Emerging Technologies and Advanced Strategies in Hemoglobin Defect Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Hb Defects
2.1. Qualitative Hb Defects
2.2. Quantitative Hb Defects
2.3. Γ, Δ Globin Mutations, and Combined Effects
3. Testing Methodologies
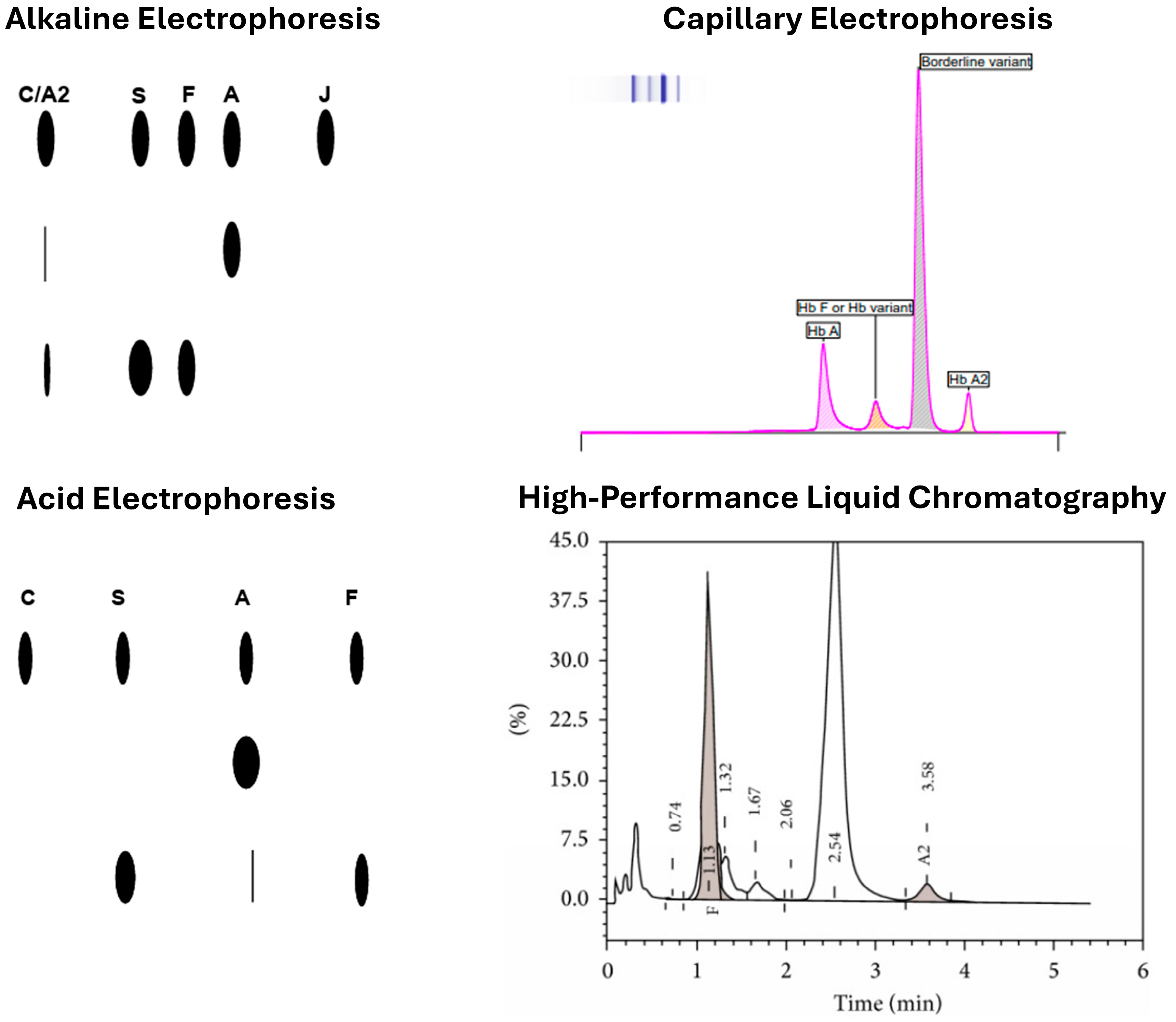
3.1. Alkaline and Acidic Gel-Based Electrophoresis
3.2. IEF
3.3. HPLC
3.4. CZE
3.5. MS
3.6. POCT
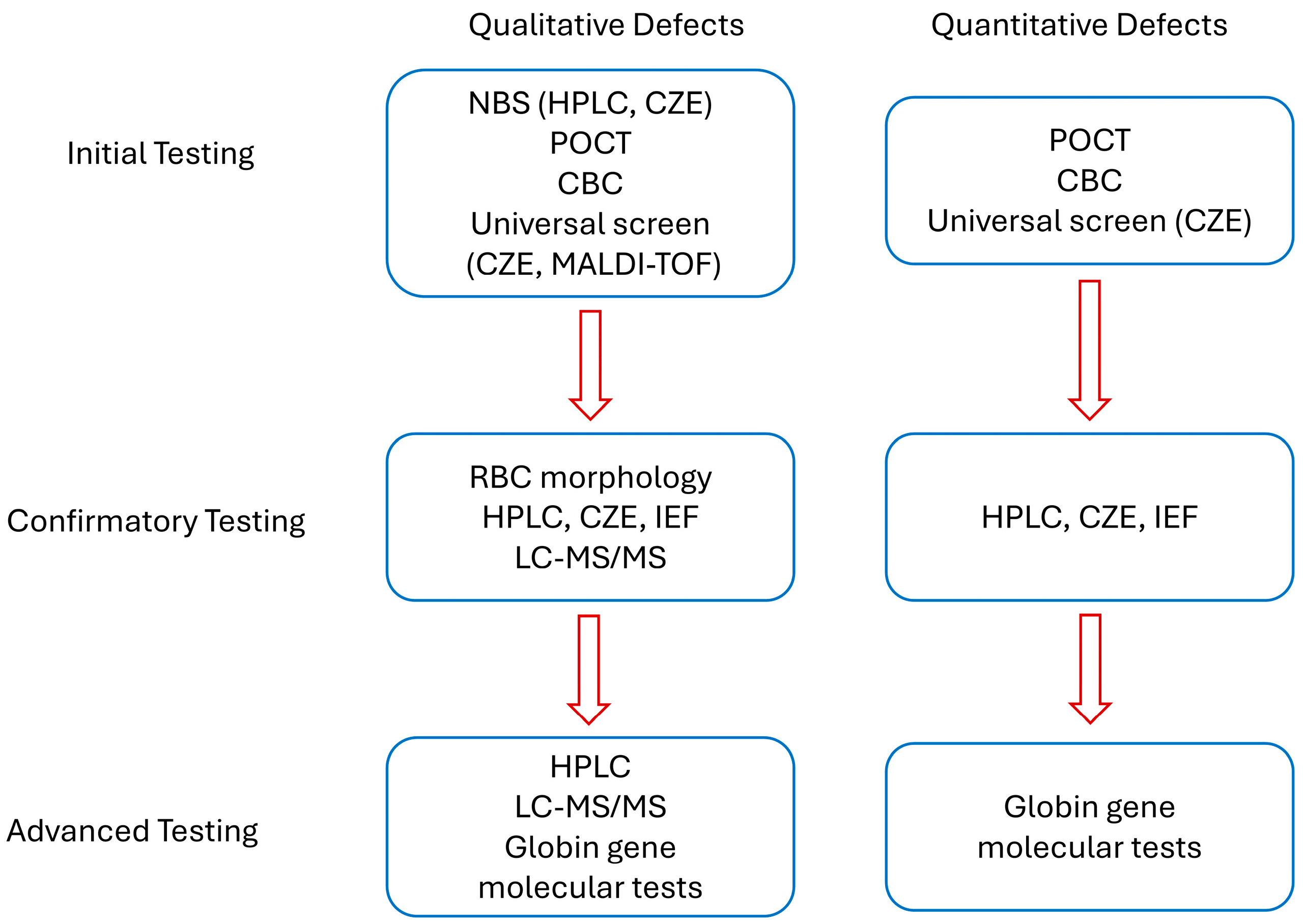
4. Screening Strategies
4.1. Guidelines on Hb Defect Screening
4.2. Evolving Screening Approaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACOG | American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| CZE | capillary zone electrophoresis |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| Hb F | Fetal Hb |
| HOA | Hb oxygen affinity |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| IEF | isoelectric focusing |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| NBS | newborn screening |
| POCT | point of care testing |
| RDT | rapid diagnostic tests |
| SCD | sickle cell disease |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Modell, B.; Darlison, M. Global Epidemiology of Haemoglobin Defects and Derived Service Indicators. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.N.; Weatherall, D.J. World Distribution, Population Genetics, and Health Burden of the Hemoglobinopathies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a011692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, A.; Idrees Khan, M.; Shah, S.; Tian, Y.; Zha, G.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, C. Diagnosis and Screening of Abnormal Hemoglobins. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2024, 552, 117685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, L.M.; Ware, R.E. Screening for Haemoglobin Defects: One Size May Not Fit All. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 204, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariharan, P.; Nadkarni, A. Insight of Fetal to Adult Hemoglobin Switch: Genetic Modulators and Therapeutic Targets. Blood Rev. 2021, 49, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, M.H.; Forget, B.G.; Higgs, D.R.; Weatherall, D.J. Defects of Hemoglobin: Genetics, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-139-48080-2. [Google Scholar]
- Inusa, B.P.D.; Hsu, L.L.; Kohli, N.; Patel, A.; Ominu-Evbota, K.; Anie, K.A.; Atoyebi, W. Sickle Cell Disease—Genetics, Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hemoglobinopathies: Current Practices for Screening, Confirmation and Follow-Up; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015.
- Agarwal, A.M.; Rets, A.V. Advances in Hemoglobinopathies and Thalassemia Evaluation. Clin. Lab. Med. 2024, 44, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucharoen, S.; Weatherall, D.J. The Hemoglobin E Thalassemias. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a011734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricchi, P.; Ammirabile, M.; Spasiano, A.; Costantini, S.; Di Matola, T.; Cinque, P.; Saporito, C.; Filosa, A.; Pagano, L. Molecular and Clinical Analysis of Haemoglobin Lepore in Campania, a Region of Southern Italy. Hematology 2017, 22, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, R.C.; Chui, D.H.; Riemer, C.R.; Miller, W.; Carver, M.F.; Molchanova, T.P.; Efremov, G.D.; Huisman, T.H. Access to a Syllabus of Human Hemoglobin Variants (1996) via the World Wide Web. Hemoglobin 1998, 22, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanash, S.M.; Shapiro, D.N. Separation of Human Hemoglobins by ION Exchange High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Hemoglobin 1981, 5, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.N.; Rognerud, C.L. Rapid Analysis of Hemoglobin Variants by Cation-Exchange HPLC. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.W.; Wong, R.; Liao, C.L.; Morales, D.R. Automated HPLC Screening of Newborns for Sickle Cell Anemia and Other Hemoglobinopathies. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B.B.; Wessels, R.A.; Ou, C.-N.; Buffone, G.J. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography in the Diagnosis of Hemoglobinopathies and Thalassemias: Report of Three Cases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1985, 84, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riou, J.; Godart, C.; Hurtrel, D.; Mathis, M.; Bimet, C.; Bardakdjian-Michau, J.; Préhu, C.; Wajcman, H.; Galactéros, F. Cation-Exchange HPLC Evaluated for Presumptive Identification of Hemoglobin Variants. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, D.F.; Hedstrom, D.; Gulbranson, R.; Ou, C.-N.; Bak, R. Comparison of Sebia Capillarys Capillary Electrophoresis With the Primus High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography in the Evaluation of Hemoglobinopathies. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 130, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, M.; Ratnaike, S. Capillary Electrophoresis of Hemoglobin. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2003, 41, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, T.N.; Khajuria, A.; Mack, M. Quantification of HbA (2) in Patients with and without Beta-Thalassemia and in the Presence of HbS, HbC, HbE, and HbD Punjab Hemoglobin Variants: Comparison of Two Systems. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 131, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, D.N.; Pyle, A.L.; Chang, J.S.; Hoke, C.; Lorey, T. Comparison of Sebia Capillarys Flex Capillary Electrophoresis with the BioRad Variant II High Pressure Liquid Chromatography in the Evaluation of Hemoglobinopathies. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; Ma, Q.; Lyu, Q.; Fu, S.; He, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Luo, Z.; Luo, J.; et al. A MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry-Based Haemoglobin Chain Quantification Method for Rapid Screen of Thalassaemia. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Sun, D.; Lin, W.; Yan, T.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, J.; Zou, S.; Xie, W.; et al. MALDI-TOF-MS for Rapid Screening and Typing of β-Globin Variant and β-Thalassemia through Direct Measurements of Intact Globin Chains. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilico, F.; Di Silvestre, D.; Sedini, S.; Petretto, A.; Levreri, I.; Melioli, G.; Farina, C.; Mori, F.; Mauri, P.L. New Approach for Rapid Detection of Known Hemoglobin Variants Using LC-MS/MS Combined with a Peptide Database. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.Y.; Wong, C.; Xia, J.Q.; Glader, B.E.; Shi, R.-Z.; Zehnder, J.L. Neutral-Coating Capillary Electrophoresis Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for Top-Down Identification of Hemoglobin Variants. Clin. Chem. 2023, 69, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosavi, M.; Chavan, R.; Bellad, M.B. NESTROFT—A Cost-Effective Mass Screening Tool for the Detection of β-Thalassemia Carrier Status in Anemic Pregnant Women: A Step Toward Reducing the National Disease Burden. J. Lab. Physicians 2021, 13, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGann, P.T.; Schaefer, B.A.; Paniagua, M.; Howard, T.A.; Ware, R.E. Characteristics of a Rapid, Point-of-Care Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Diagnosis of Sickle Cell Disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.; Sinski, A.; Asibey, J.; Hardy-Dessources, M.-D.; Elana, G.; Brennan, C.; Odame, I.; Hoppe, C.; Geisberg, M.; Serrao, E.; et al. Point-of-Care Screening for Sickle Cell Disease in Low-Resource Settings: A Multi-Center Evaluation of HemoTypeSC, a Novel Rapid Test. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivas, S.; Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Gwal, A.; Uikey, R.; Tiwari, S.K.; Verma, A.K.; Thota, P.; Das, A.; Bharti, P.K.; et al. Evaluation of Microchip-Based Point-Of-Care Device “Gazelle” for Diagnosis of Sickle Cell Disease in India. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 639208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.N.; Fraiwan, A.; An, R.; Alapan, Y.; Ung, R.; Akkus, A.; Xu, J.Z.; Rezac, A.J.; Kocmich, N.J.; Creary, M.S.; et al. Paper-Based Microchip Electrophoresis for Point-of-Care Hemoglobin Testing. Analyst 2020, 145, 2525–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, R.; Man, Y.; Iram, S.; Kucukal, E.; Hasan, M.N.; Huang, Y.; Goreke, U.; Bode, A.; Hill, A.; Cheng, K.; et al. Point-of-Care Microchip Electrophoresis for Integrated Anemia and Hemoglobin Variant Testing. Lab A Chip 2021, 21, 3863–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.P.; Siu, V.; Silva-Garcia, A.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Oksenberg, D. Development and Validation of an Oxygen Dissociation Assay, a Screening Platform for Discovering, and Characterizing Hemoglobin–Oxygen Affinity Modifiers. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2018, 12, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekyonda, Z.; Kityo, C.; Elgammal, Y.; Kalfa, T.A.; Akkus, O.; Gurkan, U.A. Rapid Assessment of Hemoglobin-Oxygen Dissociation. Blood 2023, 142, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modell, B.; World Health Organization Hereditary Diseases Programme. Guidelines for the Control of Haemoglobin Defects; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Angastiniotis, M.; Eleftheriou, A.; Galanello, R. Screening and Diagnosis for Haemoglobin Defects. In Prevention of Thalassaemias and Other Haemoglobin Defects, 2nd ed.; Thalassaemia International Federation: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Hemoglobinopathies in Pregnancy 2007. Available online: https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-bulletin/articles/2007/01/hemoglobinopathies-in-pregnancy (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Hemoglobinopathies in Pregnancy 2024. Available online: https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2022/08/hemoglobinopathies-in-pregnancy (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Osa-Andrews, B.; Desimone, N.; Sarode, R.; Paulino, S.; Cao, J. Screening for Hemoglobinopathy with Capillary Electrophoresis in Adult Patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 156, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Pasquali, M.; Jones, P.M. Newborn Screening: Current Practice and Our Journey over the Last 60 Years. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2024, 9, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streetly, A.; Sisodia, R.; Dick, M.; Latinovic, R.; Hounsell, K.; Dormandy, E. Evaluation of Newborn Sickle Cell Screening Programme in England: 2010–2016. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobitz, S.; Telfer, P.; Cela, E.; Allaf, B.; Angastiniotis, M.; Backman Johansson, C.; Badens, C.; Bento, C.; Bouva, M.J.; Canatan, D.; et al. Newborn Screening for Sickle Cell Disease in Europe: Recommendations from a Pan-European Consensus Conference. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridou, S.; Prapas, N.; Balassopoulou, A.; Boutou, E.; Vyzantiadis, T.-A.; Adamidou, D.; Delaki, E.-E.; Yfanti, E.; Economou, M.; Teli, A.; et al. Efficacy of the National Thalassaemia and Sickle Cell Disease Prevention Programme in Northern Greece: 15-Year Experience, Practice and Policy Gaps for Natives and Migrants. Hemoglobin 2018, 42, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffi, M.; Howard, N. Exploring the Effectiveness of Mandatory Premarital Screening and Genetic Counselling Programmes for β-Thalassaemia in the Middle East: A Scoping Review. Public Health Genom. 2015, 18, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindo, A.; Cisse, Z.; Keita, I.; Desmonde, S.; Sarro, Y.D.S.; Touré, B.A.; Baraika, M.A.; Tessougué, O.; Guindo, P.; Coulibaly, M.; et al. Potential for a Large-Scale Newborn Screening Strategy for Sickle Cell Disease in Mali: A Comparative Diagnostic Performance Study of Two Rapid Diagnostic Tests (SickleScan® and HemotypeSC®) on Cord Blood. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 204, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravholt, E.A.E.; Petersen, J.; Mottelson, M.; Nardo-Marino, A.; Rathe, M.; Olsen, M.; Holm, C.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Birgens, H.; Glenthøj, A. The Danish National Haemoglobinopathy Screening Programme: Report from 16 Years of Screening in a Low-Prevalence, Non-Endemic Region. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 204, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Device Name | Technology | Target Conditions | Sensitivity | Specificity | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NESTROFT | Naked Eye Osmotic Fragility Test | β-thalassemia trait | Not specified | Not specified | Cost-effective, rapid, reliable; used as initial screen in developing countries |
| Sickle SCAN | Immunoassay POCT | SCD | 98.10% | 91.10% | Portable, rapid test for SCD diagnosis |
| HemoTypeSC | Immunoassay POCT | SCD, hemoglobin C disease, and carrier states | 99.50% | 99.90% | High accuracy across various hemoglobin phenotypes |
| Gazelle | Microchip electrophoresis | HbSS, Thalassemia Major, sickle cell trait | 99% accuracy | Not specified | Portable, suitable for low-resource settings |
| HemeChip | Paper-based microchip electrophoresis | Hb S, C, and E variants | 100% | Not specified | Diagnostic accuracy: 98.4%; also detects anemia; miniaturized, paper-based format |
| Method | Cost per Test | Accuracy/Resolution | Throughput | Applicability/Settings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPLC | Moderate | High (good separation of Hb variants, including HbA2 and HbF) | High (automated analyzers allow batch processing) | Widely used in reference and hospital labs; standard in newborn and carrier screening programs |
| CZE | Moderate | High (better resolution for some variants than HPLC, e.g., HbE vs. HbA2) | High (similar to HPLC with modern systems) | Suitable for hospital and reference labs; increasingly replacing HPLC in clinical labs |
| MALDI-TOF | Moderate | Very high (can detect rare and modified hemoglobins, structural variants, and globin chain imbalances) | Moderate (requires specialized workflow) | Best suited for specialized or confirmatory testing centers; not yet standard for population-wide screening |
| POCT | Low–Moderate | Moderate (can detect major variants like HbS and HbC but not minor ones reliably) | Very high (minimal prep, rapid results) | Ideal for field settings, resource-limited areas, or urgent clinical triage; limited as a standalone screening tool |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Chen, V.C.; Osa-Andrews, B.; Cao, J. Emerging Technologies and Advanced Strategies in Hemoglobin Defect Screening. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165690
Zhang C, Chen VC, Osa-Andrews B, Cao J. Emerging Technologies and Advanced Strategies in Hemoglobin Defect Screening. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165690
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cindy, Victoria Crystal Chen, Bremansu Osa-Andrews, and Jing Cao. 2025. "Emerging Technologies and Advanced Strategies in Hemoglobin Defect Screening" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165690
APA StyleZhang, C., Chen, V. C., Osa-Andrews, B., & Cao, J. (2025). Emerging Technologies and Advanced Strategies in Hemoglobin Defect Screening. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165690






