Establishing the Clinical Utility of Glucagon-Enhanced MRCP for Improved Hepatopancreatobiliary Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Imaging Technique
2.3. Imaging Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Quantitative Analysis
3.3. Qualitative Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Yam, B.L.; Siegelman, E.S. MR imaging of the biliary system. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 52, 725–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccioni, F.; Martinelli, M.; Al Ansari, N.; Kagarmanova, A.; De Marco, V.; Zippi, M.; Marini, M. Magnetic resonance cholangiography: Past, present and future: A review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 14, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anupindi, S.A.; Victoria, T. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: Techniques and applications. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2008, 16, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Jiang, H.-Y.; Ling, W.-W.; Song, B. Noninvasive imaging of hepatic dysfunction: A state-of-the-art review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rațiu, I.; Lupușoru, R.; Lungeanu, D.; Popescu, A.; Sporea, I.; Goldiș, A.; Dănilă, M.; Miuțescu, B.; Moga, T.; Barbulescu, A.; et al. Diagnosis of malignant biliary obstruction: Pondering over the ERCP, MRCP and histology. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 3000605221076924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, M.A.; Pezzullo, M.; Pace, E.; Morone, M. Benign biliary diseases. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 93, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitellas, K.M.; Keogan, M.T.; Spritzer, C.E.; Nelson, R.C. MR cholangiopancreatography of bile and pancreatic duct abnormalities with emphasis on the single-shot fast spin-echo technique. Radiographics 2000, 20, 939–957; quiz 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlăduţ, C.; Ciocîrlan, M.; Bilous, D.; Șandru, V.; Stan-Ilie, M.; Panic, N.; Becheanu, G.; Jinga, M.; Costache, R.S.; Costache, D.O.; et al. An overview on primary sclerosing cholangitis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenouzi, R.; Welle, C.L.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Schramm, C.; Eaton, J.E. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis-Current State and Future Directions. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, G.C.; Kambadakone, A. MR imaging of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2018, 26, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaizi, A.; Hart, P.A.; Conwell, D.L. Diagnosing Chronic Pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirpal, S.; Chandok, N. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Diagnostic and management challenges. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.H.; Humes, D.J.; Pritchard, S.E.; Marciani, L.; Gowland, P.A.; Simpson, J.; Lobo, D.N. The effects of morphine-neostigmine and secretin provocation on pancreaticobiliary morphology in healthy subjects: A randomized, double-blind crossover study using serial MRCP. World J. Surg. 2011, 35, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröpil, P.; Erhardt, A.; Mehnert, S.; Beck, A.; Häussinger, D.; Mödder, U.; Blondin, D. Image quality and bile duct volumetry in MR cholangiopancreatography augmented with low-dose morphine. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, W171–W175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensson, J.; Zaheer, A.; Conwell, D.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Manfredi, R.; Tirkes, T. Secretin-Enhanced MRCP: How and Why-AJR Expert Panel Narrative Review. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbach, P.; Dewey, M.; Klessen, C.; Stemmer, A.; Ockenga, J.; Huppertz, A.; Sander, B.; Hamm, B.; Taupitz, M. Respiratory-triggered MRCP applying parallel acquisition techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther-Sørensen, M.; Galsgaard, K.D.; Santos, A.; Trammell, S.A.J.; Sulek, K.; Kuhre, R.E.; Pedersen, J.; Andersen, D.B.; Hassing, A.S.; Dall, M.; et al. Glucagon acutely regulates hepatic amino acid catabolism and the effect may be disturbed by steatosis. Mol. Metab. 2020, 42, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branum, G.D.; Bowers, B.A.; Watters, C.R.; Haebig, J.; Cucchiaro, G.; Farouk, M.; Meyers, W.C. Biliary response to glucagon in humans. Ann. Surg. 1991, 213, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Graells, M.; Ronchera-Oms, C.L. Reduction of peristaltic artifacts on magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen: A comparative evaluation of three drugs. Abdom. Imaging 1996, 21, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, J.R.; Smith, E.A.; Khalatbari, S.; Strouse, P.J. I.v. glucagon use in pediatric MR enterography: Effect on image quality, length of examination, and patient tolerance. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.F.; Whitehouse, G.H. Further experience with glucagon enhanced cholangiography. Clin. Radiol. 1980, 31, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, C.A.; Tuxen, P.L.; Bruce, D.L.; Juler, G.L. Glucagon enhancement of cholangiography. A preliminary report. Arch. Surg. 1983, 118, 84–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoe, L.; Gryspeerdt, S.; Vanbeckevoort, D.; De Jaegere, T.; Van Steenbergen, W.; Dewandel, P.; Baert, A.L.; Marchal, G. Normal Vaterian sphincter complex: Evaluation of morphology and contractility with dynamic single-shot MR cholangiopancreatography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1998, 170, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, P.U.; Howlett, D.C.; Sallomi, D.F.; Marchbank, N.D.; Watson, G.M.T.; Marr, A.; Dunk, A.A.; Smith, A.D. Does intravenous glucagon improve common bile duct visualisation during magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography? Results in 42 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2004, 49, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellund, J.C.; Storaas, T.; Gjesdal, K.I.; Klow, N.E.; Geitung, J.T. Magnetic resonance-assisted imaging of slow flow in the pancreatic and common bile duct in healthy volunteers. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.H.; Liang, P.C.; Ho, M.C.; Lee, P.H.; Jaw, F.S.; Peng, S.S.-F. Morphine- and glucagon-augmented magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography to evaluate living liver donors. Liver Transplant. 2009, 15, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

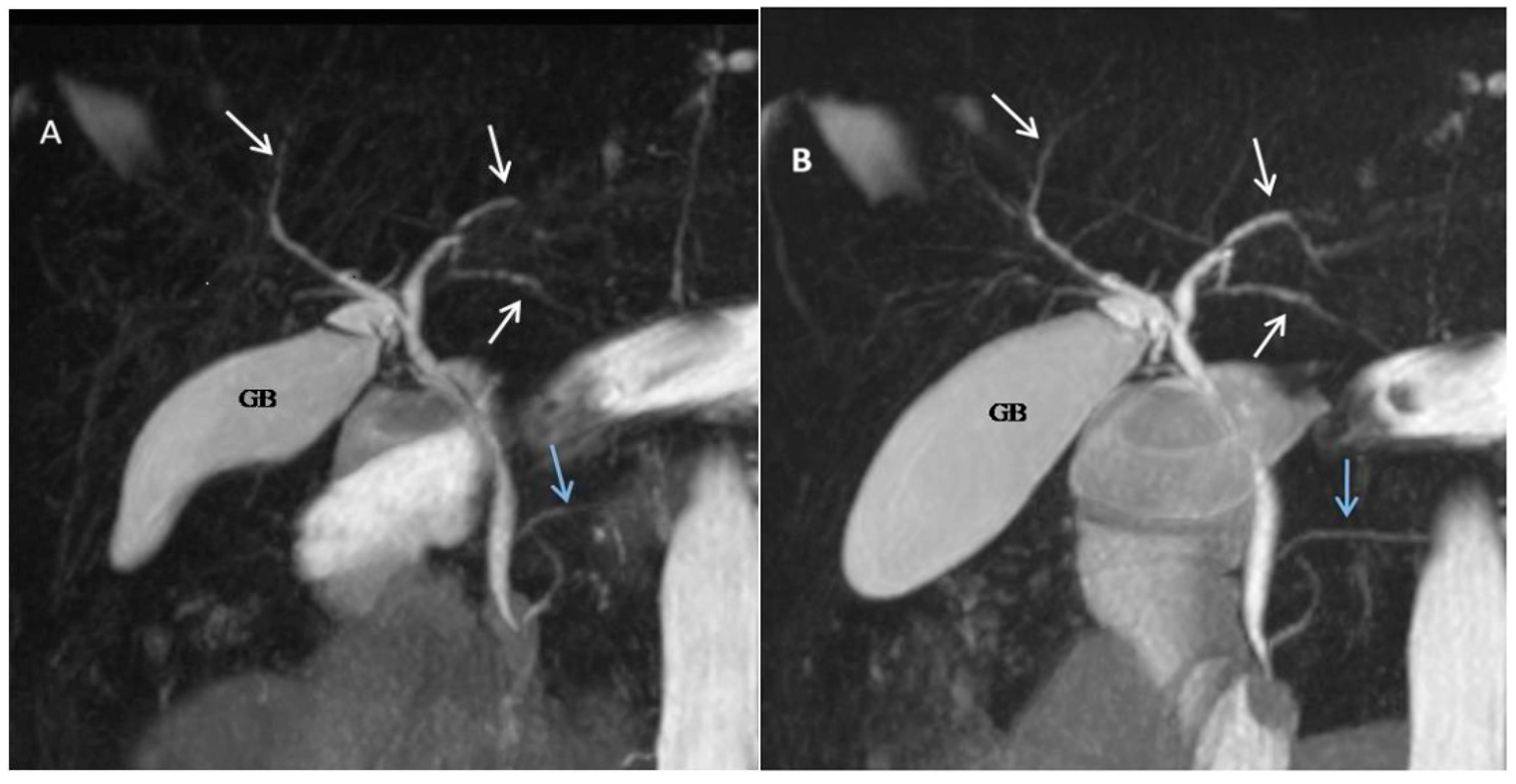
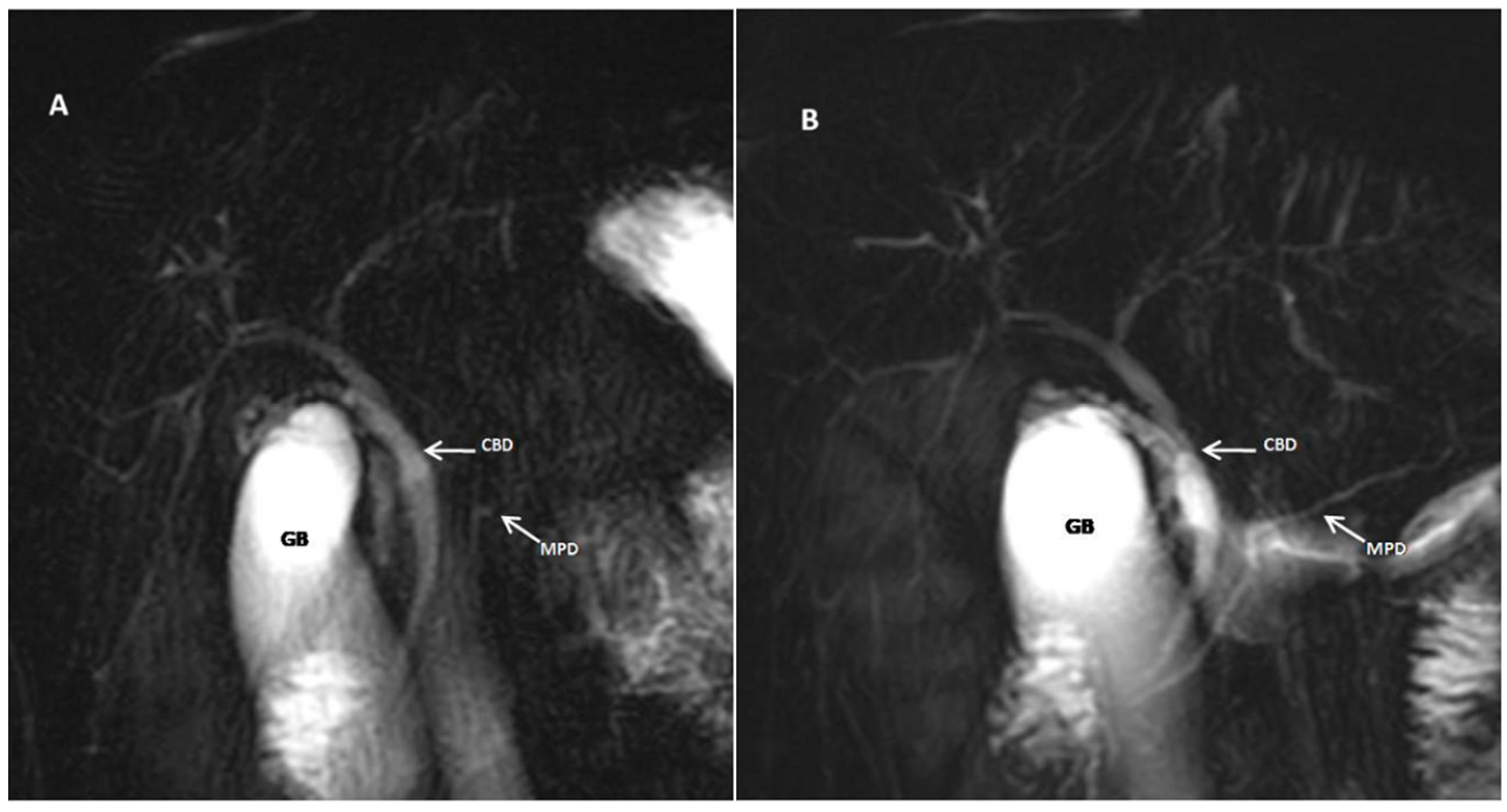
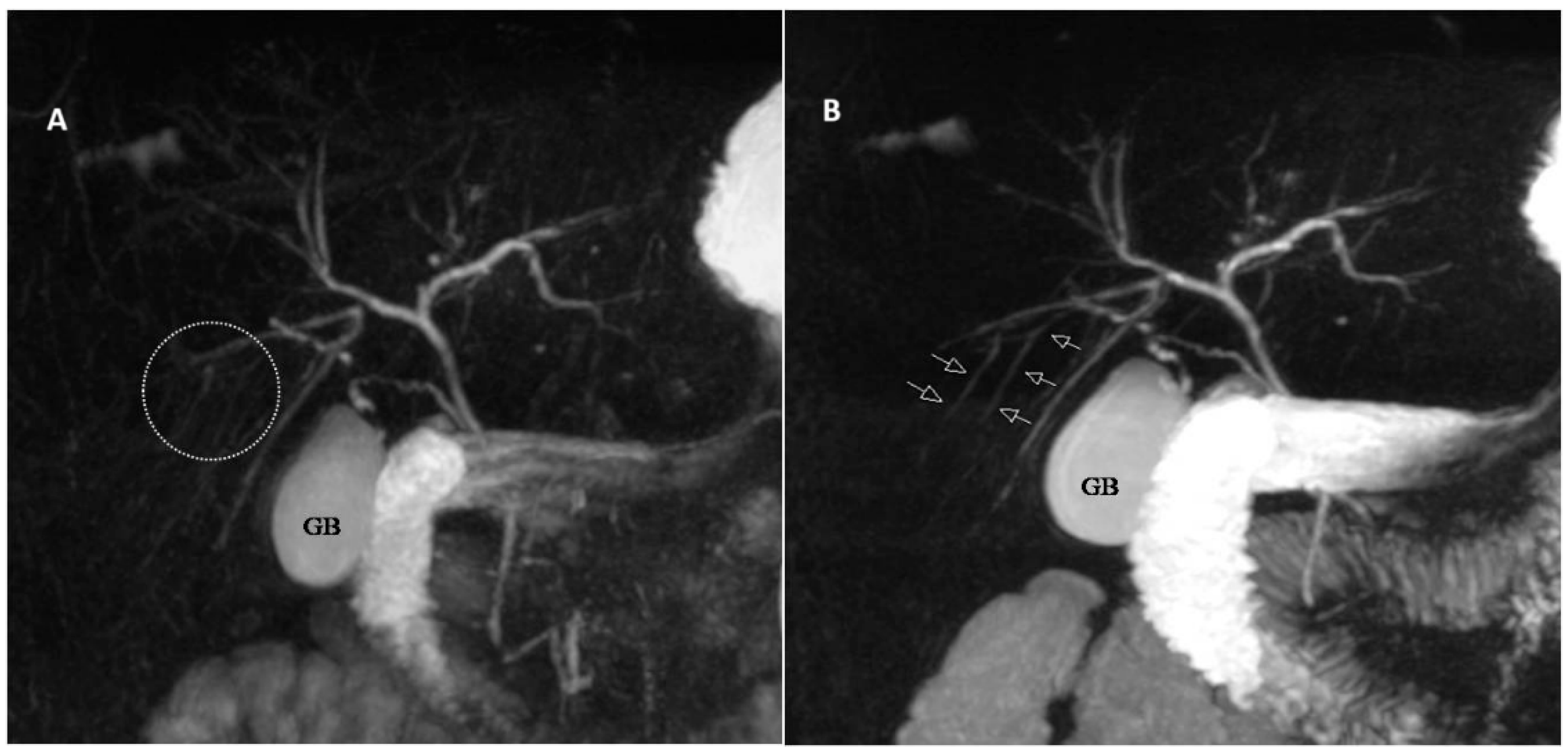
| Score | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Perfect visualization of entire ductal structure |
| 2 | Most of the ductal structure visualized |
| 3 | Ductal structure partially visible |
| 4 | Detection of ductal structure almost impossible |
| 5 | Ductal structure not visible |
| Measurements | Inferior CBD | Mid CBD | Upper CBD/CHD | RHD | LHD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Glucagon Administration | |||||
| Radiologist 1 | 1.17 ± 3.115 | 3.643 ± 1.46 | 3.792 ± 2.25 | 2.262 ± 1.25 | 2.70 ± 1.31 |
| Radiologist 2 | 3.043 ± 1.14 | 3.548 ± 1.45 | 3.680 ± 2.22 | 2.193 ± 1.24 | 2.645 ± 1.30 |
| R ratio | 0.892 | 0.915 | 0.909 | 0.907 | 0.907 |
| ICC | 0.884 [0.879–0.894] | 0.915 [0.911–0.917] | 0.919 [0.918–0.919] | 0.907 [0.904–0.908] | 0.907 [0.904–0.909] |
| Post-Glucagon Administration | |||||
| Radiologist 1 | 3.640 ± 1.07 | 4.270 ± 1.45 | 4.385 ± 1.96 | 2.980 ± 0.94 | 3.435 ± 0.84 |
| Radiologist 2 | 3.602 ± 1.03 | 4.143 ± 1.37 | 4.180 ± 1.84 | 2.927 ± 0.89 | 3.350 ± 0.79 |
| R ratio | 0.989 | 0.995 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.997 |
| ICC | 0.989 [0.979–0.994] | 0.995 [0.991–0.997] | 0.999 [0.998–0.999] | 0.997 [0.994–0.998] | 0.997 [0.994–0.999] |
| Statistical Significance Post- vs. Pre-Glucagon (p value) | |||||
| Radiologist 1 | p = 0.004 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.002 |
| Radiologist 2 | p = 0.009 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.002 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.004 |
| Measurements | Head | Body | Tail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Glucagon Administration | |||
| Radiologist 1 | 0.88 ± 1.698 | 0.99 ± 1.495 | 0.95 ± 0.803 |
| Radiologist 2 | 0.87 ± 1.652 | 0.98 ± 1.435 | 0.93 ± 0.808 |
| R ratio | 0.995 | 0.990 | 0.984 |
| ICC | [0.991–0.997] 0.99 | [0.981–0.995] 0.990 | [0.970–0.991] 0.984 |
| Post-Glucagon Administration | |||
| Radiologist 1 | 0.98 ± 2.423 | 0.72 ± 2.120 | 0.72 ± 1.490 |
| Radiologist 2 | 0.84 ± 2.315 | 0.66 ± 2.007 | 0.71 ± 1.395 |
| R ratio | 0.969 | 0.917 | 0.966 |
| ICC | [0.921–0.977] 0.957 | [0.843–0.953] 0.914 | [0.936–0.982] 0.966 |
| Statistical Significance Post- vs. Pre-Glucagon (p value) | |||
| Radiologist 1 Pre vs. post | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Radiologist 2 Pre vs. post | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Visualization Segments | Inferior CBD | Mid CBD | Upper CBD/CHD | RHD | LHD | Intrahepatic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Glucagon Administration | ||||||
| Radiologist 1 | 2.27 ± 0.68 | 2.40 ± 0.63 | 2.25 ± 0.67 | 2.65 ± 0.80 | 2.55 ± 0.68 | 2.95 ± 0.68 |
| Radiologist 2 | 2.35 ± 0.70 | 2.33 ± 0.66 | 2.23 ± 0.77 | 2.65 ± 0.89 | 2.53 ± 0.82 | 2.83 ± 0.82 |
| R ratio | 0.655 [0.435–0.802] | 0.791 [0.638–0.884] | 0.877 [0.780–0.933] | 0.929 [0.870–0.962] | 0.814 [0.719–0.913] | 0.668 [0.535–0.802] |
| ICC | 0.656 | 0.791 | 0.885 | 0.934 | 0.856 | 0.782 |
| Post-Glucagon Administration | ||||||
| Radiologist 1 | 1.35 ± 0.53 | 1.45 ± 0.55 | 1.48 ± 0.55 | 1.63 ± 0.77 | 1.45 ± 0.55 | 1.83 ± 0.77 |
| Radiologist 2 | 1.38 ± 0.59 | 1.28 ± 0.51 | 1.35 ± 0.53 | 1.55 ± 0.71 | 1.43 ± 0.55 | 1.91 ± 0.71 |
| R ratio | 0.718 | 0.555 | 0.638 | 0.707 | 0.536 | 0.653 |
| ICC | 0.715 [0.522–0.838] | 0.553 [0.295–0.736] | 0.637 [0.409–0.790] | 0.705 [0.507–0.832] | 0.536 [0.274–0.725] | 0.651 [0.396–0.843] |
| Statistical Significance Post- vs. Pre-Glucagon (p value) | ||||||
| Radiologist 1 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Radiologist 2 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Visualization | Head | Body | Tail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiologist 1 | 2.63 ± 0.77 | 3.05 ± 0.75 | 3.47 ± 0.75 |
| Radiologist 2 | 2.68 ± 0.76 | 3.15 ± 0.80 | 3.60 ± 0.74 |
| R ratio | 0.872 | 0.926 | 0.854 |
| ICC | 0.872 [0.771–0.930] | 0.923 [0.860–0.959] | 0.854 [0.740–0.920] |
| Post-Glucagon Administration | |||
| Radiologist 1 | 1.53 ± 0.72 | 1.88 ± 0.76 | 2.48 ± 0.75 |
| Radiologist 2 | 1.60 ± 0.67 | 1.95 ± 0.71 | 2.48 ± 0.72 |
| R ratio | 0.875 | 0.841 | 0.906 |
| ICC | 0.873 [0.773–0.931] | 0.840 [0.717–0.912] | 0.905 [0.827–0.948] |
| Statistical Significance Post- vs. Pre-Glucagon (p value) | |||
| Radiologist 1 Pre vs. post | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Radiologist 2 Pre vs. post | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeina, A.-R.; Shibolet, O.; Garra, M.; Taher, R.; Gal, O.; Oster, M.; Hazzan, R.; Mahamid, A.; Abu Baker, F. Establishing the Clinical Utility of Glucagon-Enhanced MRCP for Improved Hepatopancreatobiliary Assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175962
Zeina A-R, Shibolet O, Garra M, Taher R, Gal O, Oster M, Hazzan R, Mahamid A, Abu Baker F. Establishing the Clinical Utility of Glucagon-Enhanced MRCP for Improved Hepatopancreatobiliary Assessment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175962
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeina, Abdel-Rauf, Oren Shibolet, Mohamed Garra, Randa Taher, Oren Gal, Michael Oster, Rawi Hazzan, Ahmad Mahamid, and Fadi Abu Baker. 2025. "Establishing the Clinical Utility of Glucagon-Enhanced MRCP for Improved Hepatopancreatobiliary Assessment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175962
APA StyleZeina, A.-R., Shibolet, O., Garra, M., Taher, R., Gal, O., Oster, M., Hazzan, R., Mahamid, A., & Abu Baker, F. (2025). Establishing the Clinical Utility of Glucagon-Enhanced MRCP for Improved Hepatopancreatobiliary Assessment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 5962. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175962







