Continuous Flumazenil Infusion and Time to Consciousness Recovery in Benzodiazepine Poisoning: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
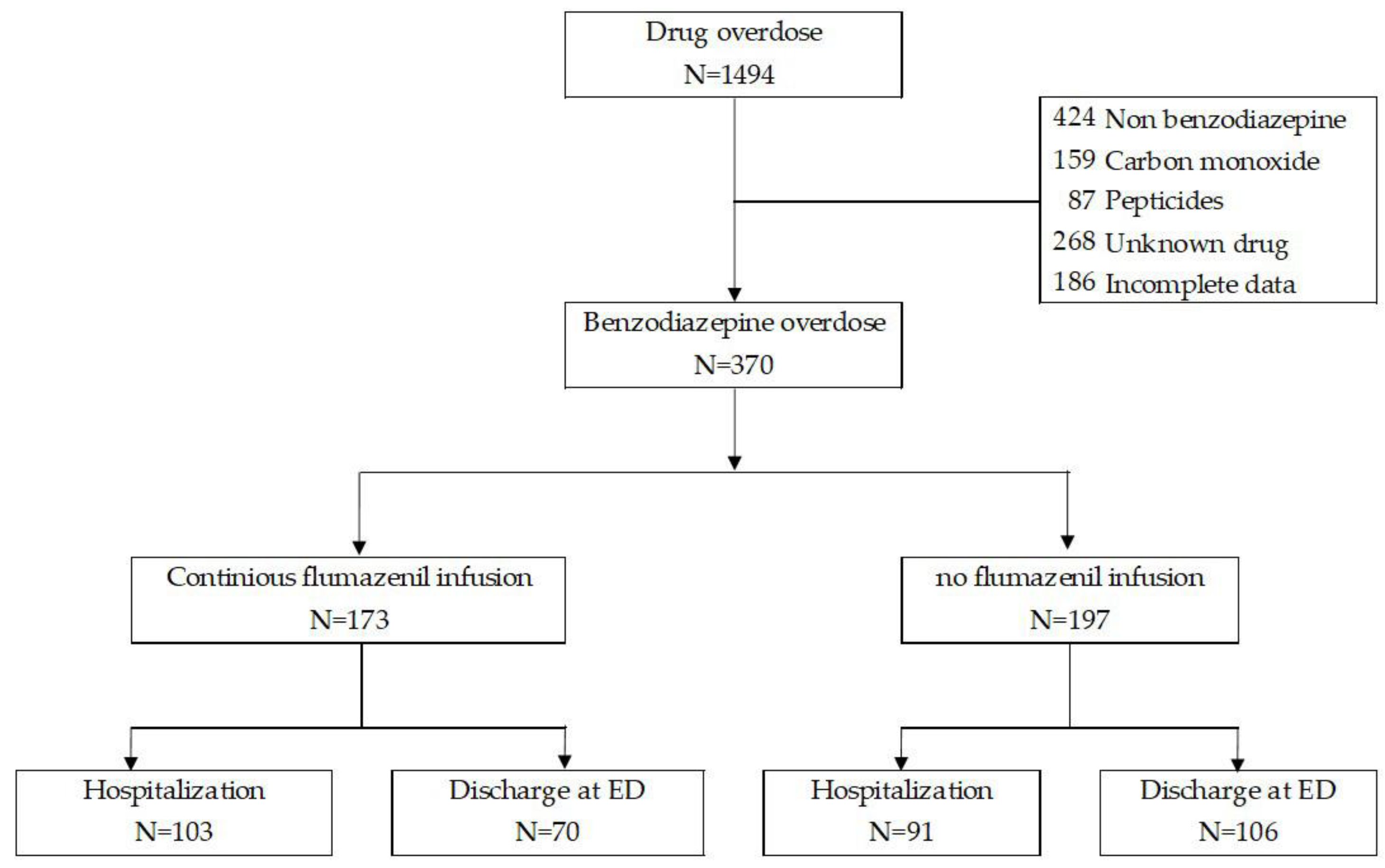
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Overdose and Treatment
2.5. Outcome Variables
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes with Flumazenil Infusion
3.3. Time to Regain Consciousness Analysis
3.4. Factors Associated with Time to Consciousness Recovery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bushnell, G.A.; Rynn, M.A.; Gerhard, T.; Keyes, K.M.; Hasin, D.S.; Cerda, M.; Nyandege, A.; Olfson, M. Drug overdose risk with benzodiazepine treatment in young adults: Comparative analysis in privately and publicly insured individuals. Addiction 2024, 119, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, I.; He, M.; Brooks, M.M.; Zhang, Y. Exposure-Response Association Between Concurrent Opioid and Benzodiazepine Use and Risk of Opioid-Related Overdose in Medicare Part D Beneficiaries. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, R.A.; Weiss, R.D. Benzodiazepine-Involved Overdose Deaths in the USA: 2000–2019. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.F.; Liaw, V.; Yu, X.; Raji, M.A. Opioid and Benzodiazepine Substitutes: Impact on Drug Overdose Mortality in Medicare Population. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, e194–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Spence, M.M.; Niu, F.; Hui, R.L.; Gray, P.; Steinberg, S. Risk of Overdose with Exposure to Prescription Opioids, Benzodiazepines, and Non-benzodiazepine Sedative-Hypnotics in Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carillo, N.J.; Golden, L.; Saraghi, M. Flumazenil: A review and implications for benzodiazepine overdose. Gen. Dent. 2020, 68, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; Godwin, J. Flumazenil in benzodiazepine overdose. CMAJ 2016, 188, E537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Mohan, C.; Aggarwal, P.; Handa, R.; Wali, J.P. Flumazenil in acute benzodiazepine overdose. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2002, 50, 1097–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, J.S.; Donald, C.; Lewin, K. Use of Flumazenil in benzodiazepine overdose. Emerg. Med. J. 2006, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veiraiah, A.; Dyas, J.; Cooper, G.; Routledge, P.A.; Thompson, J.P. Flumazenil use in benzodiazepine overdose in the UK: A retrospective survey of NPIS data. Emerg. Med. J. 2012, 29, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.J.; Cao, Y.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Yu, G.; Su, R.B. Flumazenil-Insensitive Benzodiazepine Effects in Recombinant alphabeta and Neuronal GABA(A) Receptors. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloos, J.M.; Lim Cow, C.Y.S.; Bocquet, V. Benzodiazepine high-doses: The need for an accurate definition. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 30, e1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojer, J.; Baehrendtz, S.; Magnusson, A.; Gustafsson, L.L. A placebo-controlled trial of flumazenil given by continuous infusion in severe benzodiazepine overdosage. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1991, 35, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volney, G.S.; Scatena, R. Continuous Intravenous Flumazenil Infusion Used in Iatrogenic Chlordiazepoxide Overdose in the Setting of Alcoholic Withdrawal Syndrome Management. Cureus 2020, 12, e10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Halawani, M.; Sen, P.; Abdeen, Y.; Shaaban, H.; Klukowicz, A.J.; Miller, R.A. Continuous intravenous flumazenil infusion in a patient with chlordiazepoxide toxicity and hepatic encephalopathy. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock 2015, 8, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brammer, G.; Gibly, R.; Walter, F.G.; Bey, T.; Torres, R.; Kohler, S. Continuous intravenous flumazenil infusion for benzodiazepine poisoning. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2000, 42, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Tikhonov, D.; Buldakova, S. Effect of flumazenil on GABAA receptors in isolated rat hippocampal neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C.H.; Chern, T.L.; Wang, L.M.; Hu, S.C.; Deng, J.F.; Lee, C.H. Continuous flumazenil infusion in preventing complications arising from severe benzodiazepine intoxication. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1998, 16, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninga, E.I.; Graudal, N.; Ladekarl, M.B.; Jurgens, G. Adverse Events Associated with Flumazenil Treatment for the Management of Suspected Benzodiazepine Intoxication—A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses of Randomised Trials. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 118, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, H.; So, B.; Lee, W.; Kim, S. Clinical Use of Flumazenil in the Emergency Department for Suspected Benzodiazepine Overdose. J. Korean Soc. Emerg. Med. 2003, 14, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Chang, C.I.; Huang, H.H.; Yen, D.H. Clinical Predictors for Intensive Care Unit Admission in Patients with Benzodiazepines Poisoning in the Emergency Department. J. Acute Med. 2018, 8, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; O’Regan, L.; Sibbritt, D.; Whyte, I.M. Alprazolam is relatively more toxic than other benzodiazepines in overdose. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 58, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thumtecho, S.; Wainipitapong, S.; Chunamchai, S.; Suteparuk, S. Alprazolam and lorazepam overdose and the absence of brainstem reflexes. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e248796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, M.; Smith, G.; Sharma, S.; Nielssen, O.; Singh, S.P. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical factors associated with the suicide of psychiatric in-patients. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2011, 124, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, S.Y.; Jang, S.I.; An, S.K.; Park, E.C. Impact of the mental health law revision restricting hospitalization on healthcare utilization in South Korea using interrupted time series analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total Cohort (n = 370) | Hospitalized (n = 194) | Non-Hospitalized (n = 176) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 104 (28.1%) | 55 (28.4%) | 49 (27.8%) | 1.000 |
| Age | 46.0 [29.0; 61.0] | 49.0 [28.0; 66.0] | 45.0 [29.5; 58.5] | 0.158 |
| past NP history | 224 (60.5%) | 127 (65.5%) | 97 (55.1%) | 0.054 |
| Depression | 176 (47.6%) | 99 (51.0%) | 77 (43.8%) | 0.195 |
| Psychotic disorder | 6 (1.6%) | 3 (1.5%) | 3 (1.7%) | 1.000 |
| Other | 91 (24.6%) | 52 (26.8%) | 39 (22.2%) | 0.360 |
| Employed | 69 (18.6%) | 40 (20.6%) | 29 (16.5%) | 0.375 |
| Live with family | 176 (47.6%) | 113 (58.2%) | 63 (35.8%) | <0.001 |
| Drug related | ||||
| Dose (DDD, units) | 11.1 [5.8; 21.0] | 13.1 [7.0; 28.0] | 10.0 [4.0; 20.0] | 0.004 |
| co-injestion drug | 150 (40.5%) | 84 (43.3%) | 66 (37.5%) | 0.304 |
| alcohol co-injestion | 114 (30.8%) | 55 (28.4%) | 59 (33.5%) | 0.335 |
| Reattempt | 111 (30.0%) | 67 (34.5%) | 44 (25.0%) | 0.059 |
| injestion to ED arrival | 1.5 [0.8; 5.1] | 1.6 [0.8; 4.6] | 1.5 [0.8; 5.5] | 0.856 |
| at ED arrival | ||||
| GCS | 13.0 [9.0; 13.0] | 11.0 [8.0; 13.0] | 13.0 [12.0; 13.0] | <0.001 |
| Severity of conciousness | <0.001 | |||
| GCS ≤ 8 | 84 (22.7%) | 62 (32.0%) | 22 (12.5%) | |
| GCS ≥ 9 and ≤13 | 267 (72.2%) | 122 (62.9%) | 145 (82.4%) | |
| GCS ≥ 14 | 19 (5.1%) | 10 (5.2%) | 9 (5.1%) | |
| Systolic blood pressure | 113.0 [101.0; 129.0] | 110.0 [98.5; 128.0] | 116.0 [104.5; 129.0] | 0.016 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 73.0 [63.0; 84.0] | 71.0 [62.0; 83.0] | 74.5 [64.0; 85.0] | 0.126 |
| Heart rate | 83.0 [72.0; 96.0] | 82.0 [72.0; 94.0] | 83.5 [74.0; 96.5] | 0.607 |
| Respiratory rate | 20.0 [18.0; 20.0] | 20.0 [18.0; 20.0] | 20.0 [18.0; 20.0] | 0.872 |
| Temperature | 36.5 [36.1; 36.9] | 36.5 [36.0; 36.9] | 36.5 [36.2; 36.8] | 0.491 |
| PH | 7.38 [7.35; 7.41] | 7.37 [7.33; 7.40] | 7.39 [7.36; 7.41] | <0.001 |
| PaCO2 | 40 [37; 44] | 41 [37; 45] | 39 [36; 42] | 0.005 |
| PaO2 | 82 [68; 93] | 82 [69; 94] | 81 [65; 92] | 0.305 |
| HCO3− | 23.1 [21.3; 24.9] | 23.1 [21.2; 24.9] | 23.1 [21.6; 24.9] | 0.716 |
| Saturation | 95.9 [93.4; 97.1] | 95.8 [93.5; 97.2] | 96.0 [92.4; 97.0] | 0.704 |
| ED management | ||||
| Charcoal | 64 (17.3%) | 33 (17.0%) | 31 (17.6%) | 0.988 |
| Intubation | 50 (13.5%) | 38 (19.6%) | 12 (6.8%) | 0.001 |
| Inotropics | 33 (8.9%) | 28 (14.4%) | 5 (2.8%) | <0.001 |
| Flumazenil | 289 (78.1%) | 148 (76.3%) | 141 (80.1%) | 0.374 |
| Continuous infusion | 173 (46.8%) | 103 (53.1%) | 70 (39.8%) | 0.014 |
| Dose, mg | 1.0 [0.3; 3.0] | 2.5 [0.5; 8.0] | 0.6 [0.3; 1.5] | <0.001 |
| Duration, hours | 13.0 [7.2; 24.0] | 21.0 [12.5; 26.0] | 6.9 [4.2; 11.3] | <0.001 |
| Flumazenil Infusion (n = 173) | No Infusion (n = 197) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time interval | |||
| injestion to ED arrival | 1.6 [0.8; 4.5] | 1.5 [0.8; 5.8] | 0.449 |
| injestion to regain consciousness | 11.2 [5.7; 23.1] | 14.0 [5.9; 25.5] | 0.305 |
| ED arrival to regain consciousness | 8.0 [2.8; 18.4] | 8.4 [3.4; 19.4] | 0.375 |
| Adverse events related flumazenil | 77 (44.5%) | 42 (21.3%) | <0.001 |
| Seizure | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.5%) | 1.000 |
| Tachycardia | 34 (19.7%) | 29 (14.7%) | 0.262 |
| Aggressiveness or agitation | 54 (31.2%) | 13 (6.6%) | <0.001 |
| Pneumonia | 28 (16.2%) | 24 (12.2%) | 0.339 |
| Intubation required | 24 (13.9%) | 26 (13.2%) | 0.970 |
| Inotropics | 13 (7.5%) | 20 (10.2%) | 0.481 |
| ED length of stay | 5.7 [3.5; 8.6] | 5.2 [3.2; 8.9] | 0.610 |
| Hospital days | 2.0 [1.0; 3.0] | 1.0 [1.0; 3.0] | 0.019 |
| Hospitalized | 103 (59.5%) | 91 (46.2%) | 0.014 |
| Mortality | 2 (1.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.422 |
| Q1 (0.1~3.1) | Q2 (3.2~8.2) | Q3 (8.3~19.1) | Q4 (19.2~111.6) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 92) | (n = 93) | (n = 93) | (n = 92) | ||
| Time to Regain Consciousness, mean | 1.4 | 5.3 | 12.8 | 37.5 | |
| male | 28 (30.4%) | 20 (21.5%) | 28 (30.1%) | 28 (30.4%) | 0.443 |
| Age | 48.0 [29.0; 59.5] | 45.0 [30.0; 61.0] | 43.0 [30.0; 57.0] | 50.0 [27.0; 72.0] | 0.624 |
| Injestion dose, DDD | 10.0 [5.5; 20.0] | 13.0 [6.0; 25.0] | 10.0 [4.4; 20.0] | 14.0 [8.0; 30.0] | 0.072 |
| injestion to ED arrival | 2.0 [0.9; 5.1] | 1.4 [0.7; 4.3] | 1.4 [0.9; 4.5] | 1.7 [0.8; 7.4] | 0.316 |
| Co-ingestion drug | 39 (42.4%) | 30 (32.3%) | 36 (38.7%) | 45 (48.9%) | 0.134 |
| Co-injestion alcohol | 30 (32.6%) | 29 (31.2%) | 26 (28.0%) | 29 (31.5%) | 0.914 |
| GCS on ED arrival | 13.0 [12.0; 13.0] | 13.0 [10.0; 13.0] | 12.0 [8.0; 13.0] | 11.5 [8.0; 13.0] | 0.002 |
| flumazenil infusion | 48 (52.2%) | 40 (43.0%) | 44 (47.3%) | 41 (44.6%) | 0.615 |
| total dose, mg | 0.6 [0.3; 1.5] | 0.9 [0.3; 1.8] | 2.2 [0.3; 3.8] | 2.5 [0.3; 10.2] | <0.001 |
| total duration, hours | 4.9 [3.2; 12.5] | 9.1 [7.1; 12.2] | 15.7 [13.0; 24.0] | 24.0 [17.0; 30.0] | <0.001 |
| Intubation | 4 (4.3%) | 12 (12.9%) | 14 (15.1%) | 20 (21.7%) | 0.007 |
| Inostorpics | 2 (2.2%) | 4 (4.3%) | 12 (12.9%) | 15 (16.3%) | 0.001 |
| APACHE_II | 6.0 [5.0; 10.0] | 7.0 [4.5; 11.5] | 9.0 [5.5; 13.0] | 8.0 [5.0; 14.0] | 0.505 |
| Pneumonia | 5 (5.4%) | 13 (14.0%) | 11 (11.8%) | 23 (25.0%) | 0.002 |
| PH | 7.39 [7.36; 7.41] | 7.39 [7.36; 7.41] | 7.37 [7.33; 7.40] | 7.38 [7.33; 7.41] | 0.008 |
| PaCO2 | 40 [37; 42] | 9 [36; 42] | 40 [37; 44] | 41 [37; 45] | 0.229 |
| PaO2 | 82 [68; 91] | 81 [70; 95] | 80 [65; 93] | 82 [70; 96] | 0.739 |
| HCO3− | 23.5 [21.9; 25.1] | 23.1 [21.5; 24.6] | 22.5 [21.1; 24.4] | 23.1 [21.3; 25.0] | 0.358 |
| Saturation | 96.0 [93.1; 97.0] | 95.8 [93.8; 97.2] | 95.7 [91.4; 96.9] | 95.9 [93.5; 97.2] | 0.781 |
| Glucose, mg/dl | 104.0 [95.0; 120.5] | 103.0 [92.0; 123.0] | 107.0 [96.0; 126.0] | 112.5 [100.5; 134.5] | 0.047 |
| Outcomes | |||||
| Adverse events related flumazenil | 24 (26.1%) | 24 (25.8%) | 34 (36.6%) | 37 (40.2%) | 0.077 |
| Seizure | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.387 |
| Tachycardia | 13 (14.1%) | 14 (15.1%) | 20 (21.5%) | 16 (17.4%) | 0.546 |
| Aggressiveness or agitation | 12 (13.0%) | 12 (12.9%) | 16 (17.2%) | 27 (29.3%) | 0.011 |
| Hospitalized | 23 (25.0%) | 26 (28.0%) | 57 (61.3%) | 88 (95.7%) | <0.001 |
| Mortality | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.2%) | 0.108 |
| ED length of stay | 3.2 [2.2; 4.9] | 6.0 [4.7; 7.6] | 9.1 [4.4; 12.4] | 5.8 [3.4; 9.1] | <0.001 |
| Hospital days | 1.0 [1.0; 1.0] | 1.0 [1.0; 1.0] | 2.0 [1.0; 3.0] | 4.0 [2.0; 5.0] | <0.001 |
| Total Cohort | Hospitalized | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 95% CI | p | B | 95% CI | p | |
| male | −0.009 | −3.90~3.88 | 0.996 | −0.171 | −6.71~6.37 | 0.959 |
| Age | 0.046 | −0.04~0.13 | 0.314 | 0.044 | −0.10~0.19 | 0.545 |
| GCS on ED arrival | −1.592 | −2.19~−1.00 | <0.001 | −1.063 | −1.96~−0.17 | 0.020 |
| injestion to ED arrival | 0.255 | 0.01~0.50 | 0.038 | 0.354 | −0.03~0.74 | 0.074 |
| Injestion dose, DDD (unit) | 0.099 | 0.01~0.19 | 0.038 | 0.071 | −0.06~0.21 | 0.303 |
| Co-ingestion drug | −3.553 | −7.13~0.02 | 0.051 | −3.604 | −9.55~2.35 | 0.234 |
| Co-ingestion alcohol | 2.071 | −1.59~5.73 | 0.266 | 0.356 | −5.96~6.67 | 0.911 |
| Continuous flumazenil infusion | 1.555 | −1.89~5.00 | 0.375 | 5.406 | −0.63~11.45 | 0.079 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, S.P.; Zhu, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, M.K.; Oh, J.H. Continuous Flumazenil Infusion and Time to Consciousness Recovery in Benzodiazepine Poisoning: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175983
Kim J, Kim SH, Choi SP, Zhu JH, Kim SW, Kwon MK, Oh JH. Continuous Flumazenil Infusion and Time to Consciousness Recovery in Benzodiazepine Poisoning: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175983
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jisu, Soo Hyun Kim, Seung Pill Choi, Jong Ho Zhu, Sung Wook Kim, Mi Kyong Kwon, and Jae Hun Oh. 2025. "Continuous Flumazenil Infusion and Time to Consciousness Recovery in Benzodiazepine Poisoning: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175983
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, S. H., Choi, S. P., Zhu, J. H., Kim, S. W., Kwon, M. K., & Oh, J. H. (2025). Continuous Flumazenil Infusion and Time to Consciousness Recovery in Benzodiazepine Poisoning: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 5983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175983






