Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
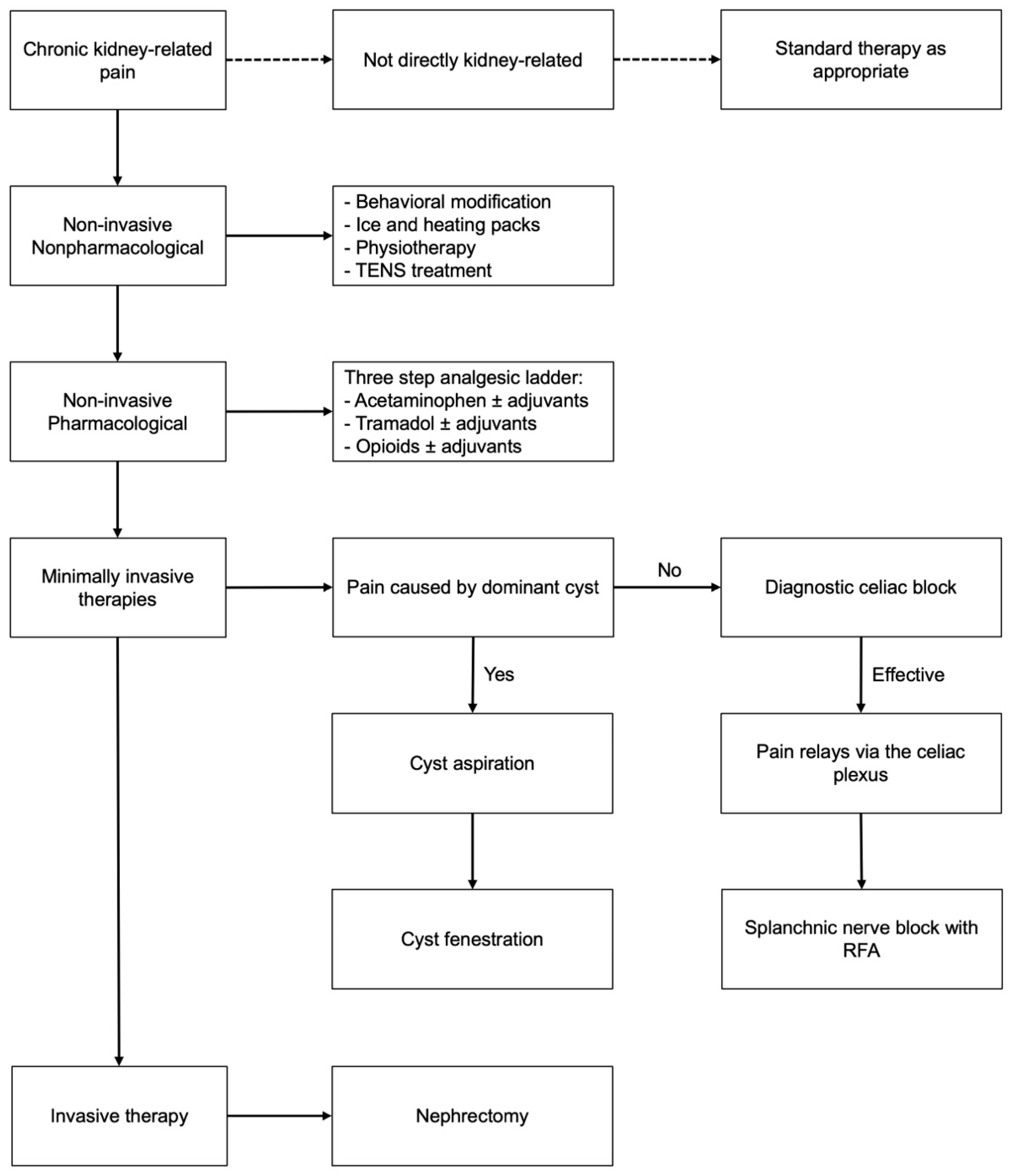
2.2. Adapted Treatment Protocol
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Sample Size Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
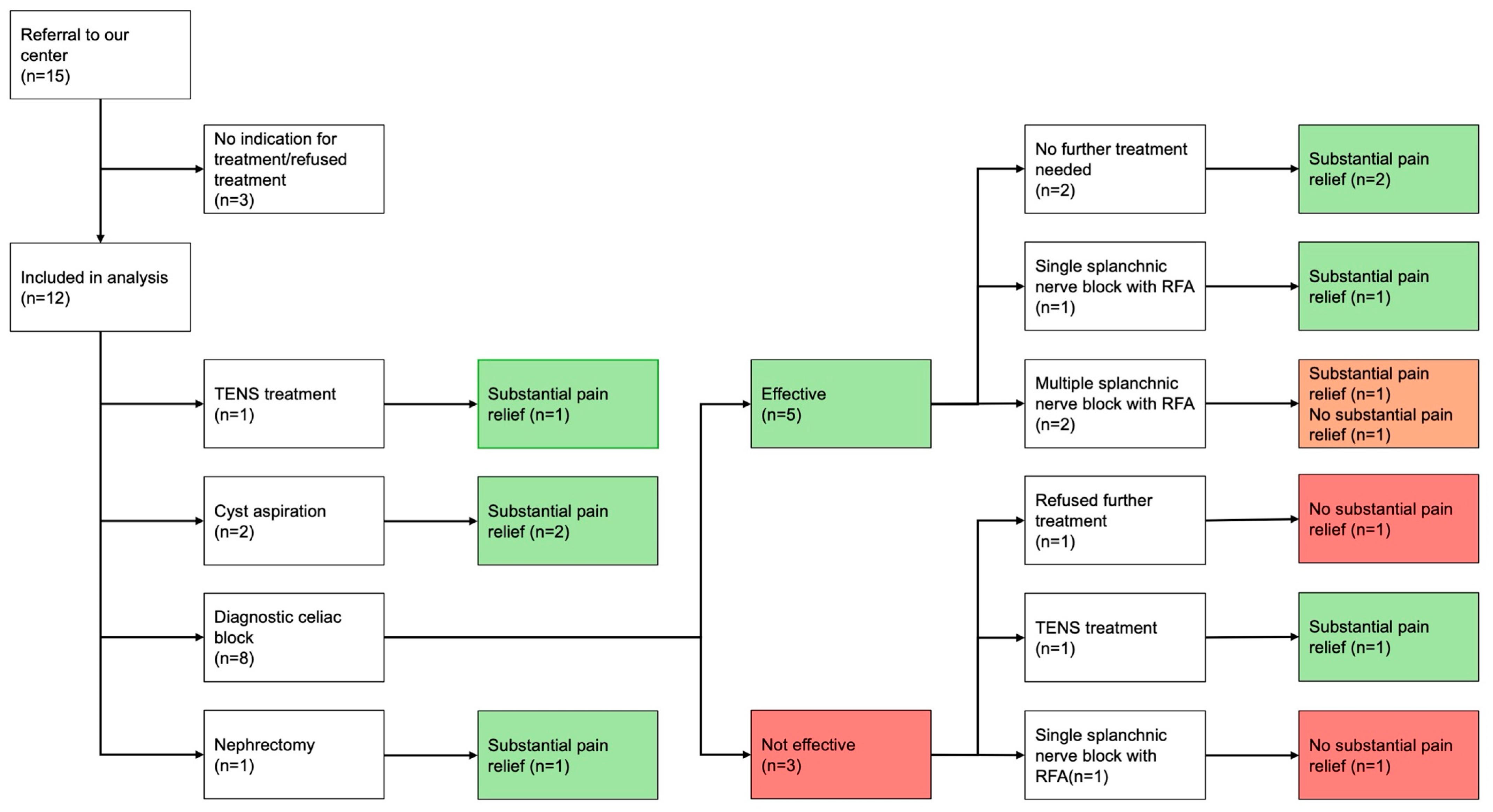
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Pain Characteristics
3.2. Protocolized Treatment
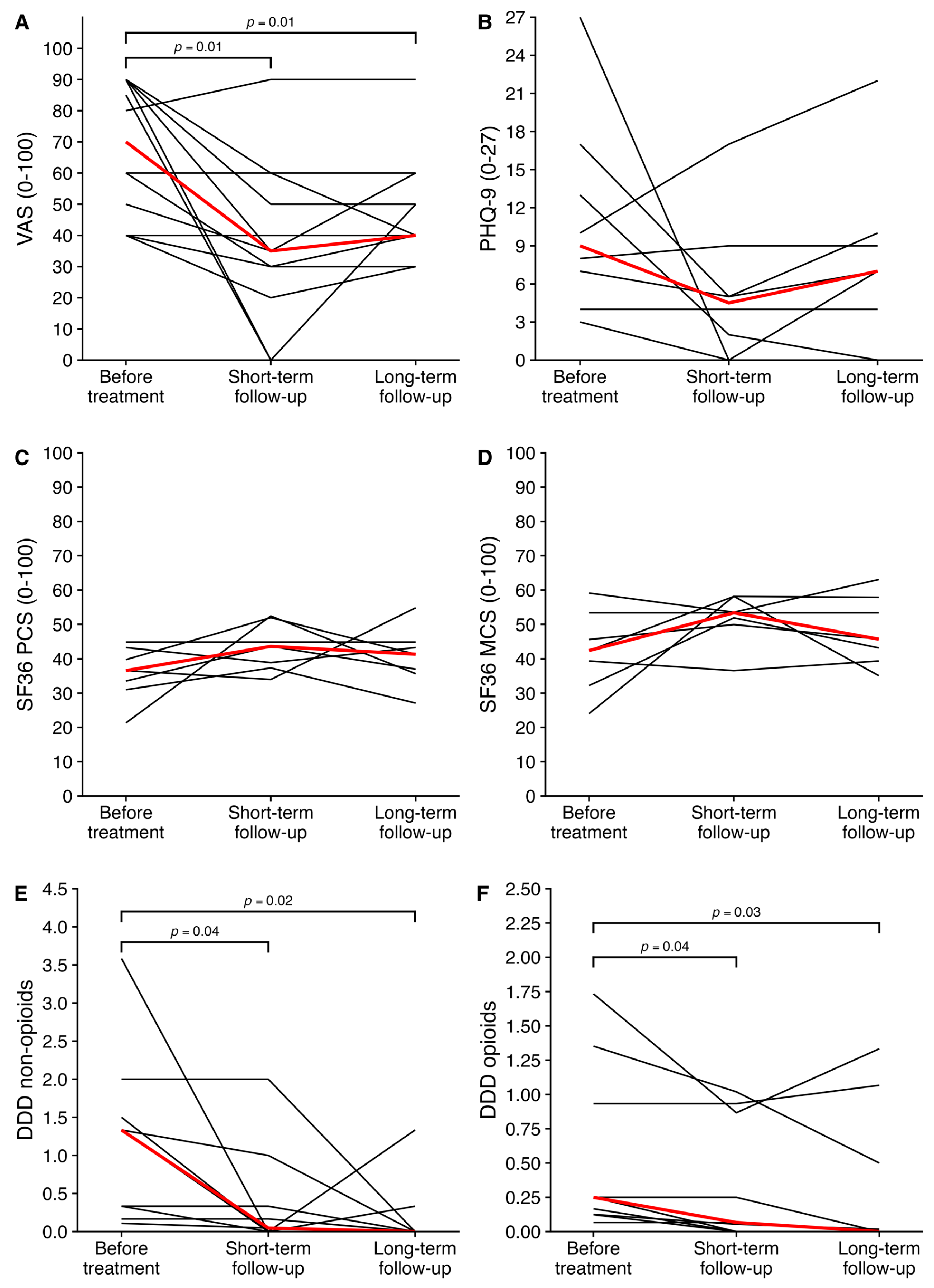
3.3. Long-Term Follow-Up
3.4. Adverse Events
3.5. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scales, C.D., Jr.; Smith, A.C.; Hanley, J.M.; Saigal, C.S. Urologic Diseases in America Project. Prevalence of kidney stones in the United States. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, R.L.; Casteleijn, N.F.; de Beus, E.; Bots, M.L.; Vonken, E.E.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Blankestijn, P.J. Catheter-based renal denervation as therapy for chronic severe kidney-related pain. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018, 33, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.V.; Drewes, A.M.; Frimodt-Moller, P.C.; Osther, P.J. Visceral pain originating from the upper urinary tract. Urol. Res. 2010, 38, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Ahmed, K.; Lee, N.; Challacombe, B.; Khan, M.S.; Dasgupta, P. Management of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in adults. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, S.; Sweeney, B.; Granata, C.; Piaggio, G.; Jasonni, V.; Puri, P. Vesicoureteral reflux and ureteropelvic junction obstruction in children with horseshoe kidney: Treatment and outcome. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 2566–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.H.; Koo, B.; Riddick, A.; Shah, N.; Stewart, G.D. Different Successful Management Strategies for Obstructing Renal Parapelvic Cysts. Urol. Int. 2018, 101, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio, A.; Salvarani, C.; Buzio, C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet 2006, 367, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, A.S.; Salameh, H.; Erickson, S.B.; Prieto, M. Loin pain hematuria syndrome. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.E.E.; Nicolson, K.P.; Smith, B.H. Chronic pain: A review of its epidemiology and associated factors in population-based studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e273–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellman, M.W.; Bahler, C.D.; Shumate, A.M.; Bacallao, R.L.; Sundaram, C.P. Management of pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and anatomy of renal innervation. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Luijk, F.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Blokzijl, H.; Groen, G.J.; de Haas, R.J.; Leliveld, A.M.; Meijer, E.; Perdok, J.M.; Stellema, R.; Wolff, A.P.; et al. Multidisciplinary management of chronic refractory pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2023, 38, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteleijn, N.F.; Visser, F.W.; Drenth, J.P.; Gevers, T.J.; Groen, G.J.; Hogan, M.C.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Consortium, D. A stepwise approach for effective management of chronic pain in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2014, 29 (Suppl. S4), iv142–iv153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteleijn, N.F.; van Gastel, M.D.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Drenth, J.P.; de Jager, R.L.; Leliveld, A.M.; Stellema, R.; Wolff, A.P.; Groen, G.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; et al. Novel treatment protocol for ameliorating refractory, chronic pain in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, J.E.; Harper, R.; Jones, N.M.; O’Cathain, A.; Thomas, K.J.; Usherwood, T.; Westlake, L. Validating the SF-36 health survey questionnaire: New outcome measure for primary care. BMJ 1992, 305, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, M.F.; Bjerre, E.; Hansen, M.D.; Hilden, J.; Landler, N.E.; Tendal, B.; Hrobjartsson, A. Pain relief that matters to patients: Systematic review of empirical studies assessing the minimum clinically important difference in acute pain. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, J.E.; Kosinski, M.; Keller, S.D. SF-36 Physical and Mental Health Summary Scales: A User’s Manual; Health Assessment Lab, New England Medical Center: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lugo-Gavidia, L.M.; Nolde, J.M.; Kiuchi, M.G.; Shetty, S.; Azzam, O.; Carnagarin, R.; Schlaich, M.P. Interventional Approaches for Loin Pain Hematuria Syndrome and Kidney-Related Pain Syndromes. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain. 2011, 152, S2–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigchelaar, E.F.; Zhernakova, A.; Dekens, J.A.M.; Hermes, G.; Baranska, A.; Mujagic, Z.; Swertz, M.A.; Muñoz, A.M.; Deelen, P.; Cénit, M.C.; et al. Cohort profile: LifeLines DEEP, a prospective, general population cohort study in the northern Netherlands: Study design and baseline characteristics. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocalevent, R.D.; Hinz, A.; Brahler, E. Standardization of the depression screener patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) in the general population. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2013, 35, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Acher, P.; Deane, A.M. Ureteric bupivicaine infusion for loin pain haematuria syndrome. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2010, 92, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goroszeniuk, T.; Khan, R.; Kothari, S. Lumbar sympathetic chain neuromodulation with implanted electrodes for long-term pain relief in loin pain haematuria syndrome. Neuromodulation 2009, 12, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwell, T.J.; Peters, J.L.; Neild, G.H.; Shah, P.J. The outcome of renal denervation for managing loin pain haematuria syndrome. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.; Giebel, S.; Garcia, F.; Goyal, K.; St Onge, J.R. Renal Denervation in Patients with Loin Pain Hematuria Syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheil, A.G.; Ibels, L.S.; Thomas, M.A.; Graham, J.C. Renal autotransplantation for severe loin-pain/haematuria syndrome. Lancet 1985, 2, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, A.; Gutierrez, J.C.B.; Vivian, E.; Shah, J.M.Y.; Dickerman, R. Robotic assisted kidney auto-transplantation as a safe alternative for treatment of nutcracker syndrome and loin pain haematuria syndrome: A case series report. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comp. 2023, 19, e2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoh, C.C.; Kumar, V.; Timoney, A.G. The use of capsaicin in loin pain-haematuria syndrome. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Bergman, J.; Pierre, J.; Tomycz, N.D. Spinal Cord Stimulation for Loin Pain Hematuria Syndrome: Clinical Report. Pain. Pract. 2019, 19, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annear, N.M.P.; Vanmassenhove, J.; Lameire, N.; Phillips, M.E.; Eastwood, J.B. Loin pain haematuria syndrome 1967-2020: A review. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfae034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, W.W.; Kuebker, J.M.; Shu, X.; Sobey, C.M.; Hsi, R.S. Celiac plexus block for chronic flank pain: A case series. Can. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 10556–10559. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.; Hans, G.; Dickenson, A.H. Peripheral input and its importance for central sensitization. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skolarikos, A.; Jung, H.; Neisius, A.; Petřík, A.; Somani, B.; Tailly, T.; Gambaro, G.; Davis, N.F.; Geraghty, R.; Lombardo, R.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Urolithiasis; European Association of Urology: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, R.A.; Doppen, C.; Bus, M.T.J.; Altobelli, E.; de Jong, I.J.; Roemeling, S. The significance of clinically insignificant residual fragments after percutaneous nephrolithotomy: An analysis into the relevance of complete stone clearance. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, S.J.; Jacques, R.M.; dos Anjos Henriques-Cadby, I.B.; Candlish, J.; Totton, N.; Xian, M.T.S. Sample size estimation for randomised controlled trials with repeated assessment of patient-reported outcomes: What correlation between baseline and follow-up outcomes should we assume? Trials 2019, 20, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n = 12 | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 50 [36–59] |
| Female sex, n (%) | 8 (67) |
| Height (cm) | 174 [167–180] |
| Weight (kg) | 83 [71–93] |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 27 [25–33] |
| History of | |
| -Kidney stones, n (%) | 8 (68) |
| -Urinary tract infection, n (%) | 4 (33) |
| -Upper urinary tract infection, n (%) | 3 (25) |
| -Episodes of macroscopic hematuria, n (%) | 4 (33) |
| -Kidney surgery, n (%) | 2 (17) |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 130 [120–143] |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 83 [74–89] |
| Use of blood pressure lowering drugs, n (%) | 6 (50) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 80 [71–89] |
| Short Form-36 Score | |
| -Physical component score (0–100) | 36.6 [32.3–41.5] |
| -Mental component score (0–100) | 42.4 [35.8–49.5] |
| PHQ-9 score (0–27) | 9.0 [6.3–14.0] |
| n = 12 | |
|---|---|
| Duration of pain (years) | 1.9 [1.0–4.7] |
| Pain severity last 4 weeks | |
| -Minimum VAS score (0–100) | 55 [38–63] |
| -Maximum VAS score (0–100) | 80 [75–91] |
| -Average VAS score (0–100) | 70 [48–90] |
| Assumed cause of chronic pain * | |
| -Kidney stones, n (%) | 6 (50) |
| -Anatomic abnormality of the kidney, n (%) | 3 (25) |
| -Upper urinary tract infection, n (%) | 1 (8) |
| -Kidney surgery, n (%) | 1 (8) |
| -Loin pain hematuria syndrome, n (%) | 1 (8) |
| -Previous radiotherapy, n (%) | 1 (8) |
| Patient reported location as ** | |
| -Left kidney, n (%) | 4 (33) |
| --Ventral side | 3 (25) |
| --Dorsal side | 4 (33) |
| -Right kidney, n (%) | 10 (83) |
| --Ventral side | 8 (67) |
| --Dorsal side | 9 (75) |
| Management of pain | |
| -Nonpharmacological therapies, n (%) | |
| --Physiotherapy | 4 (33) |
| --Cognitive behavioral therapy | 2 (14) |
| -Pharmacological therapies, n (%) | |
| --Acetaminophen | 8 (67) |
| --NSAID | 5 (42) |
| --Sleep medication | 3 (25) |
| --Low-dose opioids | 5 (42) |
| --High-dose opioids | 5 (42) |
| -Previous invasive pain therapies, n (%) | |
| --Nerve block | 2 (17) |
| Before Treatment | Short-Term Follow-Up | Long-Term Follow-Up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | p-Value | Characteristics | p-Value | ||
| Positive effect last intervention (%) | - | 75 | - | 75 | - |
| VAS score (0–100) | 70 [48–90] | 35 [28–53] | 0.01 | 40 [38–53] | 0.01 |
| Defined daily dose non-opioids * | 1.33 [0.33–1.50] | 0.05 [0–0.33] | 0.04 | 0 [0–0.02] | 0.02 |
| Defined daily dose opioids * | 0.25 [0.12–0.93] | 0.07 [0–0.87] | 0.04 | 0 [0–0.50] | 0.03 |
| Physical component score (0–100) | 36.6 [32.3–41.5] | 43.6 [38.1–48.4] | 0.1 | 41.3 [36.3–44.1] | 0.3 |
| Mental component score (0–100) | 42.4 [35.8–49.5] | 53.4 [50.9–55.8] | 0.2 | 45.7 [41.3–55.6] | 0.1 |
| PHQ-9 score (0–27) | 9.0 [6.3–14.0] | 4.5 [1.5–6.0] | 0.2 | 7.0 [3.0–9.3] | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geertsema, P.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Doornweerd, B.H.J.; de Haas, R.J.; Perdok, J.M.; Roemeling, S.; Stellema, R.; Wolff, A.P.; Casteleijn, N.F. Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165623
Geertsema P, Gansevoort RT, Doornweerd BHJ, de Haas RJ, Perdok JM, Roemeling S, Stellema R, Wolff AP, Casteleijn NF. Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(16):5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165623
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeertsema, Paul, Ron T. Gansevoort, Benjamin H. J. Doornweerd, Robbert J. de Haas, Joke M. Perdok, Stijn Roemeling, Ruud Stellema, André P. Wolff, and Niek F. Casteleijn. 2025. "Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 16: 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165623
APA StyleGeertsema, P., Gansevoort, R. T., Doornweerd, B. H. J., de Haas, R. J., Perdok, J. M., Roemeling, S., Stellema, R., Wolff, A. P., & Casteleijn, N. F. (2025). Results of a Multidisciplinary Stepwise Protocol to Treat Chronic Refractory Kidney-Related Pain. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(16), 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14165623







