The Effect of Mild Exercise in the Chemotherapy Room on the Anxiety Level of Cancer Patients: A Prospective Observational Paired Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Intervention
2.2. Statistical Analysis
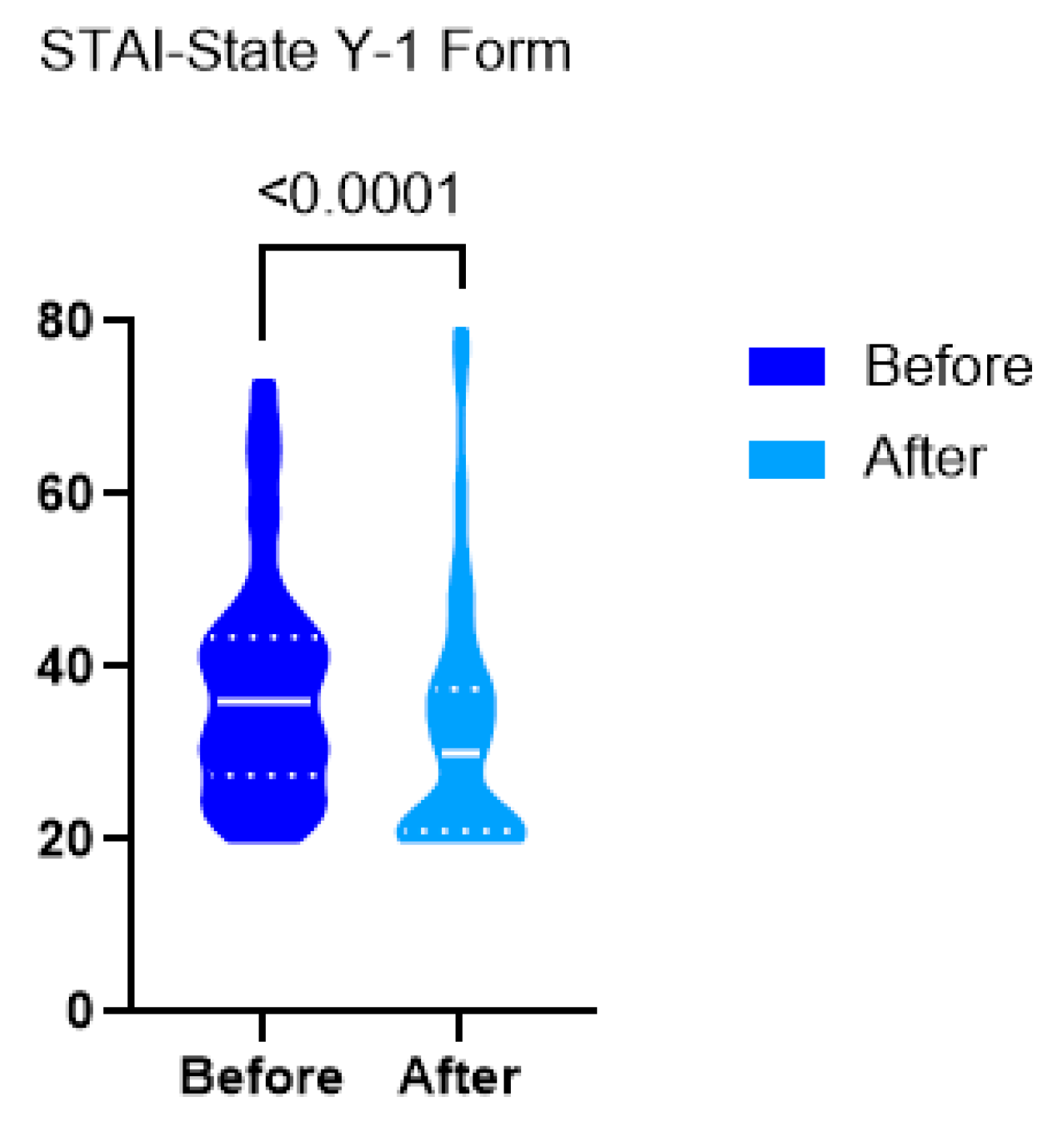
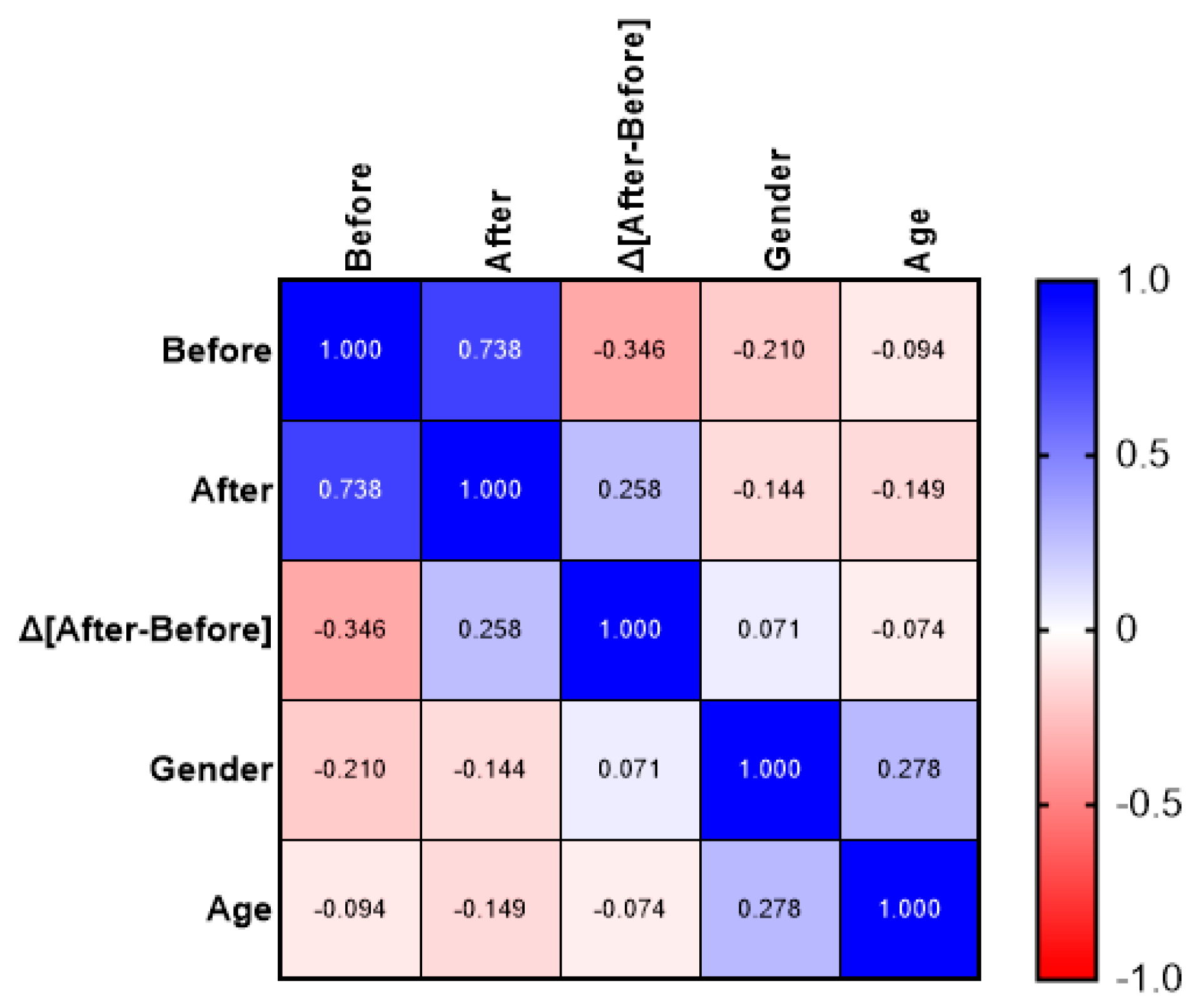
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| STAI | State–Trait Anxiety Inventory |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| ACSM | American College of Sports Medicine |
| ExCITE | Exercise and Cancer Integrative Therapy and Education Program |
References
- Wang, Y.; Feng, W. Cancer-related psychosocial challenges. Gen. Psychiatry 2022, 35, e100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, F.; Majid, E.; Florence, L.; Matthieu, L.; Mireille, C.; Les, M.; Mariana, P.; Ariana, Z.; Isabelle, S.; Freddie, B. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2024; Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Mayer, R.S.; Engle, J. Rehabilitation of Individuals with Cancer. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 46, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; Farquhar-Smith, P. Pain in cancer survivors; filling in the gaps. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Heidari, Z.; Feizi, A.; Hassanzadeh Keshteli, A.; Roohafza, H.; Afshar, H.; Adibi, P. Association of Stressful Life Events with Psychological Problems: A Large-Scale Community-Based Study Using Grouped Outcomes Latent Factor Regression with Latent Predictors. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2017, 2017, 3457103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, L.; Caruso, R.; Riba, M.B.; Lloyd-Williams, M.; Kissane, D.; Rodin, G.; McFarland, D.; Campos-Ródenas, R.; Zachariae, R.; Santini, D.; et al. Anxiety and depression in adult cancer patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, D.P.H.; House, A. Anxiety in cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Ferguson, D.W.; Gill, J.; Paul, J.; Symonds, P. Depression and anxiety in long-term cancer survivors compared with spouses and healthy controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A. Impact of Social Isolation, Physician-Patient Communication, and Self-perception on the Mental Health of Patients With Cancer and Cancer Survivors: National Survey Analysis. Interact. J. Med. Res. 2023, 12, e45382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.H.; Courneya, K.S.; Matthews, C.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Galvão, D.A.; Pinto, B.M.; Irwin, M.L.; Wolin, K.Y.; Segal, R.J.; Lucia, A.; et al. American College of Sports Medicine Roundtable on Exercise Guidelines for Cancer Survivors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffart, L.M.; Kalter, J.; Sweegers, M.G.; Courneya, K.S.; Newton, R.U.; Aaronson, N.K.; Jacobsen, P.B.; May, A.M.; Galvão, D.A.; Chinapaw, M.J.; et al. Effects and moderators of exercise on quality of life and physical function in patients with cancer: An individual patient data meta-analysis of 34 RCTs. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormie, P.; Zopf, E.M.; Zhang, X.; Schmitz, K.H. The Impact of Exercise on Cancer Mortality, Recurrence, and Treatment-Related Adverse Effects. Epidemiol. Rev. 2017, 39, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, J.K.W.; Vincent, A.J.P.E. Exercise improves quality of life in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses-Echávez, J.F.; González-Jiménez, E.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Effects of Supervised Multimodal Exercise Interventions on Cancer-Related Fatigue: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 328636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.I.; Scherer, R.W.; Snyder, C.; Geigle, P.M.; Berlanstein, D.R.; Topaloglu, O. Exercise interventions on health-related quality of life for people with cancer during active treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 8, CD008465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, R.F.; Ferreira-Júnior, J.B.; Marques, V.A.; Vieira, A.; Lira, C.A.B.; Campos, M.H.; Freitas-Junior, R.; Rahal, R.M.S.; Gentil, P.; Vieira, C.A. Resistance Training, Fatigue, Quality of Life, Anxiety in Breast Cancer Survivors. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.H.; Potiaumpai, M.; Schleicher, E.A.; Wolf, L.J.; Doerksen, S.E.; Drabick, J.J.; Yee, N.S.; Truica, C.I.; Mohamed, A.A.; Shaw, B.W.; et al. The exercise in all chemotherapy trial. Cancer 2021, 127, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. Guidelines for Implementing Exercise Programs for Cancer Patients. 2016. Available online: https://www.racgp.org.au/FSDEDEV/media/documents/Clinical%20Resources/HANDI/Guidelines-for-implementing-exercise.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Sturgeon, K.M.; Mathis, K.M.; Rogers, C.J.; Schmitz, K.H.; Waning, D.L. Cancer- and Chemotherapy-Induced Musculoskeletal Degradation. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofthagen, C.; Overcash, J.; Kip, K. Falls in persons with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, M.H. (Ed.) ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 7th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-7817-4506-2. [Google Scholar]
- Woltmann, M.L.; Foster, C.; Porcari, J.P.; Camic, C.L.; Dodge, C.; Haible, S.; Mikat, R.P. Evidence That the Talk Test Can Be Used to Regulate Exercise Intensity. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.R.; Pereira, H.M.; Silva, B.M. Perceived Exertion: Revisiting the History and Updating the Neurophysiology and the Practical Applications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, M.; Cataldi, F.; Carlucci, L.; Fairfield, B. Assessment of anxiety in older adults: A review of self-report measures. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 573–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, A.; Giannitsi, S. The reliability and validity of the Greek version of the Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Encephalos 1984, 21, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, M.; Sarita, G.P.; Devi, N.; Thomas, B.C.; Hussain, B.M.; Krishnan, R. Distress, anxiety, and depression in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.; Prust, M.; Kaiser, J. Chemotherapy, cognitive impairment and hippocampal toxicity. Hippocampal Vulnerability Mol. Dis. 2015, 309, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Bedi, C.; Humphris, G. The relationship between cancer patient’s fear of recurrence and chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychosom. Res. 2017, 98, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdizadeh, M.; Tirgari, B.; Abadi, O.; Bahaadinbeigy, K. Guided Imagery: Reducing Anxiety, Depression, and Selected Side Effects Associated with Chemotherapy. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 23, E87–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, A.; Suleman, S.; Hyde, N.; Hodgkiss, A. Depression and anxiety in patients with cancer. BMJ 2018, 361, k1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, V.; Bianco, F.; Di Blasio, A.; Morano, T.; Tuosto, D.; Mucedola, F.; Di Santo, S.; Cimini, A.; Napolitano, G.; Bucci, I.; et al. Cardiometabolic Profile, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors after Different Physical Exercise Protocols: A 34-Month Follow-Up Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcraft, K.A.; Peace, R.M.; Betof, A.S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Jones, L.W. Efficacy and Mechanisms of Aerobic Exercise on Cancer Initiation, Progression, and Metastasis: A Critical Systematic Review of In Vivo Preclinical Data. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4032–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Wentz, L.M. The compelling link between physical activity and the body’s defense system. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustian, K.M.; Sprod, L.K.; Palesh, O.G.; Peppone, L.J.; Janelsins, M.C.; Mohile, S.G.; Carroll, J. Exercise for the Management of Side Effects and Quality of Life Among Cancer Survivors. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2009, 8, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champ, C.E.; Carpenter, D.J.; Diaz, A.K.; Rosenberg, J.; Ackerson, B.G.; Hyde, P.N. Resistance Training for Patients with Cancer: A Conceptual Framework for Maximizing Strength, Power, Functional Mobility, and Body Composition to Optimize Health and Outcomes. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughney, L.; West, M.A.; Kemp, G.J.; Grocott, M.P.W.; Jack, S. Exercise intervention in people with cancer undergoing neoadjuvant cancer treatment and surgery: A systematic review. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. EJSO 2016, 42, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.M.; Zabor, E.C.; Schwitzer, E.; Koelwyn, G.J.; Adams, S.C.; Nilsen, T.S.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Matsoukas, K.; Iyengar, N.M.; Dang, C.T.; et al. Efficacy of Exercise Therapy on Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, A.; Arving, C.; Johansson, B.; Igelström, H.; Nordin, K. Perceived barriers to and facilitators of being physically active during adjuvant cancer treatment. Patient Educ. Couns. 2016, 99, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.J.; Seet-Lee, C.; Marthick, M.; Cheema, B.S.; Boyer, M.; Edwards, K.M. Aerobic exercise during chemotherapy infusion for cancer treatment: A novel randomised crossover safety and feasibility trial. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Hayes, S.C.; Spence, R.R.; Steele, M.L.; Millet, G.Y.; Gergele, L. Exercise and colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of exercise safety, feasibility and effectiveness. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avancini, A.; Borsati, A.; Toniolo, L.; Ciurnelli, C.; Belluomini, L.; Budolfsen, T.; Lillelund, C.; Milella, M.; Quist, M.; Pilotto, S. Physical activity guidelines in oncology: A systematic review of the current recommendations. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2025, 210, 104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.L.; Winters-Stone, K.M.; Wiskemann, J.; May, A.M.; Schwartz, A.L.; Courneya, K.S.; Zucker, D.S.; Matthews, C.E.; Ligibel, J.A.; Gerber, L.H.; et al. Exercise Guidelines for Cancer Survivors: Consensus Statement from International Multidisciplinary Roundtable. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.C.; Spence, R.R.; Galvão, D.A.; Newton, R.U. Australian Association for Exercise and Sport Science position stand: Optimising cancer outcomes through exercise. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2009, 12, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligibel, J.A.; Bohlke, K.; May, A.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Gilchrist, S.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Late, M.; Mansfield, S.; Marshall, T.F.; et al. Exercise, Diet, and Weight Management During Cancer Treatment: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2491–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, D.; Keteyian, S.; Ehrman, J.K.; Brown, S.; Filipiak, R.; Martinez, N.; Ihlenfeldt, D.; Varga, J.; Walker, E.M. A pilot study of aerobic exercise performed in breast cancer patients during chemotherapy infusion. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, e19527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housman, B.; Flores, R.; Lee, D.-S. Narrative review of anxiety and depression in patients with esophageal cancer: Underappreciated and undertreated. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 3160–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Li, J.-Q.; Shi, J.-F.; Que, J.-Y.; Liu, J.-J.; Lappin, J.M.; Leung, J.; Ravindran, A.V.; Chen, W.-Q.; Qiao, Y.-L.; et al. Depression and anxiety in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviola, F.; Pappaianni, E.; Monti, A.; Grecucci, A.; Jovicich, J.; De Pisapia, N. Trait and state anxiety are mapped differently in the human brain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battle, D.E. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). CoDAS 2013, 25, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Distress During Cancer Care; National Comprehensive Cancer Network; NCCN Foundation: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.nccn.org/patients/guidelines/content/PDF/distress-patient.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Üstündag, S.; Zencirci, A.D. Factors affecting the quality of life of cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: A questionnaire study. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2015, 2, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Improving the Quality of Cancer Care: Addressing the Challenges of an Aging Population; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine. Delivering High-Quality Cancer Care: Charting a New Course for a System in Crisis; Levit, L., Balogh, E., Nass, S., Ganz, P.A., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-309-28660-2. [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.R.; Jacobs, G.A. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (Form Y); Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
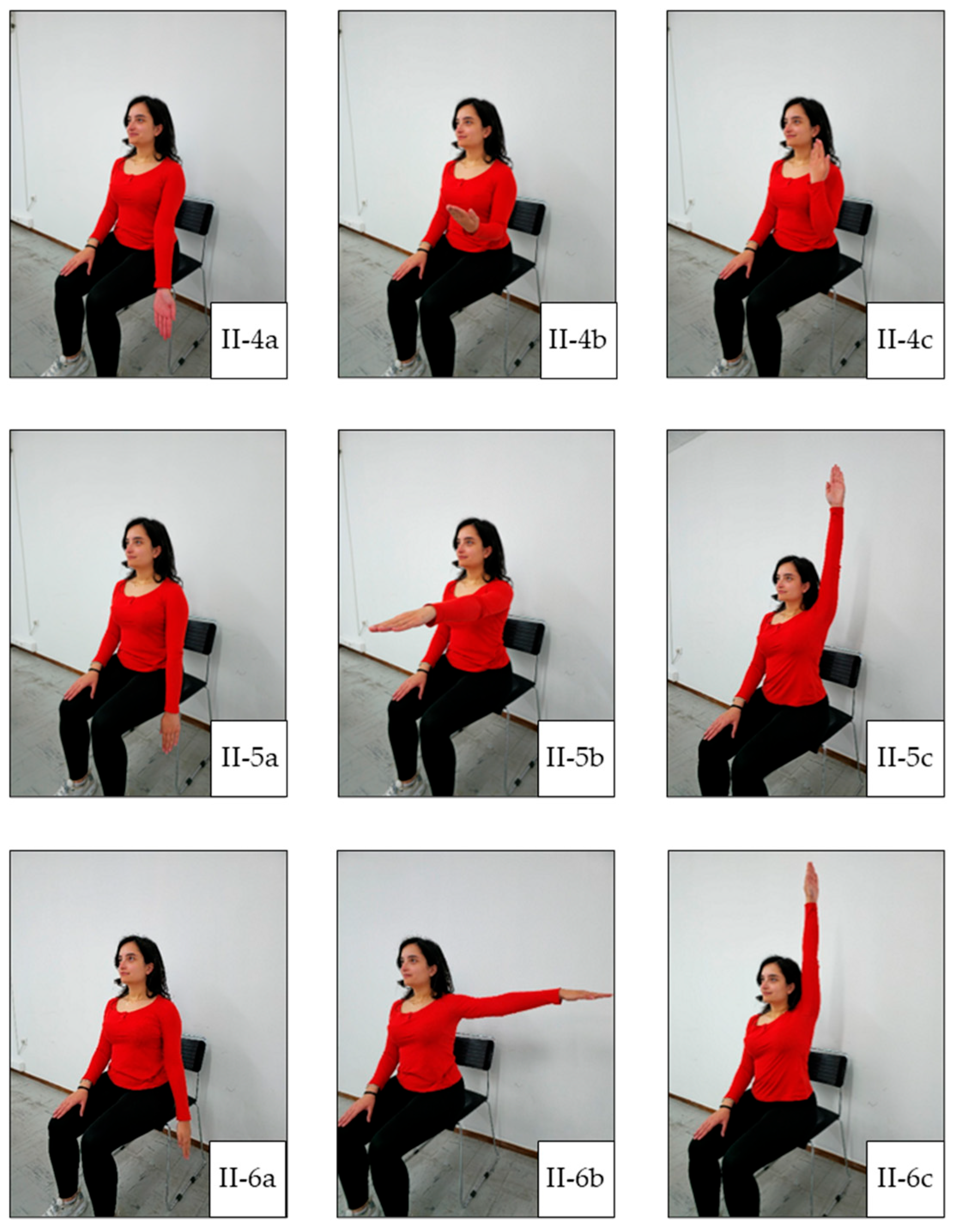






| Exercise Stage | Included Exercises |
|---|---|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
| |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavrogiannopoulou, C.; Papastratigakis, G.; Koutoulaki, E.; Vardakis, P.; Stefanakis, G.; Kourtsilidis, A.; Lasithiotakis, K.; Papaioannou, A.; Nyktari, V. The Effect of Mild Exercise in the Chemotherapy Room on the Anxiety Level of Cancer Patients: A Prospective Observational Paired Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155591
Mavrogiannopoulou C, Papastratigakis G, Koutoulaki E, Vardakis P, Stefanakis G, Kourtsilidis A, Lasithiotakis K, Papaioannou A, Nyktari V. The Effect of Mild Exercise in the Chemotherapy Room on the Anxiety Level of Cancer Patients: A Prospective Observational Paired Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155591
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavrogiannopoulou, Christina, Georgios Papastratigakis, Emmanouela Koutoulaki, Panagiotis Vardakis, Georgios Stefanakis, Athanasios Kourtsilidis, Kostantinos Lasithiotakis, Alexandra Papaioannou, and Vasileia Nyktari. 2025. "The Effect of Mild Exercise in the Chemotherapy Room on the Anxiety Level of Cancer Patients: A Prospective Observational Paired Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155591
APA StyleMavrogiannopoulou, C., Papastratigakis, G., Koutoulaki, E., Vardakis, P., Stefanakis, G., Kourtsilidis, A., Lasithiotakis, K., Papaioannou, A., & Nyktari, V. (2025). The Effect of Mild Exercise in the Chemotherapy Room on the Anxiety Level of Cancer Patients: A Prospective Observational Paired Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155591






