides fragilis group: A preliminary study on intermittent fasting. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Liu, K.; Long, D.; Faisal, S.; Hilal, M.G.; Ali, I.; Huang, X.; Long, R. Ramadan Fasting Leads to Shifts in Human Gut Microbiota Structured by Dietary Composition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 642999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Verhaar, A.; Ma, Z.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Investigating Ramadan Like Fasting Effects on the Gut Microbiome in BALB/c Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 832757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, D.; Colak, G.A.; Sahin, E.; Ekren, B.Y.; Sezerman, U.; Bas, M. Effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on gut microbiome: Is the diet key? Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1203205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Xie, Z.; Pan, Q.; Ma, Z.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Remodeling of the gut microbiome during Ramadan-associated intermittent fasting. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkul, C.; Yalinay, M.; Karakan, T. Structural changes in gut microbiome after Ramadan fasting: A pilot study. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Lee, G.; Ahmad, S.; Son, H.; Kim, M.J.; Sliti, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.E.; Shin, J.H. The Alteration of the Gut Microbiome during Ramadan Offers a Novel Perspective on Ramadan Fasting: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Ladowski, J.M.; Xu, H. The Role of Autophagy in Vascular Endothelial Cell Health and Physiology. Cells 2024, 13, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou Malhab, L.J.; Madkour, M.I.; Abdelrahim, D.N.; Eldohaji, L.; Saber-Ayad, M.; Eid, N.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Faris, M.E. Dawn-to-dusk intermittent fasting is associated with overexpression of autophagy genes: A prospective study on overweight and obese cohort. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2025, 65, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shafei, A.I. Ramadan fasting ameliorates oxidative stress and improves glycemic control and lipid profile in diabetic patients. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasap, E.; Torun, R.; Kardesler, S.; Gorgulu, G.; Bozgeyik, M.B.; Guzel, Y.; Sahin Gulec, E. The impact of Ramadan fasting on oxidative stress levels in the second trimester of pregnancy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2024, 44, 2408690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, M.A.; Hussein, R.N.; Al-Kurd, R.A.; Al-Fararjeh, M.A.; Bustanji, Y.K.; Mohammad, M.K. Impact of ramadan intermittent fasting on oxidative stress measured by urinary 15-f(2t)-isoprostane. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 802924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shafei, A.I. Ramadan fasting ameliorates arterial pulse pressure and lipid profile, and alleviates oxidative stress in hypertensive patients. Blood Press. 2014, 23, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, E.; Balat, O.; Ugur, M.G.; Yazicioglu, C.; Pence, S.; Erel, O.; Kul, S. Effect of Ramadan fasting on maternal oxidative stress during the second trimester: A preliminary study. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2011, 37, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Zunaidy, N.A.; Al-Khalifa, A.S.; Alhussain, M.H.; Althwab, S.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Faris, M.E. The effect of Ramadan intermittent fasting on anthropometric, hormonal, metabolic, inflammatory, and oxidative stress markers in pre-and post-menopausal women: A prospective cohort of Saudi women. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1437169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asemi, Z.; Samimi, M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Profiles, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Kashan, Iran. Arch. Iran. Med. 2015, 18, 806–810. [Google Scholar]
- Mrad, S.; Rejeb, H.; Ben Abdallah, J.; Graiet, H.; Ben Khelifa, M.; Abed, A.; Ferchichi, S.; Limem, K.; Ben Saad, H. The Impacts of Ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Oxidant/Antioxidant Stress Biomarkers of Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Male Patients. Am. J. Men’s Health 2019, 13, 1557988319848281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Abolfathi, A.A.; Badalzadeh, R.; Majidinia, M.; Yaghoubi, A.; Asadi, M.; Yousefi, B. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Serum Amyloid A and Protein Carbonyl Group Levels in Patients With Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2015, 7, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsen, H.; Guler, E.A.; Binici, I.; Taskiran, H.; Yildirim, S.; Koyuncu, I. Oxidant and antioxidant parameters in people who fast during Ramadan, and those who do not. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 2713–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Authors | Main Finding | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Demirci and Özkan 2023 | Significant enhancement of flow-mediated dilation post-Ramadan is ascribed to reduced plasma levels of CRP and cortisol after Ramadan. | [65] |
| Tahapary et al., 2023 | Fasting throughout Ramadan resulted in a decrease in ICAM-1 levels in both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. | [64] |
| Goser et al., 2021 | The study used the TIMI frame count to assess endothelial dysfunction and showed that Ramadan fasting improved endothelial dysfunction. | [66] |
| Yousefi et al., 2014 | Levels of nitric oxide were significantly elevated in patients following Ramadan fasting. Post-Ramadan, asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) levels significantly decreased, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels elevated, and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels lowered during Ramadan fasting; however, these alterations were not statistically significant. | [63] |
| Impacts of Ramadan Fasting | |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Risk Factors by Decreasing the Following | Gut Microbiota |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, M.; Ahmed, M.H.; Shantakumari, N. The Impact of Ramadan Fasting on Endothelial Function, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176191
Ahmed M, Ahmed MH, Shantakumari N. The Impact of Ramadan Fasting on Endothelial Function, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176191
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Musaab, Mohamed H. Ahmed, and Nisha Shantakumari. 2025. "The Impact of Ramadan Fasting on Endothelial Function, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Cardiovascular Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176191
APA StyleAhmed, M., Ahmed, M. H., & Shantakumari, N. (2025). The Impact of Ramadan Fasting on Endothelial Function, Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6191. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176191






