Objectification of the Functional Myodiagnosis Muscle Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
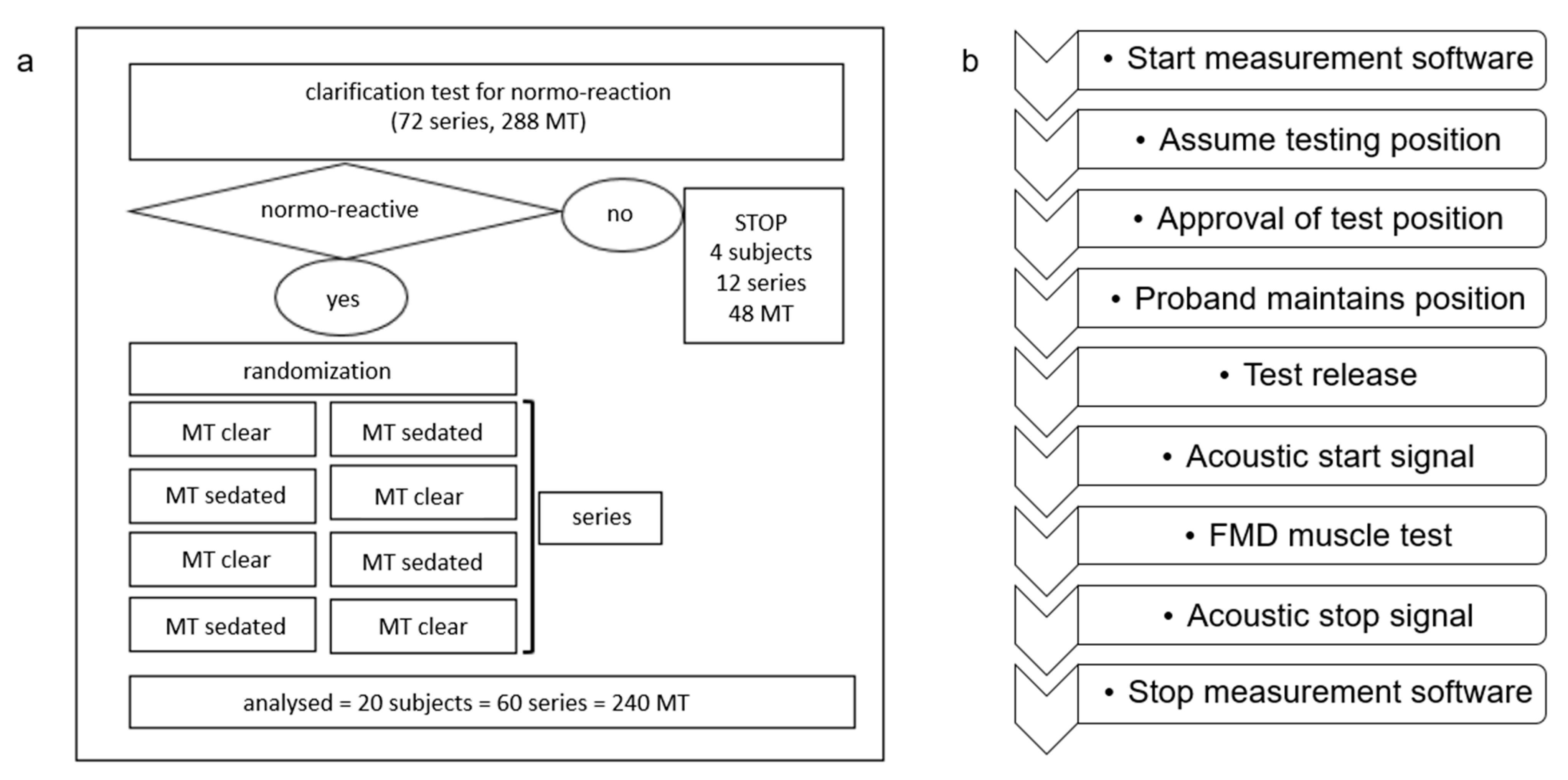
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Muscle Test Setup
2.3. Muscle Test Procedure
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
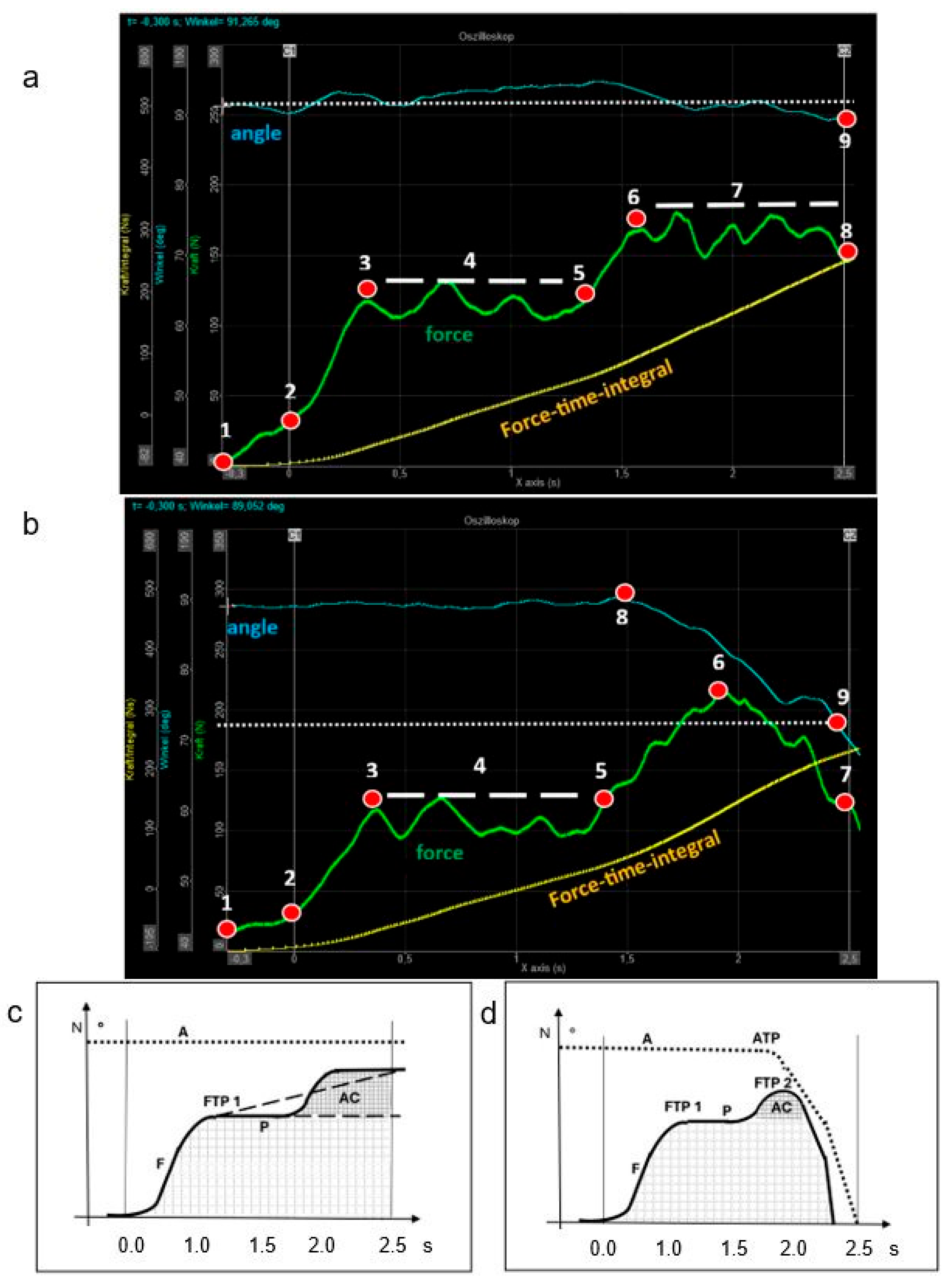
3.2. Physical Parameters of the FMD Muscle Test
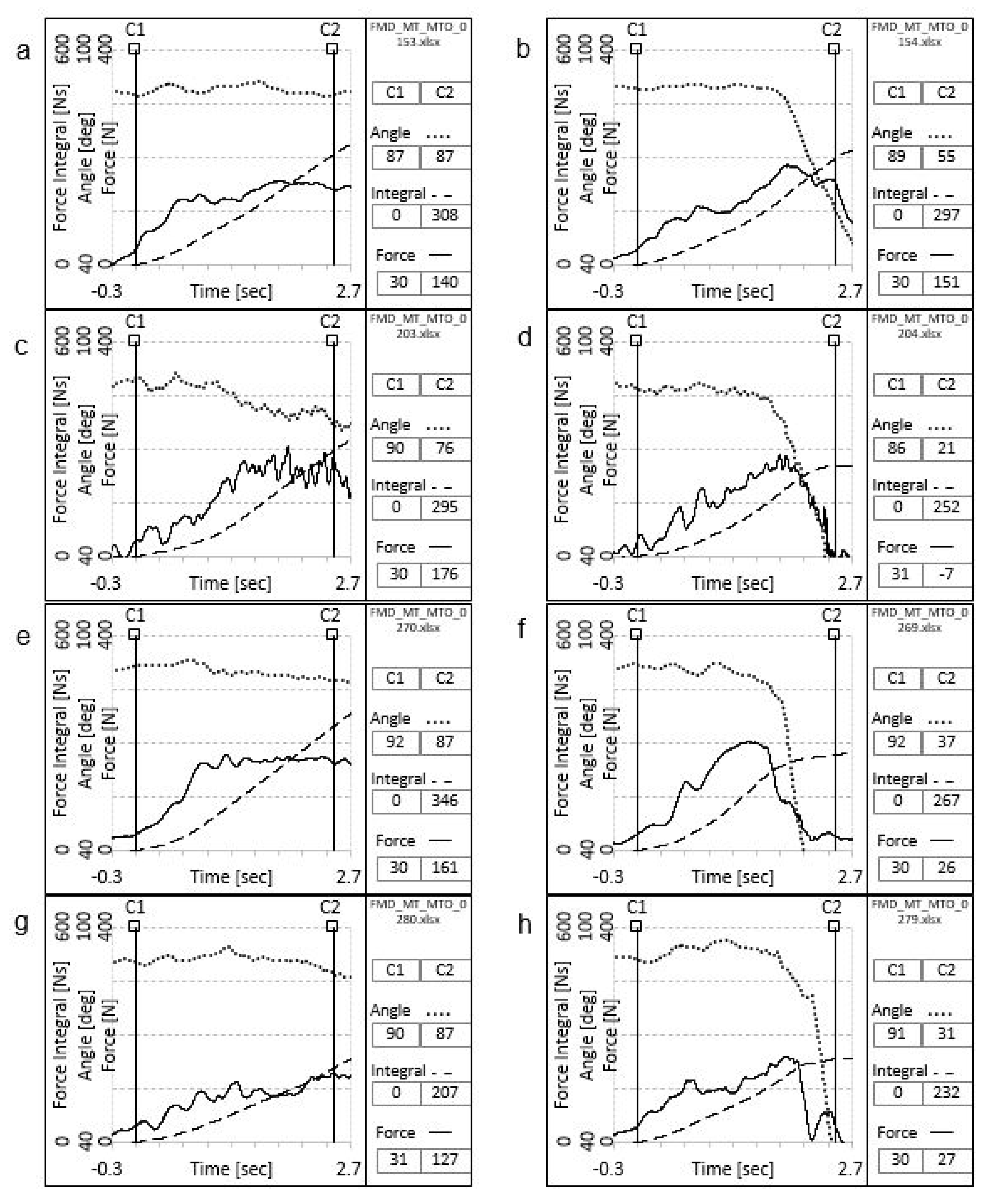
3.3. Validity of the Clinical Analysis of the FMD Muscle Test
3.4. Interrater Reliability of the FMD Muscle Test
3.5. Validity of the Instrumental Analysis of the FMD Muscle Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walter, M. Handbuch der Funktionellen Myodiagnostik; Verlagshaus der Ärzte GmbH: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsak, I. Funktionelle Myodiagnostik, Handbuch der Muskeltests, 2nd ed.; Verlagshaus der Ärzte: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burtscher, E.; Eppler-Tschiedel, M.; Gerz, W.; Suntinger, A. Lehrbuch der AK-Meridiantherapie; AKSE Verlag: Gröbenzell, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.arztakademie.at/documents/1032702/1790271/Anlage_19_OEAEK-Diplom_Funktionelle_Myodiagnostik.pdf/9b1b9f6f-0005-232c-3a77-1bbd167a7a6f?t=1677684721804 (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- IMAK—Interdisziplinär Manuell Analytisch Kausal Ärztegesellschaft für Funktionelle Myodiagnstik. Available online: https://www.funktionelle-myodiagnostik.com/ (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Liu, K.; Zhang, K.; Hu, A.; Li, Y.; Qin, H.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, T. Global burden of motor neuron disease: Unraveling socioeconomic disparities, aging dynamics, and divergent future trajectories (1990–2040). J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lovett, R.W.; Martin, E.G. Certain Aspects of Infantile Paralysis: With a Description of a Method of Muscle Testing. JAMA 1916, LXVI, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, F.P.; McCreary, E.K.; Provance, P.G. Muscles: Testing and Function; Williams &Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Walther, D.S.; System, D.C. Applied Kinesiology. System D.C.: Pueblo, CO, USA, 1981; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gerz, W. Lehrbuch der Applied Kinesiology (AK) in der Naturheilkundlichen Praxis; AKSE-Verlag: Munich, Germany, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Garten, H. Lehrbuch Applied Kinesiology; Elsevier GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert, S.C.; Goodheart, G.J., Jr. On the reliability and validity of manual muscle testing: A literature review. Chiropr Osteopat. 2007, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Janda, V. Manuelle Muskelfunktionsdiagnostik; Ullstein Medical: Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, C.; Raschner, C. Supramaximal Eccentric Training for Alpine Ski Racing—Strength Training with the Lifter. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R. Applied Kinesiology, Revised Edition: A Training Manual and Reference Book of Basic Principles and Practices; North Atlantic Books: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deetjen, P.; Speckmann, E.-J. Physiologie, 3rd ed.; Urban & Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Harms-Ringdahl, K. Muscle Strength; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, L.; Worthingham, K. Muscle Testing—Techniques of Manual Examination, 7th ed.; W.B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.; Lewith, G.; Brien, S.; Little, P. A review of the literature in applied and specialised kinesiology. Forsch Komplementmed. 2008, 15, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschernitschek, H.; Fink, M. “Angewandte Kinesiologie” in Medizin und Zahnmedizin—Eine kritische Ubersicht [“Applied kinesiology” in medicine and dentistry--a critical review]. Wien Med. Wochenschr. 2005, 155, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, G. Effect Size Guidelines for Individual and Group Differences in Physiotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163, Erratum in J. Chiropr. Med. 2017, 16, 346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2017.10.001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lawson, A.; Calderon, L. Interexaminer agreement for applied kinesiology manual muscle testing. Percept. Mot. Skills 1997, 84, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Phillips, R.B. Reliability of manual muscle testing with a computerized dynamometer. J. Manip. Physiol Ther. 1990, 13, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bittmann, F.; Schäfer, L. Gerätegestützte Simulation des Manuellen Muskeltests. Presentation at the DÄGAK Congress. Münster, Germany, 13–15 November 2015; AV Recording Service: Roge, Germany. Available online: www.avrecord.de (accessed on 3 November 2024).
- Dech, S.; Bittmann, F.N.; Schaefer, L.V. Assessment of the Adaptive Force of Elbow Extensors in Healthy Subjects Quantified by a Novel Pneumatically Driven Measurement System with Considerations of Its Quality Criteria. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, L.V.; Bittmann, F.N. The Adaptive Force as a Potential Biomechanical Parameter in the Recovery Process of Patients with Long COVID. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, S.; Blum, C.; Rosner, A. The Association of Manual Muscle Tests and Treatment Outcomes with Headache and Cranial Dysfunctions: A Retrospective Case Series Report. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2018, 24, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoff, M.; Schaefer, L.; Heinke, N.; Bittmann, F. Report on Adaptive Force, A Specific Neuromuscular Function. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2015, 25, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhuang, C.; Hao, M.; He, X.; Marquez, J.C.; Niu, C.M.; Lan, N. Coordinated alpha and gamma control of muscles and spindles in movement and posture. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caruso, W.; Leisman, G. A force/displacement analysis of muscle testing. Percept. Mot. Skills. 2000, 91, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, H.; Lakay, B.; Tucker, F.; Watson, B.; Bablis, P. Interexaminer reliability of the deltoid and psoas muscle test. J. Manip. Physiol Ther. 2005, 28, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conable, K.M. Intraexaminer comparison of applied kinesiology manual muscle testing of varying durations: A pilot study. J. Chiropr. Med. 2010, 9, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age (Years) | Mean (Range) | 51 (23–71) |
| male | 9 | |
| Sex | female | 11 |
| others | 0 | |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian | 20 |
| BMI | Mean (range) | 23.88 (18.3–28.4) |
| Fitness level | Mean (range) | 7 (4–10) |
| Strong | Weak | p-Value | Cohen’s d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Force–time integral, Ns | 264 ± 60.8 95% CI, 253.0–275.0 Range, 174–328 | 237 ± 68.1 95% CI, 224.7–249.3 Range, 147–321 | p = 0.005 | 0.64 |
| Change in joint angle, ° | 9.4 ± 5.3 95% CI, 8.4–10.3 Range, 7.2–16.8 | 38.2 ± 19.2 95% CI, 34.7–41.7 Range, 13.7–59.0 | p < 0.001 | 3.69 |
| Force turning point 1, s | 1.0 ± 0.5 95% CI, 0.9–1.1 Range, 0.10–2.50 | 1.0 ± 0.5 95% CI, 0.9–1.1 Range, 0.20–2.40 | p = 0.972 | 0.00 |
| Additional force load, % | 29.3 ± 31.0 95% CI, 23.7–34.9 Range, 7.0–60.9 | 45.9 ± 34.5 95% CI, 39.7–52.2 Range, 22.5–87.5 | p = 0.001 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahlknecht, J.F.; Burtscher, E.; Ramšak, I.; Zürcher, C.; Bernard, J. Objectification of the Functional Myodiagnosis Muscle Test. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155555
Mahlknecht JF, Burtscher E, Ramšak I, Zürcher C, Bernard J. Objectification of the Functional Myodiagnosis Muscle Test. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155555
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahlknecht, Josef Franz, Eugen Burtscher, Ivan Ramšak, Christine Zürcher, and Johannes Bernard. 2025. "Objectification of the Functional Myodiagnosis Muscle Test" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155555
APA StyleMahlknecht, J. F., Burtscher, E., Ramšak, I., Zürcher, C., & Bernard, J. (2025). Objectification of the Functional Myodiagnosis Muscle Test. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155555






