Decoding the Inflammatory Pathway in Heart Failure: The Role of Interleukins and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Disease Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Data Collection and Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of HF Patients and Control Groups
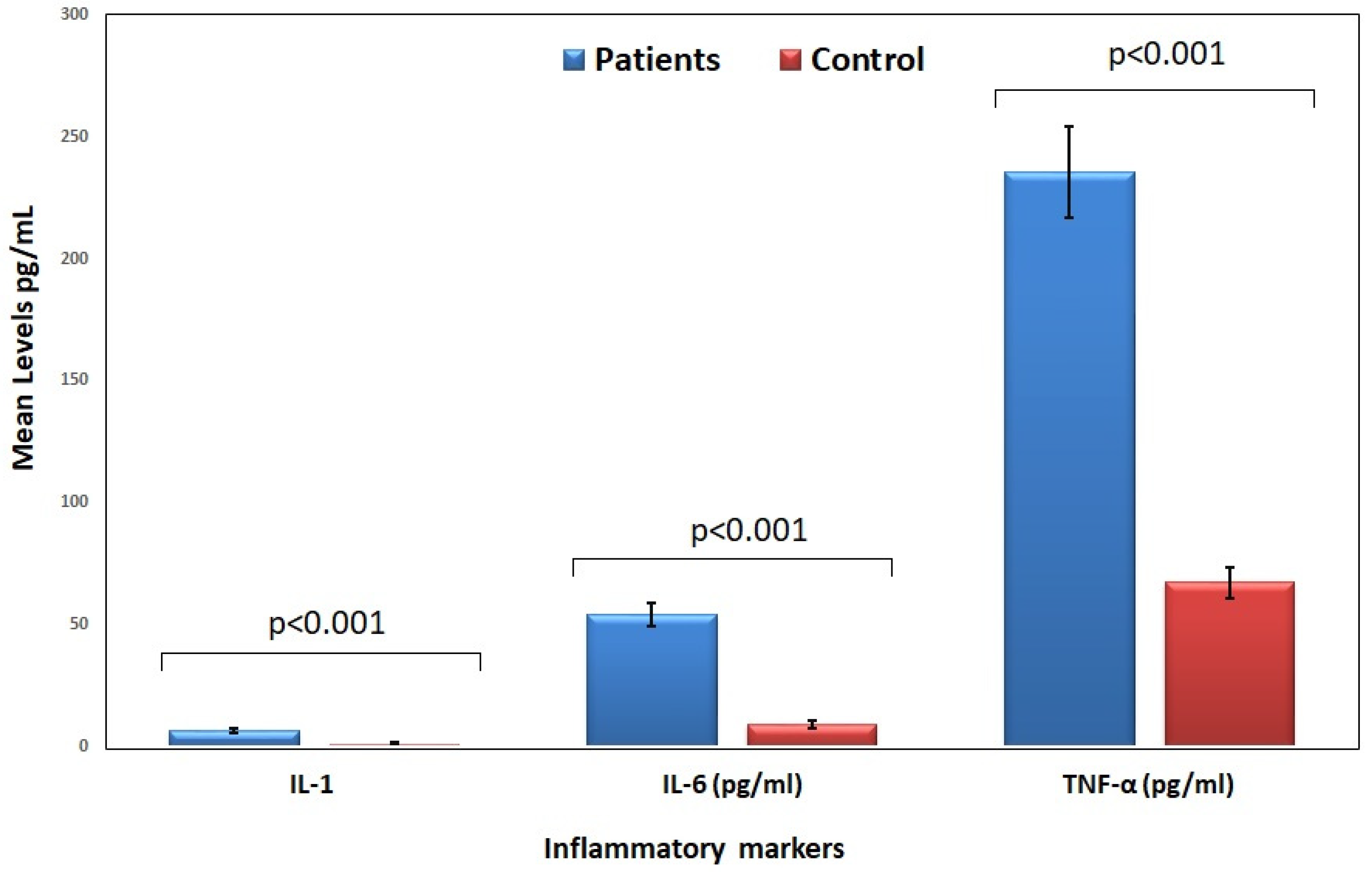
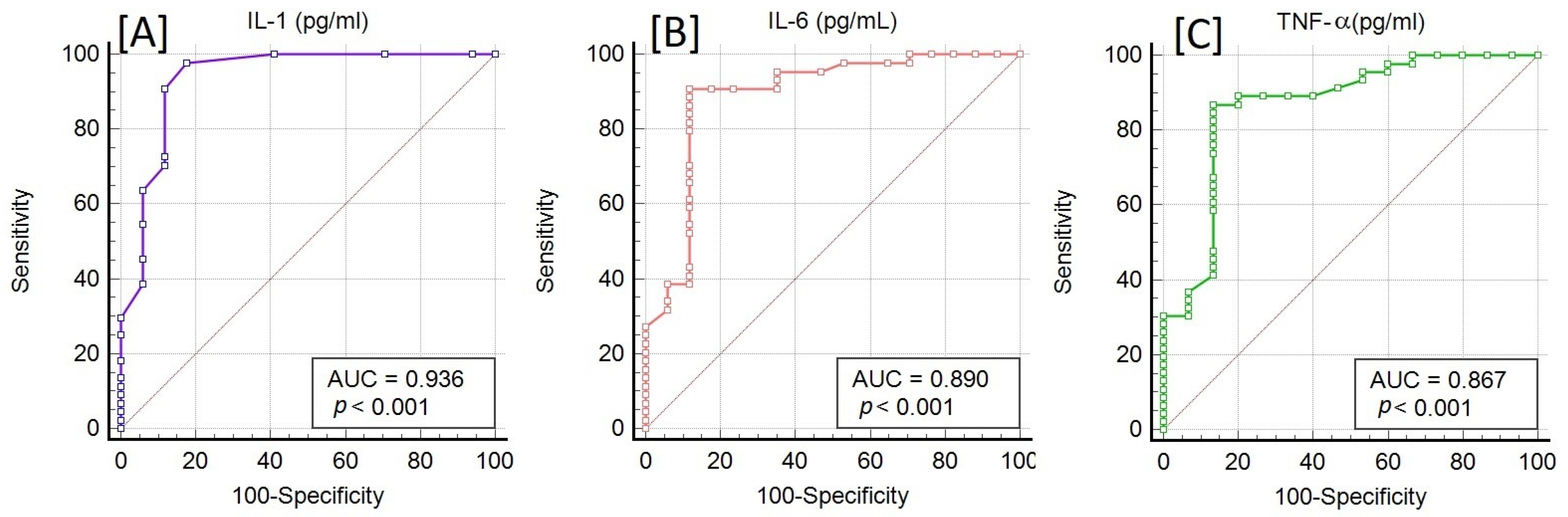
3.3. Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Patients and Control Groups
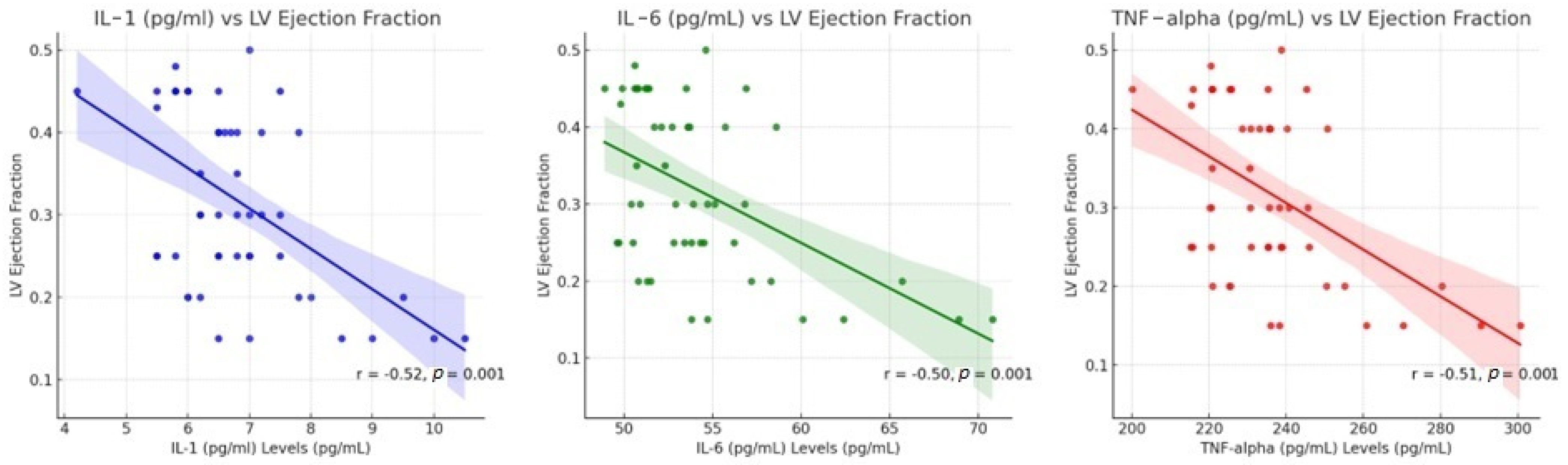
3.4. Correlation Between Inflammatory Cytokine Markers and LV Ejection in HF Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savarese, G.; Becher, P.M.; Lund, L.H.; Seferovic, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Coats, A.J.S. Global Burden of Heart Failure: A Comprehensive and Updated Review of Epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapna, F.N.U.; Raveena, F.N.U.; Chandio, M.; Bai, K.; Sayyar, M.; Varrassi, G.; Khatri, M.; Kumar, S.; Mohamad, T. Advancements in Heart Failure Management: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Emerging Therapies. Cureus 2023, 15, e46486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Sharma, K.; Shah, S.J.; Ho, J.E. Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: JACC Scientific Statement. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1810–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C. A Novel Paradigm for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines as Therapeutic Targets in Heart Failure. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2020, 34, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Pepine, D.; Serban, A.M.; Capras, R.-D.; Cismaru, C.M.; Filip, A.G. A Comprehensive Review: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in the Etiology of Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2025, 30, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, J.G.; Kamal, F.A.; Robbins, J.; Yutzey, K.E.; Blaxall, B.C. Cardiac Fibrosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1021–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, S.D.; von Haehling, S. Inflammatory Mediators in Chronic Heart Failure: An Overview. Heart 2004, 90, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Hakim, M.L.; Ahammed, M.S.; Kabir, A.; Sultana, F. Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120965752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, M.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The Role of IL-1 in the Pathogenesis of Heart Disease. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2009, 57, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafree, E.; Del Buono, M.G.; Canada, J.M.; Carbone, S.; Kron, J.; Arena, R.; Van Tassell, B.; Abbate, A.; Trankle, C.R. Interleukin-1 Inhibition for the Prevention and Treatment of Heart Failure. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2024, 83, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Fuseler, J.W.; Intwala, A.R.; Baudino, T.A. IL-6 Loss Causes Ventricular Dysfunction, Fibrosis, Reduced Capillary Density, and Dramatically Alters the Cell Populations of the Developing and Adult Heart. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2009, 296, H1694–H1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Tromp, J.; Ouwerkerk, W.; Devalaraja, M.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.; Dickstein, K.; Filippatos, G.S.; van der Harst, P.; Lang, C.C.; et al. The Clinical Significance of Interleukin-6 in Heart Failure: Results from the BIOSTAT-CHF Study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre-Amione, G.; Kapadia, S.; Lee, J.; Durand, J.-B.; Bies, R.D.; Young, J.B.; Mann, D.L. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors in the Failing Human Heart. Circulation 1996, 93, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putko, B.N.; Wang, Z.; Lo, J.; Anderson, T.; Becher, H.; Dyck, J.R.B.; Kassiri, Z.; Oudit, G.Y.; on behalf of the Alberta HEART Investigators. Circulating Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Receptor 2 Are Increased in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Relative to Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: Evidence for a Divergence in Pathophysiology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, J.; Sridhar, V.S.; Bouabdallaoui, N.; Tardif, J.-C.; White, M. Inflammation in Heart Failure: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 73, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibbs, Z.; Thornby, J.; White, B.G.; Mann, D.L. Natural Variability of Circulating Levels of Cytokines and Cytokine Receptors in Patients with Heart Failure: Implications for Clinical Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, L.F.; Abbate, A. Interleukin-1 Blockade in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Clinical Update. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, L.; Jackson, C.E.; Adamson, C.; McConnachie, A.; Welsh, P.; Myles, R.C.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Jhund, P.S.; Petrie, M.C.; Lang, N.N. Adverse Outcomes Associated with Interleukin-6 in Patients Recently Hospitalized for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circ. Heart Fail. 2023, 16, e010051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, D.N.; Boldeanu, M.-V.; Șerban, R.-E.; Florescu, L.M.; Serbanescu, M.-S.; Ionescu, M.; Streba, L.; Constantin, C.; Vere, C.C. Correlation of the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, Inflammatory Markers, and Tumor Markers with the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Life 2023, 13, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamura, M.; D’Andrea, G.; Angelini, E.; Tortorelli, F.M.P.; Balzotti, A.; Porcelli, P.; Margaglione, M.; Brunetti, N.D.; Cassano, T.; Bellomo, A. Psychosomatic Syndromes Are Associated with IL-6 pro-Inflammatory Cytokine in Heart Failure Patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavishi, A.; Patel, R.B. Addressing Comorbidities in Heart Failure: Hypertension, Atrial Fibrillation, and Diabetes. Heart Fail. Clin. 2020, 16, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.-H.; Kang, S.-M. Blood Pressure and Heart Failure: Focused on Treatment. Clin. Hypertens. 2024, 30, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, T.G. Heart Failure and Hypertension: The Diastolic Dilemma. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2004, 6, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, E.C.; Vázquez-Garza, E.; Yee-Trejo, D.; García-Rivas, G.; Torre-Amione, G. What Is the Role of the Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Heart Failure? Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-W.; Qian, J.-Y.; Ma, J.-Y.; Chang, S.-F.; Yun, H.; Jin, H.; Sun, A.-J.; Zou, Y.-Z.; Ge, J.-B. TNF-α-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis Contributes to Cardiac Dysfunction after Coronary Microembolization in Mini-Pigs. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Chen, M.; Dawood, F.; Zurawska, U.; Li, J.Y.; Parker, T.; Kassiri, Z.; Kirshenbaum, L.A.; Arnold, M.; Khokha, R.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Mediates Cardiac Remodeling and Ventricular Dysfunction After Pressure Overload State. Circulation 2007, 115, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.-H.; Luo, M.-Y.; Liang, N.; Gong, S.-X.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.-Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, A.-P. Interleukin-6: A Novel Target for Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 745061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dhalla, N.S. The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Q.; Park, A.C.; Liu, J.; Byrnes, K.; Javaheri, A.; Mann, D.L.; Schilling, J.D. Distinct Inflammatory Milieu in Patients with Right Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2023, 16, e010478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perticone, M.; Zito, R.; Miceli, S.; Pinto, A.; Suraci, E.; Greco, M.; Gigliotti, S.; Hribal, M.L.; Corrao, S.; Sesti, G.; et al. Immunity, Inflammation and Heart Failure: Their Role on Cardiac Function and Iron Status. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kažukauskienė, I.; Baltrūnienė, V.; Rinkūnaitė, I.; Žurauskas, E.; Vitkus, D.; Maneikienė, V.V.; Ručinskas, K.; Grabauskienė, V. Inflammation-Related Biomarkers Are Associated with Heart Failure Severity and Poor Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Non-Ischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Life 2021, 11, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaabi, M.A.; Abdelsalam, A.; Alhammadi, M.; Hani, H.B.; Almheiri, A.; Al Matrooshi, N.; Al Zaman, K. Evaluating Biomarkers as Tools for Early Detection and Prognosis of Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Review. Card. Fail. Rev. 2024, 10, e06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Carvajal, A.J.; De Sanctis, J.B.; Dayer, M.; Martí-Amarista, C.E.; Alegría, E.; Monge Martín, D.; Abd El Aziz, M.; Correa-Pérez, A.; Nicola, S.; Parise Vasco, J.M. Interleukin-receptor Antagonist and Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors for the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 9, CD014741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.M.; Whellan, D.J.; Lee, K.L.; Keteyian, S.J.; Cooper, L.S.; Ellis, S.J.; Leifer, E.S.; Kraus, W.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; Blumenthal, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Exercise Training in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: HF-ACTION Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymans, S.; Hirsch, E.; Anker, S.D.; Aukrust, P.; Balligand, J.-L.; Cohen-Tervaert, J.W.; Drexler, H.; Filippatos, G.; Felix, S.B.; Gullestad, L.; et al. Inflammation as a Therapeutic Target in Heart Failure? A Scientific Statement from the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglione, V.; Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Saccaro, L.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2022, 27, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Category | Patients (%) | Controls (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 45 | Yes | 83.6% | 78.5% | 0.36 |
| No | 16.4% | 21.5% | ||
| DM | Yes | 52.4% | 58.5% | 0.27 |
| No | 47.6% | 41.5% | ||
| HTN | Yes | 49.2% | 47.7% | 0.23 |
| No | 50.8% | 53.3% | ||
| Male gender | Yes | 67.2% | 70.8% | 0.17 |
| No | 32.8% | 29.2% | ||
| Smoking | Yes | 25.6% | 30.8% | 0.25 |
| No | 74.4% | 69.2% | ||
| BMI > 30 | Yes | 26.2% | 29.2% | 0.32 |
| No | 73.8% | 70.8% |
| Variable | Patients (Mean ± SE) | Control (Mean ± SE) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 116.94 ± 13.61 | 118.04 ± 11.98 | 0.915 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) HbA1c (%) | 68.73 ± 8.80 7.59 ± 2.71 | 77.95 ± 10.70 6.89 ± 2.15 | <0.001 0.38 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.04 ± 0.36 | 1.17 ± 0.11 | 0.09 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.33 ± 0.72 | 1.84 ± 0.65 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) Troponin I (ng/mL) | 1.39 ± 0.71 0.15 ± 0.02 | 1.27 ± 0.93 - | 0.036 N/A |
| Variable | Patients (Mean ± SE) | Control (Mean ± SE) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 (pg/mL) | 6.77 ± 1.17 | 1.27 ± 0.42 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 54.12 ± 4.64 | 9.29 ± 1.72 | <0.001 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 235.56 ± 18.88 | 67.37 ± 6.28 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 (pg/mL) | 2.35 | 1.45–3.81 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 1.87 | 1.12–3.14 | <0.001 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 2.92 | 1.76–4.89 | <0.001 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 1.48 | 1.03–2.12 | 0.034 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 0.82 | 0.69–0.98 | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.A.; Ismail, H.M.; Alahmedi, A.B.; Alahmadi, F.B.; Muhawish, A.F.; Alsubhi, A.A.; Almohammadi, Y.S.; Alwusaidi, A.K.; Alsaedi, A.S.; Alhazmi, T.G.; et al. Decoding the Inflammatory Pathway in Heart Failure: The Role of Interleukins and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6092. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176092
Ahmed SA, Ismail HM, Alahmedi AB, Alahmadi FB, Muhawish AF, Alsubhi AA, Almohammadi YS, Alwusaidi AK, Alsaedi AS, Alhazmi TG, et al. Decoding the Inflammatory Pathway in Heart Failure: The Role of Interleukins and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Disease Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):6092. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176092
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Sameh A., Hussein M. Ismail, Ahmed B. Alahmedi, Faisal B. Alahmadi, Abdulaziz F. Muhawish, Abed A. Alsubhi, Yazeed S. Almohammadi, Abdulrahman K. Alwusaidi, Abdullah S. Alsaedi, Tariq G. Alhazmi, and et al. 2025. "Decoding the Inflammatory Pathway in Heart Failure: The Role of Interleukins and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Disease Severity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 6092. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176092
APA StyleAhmed, S. A., Ismail, H. M., Alahmedi, A. B., Alahmadi, F. B., Muhawish, A. F., Alsubhi, A. A., Almohammadi, Y. S., Alwusaidi, A. K., Alsaedi, A. S., Alhazmi, T. G., & Busra, M. N. (2025). Decoding the Inflammatory Pathway in Heart Failure: The Role of Interleukins and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Disease Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 6092. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14176092







