Longitudinal Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Danish Adults: Changes in Speech Recognition, Self-Reported Hearing Ability, Hearing-Related Quality of Life, and Tinnitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Battery
2.2. Participant Characteristics
2.3. Statistical Methods
2.3.1. Analyses of Efficacy and Effectiveness Measures
Assessment and Handling of Missing Data
2.4. Analysis of Tinnitus Measures
2.5. Use of GenAI in Writing
3. Results
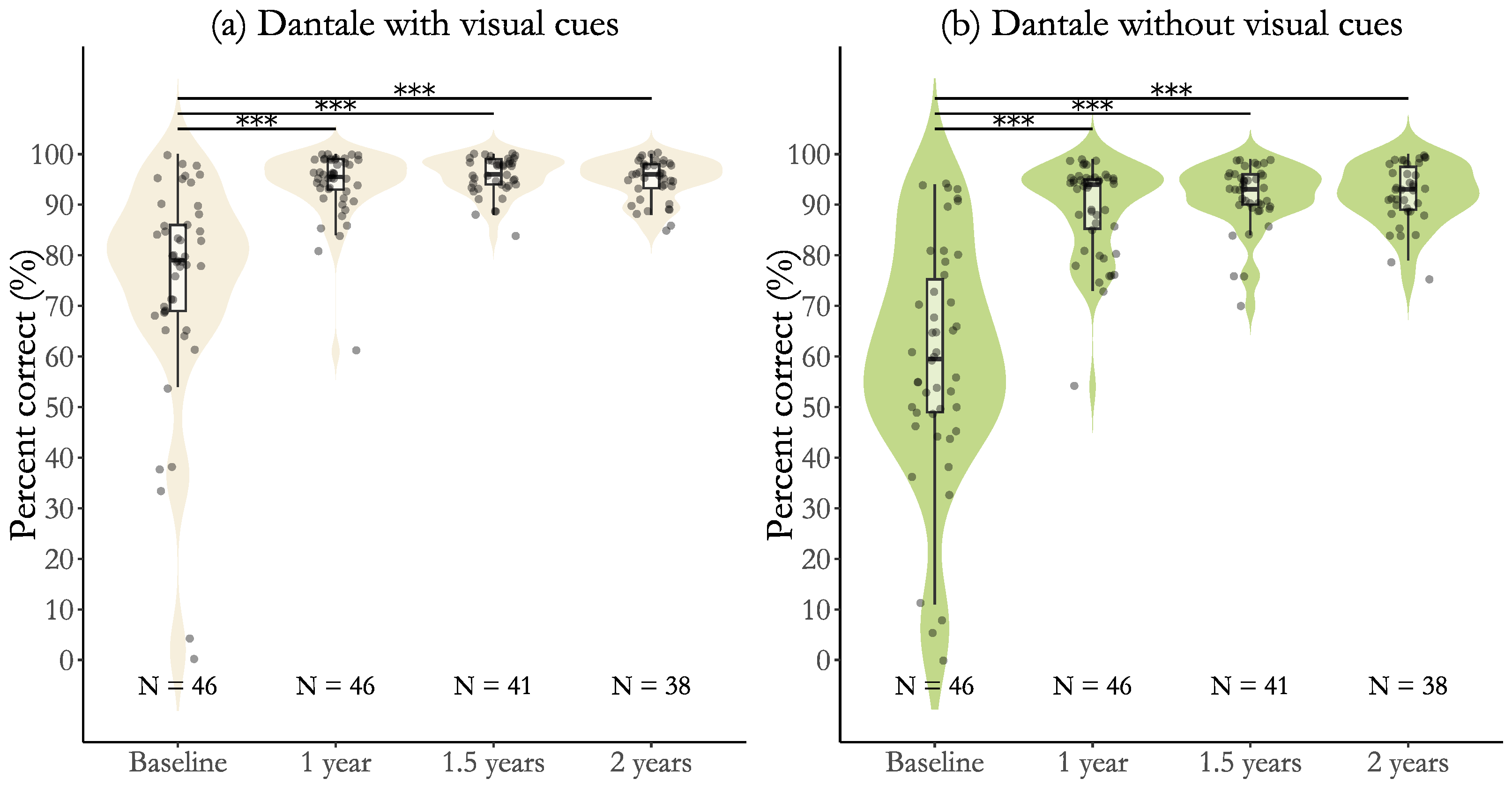
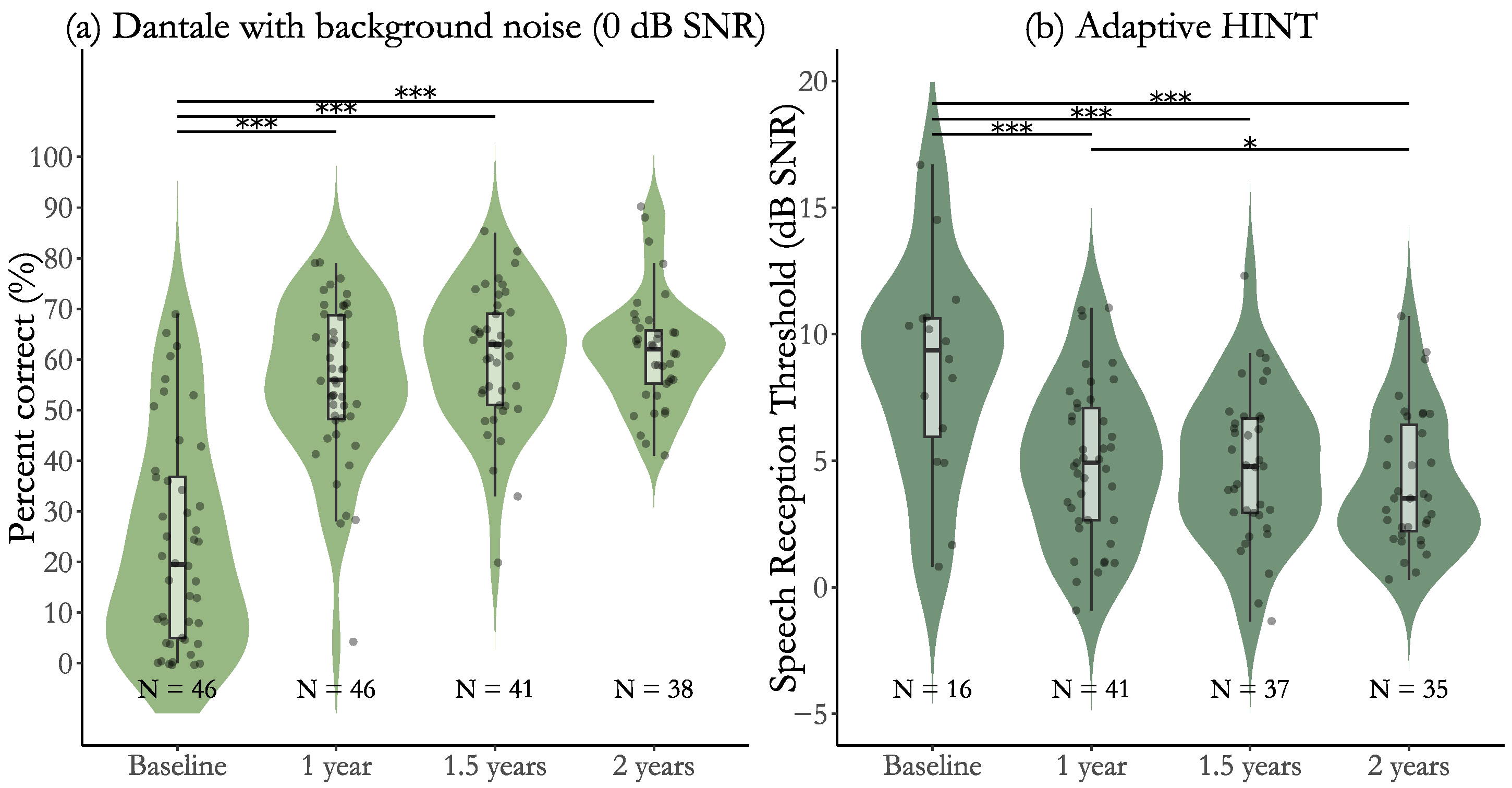
3.1. Efficacy Results for Participants with Post-Lingual Deafness
3.2. Efficacy Results for Participants with Pre-Lingual Deafness and SSD
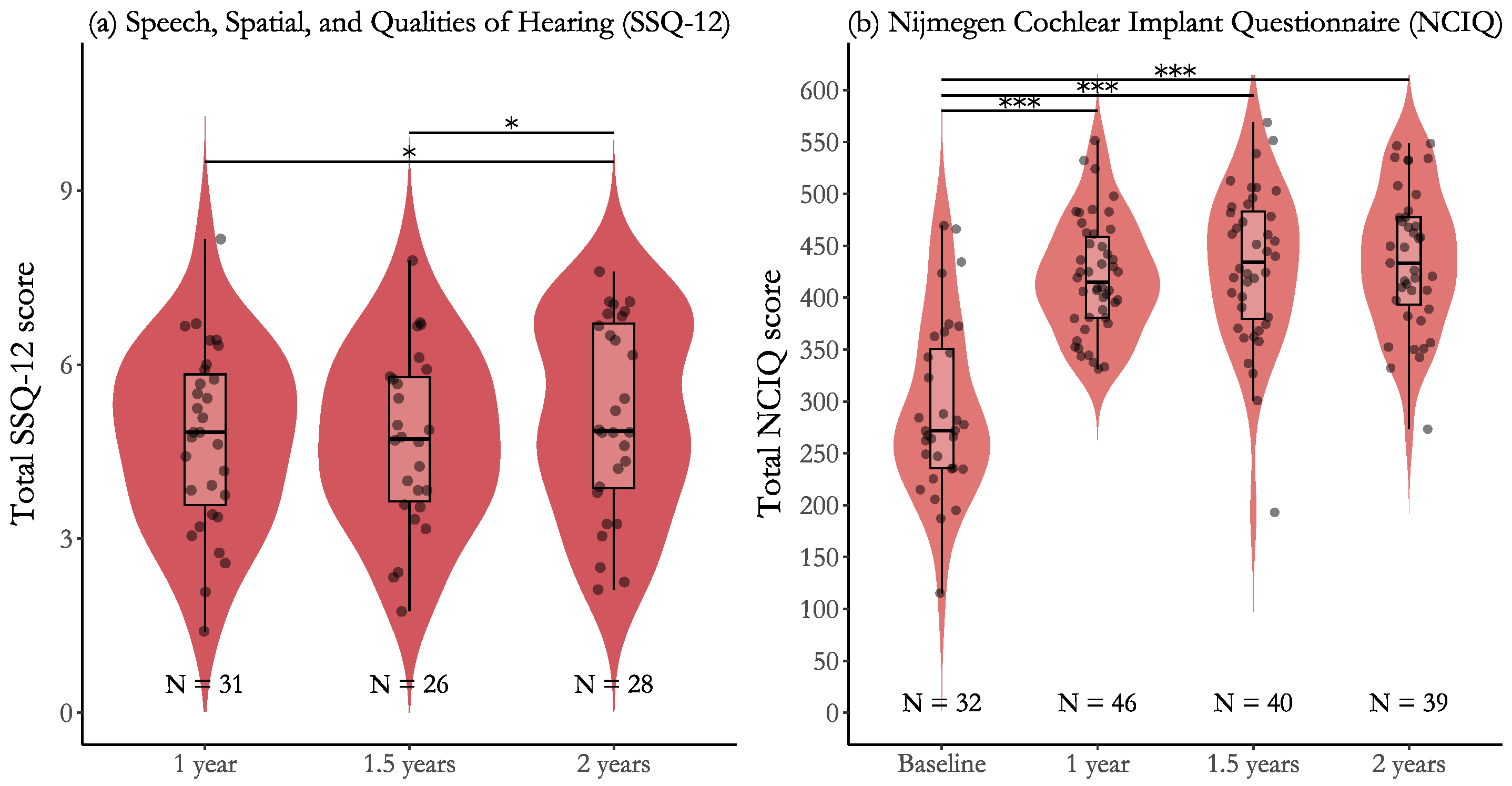
3.3. Effectiveness for Participants with Post-Lingual Deafness
3.4. Effectiveness for Participants with Pre-Lingual Deafness and SSD
3.5. Tinnitus Results for Participants with Post-Lingual Deafness
3.6. Tinnitus Results for Participants with Pre-Lingual Deafness and SSD
4. Discussion
4.1. Participant Characteristics
4.2. Efficacy Results
4.3. Effectiveness Results
4.4. Tinnitus Results
4.5. Additional Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Observed and Missing Data
| Measure | Time Point | Observed | Missing | Missing (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dantale with visual cues | Baseline | 46 | 0 | 0.0% |
| 1 year | 46 | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 1.5 years | 41 | 5 | 10.9% | |
| 2 years | 38 | 8 | 17.4% | |
| Dantale without visual cues | Baseline | 46 | 0 | 0.0% |
| 1 year | 46 | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 1.5 years | 41 | 5 | 10.9% | |
| 2 years | 38 | 8 | 17.4% | |
| Dantale with background noise | Baseline | 46 | 0 | 0.0% |
| 1 year | 46 | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 1.5 years | 41 | 5 | 10.9% | |
| 2 years | 38 | 8 | 17.4% | |
| Adaptive HINT | Baseline | 16 | 30 | 65.2% |
| 1 year | 41 | 5 | 10.9% | |
| 1.5 years | 37 | 9 | 19.6% | |
| 2 years | 35 | 11 | 23.9% | |
| NCIQ | Baseline | 32 | 14 | 30.4% |
| 1 year | 46 | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 1.5 years | 40 | 6 | 13.0% | |
| 2 years | 39 | 7 | 15.2% | |
| SSQ-12 | 1 year | 31 | 15 | 32.6% |
| 1.5 years | 26 | 20 | 43.5% | |
| 2 years | 28 | 18 | 39.1% | |
| THI | Baseline | 30 | 16 | 34.8% |
| 1 year | 46 | 0 | 0.0% | |
| 1.5 years | 40 | 6 | 13.0% | |
| 2 years | 42 | 4 | 8.7% |
References
- World Health Organization.Deafness and Hearing Loss. 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Andries, E.; Gilles, A.; Topsakal, V.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Van de Heyning, P.; Van Rompaey, V.; Mertens, G. Systematic Review of Quality of Life Assessments after Cochlear Implantation in Older Adults. Audiol. Neurotol. 2021, 26, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.R.; Yaffe, K.; Xia, J.; Xue, Q.L.; Harris, T.B.; Purchase-Helzner, E.; Satterfield, S.; Ayonayon, H.N.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M. Hearing Loss and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarant, J.Z.; Busby, P.A.; Schembri, A.J.; Briggs, R.J.S.; Masters, C.L.; Harris, D.C. COCHLEA: Longitudinal Cognitive Performance of Older Adults with Hearing Loss and Cochlear Implants at 4.5-Year Follow-Up. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarant, J.; Harris, D.; Busby, P.; Maruff, P.; Schembri, A.; Lemke, U.; Launer, S. The effect of hearing aid use on cognition in older adults: Can we delay decline or even improve cognitive function? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babajanian, E.E.; Gurgel, R.K. Cognitive and behavioral effects of hearing loss. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 30, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, I.; Reis, M.; Au, A.; Cowan, R.; Dowell, R.C. Cochlear implantation outcomes in adults: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Mealing, S.; Anderson, R.; Elston, J.; Weiner, G.; Taylor, R.S.; Hoyle, M.; Liu, Z.; Price, A.; Stein, K. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of cochlear implants for severe to profound deafness in children and adults: A systematic review and economic model. Health Technol. Assess. 2009, 13, 1–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cosetti, M. Safety and outcomes of cochlear implantation in the elderly: A review of recent literature. J. Otol. 2016, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRackan, T.R.; Bauschard, M.; Hatch, J.L.; Franko-Tobin, E.; Droghini, H.R.; Nguyen, S.A.; Dubno, J.R. Meta-analysis of quality-of-life improvement after cochlear implantation and associations with speech recognition abilities. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Tran, Y.; Lo, C.; Lee, J.N.; Turner, J.; McAlpine, D.; McMahon, C.; Gopinath, B. The Benefits of Cochlear Implantation for Adults: A Systematic Umbrella Review. Ear Hear. 2024, 45, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basura, G.; Cienkowski, K.; Hamlin, L.; Ray, C.; Rutherford, C.; Stamper, G.; Schooling, T.; Ambrose, J. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Clinical Practice Guideline on Aural Rehabilitation for Adults with Hearing Loss. Am. J. Audiol. 2023, 32, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, C.; Friedmann, D.R.; Fang, Y.; Wang, B.; Roland, J.T.; Waltzman, S.B. Performance Plateau in Prelingually and Postlingually Deafened Adult Cochlear Implant Recipients. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.C.; Zwolan, T.A.; Balkany, T.J.; Strader, H.L.; Biever, A.; Gifford, R.H.; Hall, M.W.; Holcomb, M.A.; Hill, H.; King, E.R.; et al. A Consensus to Revise the Minimum Speech Test Battery—Version 3. Am. J. Audiol. 2024, 33, 624–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R.H.; Shallop, J.K.; Peterson, A.M. Speech Recognition Materials and Ceiling Effects: Considerations for Cochlear Implant Programs. Audiol. Neurotol. 2008, 13, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenarz, M.; Sönmez, H.; Joseph, G.; Büchner, A.; Lenarz, T. Long-Term Performance of Cochlear Implants in Postlingually Deafened Adults. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 147, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, C.J.; Olsen, T.M.; Charney, L.; Madsen, B.M.; Holmes, C.E. Speech-in-Noise Testing: An Introduction for Audiologists. Semin. Hear. 2024, 45, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, G.; Andries, E.; Clement, C.; Cochet, E.; Hofkens Van den Brandt, A.; Jacquemin, L.; Joossen, I.; Vermeersch, H.; Lammers, M.J.W.; Van Rompaey, V.; et al. Contralateral hearing aid use in adult cochlear implant recipients: Retrospective analysis of auditory outcomes. Int. J. Audiol. 2024, 63, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Távora-Vieira, D.; Wedekind, A.; Acharya, A.; Kuthubutheen, J.; Voola, M.; Cavalheri, V.; Friedland, P. Advanced age is not a predictor for cochlear implantation outcomes in adults with moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 91, 101571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsall, D.; Lupo, J.; Biever, A. Longitudinal outcomes of cochlear implantation and bimodal hearing in a large group of adults: A multicenter clinical study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.M.B.; West, N.C.; Bille, M.; Sandvej, M.G.; Cayé-Thomasen, P. Cochlear Implantation Improves Both Speech Perception and Patient-Reported Outcomes: A Prospective Follow-Up Study of Treatment Benefits among Adult Cochlear Implant Recipients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, C.A.; Herzog, J.A.; McJunkin, J.L.; Wick, C.C.; Durakovic, N.; Firszt, J.B.; Kallogjeri, D. Assessment of Speech Understanding After Cochlear Implantation in Adult Hearing Aid Users: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häußler, S.M.; Knopke, S.; Wiltner, P.; Ketterer, M.; Gräbel, S.; Olze, H. Long-term Benefit of Unilateral Cochlear Implantation on Quality of Life and Speech Perception in Bilaterally Deafened Patients. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e430–e440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfelder, A.; Gräbel, S.; Olze, H. The impact of cochlear implantation on quality of life: The role of audiologic performance and variables. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 138, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plath, M.; Marienfeld, T.; Sand, M.; van de Weyer, P.S.; Praetorius, M.; Plinkert, P.K.; Baumann, I.; Zaoui, K. Prospective study on health-related quality of life in patients before and after cochlear implantation. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Fried, J.; Nguyen, S.A.; Schvartz-Leyzac, K.C.; Camposeo, E.L.; Meyer, T.A.; Dubno, J.R.; McRackan, T.R. Longitudinal Speech Recognition Changes After Cochlear Implant: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elberling, C.; Ludvigsen, C.; Lyregaard, P.E. Dantale: A New Danish Speech Material. Scand. Audiol. 1989, 18, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Dau, T. The Danish Hearing in Noise Test. Int. J. Audiol. 2011, 50, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderink, J.B.; Krabbe, P.F.; van den Broek, P. Development and application of a health-related quality-of-life instrument for adults with cochlear implants: The Nijmegen Cochlear Implant Questionnaire. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 123, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, C.S.; Schmidt, J.H. Evaluation of the Nijmegen Cochlear Implant Questionnaire in Danish. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 29, s00441788598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.; Jensen, N.S.; Naylor, G.; Bhullar, N.; Akeroyd, M.A. A short form of the Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing scale suitable for clinical use: The SSQ12. Int. J. Audiol. 2013, 52, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.W.; Jacobson, G.P.; Spitzer, J.B. Development of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996, 122, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarella, A.; Notaro, A.; Laria, C.; Serra, N.; Genovese, E.; Malesci, R.; Auletta, G.; Fetoni, A.R. State-of-the-Art on the Impact of Bimodal Acoustic Stimulation on Speech Perception in Noise in Adults: A Systematic Review. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, A.R. Understanding the Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1 Year Post-CI | 1.5 Years Post-CI | 2 Years Post-CI |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusion and outcome measures: Dantale, HINT, NCIQ, SSQ-12, and THI. | Outcome measures: Dantale, HINT, NCIQ, SSQ-12, and THI. | Outcome measures: Dantale, HINT, NCIQ, SSQ-12, and THI. |
| Registration of hearing history and baseline outcome measures: Dantale, HINT, NCIQ, and THI. |
| Demographic Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Gender (N = 50) | |
| Female | 25 (50%) |
| Male | 25 (50%) |
| Age (N = 50) | |
| Range, years | 37–83 |
| Mean (SD), years | 66.8 (10.7) |
| Hearing history (N = 50) | |
| Pre-lingual deafness | 2 (4%) |
| Post-lingual deafness | 46 (92%) |
| Single-sided deafness | 2 (4%) |
| Years of experienced functional deafness (N = 46) | |
| Range, years | 1–20 |
| Mean (SD), years | 3.8 (3.2) |
| Pre-implant hearing loss in CI ear (PTA6, N = 46) | |
| Range, dB HL | 65.8–116.7 |
| Mean (SD), dB HL | 89.0 (14.5) |
| Pre-implant hearing loss in contralateral ear (PTA6, N = 45) | |
| Range, dB HL | 29.2–116.7 |
| Mean (SD), dB HL | 77.6 (16.7) |
| Dantale with Visual Cues | ||
|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Estimate (SE) [95% CI], p-Value | [95% CI] |
| Baseline to 1 year | 19.8 (2.36) [15.2, 24.4], p < 0.001 *** | 1.75 [1.30, 2.21] |
| Baseline to 1.5 years | 21.5 (2.44) [16.7, 26.3], p < 0.001 *** | 1.90 [1.42, 2.37] |
| Baseline to 2 years | 20.7 (2.50) [15.8, 25.6], p < 0.001 *** | 1.83 [1.35, 2.31] |
| 1 year to 1.5 years | 1.7 (2.44) [−3.1, 6.5], p = 1.000 | 0.15 [−0.23, 0.63] |
| 1 year to 2 years | 0.9 (2.50) [−4.0, 5.8], p = 1.000 | 0.07 [−0.36, 0.51] |
| 1.5 years to 2 years | 0.8 (2.56) [−4.2, 5.8], p = 1.000 | 0.07 [−0.41, 0.49] |
| Dantale Without Visual Cues | ||
| Comparison | Estimate (SE) [95% CI], p-Value | [95% CI] |
| Baseline to 1 year | 30.3 (2.44) [25.5, 35.1], p < 0.001 *** | 2.59 [2.09, 3.09] |
| Baseline to 1.5 years | 32.7 (2.53) [27.7, 37.7], p < 0.001 *** | 2.79 [2.27, 3.32] |
| Baseline to 2 years | 33.1 (2.59) [28.0, 38.2], p < 0.001 *** | 2.83 [2.30, 3.37] |
| 1 year to 1.5 years | 2.4 (2.53) [−2.5, 7.3], p = 0.849 | 0.20 [−0.63, 0.23] |
| 1 year to 2 years | 2.8 (2.59) [−2.3, 7.9], p = 0.849 | 0.24 [−0.68, 0.20] |
| 1.5 years to 2 years | 0.4 (2.65) [−4.8, 5.6], p = 0.870 | 0.04 [−0.49, 0.41] |
| Dantale with Background Noise | ||
|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Estimate (SE) [95% CI], p-Value | [95% CI] |
| Baseline to 1 year | 32.3 (2.50) [27.4, 37.2], p < 0.001 *** | 2.69 [2.18, 3.20] |
| Baseline to 1.5 years | 36.9 (2.60) [31.8, 42.0], p < 0.001 *** | 3.07 [2.53, 3.62] |
| Baseline to 2 years | 37.6 (2.67) [32.4, 42.8], p < 0.001 *** | 3.13 [2.57, 3.69] |
| 1 year to 1.5 years | 4.6 (2.60) [−0.5, 9.7], p = 0.160 | 0.38 [−0.05, 0.81] |
| 1 year to 2 years | 5.3 (2.67) [0.0, 10.6], p = 0.145 | 0.44 [0.00, 0.89] |
| 1.5 years to 2 years | 0.7 (2.72) [−4.6, 6.0], p = 0.790 | 0.06 [−0.39, 0.51] |
| Adaptive HINT | ||
| Comparison | Estimate (SE) [95% CI], p-Value | [95% CI] |
| Baseline to 1 year | −4.7 (0.59) [−5.9, −3.6], p < 0.001 *** | 2.50 [1.79, 3.21] |
| Baseline to 1.5 years | −5.1 (0.61) [−6.3, −3.9], p < 0.001 *** | 2.72 [1.98, 3.46] |
| Baseline to 2 years | −5.8 (0.63) [−7.0, −4.6], p < 0.001 *** | 3.10 [2.32, 3.87] |
| 1 year to 1.5 years | −0.4 (0.44) [−1.3, 0.5], p = 0.349 | 0.22 [−0.25, 0.69] |
| 1 year to 2 years | −1.1 (0.45) [−2.0, −0.1], p = 0.042 * | 0.60 [0.12, 1.09] |
| 1.5 years to 2 years | −0.7 (0.45) [−1.6, 0.2], p = 0.236 | 0.38 [−0.10, 0.86] |
| Measure, Unit | Baseline | 1 Year | 1.5 Years | 2 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dantale with visual cues, % | 74.2 (21.9) | 94.0 (6.8) | 95.7 (3.8) | 94.9 (4.1) |
| Dantale without visual cues, % | 58.9 (23.5) | 89.3 (9.3) | 91.7 (6.4) | 92.1 (5.9) |
| Dantale with background noise, % | 23.4 (20.9) | 55.7 (15.5) | 60.2 (13.5) | 61.7 (11.2) |
| Adaptive HINT, dB SNR | 8.6 (4.2) | 4.9 (3.1) | 4.8 (2.9) | 4.2 (2.7) |
| SSQ-12, points | — | 4.7 (1.6) | 4.7 (1.5) | 5.1 (1.7) |
| NCIQ, points | 292.6 (83.6) | 420.3 (54.5) | 430.8 (74.3) | 436.3 (67.1) |
| THI, points | 9.7 (15.3) | 8.4 (14.3) | 6.2 (10.0) | 7.9 (13.6) |
| SSQ-12 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Estimate (SE) [95% CI], p-Value | [95% CI] |
| Baseline to 1 year | — | — |
| Baseline to 1.5 years | — | — |
| Baseline to 2 years | — | — |
| 1 year to 1.5 years | 0.11 (0.21) [−0.30, 0.52], p = 0.586 | 0.16 [−0.43, 0.75] |
| 1 year to 2 years | 0.60 (0.21) [0.18, 1.02], p = 0.015 * | 0.86 [0.03, 1.05] |
| 1.5 years to 2 years | 0.49 (0.20) [0.09, 0.89], p = 0.042 * | 0.70 [0.10, 1.29] |
| NCIQ | ||
| Comparison | Estimate (SE) [95% CI], p-Value | [95% CI] |
| Baseline to 1 year | 130.5 (11.1) [108.7, 152.3], p < 0.001 *** | 2.79 [2.22, 3.36] |
| Baseline to 1.5 years | 139.7 (11.5) [117.2, 162.2], p < 0.001 *** | 2.99 [2.39, 3.58] |
| Baseline to 2 years | 145.3 (11.5) [122.8, 167.8], p < 0.001 *** | 3.11 [2.50, 3.71] |
| 1 year to 1.5 years | 9.12 (10.2) [−11.0, 29.2], p = 0.751 | 0.20 [−0.24, 0.63] |
| 1 year to 2 years | 14.71 (10.3) [−5.4, 34.9], p = 0.473 | 0.32 [−0.13, 0.76] |
| 1.5 years to 2 years | 5.59 (10.6) [−15.1, 26.3], p = 0.751 | 0.12 [−0.33, 0.57] |
| THI Category | Baseline | 1 Year | 1.5 Years | 2 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No tinnitus | 32.6% | 45.7% | 47.8% | 50.0% |
| Slight | 17.4% | 37.0% | 32.6% | 28.3% |
| Mild | 10.9% | 13.0% | 2.2% | 6.5% |
| Moderate | 2.2% | 2.2% | 4.3% | 4.3% |
| Severe | 2.2% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 2.2% |
| Catastrophic | 0.0% | 2.2% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baungaard, L.H.; Sandvej, M.G.; Nellemose, M.M.O.; Hestbæk, M.K.; Brændgaard, L.B.; Hansen, M.S.; Jørgensen, M.L.; Cayé-Thomasen, P.; Percy-Smith, L. Longitudinal Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Danish Adults: Changes in Speech Recognition, Self-Reported Hearing Ability, Hearing-Related Quality of Life, and Tinnitus. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176124
Baungaard LH, Sandvej MG, Nellemose MMO, Hestbæk MK, Brændgaard LB, Hansen MS, Jørgensen ML, Cayé-Thomasen P, Percy-Smith L. Longitudinal Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Danish Adults: Changes in Speech Recognition, Self-Reported Hearing Ability, Hearing-Related Quality of Life, and Tinnitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176124
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaungaard, Line Husted, Matilde Grønborg Sandvej, Mathilde Marie Overmark Nellemose, Marianne Kyhne Hestbæk, Louise Brasen Brændgaard, Mie Stenner Hansen, Mie Lærkegård Jørgensen, Per Cayé-Thomasen, and Lone Percy-Smith. 2025. "Longitudinal Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Danish Adults: Changes in Speech Recognition, Self-Reported Hearing Ability, Hearing-Related Quality of Life, and Tinnitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176124
APA StyleBaungaard, L. H., Sandvej, M. G., Nellemose, M. M. O., Hestbæk, M. K., Brændgaard, L. B., Hansen, M. S., Jørgensen, M. L., Cayé-Thomasen, P., & Percy-Smith, L. (2025). Longitudinal Cochlear Implant Outcomes in Danish Adults: Changes in Speech Recognition, Self-Reported Hearing Ability, Hearing-Related Quality of Life, and Tinnitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176124








