Abstract
Background/Objectives: Gut microbial dysbiosis, leaky gut, and increased transepithelial translocation of commensal bacteria have been documented in multiple sclerosis (MS). Intrathecal IgGs specific for Akkermansia muciniphila, a gut bacterium, are increased in patients with MS and associated with clinical disability. Our objective here was to explore the putative involvement of intrathecal anti-A. muciniphila IgG in MS pathogenesis by characterizing patients with different anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. Methods: Serum and intrathecal IgG specific for A. muciniphila and other gut bacteria, as well as routine cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) parameters, were measured in 61 patients with MS. Examination of these patients included immunophenotyping of CSF-infiltrating and paired circulating lymphocytes, intrathecal markers of neurodegeneration and inflammation, and a detailed characterization of demographic, clinical, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features. Results: Plasma blasts (p < 0.01), B cells (p < 0.01), and Th2 cells (p < 0.01), which might be involved in antibody production, were increased in the CSF of these patients, as well as blood pro-inflammatory Th17 cells (p < 0.05). Anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices were negatively associated with blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability and circulating monocytes (p < 0.001), and positively with brain lesion load (p < 0.01). Conclusions: The differences between patients with low and high anti-A. muciniphila IgG indexes regarding BBB permeability, CSF cell infiltrates, and pro-inflammatory peripheral immune cells, as well as imaging features, support a role of anti-A. muciniphila immune response in MS pathogenesis.
1. Introduction
MS is an immune-mediated demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS) [1,2] that develops in genetically susceptible individuals and likely requires environmental triggers [3,4]. Recently, several studies have revealed a dysbiosis in the gut microbiota of MS patients, which might play a role in disease pathogenesis [5]. Supporting this hypothesis, it has been demonstrated that the transfer of gut microbiota from patients with MS, but not from healthy controls, into mice can induce or exacerbate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis [6,7]. Since gut microbiota and their metabolites are important for maintaining the gut epithelial barrier [8] and influence systemic immunity [9,10], microbiota dysbiosis affects the intestinal barrier function and immune homeostasis. In addition, gut enrichment in mucin-degrading bacteria can reduce mucus thickness and facilitate mucosal damage [11]. A leaky gut can then enable the translocation of commensal bacteria across the intestinal epithelium [12], enabling activation of the immune system. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) and metabolites from translocated bacteria can access the blood and circulate to distant organs and affect BBB permeability, leading to brain infiltration [13], as well as the maturation and function of microglia [14] and astrocytes [15]. Supporting the role of leaky gut in MS pathogenesis, altered biomarkers of gut barrier leakiness are common in patients with MS and correlate with disease progression and with increased BBB permeability [16,17]. Furthermore, circulating LPS, as a measure of gut microbiota translocation, is increased in MS patients and correlates with disability [18].
Among the different bacteria reported to be enriched in patients with MS [6,7,19], one of the most interesting is the mucin-degrading Akkermansia muciniphila [11]. We recently demonstrated higher intrathecal levels of anti-A. muciniphila immunoglobulin G (IgG) in patients with MS compared with controls and a significant correlation with disease disability [20], which supports a putative role of this bacterium in MS. Furthermore, two studies demonstrated cross-recognition between recently identified MS autoantigens and A. muciniphila-derived peptides by CD4+ T cells from patients with MS [21,22].
In order to better understand the involvement of intrathecal anti-A. muciniphila IgG in MS, we identified patients with MS with different anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices and characterized them in depth by analysis of CSF measures, ex vivo immunophenotyping of CSF, and paired blood samples, as well as demographic, clinical, and MRI characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Material
Paired CSF and blood samples were collected from 61 untreated patients with MS (Table 1). This study was approved by the Contonal Ethics Committee of Zurich (EC-No. 2013-0001 approved on 5 June 2013). Informed consent was obtained from all patients. All CSF samples were obtained for diagnostic purposes. Blood samples were collected on the same day. Patients were recruited from the Neuroimmunology and MS Research Section, Neurology Clinic, University Hospital, Zurich. Diagnosis was based on the revised McDonald criteria [23]. Fifty patients had never been treated. Eleven had previously been treated but were considered untreated at the time of lumbar puncture (seven patients received steroids, not during the last 4 weeks prior to enrolment, and four patients received glatimer acetate, not during the last 3 months prior to enrolment). Twenty-one patients were excluded from the analysis as we took the top twenty low patients (anti-A. muciniphila IgG index from 0.005 to 0.0043) and the top twenty high-index patients (from 0.063 to 0.24).

Table 1.
Demographic and clinical features.
2.2. Quantification of Anti-Bacterial Antibodies
ELISA tests were performed on paired unfrozen serum and CSF samples from −80 °C storage, as previously described, to detect antibodies against Akkermansia muciniphila [20]. Bacterial proteins were coated at 1 µg/mL in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) overnight at 4 °C. Blocking was performed using Bovine serum albumin (Sigma Aldrich, Paris, France) at 1% in PBS for 1 h at 37 °C. Patient samples were incubated for 2 h at 37 °C in PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin (dilutions 1/100 for serum, 1/10 for CSF). Anti-human IgG antibodies coupled with horseradish peroxidase (Bethyl Laboratories, Nanterre, France) at 1/5000, incubated for 1 h at 37 °C, were used for detection. The reaction with the substrate (3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine, BD Biosciences, Le Pont de Claix, France) was stopped with sulfuric acid (0.18 M, Sigma Aldrich) after 10 min. Plates were read at 450 nm using a Spark 10M multimode microplate reader (Tecan, Grodig, Austria). This ELISA test with ROC analysis showed that the AUC was 0.78 (95% CI = 0.065–0.90) with a p < 0.0058 for the dosage of anti-Akkermansia muciniphila IgG in CSF comparing patients with MS with non-inflammatory neurological disease patients. Sensitivity was 61.9, and specificity was 84.21.
2.3. Routine CSF and Serum/Blood Measures
CSF measures were determined as previously reported [24]. CSF-infiltrating cells were counted with a Fuchs–Rosenthal counting chamber under the microscope within 1 h after lumbar puncture. CSF total protein, as well as CSF and serum albumin, immunoglobulin (Ig) G, IgM, and IgA, were determined by immunonephelometry. Intrathecal indices for anti-A. muciniphila IgG were calculated using the following formula (Ig Index = (Ig CSF/Alb CSF)/(Ig Serum/Alb Serum)). Quotients (Q) were defined as Q = (concentration in CSF [mg/L]/concentration in serum [g/L]). Because QAlb increases with age, we calculated a maximum normal QAlb (QNorm) for each patient, which takes into account the age at lumbar puncture (QNorm = [age/15] + 4 × 10−3). Intrathecal neurofilament light chain (NF-L) and chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) proteins were quantified in CSF samples by ELISA (Uman Diagnostics, Umea, Sweden, and MicroVue, Athens, OH, USA, respectively) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Routine blood analyses were performed in the Hematology Department, USZ. Total white cells were counted with an automated counter. The number of neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes was manually determined using Romanofsky staining.
2.4. HLA Typing
Patients were typed for HLA-class II (DRB1*, DRB3*, DRB4*, DRB5*, DQA1*, and DQB1*) molecules using high-resolution HLA sequence-based typing at Histogenetics LLC, Ossining, NY, USA. Isolation of DNA from whole blood with a final concentration of 15 ng/μL was performed with a standard DNA isolation protocol using a Triton lysis buffer and proteinase K treatment.
2.5. Immunophenotyping
Flow cytometric immunophenotyping of CSF-infiltrating and paired circulating lymphocytes was performed as previously reported on fresh samples [24]. Antibodies: anti-CD3 AF700, anti-CD4 PE TR, anti-CD8 BV510, anti-CD45RA BV711, anti-CCR7 BV421, anti-CD27 APC Cy7, anti-CD28 PE Cy7, anti-CCR4 APC, anti-CRTh2 PE, anti-CCR6 BV785, anti-CD19 PerCPCy5.5, anti-IgD BV605 and anti-CD138 FITC. SPHEROTM AccuCount Particles (Sperotech, Inc., Lake Forest, IL, USA) were added to determine absolute counts following the manufacturer’s instructions. Sample acquisition was performed in an LSR Fortessa cytometer (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), and data were analyzed using FACSDiva (version 6.0, BD Biosciences) and FlowJO (version 10.0, TreeStar Inc., Ashland, OR, USA) software. The gating strategy is summarized in Figure 1.
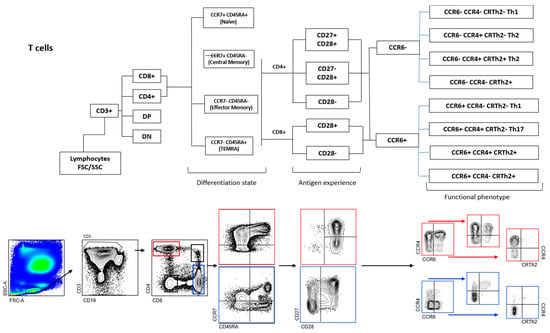
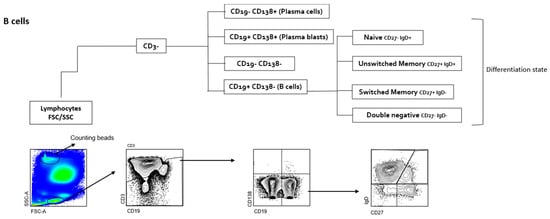
Figure 1.
Gating strategy of T and B cells. Doublets were excluded, followed by identification of lymphocytes by size. Next, CD3− are identified and among them, plasma cells (CD19− CD138+), plasma blasts (CD19+ CD138+), B cells (CD19+ CD138−) and CD19− CD138− cells. Among B cells, naïve (IgD+ CD27−), unswitched memory (IgD+ CD27+), switched memory (IgD− CD27+), and doublé negative (IgD− CD27−) B cell subsets are also identified. In CD3+ T cells, CD3+ CD4+ and CD3+ CD8+ cells are first identified and then separated in CM (CCR7+ CD45RA−), EM (CCR7− CD45RA−), TEMRA (CCR7− CD45RA+) and naive (CCR7+ CD45RA+). CM, EM, and TEMRA CD8+ T cells are then separated into CD28+ and CD28−, while CM, EM, and TEMRA CD4+ T cells are separated into CD28+ CD27+, CD28+ CD27−, and CD28−. Each one of these CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are separated first in CCR6− and CCR6+ and then in Th1 (CCR6− CCR4− CRTH2−), Th2-A (CCR6− CCR4+ CRTH2−), Th2-B (CCR6− CCR4+ CRTH2+), CCR6− CCR4− CRTH2+, Th1* (CCR6+ CCR4− CRTH2−), Th17 (CCR6− CCR4+ CRTH2−), CCR6+ CCR4+ CRTH2+ and CCR6+ CCR4− CRTH2+ cells.
2.6. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Patients were scanned with a 3T Philips Ingenia or 3T Siemens Skyra. The MRI protocol included a 3D fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence. The number and the total volume in ml of all hyperintense lesions were determined from the FLAIR images by an automatic algorithm based on convolutional neural networks [25]. Whole brain volume in ml was determined on the pre-contrast MPRAGE image using the automatic processing pipeline Biometrica MS® analysis platform (version 2.1, jung diagnostics GmbH, Hamburg, Germany).
2.7. Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). For the comparison of two groups of patients, we used the U-test (Mann–Whitney) for non-normally distributed variables. For the comparison of more than two groups of patients, we used Kruskal–Wallis test for non-normally distributed variables. Linear correlation between variables was tested using Spearman’s r for not-normally distributed variables. The significance level was set at p < 0.05. Associations were calculated using Fisher’s Exact Test with a 0.05 significance.
3. Results
3.1. IgGs Specific for Gut Commensal Bacteria
Intrathecal and serum levels of anti-A. muciniphila IgG were measured in 61 patients with MS (Figure 2a). In order to characterize patients differing in anti-A. muciniphila IgG index, we formed two patient groups: one with low and one with high index, by selecting the twenty patients with the lowest and highest anti-A. muciniphila IgG index. With 100% of sensitivity and 100% of specificity, the cut-off was >0.05717. Twenty-one patients between 0.044 and 0.036 were excluded from the analysis as we took the top twenty low patients (0.005–0.0043) and the top twenty high-index patients (0.063–0.24). We verified that patients with prior treatments were not different from untreated patients. There were no significant differences between anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices in patients who had never been treated and those with prior treatment (Figure 2b). Therefore, the duration of stopping the treatments is long enough not to disrupt the dosages.
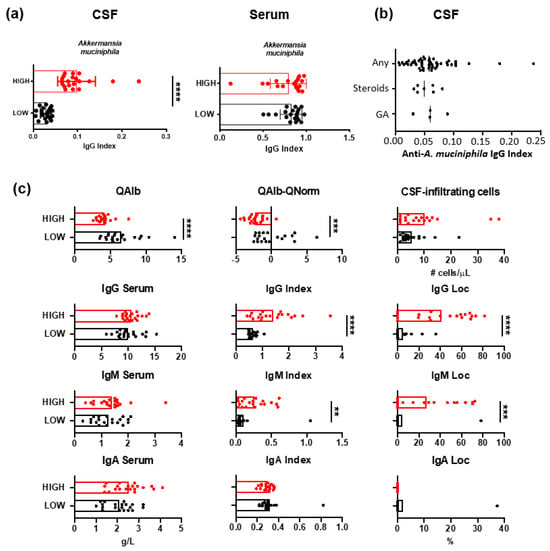
Figure 2.
IgG specific for A. muciniphila bacteria in MS and their association with CSF measures. (a) IgG index and serum levels of IgG specific for A. muciniphila in patients with MS. (b) Anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices in patients with MS never treated, previously treated with steroids, and previously treated with glatiramer acetate (GA). (c) CSF measures in patients with high (red) and low (black) anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. Each dot in the graphs corresponds to a single patient, and the bars show the mean. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare more than two groups of patients, and the Mann–Whitney test to compare two groups. Linear correlation between variables was tested using Spearman’s r correlation. Statistical significance (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001) is shown.
3.2. CSF Measures in Patients with MS with Different Anti-A. muciniphila IgG Index
Patients with low anti-A. muciniphila IgG index showed significantly higher QAlb as well as QAlb-QNorm values, suggesting altered BBB permeability, but not higher numbers of CSF-infiltrating cells (Figure 2c). Intrathecal IgG and IgM indices and synthesis were increased in patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index (Figure 2c).
3.2.1. B Cells in Patients with MS with Different Anti-A. muciniphila IgG Index
Immunophenotyping of CSF samples demonstrated significantly elevated relative frequencies (Figure 3a) and absolute numbers (Figure 3b) of plasma blasts (CD3− CD138+ CD19+) and B cells (CD3− CD138− CD19+) in patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index. Further, these frequencies (Figure 3a) and numbers (Figure 3b) correlated positively with the total- and anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. The absolute numbers of circulating plasma blasts and B cells were also significantly higher in patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index (Figure 3c). While these counts did not correlate with the total IgG indices, they interestingly did with the anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 3c).
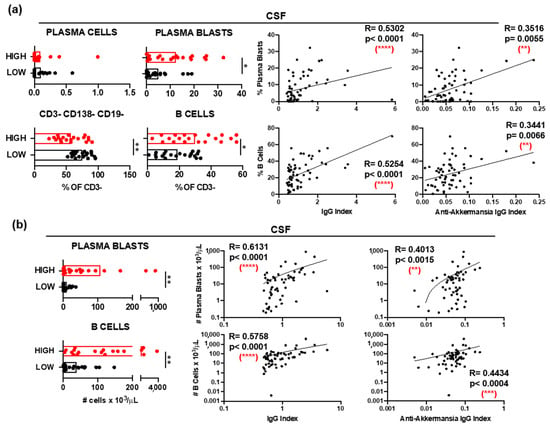
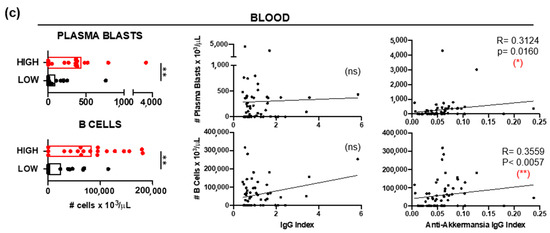
Figure 3.
B cells and anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. (a) Comparison between patients with high (red) and low (black) anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices of frequencies among CSF-infiltrating CD3− cells of plasma cells (CD138+ CD19−), plasma blasts (CD138+ CD19+), B cells (CD138− CD19+), and CD138− CD19− cells. Correlation between IgG indices (total- and anti-A. muciniphila) and frequencies of CSF-infiltrating plasmablasts and B cells. (b,c) Comparison between patients with high (red) and low (black) anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices of absolute numbers of CSF-infiltrating (b) and circulating (c) plasma blasts and B cells, as well as correlations of these numbers with IgG indices (total- and anti-A. muciniphila) (b,c). Each dot in the graphs corresponds to a single patient, and the bars show the mean. The Mann–Whitney test was used to compare two groups of patients. Linear correlation between variables was tested using Spearman’s r correlation. Statistical significance (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001) is shown. ns = not significant.
3.2.2. Th2 Cells in Patients with MS with Different Anti-A. muciniphila IgG Index
The relative frequencies and the absolute numbers of CD4+ central memory (CM, CCR7+ CD45RA−) T cells expressing the coreceptor CD28 but not CD27, and with a Th2-B (CCR6− CCR4+ CRTh2+) functional phenotype were significantly higher in the CSF of patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index (Figure 4a). Furthermore, both the relative frequencies and absolute numbers correlated with the anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 4b). In contrast, the relative frequencies and absolute numbers of these cells in peripheral blood did not show differences between patients, nor did they correlate with anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 4c,d).
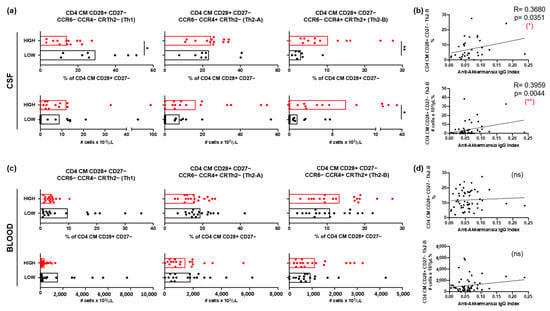
Figure 4.
CSF-infiltrating T cells and anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. (a,c) Relative frequencies and absolute numbers of CSF infiltrating (a) and circulating (c) CD4 CM CD28+ CD27− T cells with the following functional phenotypes Th1 (CCR6− CCR4− CRTh2−), Th2-A (CCR6− CCR4+ CRTh2−) and Th2-B (CCR6− CCR4+ CRTh2+) in patients with high (red) and low (black) anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. (b,d) Correlation between IgG indices (total- and anti-A. muciniphila) and relative frequencies and absolute numbers of CSF-infiltrating (b) and circulating (d) CD4 CM CD28+ CD27− Th2 cells. Each dot in the graphs corresponds to a single patient, and the bars show the mean. The Mann–Whitney test was used to compare two groups of patients. Linear correlation between variables was tested using Spearman’s r correlation. Statistical significance (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) is shown. ns = non significant.
Immunophenotyping of blood samples revealed that only T cells with a Th17 (CCR6+ CCR4+ CRTh2−) functional phenotype were increased in patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 5). Circulating CM and TEMRA CD4+ T expressing the co-stimulatory molecules CD28 and CD27, as well as EM and TEMRA CD8+ T cells expressing the co-stimulatory molecule CD28 and all with a Th17 functional phenotype, were more frequent and/or more abundant in blood from patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 5).
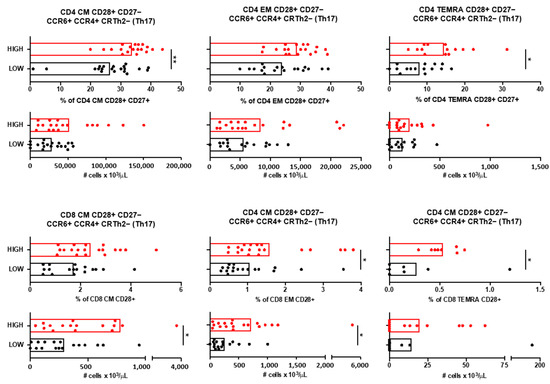
Figure 5.
Circulating T cells and anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. Relative frequencies and absolute numbers of circulating CD4 CD28+ CD27− and CD8 CD28+ T cells that have CM, EM, and TEMRA differentiation state and a Th17 (CCR6+ CCR4+ CRTh2−) functional phenotype in patients with high (red) and low (black) anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. Each dot in the graphs corresponds to a single patient, and the bars show the mean. The Mann–Whitney test was used to compare two groups of patients. Statistical significance (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) is shown.
3.3. Characterization of Patients with Different Anti-A. muciniphila IgG Index
Demographic and clinical features did not differ between patients with low and high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index (Table 1).
Although brain MRI scans that have been obtained at the time of lumbar puncture were only available from twelve patients, these showed a statistically significant correlation between anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices and the total number and volume of FLAIR T2 lesions, but not with the whole brain volume (Figure 6a). We also addressed CNS damage and inflammation by using neurofilament light chain (NF-L) [26] and chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) [27] as biomarkers. Neither intrathecal NF-L nor CHI3L1 correlated with anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 6b).
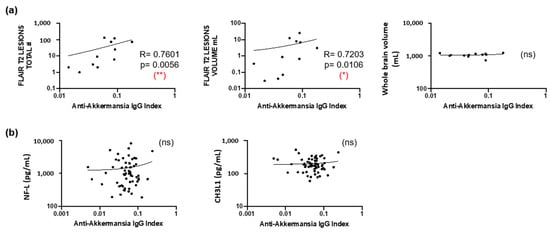
Figure 6.
Association of anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices with MRI features. (a) Correlation between anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices and total number and volume of FLAIR T2 lesions and whole brain volume. (b) Correlation between anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices and intrathecal NF-L, CHI3L1, and number of monocytes in whole blood. Each dot in the graphs corresponds to a single patient, and the bars show the mean. Linear correlation between variables was tested using Spearman’s r correlation. Statistical significance (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) is shown. ns = non significant.
Finally, we compared the number of circulating neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes and found a negative correlation between the number of circulating monocytes and the anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices (Figure 7).
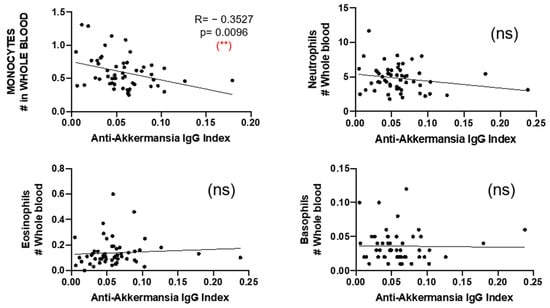
Figure 7.
Correlation between anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices and number of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils in whole blood. Each dot in the graphs corresponds to a single patient, and the bars show the mean. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare more than two groups of patients, and the Mann–Whitney test was used to compare two groups. Linear correlation between variables was tested using Spearman’s r correlation. Statistical significance (** p < 0.01) is shown. ns = non significant.
4. Discussion
In this study, we aimed to find new evidence supporting a role for intrathecal anti-A. muciniphila IgG in MS pathogenesis and thoroughly characterized patients with different anti-A. muciniphila IgG index. The comparison of patients with low and high intrathecal IgG production against this gut bacterium identified significant differences regarding BBB permeability, CSF infiltrates, pro-inflammatory circulating immune cells, as well as imaging features that indicate the role of these antibodies in MS pathogenesis.
Patients with MS with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index also produced higher intrathecal IgG against other gut bacteria such as P. melaninogenica, E. coli, and B. fragilis [20,28], suggesting a leaky gut and a general translocation of gut commensal bacteria in these patients. However, intrathecal production of anti-A. muciniphila IgG did not correlate with serum levels of IgG specific for gut bacteria, which may indicate a selective recruitment into the CNS compartment of B cells producing these antibodies. The intrathecal synthesis of anti-A. muciniphila IgG is supported by higher intrathecal IgG and IgM synthesis in patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index. The proliferation and activation of the corresponding secreting B cells present in the CNS and not in the periphery are probably favored by the inflammatory environment and interactions with immune cells. Indeed, there are higher amounts of CSF-infiltrating cells, which may be involved in antibody production, such as plasma blasts, B cells, and CD4+ CM CD28+ CD27− Th2-B cells. Furthermore, both the relative frequencies and absolute numbers of these cells correlated with anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices. CD4+ CM CD28+ CD27− Th2-B cells are probably relevant for providing B cell help since the downregulation of CD27 indicates repetitive stimulation with antigen and the expression of CCR4 and CRTh2 [24], a Th2 phenotype. Unexpectedly, patients with MS with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index had lower QAlb, suggesting that trafficking of albumin and cells through the BBB uses different mechanisms. Indeed, passage of immune cells is considered an active phenomenon due to inflammation, while albumin could be considered as a passive transfer after BBB breakdown. The study of specific inflammatory mediators in correlation with the A. muciniphila IgG index would be informative. Indeed, a meta-analysis on 226 studies, including more than 13,000 patients with MS, clearly showed that TNF-α, CXCL8, CXCL13, IL-15, and IL12-p40 are increased in the CSF of MS compared to controls [29]. So, this cytokine/chemokine environment in the CNS is conducive to the attraction and proliferation of immune cells. In line with this general CNS inflammatory environment, we found inverse correlations between anti-A. muciniphila IgG index in CSF and granulocyte/monocyte number in blood, suggesting a recruitment of those cells in the CNS and a corresponding decrease in blood.
Patients with high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index also showed slightly higher pro-inflammatory Th17 cells. This is of interest since Th17 cells have been associated with many autoimmune diseases and are crucial in immune responses against bacterial infections [30] and also against bacterial translocation [31]. In the EAE model, gut microbiota dysbiosis was associated with an aberrant Th17 response in the gut, leading to exacerbation of neuroinflammation [6,7].
Despite the low number of patients from whom brain MRI scans were available at the time of lumbar puncture, anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices nicely correlated with the number and volume of FLAIR T2 lesions in the brain, suggesting a possible involvement of these antibodies in the demyelination process due to inflammation. The whole brain volume and markers of CNS damage/inflammation, such as NF-L [26] and CHI3L1 [27], did not correlate with anti-A. muciniphila IgG indices, which render an involvement of these antibodies in neurodegeneration unlikely.
In this study, we highlighted that IgG responses against Akkermansia muciniphila in CSF of patients with MS correlated with the presence of immune cells in CSF, activity of disease, and markers of CNS damage. However, in the literature, Akkermansia muciniphila is considered a probiotic for metabolic disorders and inflammatory bowel disease [31]. Gut Akkermansia muciniphila increase was beneficial in an animal model of neuroinflammation, increasing regulatory T cell responses [32], but depending on the composition of gut microbiota (environmental community), Akkermansia muciniphila exhibited variable effects on EAE course [33]. A better comprehension of Akkermansia muciniphila functions and interactions with other microbes and immune cells is crucial to develop new therapeutic options for multiple sclerosis.
5. Limitations
The design of this study was a cross-sectional study without the inclusion of healthy controls. The number of patients with MS was relatively small (n = 20 per group) due to the exclusion of 21 patients for anti-Akkermansia muciniphila IgG index cutting selection. Moreover, MRI data were available for only 12 patients. Further prospective studies on larger patient cohorts are needed to confirm the findings.
6. Conclusions
Our results demonstrate an association between intrathecal anti-A. muciniphila IgG and CSF-infiltrating cells that are known to be involved in antibody production, consistent with an intrathecal synthesis of anti-gut microbiota antibodies and a selective recruitment of specific immune cells into the CNS. The significant differences between patients with low and high anti-A. muciniphila IgG index regarding BBB permeability, MRI lesion load, or peripheral inflammation, while preliminary, suggests an involvement of these antibodies in MS pathogenesis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. and L.B.; methodology, C.M. and C.C.; validation, C.C. and C.M.; resources, M.J.D. and I.J.; formal analysis, M.P. and R.O.; ressources, P.T.-O. and M.J.D.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S. and L.B.; writing—review and editing, C.C., C.M., M.P., P.T.-O., M.J.D., R.O., I.J., A.B.N., D.-A.L., R.M., M.S., and L.B.; supervision, D.-A.L., R.M., M.S., and L.B.; project administration, M.S.; funding acquisition, R.M., D.-A.L., M.S., and L.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Research Council Advanced Grant (340733) (R.M.), Clinical Research Priority Programs (CRPPs) “Heterogeneity MS” and “Precision MS” of the University Zurich (R.M., M.S.), Clinical, Swiss National Science Foundation (Sinergia UnmetMS) (R.M., M.S.), the Swiss MS Society (R.M.), Region Pays de la Loire (“Loire-Times” project, L.B.), ANTARES (D.-A.L.), FranceSEP (D.-A.L. and L.B.) and NotreSclérose (D.-A.L. and L.B.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Cantonal Ethics Committee of Zurich approved the study procedures (EC-No. 2013-0001) on 5 June 2013.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and their relatives involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable requests.
Acknowledgments
This work has been carried out thanks to the support of the LabEx IGO project (n° ANR-11-LABX0016-01) funded by the «Investissements d’Avenir» French Government program, managed by the French National Research Agency (ANR).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Roland Opfer was employed by the company Jung Diagnostics GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Bar-Or, A.; Li, R. Cellular immunology of relapsing multiple sclerosis: Interactions, checks, and balances. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoftberger, R.; Lasmann, H.; Berger, T.; Reindl, M. Pathogenic autoantibodies in multiple sclerosis—From a simple idea to a complex concept. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, T.; Barcellos, L.F.; Alfredsson, L. Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, R.; Yamauchi, J. New insights into risk gens and their cnadidates in Multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, S.N.; Shahi, S.K.; Mangalam, A.K. The “Gut Feeling”: Breaking Down the Role of Gut Microbiome in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Yoo, B.B.; Runia, T.F.; Debelius, J.W.; Singh, S.; Nelson, C.A.; Kanner, R.; Bencosme, Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Hauser, S.L.; et al. Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and exacerbate symptoms in mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10713–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berer, K.; Gerdes, L.A.; Cekanaviciute, E.; Jia, X.; Xiao, L.; Xia, Z.; Liu, C.; Klotz, L.; Stauffer, U.; Baranzini, S.E.; et al. Gut microbiota from multiple sclerosis patients enables spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10719–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Kirby, J.; Reilly, C.M.; Luo, X.M. Leaky Gut As a Danger Signal for Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghikia, A.; Jorg, S.; Duscha, A.; Berg, J.; Manzel, A.; Waschbisch, A.; Hammer, A.; Lee, D.H.; May, C.; Wilck, N.; et al. Dietary Fatty Acids Directly Impact Central Nervous System Autoimmunity via the Small Intestine. Immunity 2015, 43, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.S.; Seekatz, A.M.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Kamada, N.; Hickey, C.A.; Wolter, M.; Pudlo, N.A.; Kitamoto, S.; Terrapon, N.; Muller, A.; et al. A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility. Cell 2016, 167, 1339–1353.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Douek, D.C. Microbial translocation across the GI tract. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharaj, A.; Galea, I. The blood-brain barrier in systemic inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabe de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhammer, V.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Bunse, L.; Takenaka, M.C.; Kenison, J.E.; Mayo, L.; Chao, C.C.; Patel, B.; Yan, R.; Blain, M.; et al. Type I interferons and microbial metabolites of tryptophan modulate astrocyte activity and central nervous system inflammation via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Silva, C.; Greenfield, J.; Liu, W.Q.; Metz, L.M.; Yong, V.W. Biomarkers of intestinal barrier function in multiple sclerosis are associated with disease activity. Mult. Sclerosis J. 2020, 26, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarinu, M.C.; Fornasiero, A.; Romano, S.; Ferraldeschi, M.; Mechelli, R.; Renie, R.; Ferraldeschi, M.; Mechelli, R.; Reniè, R.; Morena, E.; et al. The Contribution of Gut Barrier Changes to Multiple Sclerosis Pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Bittencourt, V.C.; Ferreira, T.B.; Kasahara, T.M.; Barros, P.O.; Alvarenga, R.; Hygino, J.; Andrade, R.M.; Andrade, A.F.; Bento, C.A. Low sensitivity to glucocorticoid inhibition of in vitro Th17-related cytokine production in multiple sclerosis patients is related to elevated plasma lipopolysaccharide levels. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 148, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.; Gandhi, R.; Cox, L.M.; Li, N.; von Glehn, F.; Yan, R.; Patel, B.; Mazzola, M.A.; Liu, S.; Glank, B.L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallino, A.; Dos Santos, A.; Mathe, C.V.; Garcia, A.; Morille, J.; Dugast, E.; Shah, S.P.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Guilloux, C.A.; Gleeson, P.J.; et al. Gut bacteria Akkermansia elicit a specific IgG response in CSF of patients with MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, R.; Santos, R.; Tomas-Ojer, P.; Cruciani, C.; Lutterotti, A.; Faigle, W.; Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; Espejo, C.; Eixarch, H.; Pinilla, C.; et al. GDP-l-fucose synthase is a CD4(+) T cell-specific autoantigen in DRB3*02:02 patients with multiple sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jelcic, I.; Mühlenbruch, L.; Haunerdinger, V.; Toussaint, N.C.; Zhao, Y.; Cruciani, C.; Faigle, W.; Naghavian, R.; Foege, M.; et al. HLA-DR15 Molecules Jointly Shape an Autoreactive T Cell Repertoire in Multiple Sclerosis. Cell 2020, 183, 1264–1281.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthenparampil, M.; Tomas-Ojer, P.; Hornemann, T.; Lutterotti, A.; Jelcic, I.; Ziegler, M.; Hulsmeier, A.J.; Cruciani, C.; Faigle, W.; Martin, R.; et al. Altered CSF Albumin Quotient Links Peripheral Inflammation and Brain Damage in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Opfer, R.; Gessert, N.; Ostwaldt, A.C.; Manogaran, P.; Kitzler, H.H.; Schlaefer, A.; Schippling, S. Fully automated longitudinal segmentation of new or enlarged multiple sclerosis lesions using 3D convolutional neural networks. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 28, 102445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, J.; Dring, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Norgren, N.; Gilthorpe, J.; Bergenheim, T.; Svenningsson, A. Neurofilament light in CSF and serum is a sensitive marker for axonal white matter injury in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonneh-Barkay, D.; Bissel, S.J.; Kofler, J.; Starkey, A.; Wang, G.; Wiley, C.A. Astrocyte and macrophage regulation of YKL-40 expression and cellular response in neuroinflammation. Brain Pathol. 2012, 22, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckman, E.; Laman, J.D.; Fischer, K.F.; Lopansri, B.; Martins, T.B.; Hill, H.R.; Kriesel, J.D. Spinal fluid IgG antibodies from patients with demyelinating diseases bind multiple sclerosis associated-bacteria. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Yu, Y.; Yan, T.; Cheng, Y. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood Cytokines as Biomarkers for Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 226 Studies with 13,526 Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouch, R.J.; Zhang, J.; Miller, B.C.; Robbins, C.J.; Mosher, T.H.; Li, W.; Krupenko, S.A.; Nagpal, R.; Zhao, J.; Bloomfeld, R.S.; et al. Distinct inflammatory Th17 subsets emerge in autoimmunity and infection. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20221911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdis, C.A. Does the epithelial barrier hypothesis explain the increase in allergy, autoimmunity and other chronic conditions? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Yang, S.; Xue, W.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B.; Xu, D. Akkermansia muciniphila: A promising probiotic against inflammation and metabolic disorders. Virulence 2024, 15, 2375555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Rezende, R.M.; Moreira, T.G.; Tankou, S.K.; Cox, L.M.; Wu, M.; Song, A.; Dhang, F.H.; Wei, Z.; Costamagna, G.; et al. Oral Administration of miR-30d from Feces of MS Patients Suppresses MS-like Symptoms in Mice by Expanding Akkermansia muciniphila. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).