The Human Disharmony Loop: The Anatomic Source Behind Subacromial Impingement and Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PM | Pectoralis minor |
| SAPS | Subacromial pain syndrome |
| HDL | Human disharmony loop |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| ROM | Range of motion |
| CA | Coraco-acromial |
| AC | Acromio-clavicular |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| TSA | Total shoulder arthroplasty |
| SLAP | Superior Labrum Anterior–Posterior |
References
- Greenberg, D.L. Evaluation and treatment of shoulder pain. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 98, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, E.H.; Aibinder, W.R. Shoulder Impingement Syndrome. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 34, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, J.; van Doorn, P.; Hegedus, E.; Lewis, J.; van der Windt, D. A systematic review of the global prevalence and incidence of shoulder pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garving, C.; Jakob, S.; Bauer, I.; Nadjar, R.; Brunner, U.H. Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brattberg, G.; Parker, M.G.; Thorslund, M. The prevalence of pain among the oldest old in Sweden. Pain 1996, 67, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Ditsios, K.; Middleton, W.D.; Hildebolt, C.F.; Galatz, L.M.; Teefey, S.A. The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease. A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic shoulders. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myklebust, G.; Hasslan, L.; Bahr, R.; Steffen, K. High prevalence of shoulder pain among elite Norwegian female handball players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Qadir, I.; Azam, M. Subacromial impingement syndrome. Orthop. Rev. (Pavia) 2012, 4, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consigliere, P.; Haddo, O.; Levy, O.; Sforza, G. Subacromial impingement syndrome: Management challenges. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neer, C.S., 2nd. Anterior acromioplasty for the chronic impingement syndrome in the shoulder: A preliminary report. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1972, 54, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, K.S. Subacromial Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder: A Musculoskeletal Disorder or a Medical Myth? Malays. Orthop. J. 2019, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, A.K.; Flatow, E.L. Subacromial impingement syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2011, 19, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelein, B.; Cagnie, B.; Cools, A. Scapular muscle dysfunction associated with subacromial pain syndrome. J. Hand Ther. 2017, 30, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Graf, A.R.; Karzon, A.L.; Graulich, B.L.; Egger, A.C.; Taub, S.M.; Gottschalk, M.B.; Bowers, R.L.; Wagner, E.R. Pectoralis minor syndrome—Review of pathoanatomy, diagnosis, and management of the primary cause of neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome. JSES Rev. Rep. Tech. 2022, 2, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S.J.; Funk, L.; Sciascia, A.; Kibler, W.B. Scapular dyskinesis: The surgeon’s perspective. Shoulder Elb. 2015, 7, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.A.; Arons, R.R.; Hurwitz, S.; Ahmad, C.S.; Levine, W.N. The rising incidence of acromioplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrestijn, O.; Stevens, M.; Winters, J.C.; van der Meer, K.; Diercks, R.L. Conservative or surgical treatment for subacromial impingement syndrome? A systematic review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2009, 18, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, L.; Hay, E.M.; Koes, B.W.; Huisstede, B.M. Effectiveness of surgical and postsurgical interventions for the subacromial impingement syndrome: A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, T.V.; Jain, N.B.; Page, C.M.; Lahdeoja, T.A.; Johnston, R.V.; Salamh, P.; Kavaja, L.; Ardern, C.L.; Agarwal, A.; Vandvik, P.O.; et al. Subacromial decompression surgery for rotator cuff disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 1, CD005619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahdeoja, T.; Karjalainen, T.; Jokihaara, J.; Salamh, P.; Kavaja, L.; Agarwal, A.; Winters, M.; Buchbinder, R.; Guyatt, G.; Vandvik, P.O.; et al. Subacromial decompression surgery for adults with shoulder pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, R.; Bron, C.; Dorrestijn, O.; Meskers, C.; Naber, R.; de Ruiter, T.; Willems, J.; Winters, J.; van der Woude, H.J.; Dutch Orthopaedic, A. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of subacromial pain syndrome: A multidisciplinary review by the Dutch Orthopaedic Association. Acta Orthop. 2014, 85, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, D.J.; Rees, J.L.; Cook, J.A.; Rombach, I.; Cooper, C.; Merritt, N.; Shirkey, B.A.; Donovan, J.L.; Gwilym, S.; Savulescu, J.; et al. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression for subacromial shoulder pain (CSAW): A multicentre, pragmatic, parallel group, placebo-controlled, three-group, randomised surgical trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, J.; Mall, N.; MacDonald, P.B.; Van Thiel, G.; Cole, B.J.; Romeo, A.A.; Verma, N.N. The role of subacromial decompression in patients undergoing arthroscopic repair of full-thickness tears of the rotator cuff: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthroscopy 2012, 28, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Miao, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.L. Does concomitant acromioplasty facilitate arthroscopic repair of full-thickness rotator cuff tears? A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Springerplus 2016, 5, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, T.V.; Jain, N.B.; Heikkinen, J.; Johnston, R.V.; Page, C.M.; Buchbinder, R. Surgery for rotator cuff tears. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, CD013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, A.M.; Michener, L.A. Shoulder pain: Can one label satisfy everyone and everything? Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J. The End of an Era? J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2018, 48, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigliani, L.U.; Levine, W.N. Subacromial impingement syndrome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1997, 79, 1854–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Friedman, J.M. The Human Disharmony Loop: A Case Series Proposing the Unique Role of the Pectoralis Minor in a Unifying Syndrome of Chronic Pain, Neuropathy, and Weakness. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibler, W.B.; McMullen, J. Scapular dyskinesis and its relation to shoulder pain. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2003, 11, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.S.; Pham, B.; Scala, V. Arthroscopic pectoralis minor release in the beach chair position. JSES Rev. Rep. Tech. 2022, 2, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.A.; Munshi, M.-A.H.; Woodard, D.R.; DeFroda, S.F.; Nuelle, C.W.; Richard Ma, S.-Y. Arthroscopic Pectoralis Minor Release. Arthrosc. Tech. 2025, 14, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, S.T.; Hoyle, M.; Tokish, J.M. Arthroscopic Pectoralis Minor Release. Arthrosc. Tech. 2018, 7, e589–e594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, M.T.; Kirby, H.; McDonald, L.S.; Golijanin, P.; Gross, D.; Campbell, K.J.; LeClere, L.; Sanchez, G.; Anthony, S.; Romeo, A.A. Surgical Release of the Pectoralis Minor Tendon for Scapular Dyskinesia and Shoulder Pain. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servasier, L.; Jeudy, J.; Raimbeau, G.; Bigorre, N. Arthroscopic release of the pectoralis minor tendon as an adjunct to acromioplasty in the treatment of subacromial syndrome associated with scapular dyskinesia. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2022, 108, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struyf, F.; Nijs, J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Mottram, S.; Meeusen, R. Scapular positioning and movement in unimpaired shoulders, shoulder impingement syndrome, and glenohumeral instability. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2011, 21, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S.; Wright, C.; Green, A. Subacromial impingement syndrome: The effect of changing posture on shoulder range of movement. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2005, 35, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludewig, P.M.; Braman, J.P. Shoulder impingement: Biomechanical considerations in rehabilitation. Man. Ther. 2011, 16, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, T.; Hallgren, H.B.; Oberg, B.; Adolfsson, L.; Johansson, K. Effect of specific exercise strategy on need for surgery in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: Randomised controlled study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1456–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, S.; Meisel, C.; Tate, A. A cross-sectional study examining shoulder pain and disability in Division I female swimmers. J. Sport. Rehabil. 2014, 23, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeser, J.C.; Joy, E.A.; Porucznik, C.A.; Berg, R.L.; Colliver, E.B.; Willick, S.E. Risk factors for volleyball-related shoulder pain and dysfunction. PMR 2010, 2, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, A.; Turner, G.N.; Knab, S.E.; Jorgensen, C.; Strittmatter, A.; Michener, L.A. Risk factors associated with shoulder pain and disability across the lifespan of competitive swimmers. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelein, B.; Cagnie, B.; Parlevliet, T.; Cools, A. Scapulothoracic muscle activity during elevation exercises measured with surface and fine wire EMG: A comparative study between patients with subacromial impingement syndrome and healthy controls. Man. Ther. 2016, 23, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, H.; Janakiraman, B.; Gelaw, A.Y.; Fisseha, B.; Sundaram, S.; Sharma, H.R. Effect of scapular stabilization exercise program in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome: A systematic review. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarsen, B.; Bahr, R.; Andersson, S.H.; Munk, R.; Myklebust, G. Reduced glenohumeral rotation, external rotation weakness and scapular dyskinesis are risk factors for shoulder injuries among elite male handball players: A prospective cohort study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G.P.; Goodman, D.A.; Flatow, E.L.; Bigliani, L.U. The acromion: Morphologic condition and age-related changes. A study of 420 scapulas. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 1996, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Yildiz, V.; Kalali, F.; Yildirim, O.S.; Topal, M.; Dostbil, A. The role of acromion morphology in chronic subacromial impingement syndrome. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2011, 77, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.; Bergstrom, A.; Schroder, K.; Foldevi, M. Subacromial corticosteroid injection or acupuncture with home exercises when treating patients with subacromial impingement in primary care—A randomized clinical trial. Fam. Pract. 2011, 28, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Thompson, L.; Kjoenoe, A.; Juul-Kristensen, B.; Cavalheri, V.; McKenna, L. No relationship between the acromiohumeral distance and pain in adults with subacromial pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, E.J.; Goode, A.P.; Cook, C.E.; Michener, L.; Myer, C.A.; Myer, D.M.; Wright, A.A. Which physical examination tests provide clinicians with the most value when examining the shoulder? Update of a systematic review with meta-analysis of individual tests. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 964–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
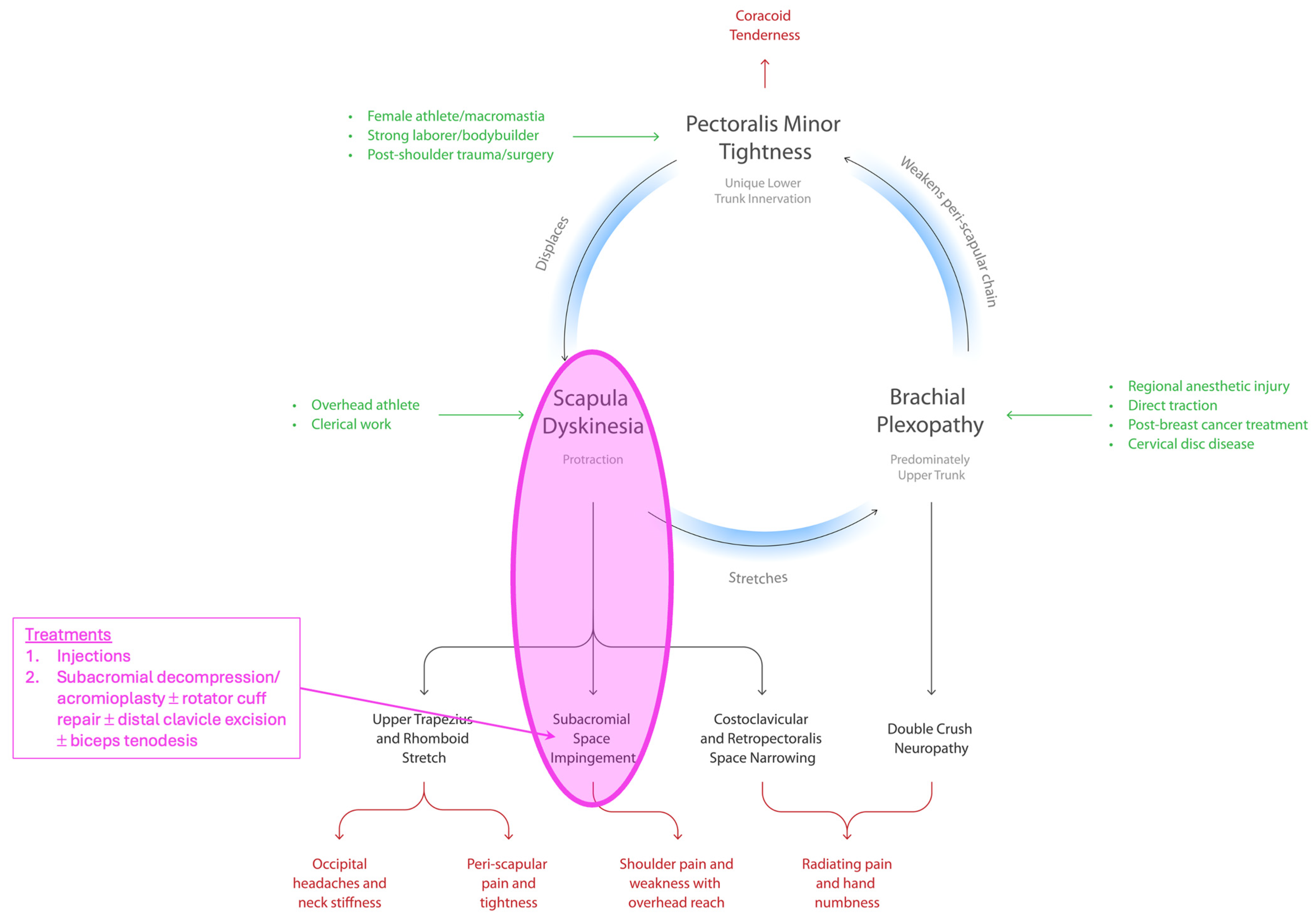
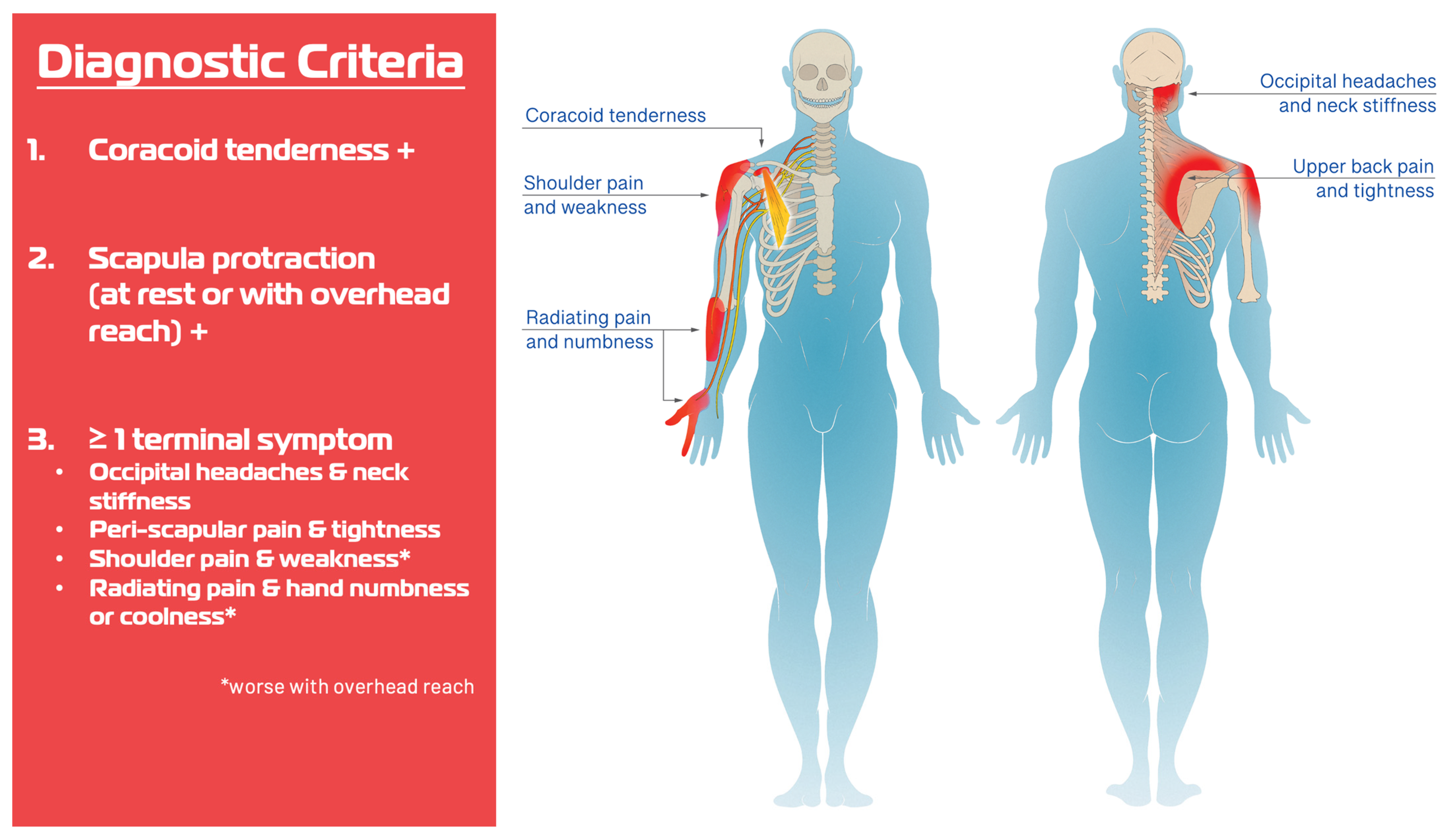



| Variable | N = 140 |
|---|---|
| Age | 49 [37–60] |
| Sex | Male 58 (41%) |
| Female 82 (59%) | |
| BMI | 29 [25–33] |
| Workers Compensation | 35 (25%) |
| Surgical History | |
| Subacromial decompression | 38 (27%) |
| Rotator cuff repair | 29 (21%) |
| Biceps tenodesis | 23 (16%) |
| SLAP repair | 5 (4%) |
| Labral repair | 3 (2%) |
| Bankart repair | 2 (2%) |
| Distal clavicle resection | 10 (7%) |
| Clavicle ORIF | 1 (1%) |
| Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty | 14 (10%) |
| 1st rib resection + scalenectomy | 2 (1%) |
| Cervical spine fusion | 22 (16%) |
| Distal neurolysis (carpal, cubital) | 39 (28%) |
| MRI Findings | (n = 52) |
| Supraspinatus tendinopathy or tear | 42 (81%) |
| Subscapularis tendinopathy or tear | 2 (4%) |
| Bicipital tendonitis | 9 (17%) |
| SLAP tear | 8 (15%) |
| Labral tear | 6 (12%) |
| Laterality | Right 80 (57%) |
| Left 60 (43%) | |
| Hand Dominance | Right 114 (81%) |
| Left 26 (19%) | |
| Medial Coracoid Injection | Provided Relief 99 (88%) |
| Symptom | Preoperative | Postoperative 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | 8 [6–9] | 2 [0–3] | <0.01 |
| Scapular Dyskinesia Stage | |||
| Stage I | 0 (0%) | 132 (94%) | |
| Stage II | 4 (3%) | 8 (6%) | <0.01 |
| Stage III | 68 (49%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Stage IV | 68 (49%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Shoulder Abduction ROM | 90 [90–100] | 180 [180–180] | <0.01 |
| Positive Impingement Signs | 140 (100%) | 15 (11%) | <0.01 |
| Neuropathic Lesions 2 | |||
| Scalene muscles | 86 (61%) | 3 (2%) | |
| Suprascapular notch | 88 (63%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Quadrilateral space | 127 (91%) | 17 (12%) | <0.01 |
| Radial tunnel | 96 (69%) | 28 (20%) | |
| Cubital tunnel | 37 (26%) | 31 (22%) | |
| Carpal tunnel | 72 (51%) | 33 (24%) | |
| Secondary Neurolysis 3 | 27 (19%) | ||
| Suprascapular | 0 (0%) | ||
| Quadrilateral space | N/A | 9 (6%) | N/A |
| Radial | 13 (9%) | ||
| Cubital | 14 (10%) | ||
| Carpal | 9 (6%) |
| PMS | HDL | |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Unknown | Unique asymmetric lower trunk innervation |
| Mechanism | Compressive neuropathy | Deformation of scapula |
| Symptoms | Distal neuropathy only | All: headaches, neck pain, shoulder impingement, myofascial trigger points, and distal and proximal neuropathy |
| Anatomic Relationships to Other Chronic Pain Entities | Completely unknown | Clearly specifies cause and effect |
| Prognostic Value | Minimal | Strong |
| Epidemiology | Very rare | Ubiquitous |
| Relative Importance in Upper Limb Chronic Pain | After-thought | Central |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, K.; Iyengar, J.; Friedman, J. The Human Disharmony Loop: The Anatomic Source Behind Subacromial Impingement and Pain. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165650
Sharma K, Iyengar J, Friedman J. The Human Disharmony Loop: The Anatomic Source Behind Subacromial Impingement and Pain. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Ketan, Jaicharan Iyengar, and James Friedman. 2025. "The Human Disharmony Loop: The Anatomic Source Behind Subacromial Impingement and Pain" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165650
APA StyleSharma, K., Iyengar, J., & Friedman, J. (2025). The Human Disharmony Loop: The Anatomic Source Behind Subacromial Impingement and Pain. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165650





