Chronic and Heavy Drinking, Nutrition Status, and Progression of Liver Injury Negatively Affect the Mortality Risk in Patients Suffering from Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Measures, Markers, and Determinants
2.2. Analyses, Design, and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Drinking Patterns
3.2. Clinical Presentation in Severe and Non-Severe AH
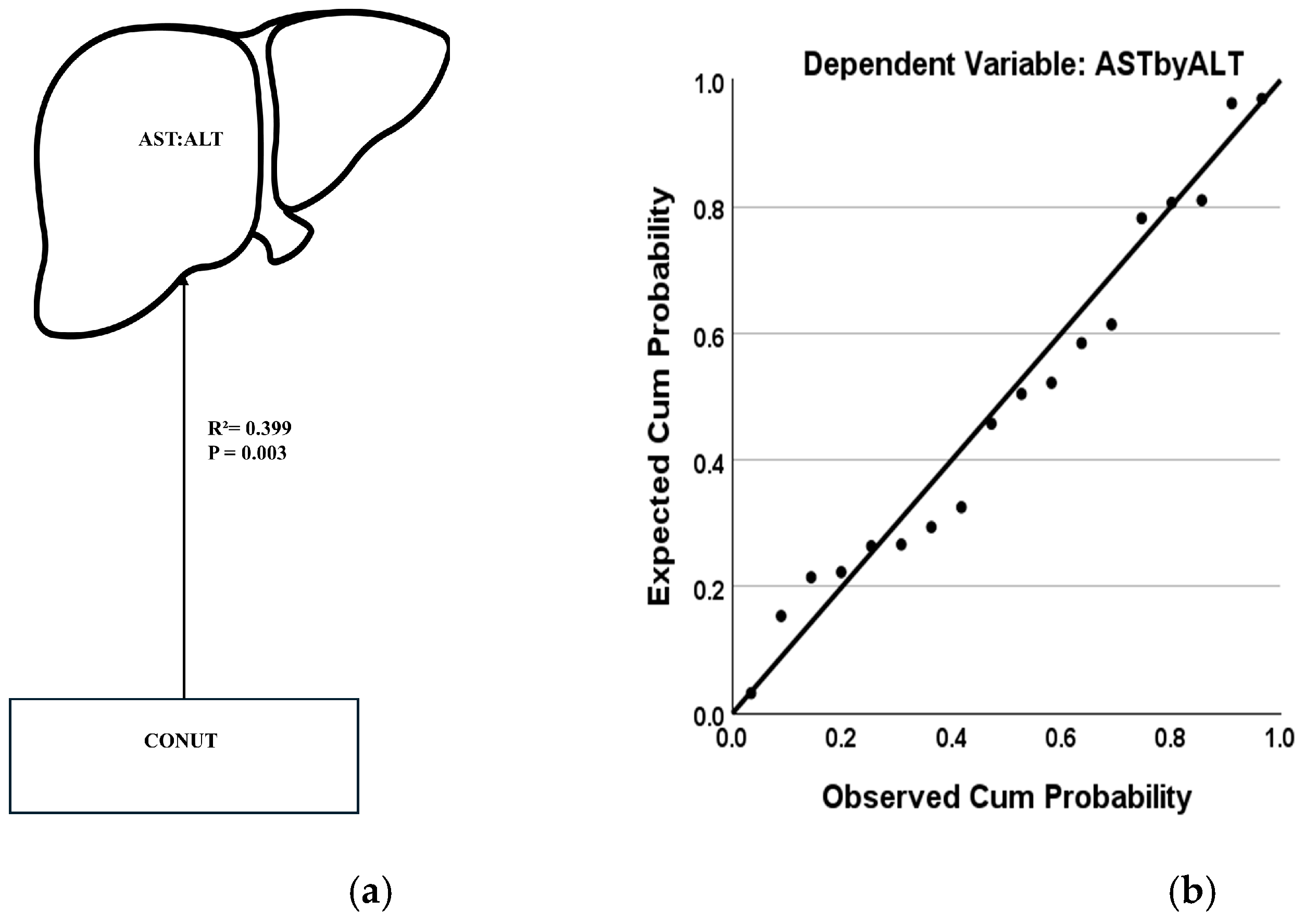
3.3. Factors for Liver Injury Progression in AH
3.4. Clinical Presentation of Mortality Risk in Severe AH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABIC | Algorithm of “Age-Bilirubin-INR-Creatinine” |
| AH | Alcohol-associated Hepatitis |
| ALD | Alcohol-associated Liver Disease |
| AST:ALT | Aspartate transaminase: Alanine transaminase ratio |
| AUD | Alcohol use disorder |
| AUDIT | Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test |
| BAC | Blood alcohol concentration |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CONUT | Controlling Nutritional Status Test |
| CS | Clinically significant |
| CTP | Child–Turcotte–Pugh Score |
| CMP | Complete Metabolic Panel |
| CBC | Complete Blood Count |
| Lille | Lille Model for Alcohol-associated Hepatitis (Mortality Assessment at day 7) |
| LTDH | Lifetime drinking history, one-year drinking |
| Maddrey-DF | Maddrey’s Discriminant Function |
| MELD | Model for End-Stage Liver Disease |
| NCS | Clinically non-significant |
References
- Lefkowitch, J.H. Morphology of alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2005, 9, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsano, L.S.; Vatsalya, V.; Hassan, A.; McClain, C. Clinical features, disease modifiers, and natural history of alcoholic liver disease. In Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; Chalasani, N., Szabo, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.; Shor, J.; Szabo, G. Alcoholic Hepatitis: A Review. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, B.; Fu, Y.; Maccioni, L.; Gao, B. Alcohol-associated liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, P.; Lang, S.; Steffen, H.; Demir, M. Management of alcoholic hepatitis: A clinical perspective. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2078–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataller, R.; Arab, J.P.; Shah, V.H. Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2436–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sersté, T.; Cornillie, A.; Njimi, H.; Pavesi, M.; Arroyo, V.; Putignano, A.; Weichselbaum, L.; Deltenre, P.; Degré, D.; Trépo, E.; et al. The prognostic value of acute-on-chronic liver failure during the course of severe alcoholic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, N.; Lam, D.; Krebs, W.; Lin, W.; Liangpunsakul, S. Prevalence, co-morbidities, and in-hospital mortality of patients hospitalized with alcohol-associated hepatitis in the United States from 2015 to 2019. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatsalya, V.; Cave, M.C.; Kong, M.; Gobejishvili, L.; Falkner, K.C.; Craycroft, J.; Mitchell, M.; Szabo, G.; McCullough, A.; Dasarathy, S.; et al. Keratin 18 Is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Factor for Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S. Nutrition and alcoholic liver disease: Effects of alcoholism on nutrition, Effects of nutrition on ALD and nutritional therapies for ALD. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursz, M.; Lingford-Hughes, A. Advances in the understanding and management of alcohol-related liver disease. BMJ 2023, 383, e077090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsalya, V.; Gala, K.S.; Mishra, M.; Schwandt, M.L.; Umhau, J.; Cave, M.C.; Parajuli, D.; Ramchandani, V.A.; McClain, C.J. Lower Serum Magnesium Concentrations are associated with Specific Heavy Drinking Markers, Pro-Inflammatory Response and Early-Stage Alcohol-associated Liver Injury§. Alcohol Alcohol. 2020, 55, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Szabo, G. Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McClain, C.J.; Rios, C.D.; Condon, S.; Marsano, L.S. Malnutrition and Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2021, 25, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, Y.P.; Becchetti, C.; Wan, T.; Nett, P.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Dufour, J.-F.; Berzigotti, A. Malnutrition and Alcohol in Patients Presenting with Severe Complications of Cirrhosis After Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsalya, V.; Song, M.; Schwandt, M.L.; Cave, M.C.; Barve, S.S.; George, D.T.; Ramchandani, V.A.; McClain, C.J. Effects of Sex, Drinking History, and Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids Dysregulation on the Onset of Liver Injury in Very Heavy Drinking Alcohol-Dependent Patients. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vell, M.S.; Creasy, K.T.; Scorletti, E.; Seeling, K.S.; Hehl, L.; Rendel, M.D.; Schneider, K.M.; Schneider, C.V. Omega-3 intake is associated with liver disease protection. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1192099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakurdesai, A.; Jha, S.K.; Erinkitola, I.; Said, A.; Joshi, T.; Schwandt, M.L.; Parajuli, D.; Singal, A.K.; Kong, M.; Cave, M.C.; et al. The gut-immune-liver axis in patients with alcohol use disorder and clinically low serum zinc levels. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 48, 1740–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, R.; Gerasimidis, K.; Forrest, E. The Role of Micronutrients in the Pathogenesis of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. Alcohol Alcohol. 2022, 57, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas, J. Management of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease and Its Complications. Clin. Drug Investig. 2022, 42, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsan, H.A.; Parekh, S. Management of alcoholic hepatitis: Current concepts. World J. Hepatol. 2012, 4, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajan, H.K. Alcoholic Hepatitis: Diagnosis and Management Procedures. Innov. Sci. Technol. 2024, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Thursz, M.R.; Kim, D.J.; Labreuche, J.; Atkinson, S.R.; Sidhu, S.S.; O’Grady, J.G.; Akriviadis, E.; Sinakos, E.; Carithers, R.L.; et al. Corticosteroids Reduce Risk of Death Within 28 Days for Patients With Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis, Compared With Pentoxifylline or Placebo—A Meta-analysis of Individual Data From Controlled Trials. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 458–468.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, P.S.; Wiesner, R.H.; Malinchoc, M.; Kremers, W.; Therneau, T.M.; Kosberg, C.L.; D’AMico, G.; Dickson, R.E.; Kim, R.W. A Model to Predict Survival in Patients With End–Stage Liver Disease. Hepatology 2001, 33, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnsworth, N.; Fagan, S.P.; Berger, D.H.; Awad, S.S. Child-Turcotte-Pugh versus MELD score as a predictor of outcome after elective and emergent surgery in cirrhotic patients. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 188, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabb, D.W.; Bataller, R.; Chalasani, N.P.; Kamath, P.S.; Lucey, M.; Mathurin, P.; McClain, C.; McCullough, A.; Mitchell, M.C.; Morgan, T.R.; et al. Standard Definitions and Common Data Elements for Clinical Trials in Patients With Alcoholic Hepatitis: Recommendation From the NIAAA Alcoholic Hepatitis Consortia. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, P.S.; Kim, W.R. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology 2007, 45, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.M.; Cole, T.J. What use is the BMI? Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babor, T.F.; Higgins-Biddle, J.C.; Saunders, J.B.; Monteiro, M.G. AUDIT: The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Guidelines for Use in Primary Health Care; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, H.A.; Sheu, W.J. Reliability of alcohol use indices. The Lifetime Drinking History and the MAST. J. Stud. Alcohol 1982, 43, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio de Ulíbarri, J.; González-Madroño, A.; de Villar, N.G.P.; González, P.; González, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández, G. CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mathurin, P.; Mendenhall, C.L.; Carithers, R.L.; Ramond, M.-J.; Maddrey, W.C.; Garstide, P.; Rueff, B.; Naveau, S.; Chaput, J.-C.; Poynard, T. Corticosteroids improve short-term survival in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis (AH): Individual data analysis of the last three randomized placebo controlled double blind trials of corticosteroids in severe AH. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Valla, D. Assessment of the prognosis of cirrhosis: Child–Pugh versus MELD. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, S100–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Hussain, S.; Hair, M.; Shah, A.A. Comparison of Maddrey Discriminant Function, Child–Pugh Score and Glasgow Alcoholic Hepatitis Score in predicting 28-day mortality on admission in patients with acute hepatitis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 182, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Naveau, S.; Abdelnour, M.; Ramond, M.-J.; Diaz, E.; Fartoux, L.; Dharancy, S.; Texier, F.; Hollebecque, A.; Serfaty, L.; et al. The Lille model: A new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyblom, H.; Berggren, U.; Balldin, J.; Olsson, R. High ast/alt ratio may indicate advanced alcoholic liver disease rather than heavy drinking. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basra, S.; Anand, B.S. Definition, epidemiology and magnitude of alcoholic hepatitis. World J. Hepatol. 2011, 3, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Smadi, K.; Qureshi, A.; Buitrago, M.; Ashouri, B.; Kayali, Z.; Uhlmann, D. Survival and Disease Progression in Older Adult Patients With Cirrhosis: A Retrospective Study. Int. J. Hepatol. 2024, 2024, 5852680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins-Biddle, J.C.; Babor, T.F. A review of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), AUDIT-C, and USAUDIT for screening in the United States: Past issues and future directions. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2018, 44, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osna, N.A.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current Management. Alcohol. Res. 2017, 38, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samala, N.; Gawrieh, S.; Tang, Q.; Lourens, S.G.; Shah, V.H.; Sanyal, A.J.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Chalasani, N. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of mild to moderate alcoholic hepatitis. GastroHep 2019, 1, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, N.; Di Marco, M.; Alaimo, S.; Coppolino, G.; L’episcopo, G.; Leggio, S.; Scicali, R.; Piro, S.; Purrello, F.; Di Pino, A. Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Potential Prognostic Indicator of In-Hospital Mortality, Sepsis and Length of Stay in an Internal Medicine Department. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, L.A.; König, D.; Weber, S.; Ayares, G.; Fuentealba, J.M.; Vázquez, V.; Bataller, R.; Kamath, P.S.; Winder, G.S.; Leggio, L.; et al. Management of alcohol use disorder: A gastroenterology and hepatology-focused perspective. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 10, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, D.J.; Rogers, A.H.; Capron, D.W.; Zvolensky, M.J. Maximizing the use of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) as a two-step screening tool. Addict. Behav. 2022, 137, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schütz, T.; Plauth, M.; Peláez, R.B.; Irigoin, R.R. ESPEN Practical Guideline: Clinical nutrition in liver disease. Nutr. Hosp. 2022, 39, 434–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, M.; Hansell, M.; Lardo, O. Alcoholic Hepatitis: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Phys. 2022, 105, 412–420. [Google Scholar]
- Tadokoro, T.; Morishita, A.; Himoto, T.; Masaki, T. Nutritional Support for Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalas, M.A.; Chavez, L.; Leon, M.; Taweesedt, P.T.; Surani, S. Abnormal liver enzymes: A review for clinicians. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Yin, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, G.; Zhou, X.; Ge, P.; Yang, H.; Mao, Y. Impaired albumin function: A novel potential indicator for liver function damage? Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Bridges, B.W.; Dunn, W.; Olson, J.C.; Weinman, S.A.; Jaeschke, H. Cell Death and Prognosis of Mortality in Alcoholic Hepatitis Patients Using Plasma Keratin-18. Gene Expr. 2017, 17, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.R.; Grove, J.I.; Liebig, S.; Astbury, S.; Vergis, N.; Goldin, R.; Quaglia, A.; Bantel, H.; Guha, I.N.; Thursz, M.R.; et al. In Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis, Serum Keratin-18 Fragments Are Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Theragnostic Biomarkers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaram, M.; Frimodig, J.; Jayanty, D.; Hu, H.; Royer, A.J.; Bruner, R.; Kong, M.; Schwandt, M.L.; Vatsalya, V. One-month assessment of Th-cell axis related inflammatory cytokines, IL-17 and IL-22 and their role in alcohol-associated liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1202267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Simonetto, D.A.; Verma, V.K.; Feng, D.; Tang, T.; Shah, V.H. An open-label, dose-escalation study to assess the safety and efficacy of IL-22 agonist F-652 in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.Q.; Ajmo, J.M.; You, M. Adiponectin and alcoholic fatty liver disease. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluschinski, M.; Kordes, C.; Vucur, M.; Buettner, V.; Roderburg, C.; Xu, H.C.; Shinte, P.V.; Lang, P.A.; Luedde, T.; Castoldi, M. Differential Modulation of miR-122 Transcription by TGFβ1/BMP6: Implications for Nonresolving Inflammation and Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cells 2023, 12, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Chu, H.; Gao, B.; Lang, S.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Schnabl, B. Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Novel Hepatic and Intestinal Genes Following Chronic Plus Binge Ethanol Feeding in Mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 3592–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar-Burke, I.; Jansson-Knodell, C.L.; Gilmore, A.C.; Crabb, D.W. The role of nutrition in alcohol-associated liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 53, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addolorato, G.; Vassallo, G.A.; Mirijello, A.; Gasbarrini, A. Diagnosis and Management of Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients with Liver Disease: Lights and Shadows. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgill, A.; Jew, M.H.; Soltani, M.; Deioma, A.; Grant, M.; Patton, H.M.; Hsu, C.L. Early detection of liver disease in patients with alcohol use disorder improves long-term abstinence. Alcohol Alcohol. 2024, 59, agae074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Addolorato, G.; Mathurin, P.; Thursz, M.R. Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: Integrated Management With Alcohol Use Disorder. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healey, M.A.; Ramalingam, G.; Hang, Y.; Smirnova, E.; Asgharpour, A.; Patel, V.; Lee, H.; Luketic, V.; Matherly, S.; Siddiqui, M.; et al. Utility of Lille Score in Predicting 30-Day Survival in Steroid-Treated Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 69, 3043–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharda, B.V.; Gupta, M.; Singh, R.; Lehl, S.S. Predictive Ability of Different Scoring Models in Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis. Med. J. Dr. D.Y. Patil Vidyapeeth 2024, 17, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haderer, M.; Neubert, P.; Rinner, E.; Scholtis, A.; Broncy, L.; Gschwendtner, H.; Kandulski, A.; Pavel, V.; Mehrl, A.; Brochhausen, C.; et al. Novel pathomechanism for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Disruption of cell junctions by cellular and bacterial proteases. Gut 2021, 71, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggio, L.; Mellinger, J.L. Alcohol use disorder in community management of chronic liver diseases. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, D.H.; Kang, D.; Guallar, E.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Zhao, D.; Hong, Y.S.; Cho, J.; Gwak, G.-Y. Alcohol Intake and Mortality in Patients With Chronic Viral Hepatitis: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol.|ACG 2021, 116, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musto, J.A.; Lucey, M.R. Prognostic models in alcohol-related liver disease and alcohol-related hepatitis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 67, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.; Botta, F.; Fasoli, A.; Ceppa, P.; Risso, D.; Lantieri, P.B.; Celle, G.; Testa, R. Progressive Liver Functional Impairment Is Associated with an Increase in AST/ALT Ratio. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 44, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Measures | Group 1 (Non-Severe AH, MELD < 20) | Group 2 (Severe AH, MELD ≥ 20) | Between-Group p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Risk (ABIC < 6.71) (n = 10; 16.40%) | Moderate Risk (ABIC 6.71 to <9) (n = 16; 26.23%) | Total (n = 26; 42.62%) | Low Risk (ABIC < 6.71) (n = 6; 9.84%) | Moderate Risk (ABIC 6.71 to <9) (n = 20; 32.79%) | High Risk (ABIC ≥ 9) (n = 9; 14.75%) | Total (n = 35; 57.38%) | ||
| Age (yrs.) a,b,c,d,e,f | 45.10 ± 5.70 | 56.50 ± 5.80 | 52.12 ± 7.99 | 32.17 ± 4.62 | 46.35 ± 9.34 | 54.78 ± 8.87 | 46.09 ± 11.17 | 0.023 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 39.48 ± 11.27 | 31.07 ± 6.03 | 33.18 ± 7.70 | 28.78 ± 12.98 | 31.76 ± 9.02 | 33.54 ± 10.11 | 31.20 ± 9.93 | 0.625 |
| Sex (F/M) | 5/5 | 3/13 | 8/18 | 3/3 | 9/11 | 1/8 | 13/22 | NA |
| Race (AA/Cau) | 0/10 | 1/15 | 1/25 | 1/5 | 4/16 | 2/7 | 7/28 | NA |
| Drinking Patterns | ||||||||
| AUDIT score | 30.00 ± 6.08 | 19.50 ± 9.61 | 23.00 ± 9.72 | 26.60 ± 3.36 | 23.91 ± 9.15 | 21.33 ± 6.03 | 24.21 ± 7.49 | 0.719 |
| LTDH c | 15.67 ± 6.03 | 26.40 ± 11.06 | 22.38 ± 10.54 | 13.50 ± 4.80 | 21.91 ± 10.61 | 35.33 ± 14.22 | 21.81 ± 11.82 | 0.909 |
| Laboratory Parameters | ||||||||
| ALT (IU/L) | 66.00 ± 51.13 | 60.31 ± 48.63 | 62.50 ± 48.67 | 45.17 ± 15.01 | 51.60 ± 59.33 | 59.89 ± 41.26 | 52.63 ± 49.24 | 0.440 |
| AST (IU/L) | 140.50 ± 81.07 | 123.81 ± 99.35 | 130.23 ± 91.42 | 168.50 ± 62.62 | 189.70 ± 301.14 | 146.11 ± 45.13 | 174.86 ± 226.23 | 0.351 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) d,e,f | 4.22 ± 4.44 | 4.25 ± 4.12 | 4.24 ± 4.16 | 13.10 ± 7.73 | 13.65 ± 7.36 | 20.46 ± 7.16 | 15.30 ± 7.79 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.83 ± 0.47 | 0.73 ± 0.22 | 0.77 ± 0.34 | 0.60 ± 0.18 | 0.90 ± 0.37 | 1.79 ± 1.65 | 1.08 ± 0.96 | 0.122 |
| INR d,e,f | 1.23 ± 0.27 | 1.45 ± 0.45 | 1.37 ± 0.40 | 2.07 ± 0.41 | 2.03 ± 0.44 | 2.76 ± 1.49 | 2.22 ± 0.87 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) e,f | 3.29 ± 0.81 | 3.11 ± 0.73 | 3.18 ± 0.75 | 2.18 ± 0.57 | 2.43 ± 0.66 | 2.24 ± 0.56 | 2.34 ± 0.62 | <0.001 |
| Survival/Prognostic Markers | ||||||||
| ABIC score a,b,c | 6.08 ± 0.49 | 7.37 ± 0.50 | 6.87 ± 0.81 | 6.1 ± 0.28 | 7.62 ± 0.63 | 9.86 ± 0.63 | 7.93 ± 1.40 | 0.001 |
| Nutritional Parameters | ||||||||
| CONUT c,e,f | 5.14 ± 2.27 | 5.83 ± 2.41 | 5.58 ± 2.32 | 10.00 ± 2.00 | 7.62 ± 2.19 | 7.57 ± 1.27 | 7.88 ± 2.05 | 0.001 |
| Liver Disease Severity Markers | ||||||||
| Meld score c,d,e,f | 13.50 ± 3.98 | 13.88 ± 4.43 | 13.73 ± 4.18 | 23.50 ± 1.87 | 24.60 ± 3.58 | 31.56 ± 6.84 | 26.20 ± 5.39 | NA (<0.001) |
| Maddrey score d,e,f | 16.16 ± 13.83 | 28.17 ± 24.59 | 24.16 ± 21.94 | 60.48 ± 17.37 | 56.71 ± 23.09 | 99.65 ± 68.98 | 68.40 ± 42.57 | <0.001 |
| CTP score e,f | 7.80 ± 2.44 | 8.06 ± 1.88 | 7.96 ± 2.07 | 10.50 ± 1.38 | 10.80 ± 1.24 | 11.44 ± 1.01 | 10.91 ± 1.22 | <0.001 |
| Lille score c | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.12 | 0.17 ± 0.12 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.29 | 0.58 ± 0.19 | 0.40 ± 0.29 | 0.043 |
| AST/ALT ratio f | 2.84 ± 2.78 | 2.45 ± 1.70 | 2.60 ± 2.14 | 4.17 ± 2.35 | 3.52 ± 1.28 | 2.84 ± 0.90 | 3.46 ± 1.46 | Trend (0.067) |
| Clinical Parameters | ||||||||
| Ascites (Yes/No) | 4/6 | 8/8 | 12/14 | 5/1 | 17/3 | 8/1 | 30/5 | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thakurdesai, A.; Kumari, A.; Shay, H.; Elgharabawy, K.; Winrich, E.J.; Zhang, W.; Jackson, A.; Cave, M.C.; Kong, M.; Zhang, X.; et al. Chronic and Heavy Drinking, Nutrition Status, and Progression of Liver Injury Negatively Affect the Mortality Risk in Patients Suffering from Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176157
Thakurdesai A, Kumari A, Shay H, Elgharabawy K, Winrich EJ, Zhang W, Jackson A, Cave MC, Kong M, Zhang X, et al. Chronic and Heavy Drinking, Nutrition Status, and Progression of Liver Injury Negatively Affect the Mortality Risk in Patients Suffering from Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176157
Chicago/Turabian StyleThakurdesai, Aishwarya, Anjali Kumari, Henry Shay, Khaled Elgharabawy, Evan J. Winrich, Wanyu Zhang, Amber Jackson, Matthew C. Cave, Maiying Kong, Xiang Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Chronic and Heavy Drinking, Nutrition Status, and Progression of Liver Injury Negatively Affect the Mortality Risk in Patients Suffering from Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176157
APA StyleThakurdesai, A., Kumari, A., Shay, H., Elgharabawy, K., Winrich, E. J., Zhang, W., Jackson, A., Cave, M. C., Kong, M., Zhang, X., Singal, A. K., McClain, C. J., & Vatsalya, V. (2025). Chronic and Heavy Drinking, Nutrition Status, and Progression of Liver Injury Negatively Affect the Mortality Risk in Patients Suffering from Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176157






