Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use with COVID-19 Mortality in Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Record Linkage
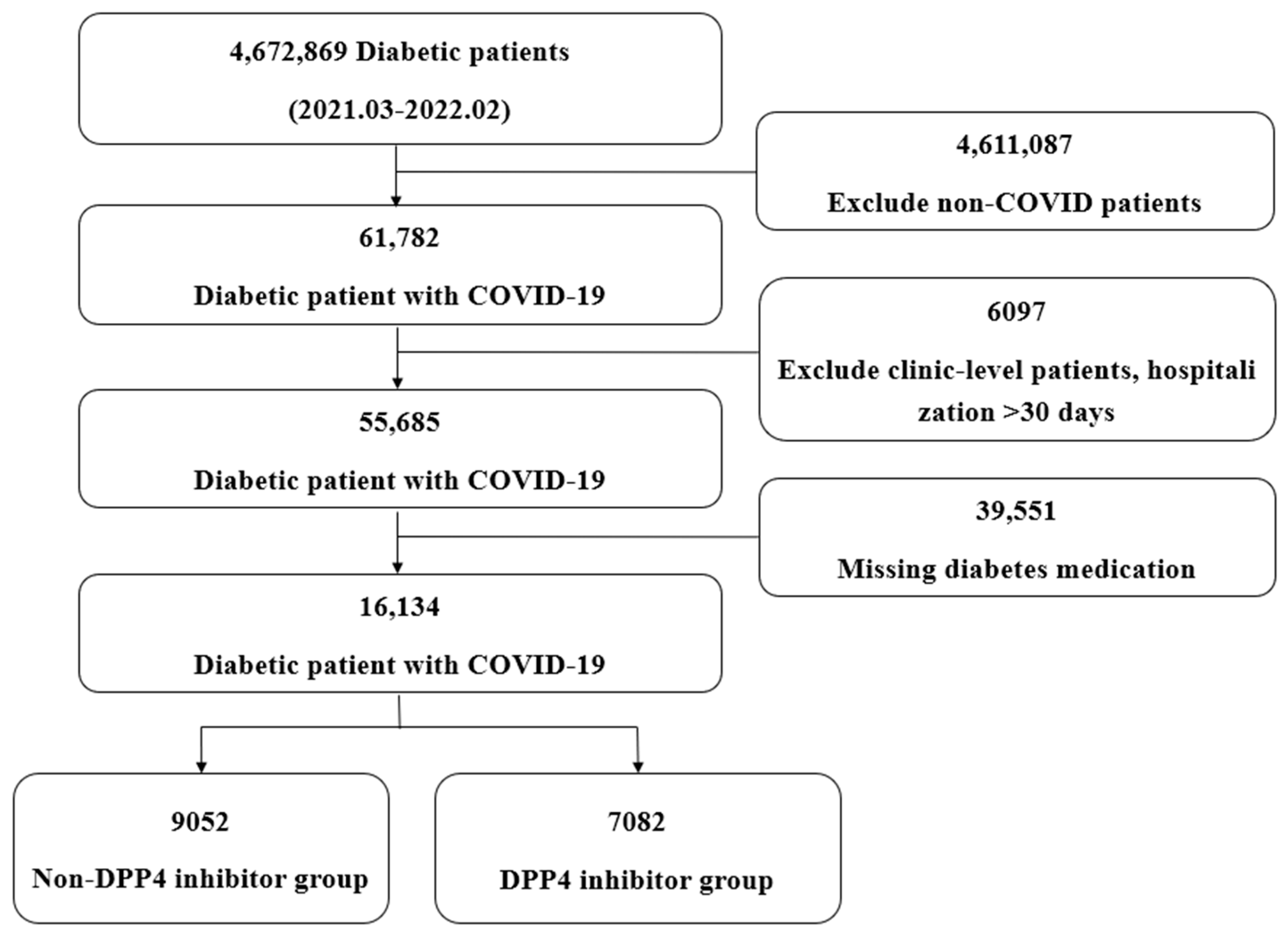
2.2. Study Population (Case Definition)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Impact of DPP-4 Inhibitors in Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Users
3.3. Impact of DPP-4 Inhibitors in Insulin Users
3.4. Impact of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors in COVID-19 Patients
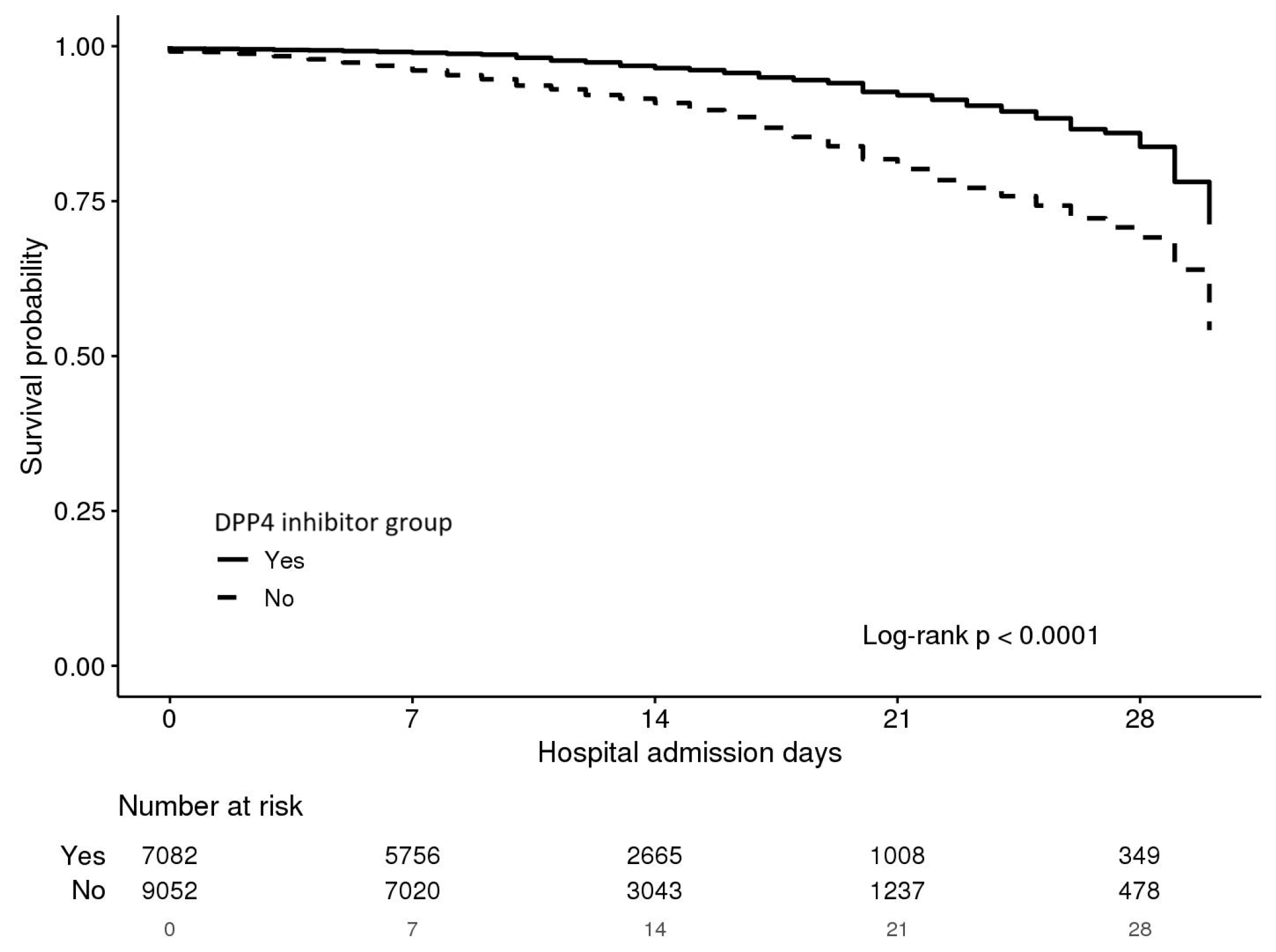
3.5. Analysis of Mortality Effects-COX Regression, Kaplan-Meier Curves
3.6. Sensitivity Analyses Confirming Robustness of Findings
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. 2024. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19 (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Dessie, Z.G.; Zewotir, T. Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Khunti, K. Assessment of risk, severity, mortality, glycemic control and antidiabetic agents in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A narrative review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 165, 108266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Cheng, B.; Chen, J.; Peng, A.; Yang, C.; Liu, C.; Xiong, M.; Deng, A.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and COVID-19 in association with glucose-lowering medication. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunti, K.; Knighton, P.; Zaccardi, F.; Bakhai, C.; Barron, E.; Holman, N.; Kar, P.; Meace, C.; Sattar, N.; Sharp, S.; et al. Prescription of glucose-lowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide observational study in England. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyland, J.E.; Raja-Khan, N.T.; Bettermann, K.; Haouzi, P.A.; Leslie, D.L.; Kraschnewski, J.L.; Parent, L.J.; Grigson, P.S. Diabetes, drug treatment, and mortality in COVID-19: A multinational retrospective cohort study. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keels, J.N.; McDonald, I.R.; Lee, C.S.; Dwyer, A.A. Antidiabetic agent use and clinical outcomes in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1482853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelkheir, M.; El-Metwally, T.H. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors can inhibit angiotensin converting enzyme. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, S.; Rossini, A.; Poli, R.; Dughera, F.; Pia, A.; Terzolo, M.; Reimondo, G. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 738848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Penninger, J.M. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the Pathogenesis of ARDS in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 732690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhmat, I.I.; Kusmala, Y.Y.; Handayani, D.R.; Juliastuti, H.; Nawangsih, E.N.; Wibowo, A.; Lim, M.A.; Pranata, R. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)—A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2021, 15, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, H.; Audi Yanto, T.; Ivan Hariyanto, T. Pre-admission use of sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT-2i) may significantly improves Covid-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 195, 110205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, M.; Abosheaishaa, H.; Singh, A.K.; Misra, A.; Bloomgarden, Z. Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes 2023, 15, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, N.; Naik, D.; Sahoo, J.; Kamalanathan, S. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in COVID-19: Beyond glycemic control. World J. Virol. 2022, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, B.M.; Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. Disentangling conflicting evidence on DPP-4 inhibitors and outcomes of COVID-19: Narrative review and meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.W.E.; Alamer, A.; Alnami, S.S.; Alhawaj, I.A.; Alsmail, A.H.; Alshawaf, M.A.; Aljazeeri, M.A.; Alghafli, M.J.; Alhejji, F.Y.; Alfayez, O.M.; et al. DPP-4 inhibitors and COVID19 outcomes in patients with type II diabetes: A multicenter retrospective cohort study in Saudi Arabia. Cardiovasc. Diabetol.–Endocrinol. Rep. 2025, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoulias, D.; Doumas, M. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and COVID-19-Related Deaths among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Lian, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, S.; Xin, S.; Cao, P.; Lu, J. The MERS-CoV Receptor DPP-4 as a Candidate Binding Target of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike. iScience 2020, 23, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emral, R.; Haymana, C.; Demirci, I.; Tasci, I.; Sahin, M.; Cakal, E.; Ata, N.; Unluturk, U.; Demir, T.; Ertugrul, D.; et al. Lower COVID-19 Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Taking Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Results from a Turkish Nationwide Study. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 2857–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. DPP-4 inhibition and COVID-19: From initial concerns to recent expectations. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 47, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhou, Y.J.J.; Hor, A.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.F.; Jose, S.; Chipps, D.R.; Cheung, N.W. Dexamethasone-induced hyperglycaemia in COVID-19: Glycaemic profile in patients without diabetes and factors associated with hyperglycaemia. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 194, 110151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Masui, Y.; Yoshikawa, R.; Kunimatsu, J.; Kaneko, H. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor for steroid-induced diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Reeves, A.A.; Hopefl, R.; Bejusca, R. ADME and Pharmacokinetic Properties of Remdesivir: Its Drug Interaction Potential. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatovkaňuková, P.; Veselý, D.; Slíva, J. Evaluating Drug Interaction Risks: Nirmatrelvir & Ritonavir Combination (PAXLOVID®) with Concomitant Medications in Real-World Clinical Settings. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solerte, S.B.; D’Addio, F.; Trevisan, R.; Lovati, E.; Rossi, A.; Pastore, I.; Dell, M.; Ippolito, E.; Scaranna, C.; Bellante, R.; et al. Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.; Mandal, S.; Mukherjee, O.; Mukherjee, S.; Kundu, R. DPP-4 Inhibitors as a savior for COVID-19 patients with diabetes. Future Virol. 2023, 18, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 16,134) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 9052) | DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 7082) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 69.19 ± 13.99 | 69.94 ± 13.83 | 68.23 ± 14.13 | <0.0001 |
| Sex (Male) | 8823 (54.7) | 4806 (53.1) | 4017 (56.7) | <0.0001 |
| Length of Stay (days) | 12.08 ± 7.25 | 11.81 ± 7.26 | 12.42 ± 7.23 | <0.0001 |
| Death | 1237 (7.7) | 933 (10.3) | 304 (4.3) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension | 4341 (26.9) | 1669 (18.4) | 2672 (37.7) | <0.0001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 5378 (33.3) | 2257 (24.9) | 3121 (44.1) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 1209 (7.5) | 486 (5.4) | 723 (10.2) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 895 (5.5) | 511 (5.6) | 384 (5.4) | 0.5392 |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 1682 (10.4) | 865 (9.6) | 817 (11.5) | <0.0001 |
| Stroke | 0 * | 0 | 0 | |
| Congestive Heart Failure | 1 (0.0) | 1 (0.0) | 0 | >0.999 |
| End-Stage Renal Disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Oxygen demand | 4166 (25.8) | 2261 (25.0) | 1905 (26.9) | 0.0057 |
| Intensive care unit admit | 2496 (15.5) | 1503 (16.6) | 993 (14.0) | <0.0001 |
| Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (−) | Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (+) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 11,920) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 7432) | DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 4488) | p-Value | Total (n = 4214) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 1620) | DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 2594) | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 68.4 ± 14.3 | 69.3 ± 14.00 | 66.9 ± 14.8 | <0.0001 | 71.4 ± 12.7 | 72.9 ± 12.8 | 70.5 ± 12.6 | <0.0001 |
| Sex (Male) | 6633 (55.6) | 4003 (53.9) | 2630 (58.6) | <0.0001 | 2190 (52.0) | 803 (49.6) | 1387 (53.5) | 0.014 |
| Length of Stay (days) | 11.8 ± 7.0 | 11.6 ± 7.1 | 12.2 ± 7.0 | <0.0001 | 12.9 ± 7.8 | 13.0 ± 8.0 | 12.8 ± 7.6 | 0.416 |
| Death | 1027 (8.6) | 817 (11.0) | 210 (4.7) | <0.0001 | 210 (5.0) | 116 (7.2) | 94 (3.6) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension | 127 (1.1) | 49 (0.7) | 78 (1.7) | 0.056 | 4214 (100) | 1620 (100) | 2594 (100) | >0.999 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 3135 (26.3) | 1538 (20.7) | 1597 (35.6) | <0.0001 | 2243 (53.2) | 719 (44.4) | 1524 (58.8) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 702 (5.9) | 340 (4.6) | 362 (8.1) | <0.0001 | 507 (12.0) | 146 (9.0) | 361 (13.9) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 671 (5.6) | 444 (6.0) | 227 (5.1) | 0.0355 | 224 (5.3) | 67 (4.1) | 157 (6.1) | 0.007 |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 1055 (8.9) | 647 (8.7) | 408 (9.1) | 0.4730 | 627 (14.9) | 218 (13.5) | 409 (15.8) | 0.0404 |
| Stroke | 0 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Congestive Heart Failure | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.0) | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | |
| End-Stage Renal Disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Oxygen demand | 3078 (25.8) | 1894 (25.5) | 1184 (26.4) | 0.2782 | 1088 (25.8) | 367 (22.7) | 721 (27.8) | <0.0001 |
| Intensive care unit admit | 1923 (16.1) | 1296 (17.4) | 627 (14.0) | <0.0001 | 573 (13.6) | 207 (12.8) | 366 (14.1) | 0.2199 |
| Insulin (−) | Insulin (+) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 6170) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 2818) | DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 3352) | p-Value | Total (n = 9964) | Non-DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 6234) | DPP-4 Inhibitor Group (n = 3730) | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 69.2 ± 14.6 | 70.6 ± 14.5 | 68.1 ± 14.5 | <0.0001 | 69.2 ± 13.6 | 69.7 ± 13.5 | 68.3 ± 13.8 | <0.0001 |
| Sex (Male) | 3191 (51.7) | 1338 (47.5) | 1853 (55.3) | <0.0001 | 5632 (56.5) | 3468 (55.6) | 2164 (58.0) | 0.0201 |
| Length of Stay (days) | 11.8 ± 7.3 | 12.5 ± 7.8 | 11.2 ± 6.8 | <0.0001 | 12.2 ± 7.2 | 11.5 ± 7.0 | 13.5 ± 7.4 | <0.0001 |
| Death | 77 (1.2) | 37 (1.3) | 40 (1.2) | 0.6732 | 1160 (11.6) | 896 (14.4) | 264 (7.1) | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension | 2047 (33.2) | 804 (28.5) | 1243 (37.1) | <0.0001 | 2294 (23.0) | 865 (13.9) | 1429 (38.3) | <0.0001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 2271 (36.8) | 827 (29.3) | 1444 (43.1) | <0.0001 | 3107 (31.2) | 1430 (22.9) | 1677 (45.0) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 314 (5.1) | 53 (1.9) | 261 (7.8) | <0.0001 | 895 (9.0) | 433 (6.9) | 462 (12.4) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 238 (3.9) | 100 (3.5) | 138 (431) | 0.2482 | 657 (6.6) | 411 (6.6) | 246 (6.6) | 0.9964 |
| Ischemic Heart Disease | 574 (9.3) | 233 (8.3) | 341 (10.2) | 0.0001 | 1108 (11.1) | 632 (10.1) | 476 (12.8) | <0.0001 |
| Stroke | 0 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Congestive Heart Failure | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.0) | 1 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | >0.999 | |
| End-Stage Renal Disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Oxygen demand | 699 (11.3) | 292 (10.4) | 407 (12.1) | 0.0280 | 3467 (34.8) | 1969 (31.6) | 1498 (40.2) | <0.0001 |
| Intensive care unit admit | 149 (2.4) | 47 (1.7) | 102 (3.0) | 0.0005 | 2347 (23.6) | 1456 (23.4) | 891 (23.9) | 0.545 |
| Univariable | Multivariable-Stepwise | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age | 1.051 (1.036–1.047) | <0.0001 | ||
| Sex (Male) | 1.188 (1.057–1.335) | 0.0037 | 1.166 (1.071–1.267) | 0.0003 |
| Hypertension | 0.544 (0.468–0.632) | <0.0001 | 0.555 (0.498–0.617) | <0.0001 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.748 (0.654–0.855) | <0.0001 | 0.744 (0.675–0.819) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic kidney diseases | 1.514 (1.263–1.814) | <0.0001 | 1.519 (1.336–1.727) | <0.0001 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases | 1.091 (0.87–1.368) | 0.451 | ||
| Ischemic heart disease | 1.158 (0.974–1.377) | 0.097 | 1.171 (1.034–1.326) | <0.0001 |
| Stroke | - | - | ||
| Congestive heart failure | - | - | ||
| End-stage renal diseases | - | - | ||
| DPP-4 inhibitor | 0.455 (0.397–0.521) | <0.0001 | 0.455 (0.414–0.499) | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.W.; Kwak, M.K.; Park, S.; Heo, N.H.; Lee, E.Y. Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use with COVID-19 Mortality in Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165815
Park JW, Kwak MK, Park S, Heo NH, Lee EY. Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use with COVID-19 Mortality in Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165815
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jung Wan, Mi Kyung Kwak, Samel Park, Nam Hun Heo, and Eun Young Lee. 2025. "Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use with COVID-19 Mortality in Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165815
APA StylePark, J. W., Kwak, M. K., Park, S., Heo, N. H., & Lee, E. Y. (2025). Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Use with COVID-19 Mortality in Diabetic Patients: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165815






