Efficacy of an Endoscopic Device Integrating a Sphincterotome and a Dilation Balloon Catheter for the Treatment of Choledocholithiasis (with Video)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Endpoints
2.3. ERCP
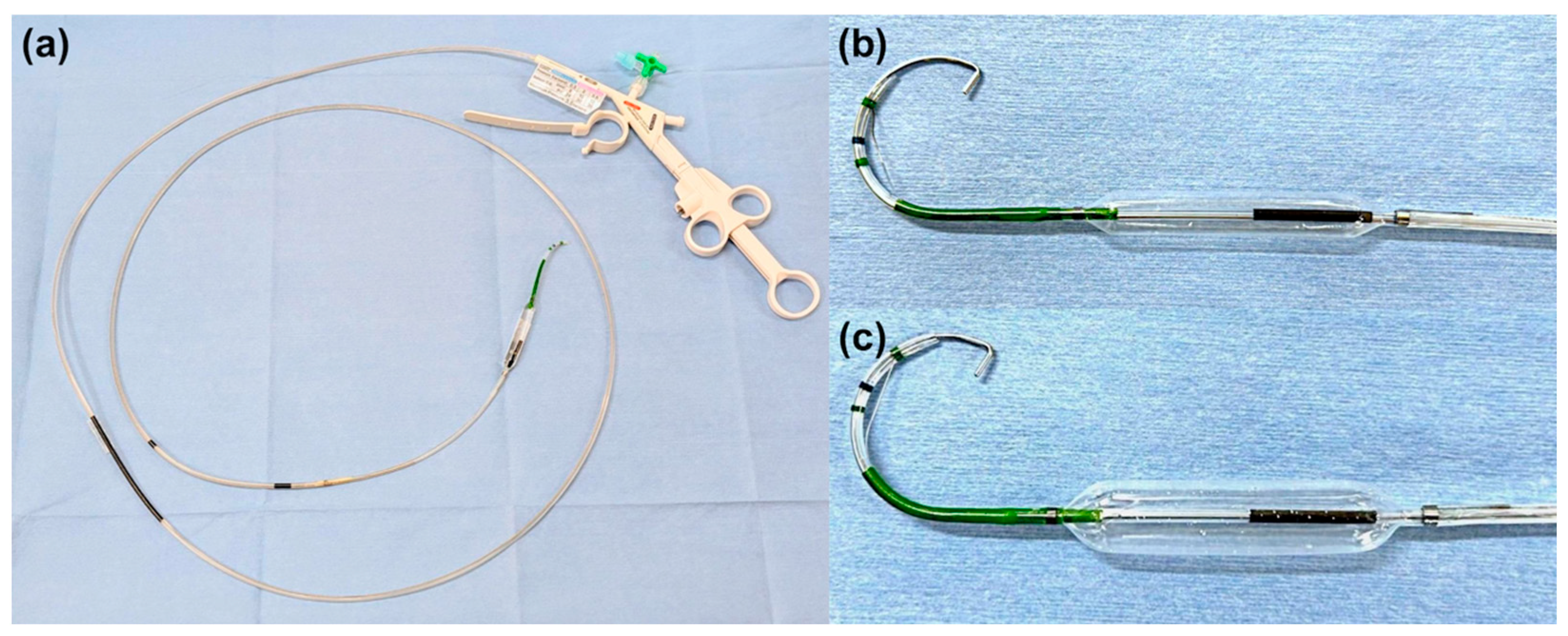
2.4. ESBD and ESLBD
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Impact of the Integrated Device on CBD Stone Removal
3.3. Comparison Based on Stone Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBD | Common bile duct |
| CBDS | Common bile duct stones |
| EML | Endoscopic mechanical lithotripsy |
| EPBD | Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation |
| EPD | Endoscopic papillary dilation |
| EPLBD | Endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation |
| ESBD | Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation |
| ESLBD | Endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation |
| ERCP | Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography |
| EST | Endoscopic sphincterotomy |
| HSE | Hypertonic saline epinephrine solution |
| PEP | Post-ERCP pancreatitis |
References
- Williams, E.; Beckingham, I.; El Sayed, G.; Gurusamy, K.; Sturgess, R.; Webster, G.; Young, T. Updated guideline on the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). Gut 2017, 66, 765–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipahi, S.; Çelik, K.E.K.; Doğan, N.; Mouratidou, T.; Baş, M. Global trends and developments in diet and longevity research: A bibliometric analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, K.; Akasaka, Y.; Murakami, K.; Tada, M.; Kohli, Y.; Nakajima, M. Endoscopic sphincterotomy of the ampulla of vater. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1974, 20, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Kurita, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; Nihei, S.; Iizuka, T.; Misawa, N.; Hosono, K.; Endo, I.; Kobayashi, N.; Kubota, K. Post-endoscopic sphincterotomy delayed bleeding occurs in patients with just 1-day interruption of direct oral anticoagulants or hemodialysis. DEN Open 2025, 5, 70060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plecic, N.; Malenkovic, A.; Begovic, A.; Pavlovic, A.; Bulajic, M.; Bulajic, M.; Đukic, V.; Milanovic, M.; Savic, P.; Panic, N. Management of ERCP-related perforations: A single-center experience. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, I. Can endoscopic papillary balloon dilation really preserve sphincter of oddi function? Gut 2001, 49, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Isayama, H.; Ushio, M.; Takahashi, S.; Yamagata, W.; Takasaki, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Ochiai, K.; Tomishima, K.; Kanazawa, R. Best Procedure for the management of common bile duct stones via the papilla: Literature review and analysis of procedural efficacy and safety. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staritz, M.; Ewe, K.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.-H. Endoscopic papillary dilation (EPD) for the treatment of common bile duct stones and papillary stenosis. Endoscopy 1983, 15, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSario, J.; Freeman, M.L.; Bjorkman, D.; MacMathuna, P.; Petersen, B.; Sherman, S.; Lehman, G.; Hixson, L.; Jaffe, P.; Al-Kawas, F. Endoscopic balloon dilation compared to sphincterotomy (EDES) for extraction of bile duct stones: Preliminary results. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoz, G.; Tekesin, O.; Ozutemiz, A.O.; Gunsar, F. Biliary sphincterotomy plus dilation with a large balloon for bile duct stones that are difficult to extract. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 57, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isayama, H.; Ishii, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Ushio, M.; Takahashi, S.; Yamagata, W.; Takasaki, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Okawa, Y.; Ochiai, K. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of minimal endoscopic sphincterotomy followed by papillary balloon dilation for the removal of common bile duct stones. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoi, T.; Itokawa, F.; Sofuni, A.; Kurihara, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tsuji, S.; Ikeuchi, N.; Moriyasu, F. Endoscopic sphincterotomy combined with large balloon dilation can reduce the procedure time and fluoroscopy time for removal of large bile duct stones. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, B. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation after sphincterotomy for difficult choledocholithiasis: A case-controlled study. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 5, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, H.; Kawahata, S.; Mukai, T.; Doi, S.; Iwashita, T.; Ban, T.; Ito, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Hayashi, T.; Sasahira, N. Multicenter randomized trial of endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation without sphincterotomy versus endoscopic sphincterotomy for removal of bile duct stones: Marvelous trial. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, T.; Sofuni, A.; Itokawa, F.; Kurihara, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tsuji, S.; Ikeuchi, N.; Umeda, J.; Moriyasu, F. New large-diameter balloon-equipped sphincterotome for removal of large bile duct stones (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, F.; Okamoto, K.; Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Asbun, H.J.; Pitt, H.A.; Gomi, H.; Solomkin, J.S.; Schlossberg, D.; Han, H.S. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Initial management of acute biliary infection and flowchart for acute cholangitis. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2018, 25, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, P.B.; Eisen, G.M.; Aabakken, L.; Baron, T.H.; Hutter, M.M.; Jacobson, B.C.; Mergener, K.; Nemcek, A.; Petersen, B.T.; Petrini, J.L. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: Report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J. Endoscopic treatment of difficult extrahepatic bile duct stones, EPBD or EST: An anatomic view. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.; Itoi, T.; Baron, T.H.; Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Pitt, H.A.; Ukai, T.; Shikata, S.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Kim, M. Indications and techniques of biliary drainage for acute cholangitis in updated Tokyo Guidelines 2018. J. Hepatobiliary. Pancreat. Sci. 2017, 24, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, G.; Viazis, N.; Pleskow, D.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Theocharis, L.; Christodoulou, C.; Kotsikoros, N.; Giannousis, J.; Sgouros, S.; Rodias, M. Large balloon dilation vs. mechanical lithotripsy for the management of large bile duct stones: A prospective randomized study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofuni, A.; Maguchi, H.; Mukai, T.; Kawakami, H.; Irisawa, A.; Kubota, K.; Okaniwa, S.; Kikuyama, M.; Kutsumi, H.; Hanada, K. Endoscopic pancreatic duct stents reduce the incidence of post–endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in high-risk patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Maguchi, H.; Komatsu, Y.; Yasuda, I.; Hasebe, O.; Igarashi, Y.; Murakami, A.; Mukai, H.; Fujii, T.; Yamao, K. Endoscopic sphincterotomy and endoscopic papillary balloon dilatation for bile duct stones: A prospective randomized controlled multicenter trial. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2003, 57, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Yokoyama, J.; Shibata, O.; Kojima, Y.; Kawata, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Tominaga, K.; Satoshi, I.; Kazunao, H.; Terai, S. Safety of edoxaban for delayed bleeding in gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures with a high risk of bleeding. DEN Open 2025, 5, 70018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Conventional Group (n = 106) | Integrated Device Group (n = 54) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range), years | 81 (27–95) | 81 (45–98) | 0.51 |
| Sex, male/female, n | 55:51 | 33:21 | 0.32 |
| Performance status score of 0–1, n (%) | 103 (97.2%) | 47 (87.0%) | 0.03 |
| Antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy, n (%) | 29 (27.4%) | 20 (37.0%) | 0.28 |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 35 (33.0%) | 24 (44.4%) | 0.17 |
| History of cerebrovascular disease, n (%) | 15 (14.2%) | 4 (7.4%) | 0.30 |
| Dementia, n (%) | 4 (3.8%) | 4 (7.4%) | 0.44 |
| History of malignant neoplasm, n (%) | 27 (25.5%) | 11 (20.4%) | 0.56 |
| Billroth I reconstruction, n (%) | 4 (3.8%) | 5 (9.3%) | 0.17 |
| Previous history of EST/EPBD/EPLBD | 15 (14.2%) | 3 (5.6%) | 0.12 |
| Periampullary diverticulum, n (%) | 38 (35.8%) | 30 (55.6%) | 0.02 |
| Complications of acute cholangitis, n (%) | 67 (63.2%) | 42 (77.8%) | 0.07 |
| Severity of cholangitis, mild/moderate to severe, n | 27/40 | 20/22 | 0.55 |
| Complication of gallstone pancreatitis, n (%) | 2 (1.9%) | 1 (1.9%) | 1.00 |
| Number of stones, median (range), n | 2 (1–10) | 2 (1–10) | 0.33 |
| Diameter of stones, median (range), mm | 11 (2–24) | 10 (2–32) | 0.66 |
| Diameter of common bile duct, median (range), mm | 12 (5–25) | 11 (6–24) | 0.12 |
| Conventional Group n = 106 | Integrated Device Group n = 54 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESBD (balloon size < 12 mm): ESLBD (balloon size ≥ 12 mm), n | 58:48 | 32:22 | 0.62 |
| Complete stone removal, n (%) | 105 (99.1%) | 54 (100%) | 1.00 |
| Single-stage stone removal, n (%) | 43 (40.6%) | 33 (61.1%) | 0.02 |
| Total number of sessions for complete stone removal, median (range), n | 1 (1–3) | 1 (1–3) | 0.01 |
| Use of mechanical lithotripsy for stone removal | 53 (50.0%) | 12 (22.2%) | <0.01 |
| Total procedure time, median (range), minutes | 40 (10–119) | 27 (12–67) | 0.01 |
| Time required for selective biliary cannulation, median (range), minutes | 4 (1–87) | 3 (1–31) | 0.06 |
| Rectal diclofenac administration before procedure | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.00 |
| Pancreatic guidewire method for selective biliary cannulation | 16 (15.1%) | 6 (11.1%) | 0.63 |
| Pancreatic stent placement | 4 (3.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.31 |
| Pre-cutting for selective biliary cannulation | 2 (1.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.55 |
| Length of hospital stay, median (range), days | 12 (3–58) | 8 (2–30) | 0.02 |
| Conventional Group (n = 106) | Integrated Device Group (n = 54) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse events, n (%) | 13 (12.3%) | 7 (13.0%) | 1.00 |
| Pancreatitis, n (%) | 3 (2.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0.55 |
| Bleeding, n (%) | 6 (5.7%) | 3 (5.6%) | 1.00 |
| Perforation, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Bile leakage, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Cholecystitis, n (%) | 1 (0.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Cholangitis, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (3.7%) | 0.11 |
| Deterioration of respiratory condition, n (%) | 2 (1.9%) | 2 (3.7%) | 0.60 |
| Aspiration pneumonia, n (%) | 2 (1.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0.55 |
| Immediate Bleeding | Delayed Bleeding | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Group | Integrated Device Group | Conventional Group | Integrated Device Group | |
| Patients, n | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Mild/moderate/severe (lexicon criteria) | 4/0/0 | 2/0/0 | 1/1/0 | 1/0/0 |
| Blood transfusion | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Endoscopic treatment for bleeding, n | ||||
| Diluted epinephrine spray | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Balloon tamponade | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| HSE injection | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Clipping | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Small-Stone Group (n = 80) | Large-Stone Group (n = 80) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete stone removal, n (%) | 80 (100%) | 79 (98.8%) | 1.00 |
| Single-stage stone removal, n (%) | 41 (51.2%) | 35 (43.8%) | 0.43 |
| Total number of sessions for complete stone removal, median (range), n | 1 (1–3) | 1 (1–3) | 0.27 |
| ESBD (balloon size < 12 mm): ESLBD (balloon size ≥ 12 mm), n | 64:16 | 26:54 | <0.01 |
| Conventional device: Integrated device | 51:29 | 55:25 | 0.62 |
| Use of mechanical lithotripsy for stone removal | 20 (25.0%) | 45 (56.2%) | <0.01 |
| Total procedure time, median (range), min | 28.5 (6–88) | 39.5 (10–119) | <0.01 |
| Time required for selective biliary cannulation, median (range), min | 4.5 (1–40) | 5.0 (1–87) | 0.80 |
| Rectal diclofenac administration before procedure | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Pancreatic guidewire method for selective biliary cannulation | 9 (11.2%) | 13 (16.2%) | 0.49 |
| Pancreatic stent placement | 1 (1.2%) | 3 (3.8%) | 0.62 |
| Pre-cutting for selective biliary cannulation | 1 (1.2%) | 1 (1.2%) | 1.00 |
| Length of hospital stay, median (range), days | 10 (2–32) | 11 (4–58) | 0.33 |
| Adverse events, n (%) | 9 (11.2%) | 11 (13.8%) | 0.81 |
| Pancreatitis, n (%) | 1 (1.2%) | 2 (2.5%) | 1.00 |
| Bleeding, n (%) | 5 (6.2%) | 4 (5.0%) | 1.00 |
| Perforation, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Bile leakage, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Cholecystitis, n (%) | 1 (1.2%) | 0 (0%) | 1.00 |
| Cholangitis, n (%) | 2 (2.5%) | 0 (3.7%) | 0.50 |
| Deterioration of respiratory condition, n (%) | 1 (1.2%) | 3 (3.8%) | 0.62 |
| Aspiration pneumonia, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (2.5%) | 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanatani, J.-I.; Kitagawa, K.; Asada, S.; Motokawa, Y.; Osaki, Y.; Iwata, T.; Fujinaga, Y.; Nishimura, N.; Kaji, K.; Sato, S.; et al. Efficacy of an Endoscopic Device Integrating a Sphincterotome and a Dilation Balloon Catheter for the Treatment of Choledocholithiasis (with Video). J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175930
Hanatani J-I, Kitagawa K, Asada S, Motokawa Y, Osaki Y, Iwata T, Fujinaga Y, Nishimura N, Kaji K, Sato S, et al. Efficacy of an Endoscopic Device Integrating a Sphincterotome and a Dilation Balloon Catheter for the Treatment of Choledocholithiasis (with Video). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(17):5930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175930
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanatani, Jun-Ichi, Koh Kitagawa, Shohei Asada, Yuki Motokawa, Yui Osaki, Tomihiro Iwata, Yukihisa Fujinaga, Norihisa Nishimura, Kosuke Kaji, Shinya Sato, and et al. 2025. "Efficacy of an Endoscopic Device Integrating a Sphincterotome and a Dilation Balloon Catheter for the Treatment of Choledocholithiasis (with Video)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 17: 5930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175930
APA StyleHanatani, J.-I., Kitagawa, K., Asada, S., Motokawa, Y., Osaki, Y., Iwata, T., Fujinaga, Y., Nishimura, N., Kaji, K., Sato, S., Namisaki, T., Mitoro, A., & Yoshiji, H. (2025). Efficacy of an Endoscopic Device Integrating a Sphincterotome and a Dilation Balloon Catheter for the Treatment of Choledocholithiasis (with Video). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(17), 5930. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14175930





