Mortality During In-Hospital Stay and the First 24 h After Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multi-Center, Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Primary In-Hospital Stay (Primary Hospitalisation)
2.4. Procedures
2.5. Assessments and Data Collection
2.6. Outcome Measures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Survival After Trauma
4.2. Survival After TBI
4.3. Survival After TBI and DC
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ARDS | Acquired respiratory distress syndrome |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DC | Decompressive craniectomy |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| ICP | Intracranial pressure |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| MRI | Magnet resonance imaging |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PSM | Propensity score matching |
| PTT | Partial thromboplastin time |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
References
- Wagner, M.L.; Farooqui, Z.; Elson, N.C.; Makley, A.T.; Pritts, T.A.; Goodman, M.D. Characterizing Early Inpatient Death After Trauma. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 255, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunst, M.; Ghaemmaghami, V.; Gruszecki, A.; Urban, J.; Frankel, H.; Shafi, S. Changing epidemiology of trauma deaths leads to a bimodal distribution. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2010, 23, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, G.; Lu, X.; Xu, F.; Xu, D.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Guo, F. Early Mortality Risk in Acute Trauma Patients: Predictive Value of Injury Severity Score, Trauma Index, and Different Types of Shock Indices. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.; Shafi, S. Timing and causes of death after injuries. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2013, 26, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.L.; Cipolle, M.D.; Anderson, M.; Sabella, V.; Shollenberger, D.; Li, P.M.; Pasquale, M.D. Outcome after decompressive craniectomy for the treatment of severe traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma. 2008, 65, 380–385, discussion 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, J.N. Primary Decompressive Craniectomy After Traumatic Brain Injury: A Literature Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e29894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jishi, A.; Saluja, R.S.; Al-Jehani, H.; Lamoureux, J.; Maleki, M.; Marcoux, J. Primary or secondary decompressive craniectomy: Different indication and outcome. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 38, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, P.J.; Adams, H.; Mohan, M.; Devi, B.I.; Uff, C.; Hasan, S.; Mee, H.; Wilson, M.H.; Gupta, D.K.; Bulters, D.; et al. Decompressive Craniectomy versus Craniotomy for Acute Subdural Hematoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.J.; Jung, W.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Kwak, H.J. Preoperative serum lactate cannot predict in-hospital mortality after decompressive craniectomy in traumatic brain injury. J. Anesth. 2016, 30, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.J.; Rosenfeld, J.V.; Murray, L.; Arabi, Y.M.; Davies, A.R.; D’Urso, P.; Kossmann, T.; Ponsford, J.; Seppelt, I.; Reilly, P.; et al. Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, P.J.; Kolias, A.G.; Timofeev, I.S.; Corteen, E.A.; Czosnyka, M.; Timothy, J.; Anderson, I.; Bulters, D.O.; Belli, A.; Eynon, C.A.; et al. Trial of Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Intracranial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghari, A.A.; Bari, M.E.; Waqas, M.; Ahmed, S.I.; Nathani, K.R.; Moazzam, W. Outcome of Decompressive Craniectomy in Traumatic Closed Head Injury. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2018, 13, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhong, M.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, H. Predictors of 30-Day Mortality in Traumatic Brain-Injured Patients after Primary Decompressive Craniectomy. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, e298–e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N. Impact of Early Decompressive Craniectomy Following Blunt Traumatic Brain Injury on Mortality: Propensity Matched Analysis. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2017, 78, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pingue, V.; Boetto, V.; Bassetto, A.; Nava, M.; Nardone, A.; Mele, C. The Role of Decompressive Craniectomy on Functional Outcome, Mortality and Seizure Onset after Traumatic Brain Injury. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanko, M.; Grendar, M.; Snopko, P.; Opsenak, R.; Sutovsky, J.; Benco, M.; Sorsak, J.; Zelenak, K.; Kolarovszki, B. Random Forest-Based Prediction of Outcome and Mortality in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury Undergoing Primary Decompressive Craniectomy. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e450–e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, J.; Skrifvars, M.B.; Kivisaari, R.; Siironen, J.; Raj, R. Primary decompressive craniectomy is associated with worse neurological outcome in patients with traumatic brain injury requiring acute surgery. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Ge, S.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Lui, H.; Zhu, G.; Guo, H.; Feng, D.; Qu, Y. Death after discharge: Prognostic model of 1-year mortality in traumatic brain injury patients undergoing decompressive craniectomy. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2021, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Lee, T.C.; Lee, T.H.; Liao, C.C.; Sheehan, J.; Kwan, A.L. Thirty-day mortality in traumatically brain-injured patients undergoing decompressive craniectomy. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchi, G.; Bonizzoli, M.; Zagli, G.; di Valvasone, S.; Biondi, S.; Ciapetti, M.; Perretta, L.; Mariotti, F.; Peris, A. Late decompressive craniectomyafter traumatic brain injury: Neurological outcome at 6 months after ICU discharge. J. Trauma. Manag. Outcomes 2012, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhashem, S.; Eldawoody, H. Functional Outcome After Primary Decompressive Craniectomy for Acute Subdural Hematoma in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Turk. Neurosurg. 2022, 32, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisherman, S.A.; Schmicker, R.H.; Brasel, K.J.; Bulger, E.M.; Kerby, J.D.; Minei, J.P.; Powell, J.L.; Reiff, D.A.; Rizoli, S.B.; Schreiber, M.A. Detailed description of all deaths in both the shock and traumatic brain injury hypertonic saline trials of the Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Olmedo, J.I.; Flores-Cordero, J.M.; Rincon-Ferrari, M.D.; Perez-Ale, M.; Munoz-Sanchez, M.A.; Dominguez-Roldan, J.M.; Murillo-Cabezas, F. Brain death after severe traumatic brain injury: The role of systemic secondary brain insults. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 1990–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzler, D.; Cooper, D.J.; Tremayne, A.B.; Rossaint, R.; Higgins, A. Early modifiable factors associated with fatal outcome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: A case control study. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.B.; Paudel, P.; Joshi, S.; Karki, P.; Sharma, G.R. Outcome of Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Brain Injury: An Institutional-Based Analysis from Nepal. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2021, 16, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, F.; Saal-Zapata, G. Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Brain Injury: In-hospital Mortality-Associated Factors. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2020, 11, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Greenberg, P.; Shin, S. Mortality Outcome of Emergency Decompressive Craniectomy and Craniotomy in the Management of Acute Subdural Hematoma: A National Data Analysis. Am. Surg. 2021, 87, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Liu, W.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B.; Tao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, B. Prognostic Predictors of Early Outcomes and Discharge Status of Patients Undergoing Decompressive Craniectomy After Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, e101–e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.V.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Taylor, G.S.; Marmarou, A.; Habbema, J.D.; Maas, A.I. Subgroup analysis and covariate adjustment in randomized clinical trials of traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 1244–1253, discussion 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Manley, G.T.; Abrams, M.; Akerlund, C.; Andelic, N.; Aries, M.; Bashford, T.; Bell, M.J.; Bodien, Y.G.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Progress and challenges in prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, N.; Totten, A.M.; O’Reilly, C.; Ullman, J.S.; Hawryluk, G.W.; Bell, M.J.; Bratton, S.L.; Chesnut, R.; Harris, O.A.; Kissoon, N.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firsching, R.; Rickels, E.; Mauer, U.M.; Sakowitz, O.W.; Messing-Junger, M.; Engelhard, K.; Schwenkreis, P.; Linn, J.; Schwerdtfeger, K. Guidelines for the Treatment of Head Injury in Adults. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2017, 78, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Rubiano, A.M.; Totten, A.M.; O’Reilly, C.; Ullman, J.S.; Bratton, S.L.; Chesnut, R.; Harris, O.A.; Kissoon, N.; Shutter, L.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: 2020 Update of the Decompressive Craniectomy Recommendations. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, P.J.; Kolias, A.G.; Tajsic, T.; Adeleye, A.; Aklilu, A.T.; Apriawan, T.; Bajamal, A.H.; Barthelemy, E.J.; Devi, B.I.; Bhat, D.; et al. Consensus statement from the International Consensus Meeting on the Role of Decompressive Craniectomy in the Management of Traumatic Brain Injury: Consensus statement. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical, A. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, G.; Jennett, B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet 1974, 2, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, L.F.; Marshall, S.B.; Klauber, M.R.; Van Berkum Clark, M.; Eisenberg, H.; Jane, J.A.; Luerssen, T.G.; Marmarou, A.; Foulkes, M.A. The diagnosis of head injury requires a classification based on computed axial tomography. J. Neurotrauma 1992, 9 (Suppl. 1), S287–S292. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoemmes, F. Propensity score matching in SPSS. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1201.6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2011, 46, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterov, D.; Bellamkonda, E.; Mandrekar, J.; Ransom, J.E.; Brown, A.W. Cause of Death after Traumatic Brain Injury: A Population-Based Health Record Review Analysis Referenced for Nonhead Trauma. Neuroepidemiology 2021, 55, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, K.; Chong, S.; Mitchell, R.; Newcombe, M.; Black, D.; Langcake, M. Outcomes of severely injured adult trauma patients in an Australian health service: Does trauma center level make a difference? World J. Surg. 2011, 35, 2332–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garwe, T.; Cowan, L.D.; Neas, B.; Cathey, T.; Danford, B.C.; Greenawalt, P. Survival benefit of transfer to tertiary trauma centers for major trauma patients initially presenting to nontertiary trauma centers. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2010, 17, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, P.; Lefering, R.; Stuttmann, R. Trauma care in Germany: Major differences in case fatality rates between centers. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.B.; Rosengart, M.R.; Kahn, J.M.; Mohan, D.; Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Billiar, T.R.; Peitzman, A.B.; Angus, D.C.; Sperry, J.L. Impact of Volume Change Over Time on Trauma Mortality in the United States. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, D.; Paffrath, T.; Schmidt, A.; Vollmecke, M.; Lefering, R.; Kulla, M.; Kollig, E.; Franke, A.; Sektion, N.I.S.o.t.G.T.S. Why do some trauma patients die while others survive? A matched-pair analysis based on data from Trauma Register DGU(R). Chin. J. Traumatol. 2020, 23, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisco, L.; Iscra, F.; Ganau, M.; Berlot, G. Early predictive factors on mortality in head injured patients: A retrospective analysis of 112 traumatic brain injured patients. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2012, 56, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde, G.; Shemilt, M.; Lauzier, F.; Desjardins, P.; Boutin, A.; Moore, L.; Fergusson, D.; Zarychanski, R.; Turgeon, A. Outcome measures in randomized controlled trials of patients with severe traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Devi, B.I.; Agrawal, A. Outcome measures for traumatic brain injury. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2011, 113, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Buki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsching, R.; Woischneck, D.; Klein, S.; Ludwig, K.; Dohring, W. Brain stem lesions after head injury. Neurol. Res. 2002, 24, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, C.; Zangrossi, P.; Mantovani, G.; Cavallo, M.A.; De Bonis, P.; Scerrati, A. The effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies on clinical outcome of patients undergoing decompressive craniectomy: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1336760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juskys, R.; Vilcinis, R.; Piliponis, L.; Tamasauskas, A. Degree of basal cisterns compression predicting mortality and functional outcome after craniotomy and primary decompressive craniectomy in acute subdural hematoma population. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 4013–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Jeon, I.; Seo, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, D. Radiographic predictors of clinical outcome in traumatic brain injury after decompressive craniectomy. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woischneck, D.; Firsching, R.; Schmitz, B.; Kapapa, T. The prognostic reliability of the Glasgow coma score in traumatic brain injuries: Evaluation of MRI data. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2013, 39, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmarou, A.; Lu, J.; Butcher, I.; McHugh, G.S.; Murray, G.D.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Mushkudiani, N.A.; Choi, S.; Maas, A.I. Prognostic value of the Glasgow Coma Scale and pupil reactivity in traumatic brain injury assessed pre-hospital and on enrollment: An IMPACT analysis. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, M.R.; Chesnut, R.; Ghajar, J.; Gordon, D.; Hartl, R.; Newell, D.W.; Servadei, F.; Walters, B.C.; Wilberger, J.E.; Surgical Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Author Group. Surgical management of acute subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery 2006, 58 (Suppl. 3), S16–S24, discussion Si–iv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Bai, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. Clinical predictors of prognosis in patients with traumatic brain injury combined with extracranial trauma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.D.; Gambert, S.; Gruber-Baldini, A.; Guralnik, J.; Kozar, R.; Qato, D.M.; Shardell, M.; Albrecht, J.S. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Long-Term Nursing Home Entry among Older Adults: An Analysis of Medicare Administrative Claims Data. J. Neurotrauma 2023, 40, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Wennervirta, J.M.; Tjerkaski, J.; Luoto, T.M.; Posti, J.P.; Nelson, D.W.; Takala, R.; Bendel, S.; Thelin, E.P.; Luostarinen, T.; et al. Dynamic prediction of mortality after traumatic brain injury using a machine learning algorithm. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, J.G.; Mushkudiani, N.A.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Butcher, I.; McHugh, G.S.; Lu, J.; Marmarou, A.; Murray, G.D.; Maas, A.I. Prognostic value of admission laboratory parameters in traumatic brain injury: Results from the IMPACT study. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushkudiani, N.A.; Engel, D.C.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Butcher, I.; Lu, J.; Marmarou, A.; Slieker, F.; McHugh, G.S.; Murray, G.D.; Maas, A.I. Prognostic value of demographic characteristics in traumatic brain injury: Results from the IMPACT study. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, G.D.; Butcher, I.; McHugh, G.S.; Lu, J.; Mushkudiani, N.A.; Maas, A.I.; Marmarou, A.; Steyerberg, E.W. Multivariable prognostic analysis in traumatic brain injury: Results from the IMPACT study. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, M.C.T.; Perel, P.; Arango, M.; Clayton, T.; Edwards, P.; Komolafe, E.; Poccock, S.; Roberts, I.; Shakur, H.; Steyerberg, E.; et al. Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: Practical prognostic models based on large cohort of international patients. BMJ 2008, 336, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Mushkudiani, N.; Perel, P.; Butcher, I.; Lu, J.; McHugh, G.S.; Murray, G.D.; Marmarou, A.; Roberts, I.; Habbema, J.D.; et al. Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: Development and international validation of prognostic scores based on admission characteristics. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e165, discussion e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cassia Almeida Vieira, R.; Silveira, J.C.P.; Paiva, W.S.; de Oliveira, D.V.; de Souza, C.P.E.; Santana-Santos, E.; de Sousa, R.M.C. Prognostic Models in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurocri. Care 2022, 37, 790–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.K.; Lee, Y.M.; Sun, X.; van Essen, T.A.; Elguindy, M.M.; Belton, P.J.; Pisica, D.; Mikolic, A.; Deng, H.; Kanter, J.H.; et al. Performance of the IMPACT and CRASH prognostic models for traumatic brain injury in a contemporary multicenter cohort: A TRACK-TBI study. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 141, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Luostarinen, T.; Pursiainen, E.; Posti, J.P.; Takala, R.S.K.; Bendel, S.; Konttila, T.; Korja, M. Machine learning-based dynamic mortality prediction after traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, E.; Kazim, S.F.; Vellek, J.; Tarawneh, O.; Stack, J.; Roster, K.; Roy, J.; Schmidt, M.; Bowers, C. Machine learning algorithms for predicting outcomes of traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2023, 14, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
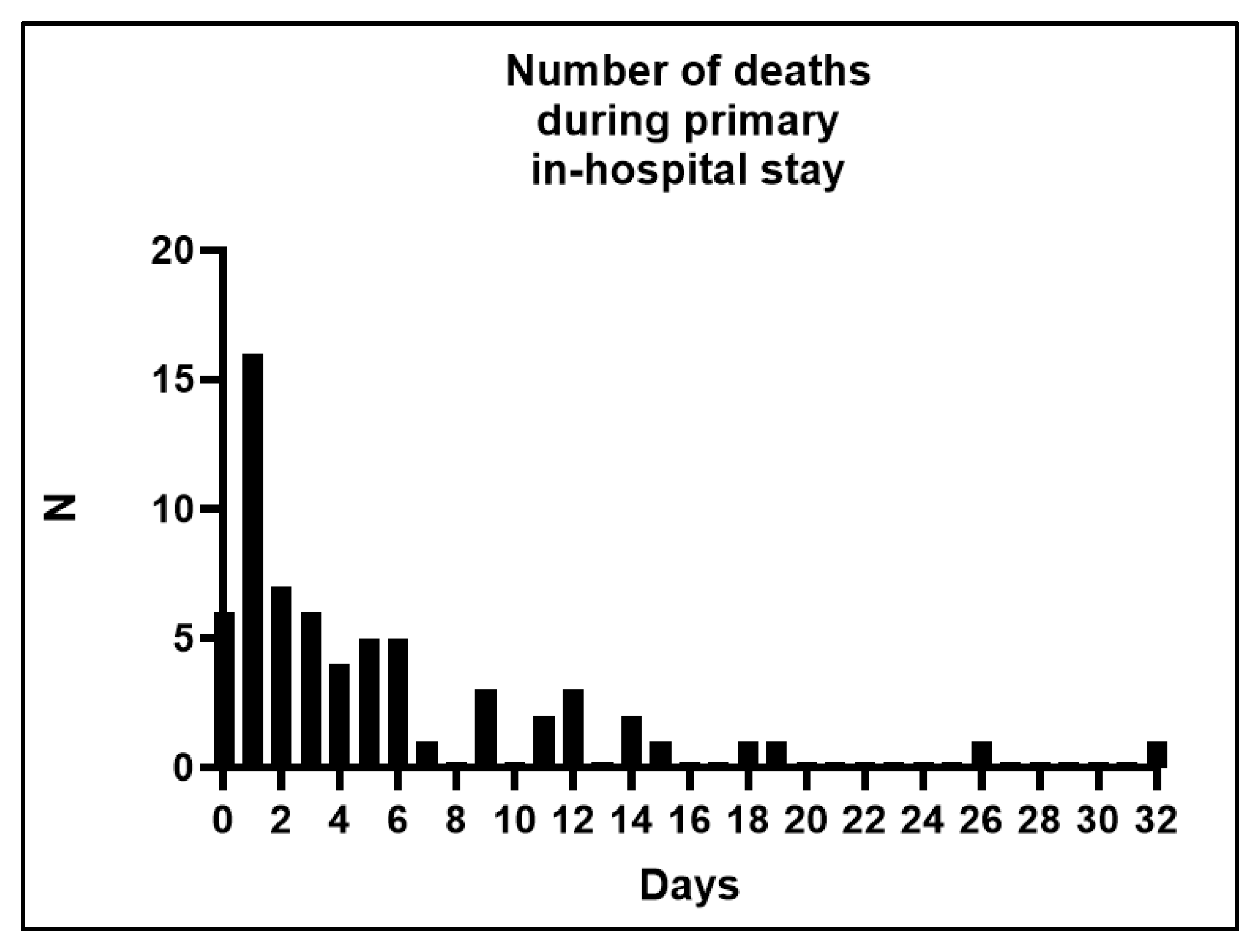

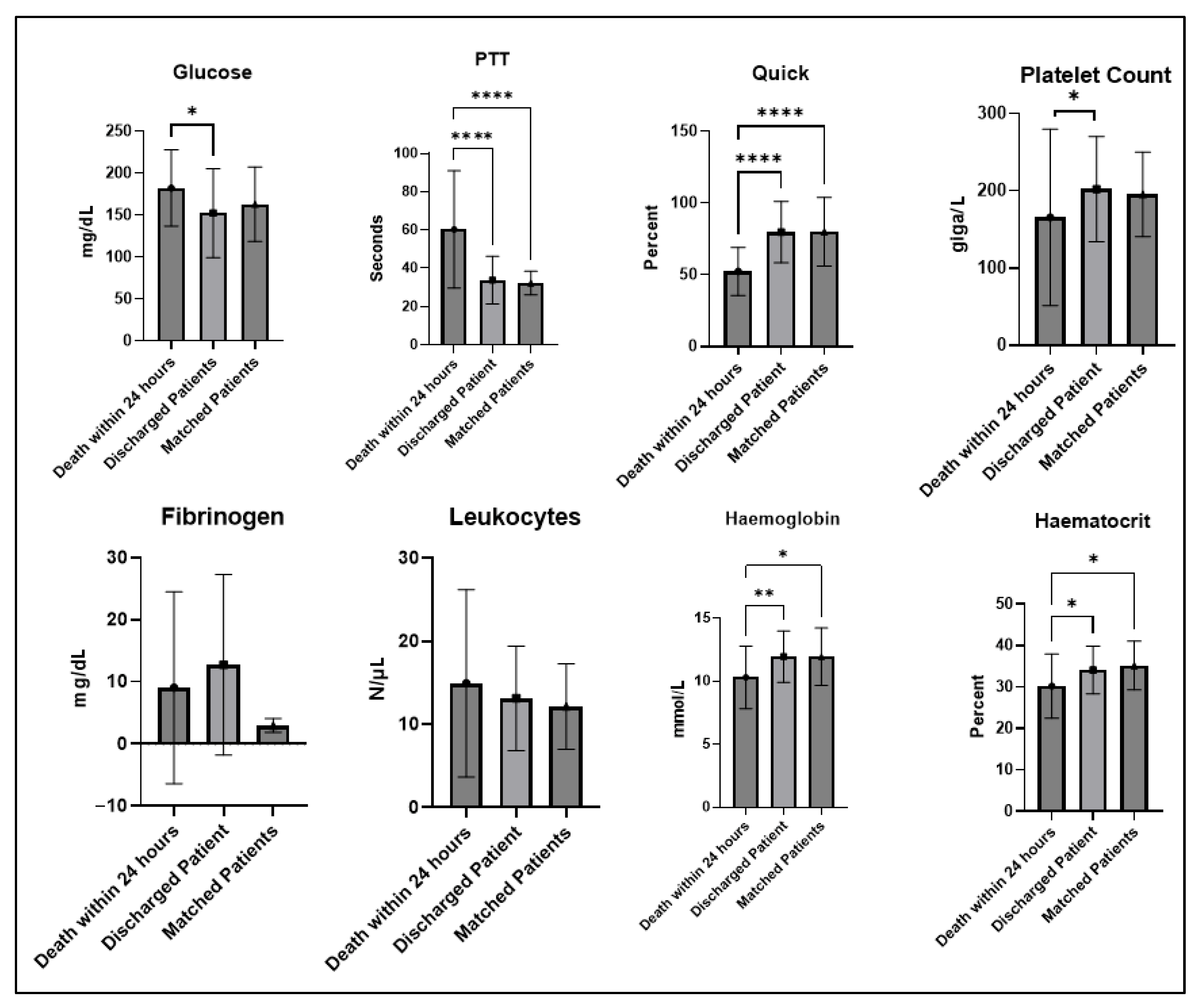
| Total | Patients with In-Hospital Death | Discharged Patient | p | Propensity-Matched Control Patients (Discharged, Matching Tolerance = 0.05) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 223 | 65 (29.1) | 158 (70.9) | 41 (18.4) | ||
| Age in Years | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 49.9 (21.38) | 55.2 (22.23) | 47.7 (20.69) | 0.010 | 57.0 (20.70) | 0.800 |
| Median (range) | 52.0 (1–93) | 59 (5–86) | 49 (1–93) | 61 (16–93) | ||
| Sex | ||||||
| Female N (%) | 60 (26.9) | 16 (24.6) | 44 (27.8) | 0.740 | 13 (31.7) | 0.504 |
| Time Between Trauma and Surgery | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 28.8 (81.48) | 12.2 (16.90) | 35.2 (94.63) | 0.186 | 28.7 (63.74) | 0.559 |
| Median (range) | 7.0 (1–936) | 5.8 (1–94) | 7.3 (1–936) | 7.62 (1–288) | ||
| Mean (SD) without case (936 h) | 23.8 (45.02) | 12.2 (16.90) | 28.2 (51.35) | 0.211 | ||
| Median (range) without case (936 h) | 7.0 (1–288) | 5.8 (1–94) | 7.0 (1–288) | |||
| Rate of pupil function disturbance, N (%) | 94 (44.5) | 37 (63.8) | 57 (37.3) | <0.001 | 24 (58.5) | 0.676 |
| Glasgow Coma Score at Admission | ||||||
| Total | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 5.0 (3.89) | 5.1 (3.74) | 5.0 (3.96) | 0.581 | 6.2 (4.79) | 0.272 |
| Median (range) | 3 (3–15) | 3 (3–14) | 3 (3–15) | 3 (3–15) | ||
| Eye Opening | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.5 (1.03) | 1.5 (1.02) | 1.5 (1.03) | 0.939 | 1.8 (1.23) | 0.128 |
| Median (range) | 1 (1–4) | 1 (1–4) | 1 (1–4) | 1 (1–4) | ||
| Motor Response | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.9 (1.81) | 2.0 (1.80) | 1.9 (1.81) | 0.700 | 2.5 (2.22) | 0.243 |
| Median (range) | 1 (1–6) | 1 (1–6) | 1 (1–6) | 1 (1–6) | ||
| Verbal Response | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.5 (1.16) | 1.5 (1.04) | 1.5 (1.21) | 0.863 | 1.9 (1.50) | 0.208 |
| Median (range) | 1–5 | 1 (1–5) | 1 (1–5) | 1 (1–5) | ||
| Marshall Score | ||||||
| Mean (SD) | 4.3 (1.26) | 4.5 (1.29) | 4.2 (1.24) | 0.239 | 4.3 (1.40) | 0.501 |
| Median (range) | 4 (1–6) | 4 (1–6) | 4 (1–6) | 4 (1–6) | ||
| Vital Signs at Admission (Mean, SD) | ||||||
| Initial MAP (mmHg) | 89.9 (35.08) | 92.6 (36.75) | 88.9 (34.48) | 0.679 | 100.2 (22.20) | 0.288 |
| Initial pulse (beats/minute) | 85.9 (24.76) | 95.2 (32.37) | 82.0 (19.68) | <0.001 | 84.9 (17.23) | 0.030 |
| Length of ICU in days (mean, SD) | 12.6 (11.40) | 5.4 (6.33) | 15.5 (11.72) | <0.001 | 6.8 (4.10) | 0.009 |
| Additional Injuries | ||||||
| Thorax | 25 (11.2) | 8 (12.3) | 17 (10.8) | 0.816 | 4 (9.8) | 0.763 |
| Abdomen | 6 (2.7) | 3 (4.6) | 3 (1.9) | 0.361 | 1 (2.4) | 1.000 |
| Extremities | 18 (8.1) | 5 (7.7) | 13 (8.2) | 1.000 | 7 (17.1) | 0.207 |
| Spine | 17 (7.6) | 7 (10.8) | 10 (6.3) | 0.273 | 2 (4.9) | 0.477 |
| Patients with In-Hospital Death Within 24 h | Discharged Patient | p | Propensity-Matched Control Patients (Discharged, Matching Tolerance = 0.2) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 22 (9.9) | 158 (70.9) | 21 (9.4) | ||
| Age in Years | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 57.1 (24.65) | 47.7 (20.69) | 0.036 | 59.2 (18.50) | 0.808 |
| Median (range) | 69 (16–86) | 49 (1–93) | 65 (20–81) | ||
| Sex | |||||
| Female N (%) | 6 (27.3) | 44 (27.8) | 1.000 | 6 (28.6) | 1.000 |
| Time between Trauma and Surgery in Hours | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 6.5 (6.76) | 35.2 (94.63) | 0.033 | 31.4 (75.56) | 0.357 |
| Median (range) | 4 (1–29) | 7.3 (1–936) | 5 (2–288) | ||
| Rate of pupil function disturbance, N (%) | 16 (76.2) | 57 (37.3) | <0.001 | 14 (66.7) | 0.743 |
| Glasgow Coma Score at Admission | |||||
| Total | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 4.2 (2.74) | 5.0 (3.96) | 0.914 | 7.1 (5.39) | 0.175 |
| Median (range) | 3 (3–13) | 3 (3–15) | 3 (3–15) | ||
| Eye Opening | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.3 (0.80) | 1.5 (1.03) | 0.497 | 2.0 (1.38) | 0.072 |
| Median (range) | 1 (1–4) | 1 (1–4) | 1 (1–4) | ||
| Motor Response | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.6 (1.28) | 1.9 (1.81) | 0.623 | 2.8 (2.38) | 0.091 |
| Median (range) | 1 (1–5) | 1 (1–6) | 1 (1–6) | ||
| Verbal Response | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.3 (0.92) | 1.5 (1.21) | 0.664 | 2.3 (1.67) | 0.071 |
| Median (range) | 1 (1–5) | 1 (1–5) | 1 (1–5) | ||
| Marshall Score | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 4.2 (1.10) | 4.2 (1.24) | 0.861 | 4.38 (1.28) | 0.583 |
| Median (range) | 4 (1–6) | 4 (1–6) | 4 (1–6) | ||
| Vital Signs at Admission (Mean, SD) | |||||
| Initial MAP (mmHg) | 93.5 (31.26) | 88.9 (34.48) | 0.824 | 95.5 (35.69) | 0.456 |
| Initial pulse (beats/minute) | 103.3 (25.84) | 82.0 (19.68) | <0.001 | 76.7 (14.08) | <0.001 |
| Length of ICU in days (mean, SD) | 0.7 (0.46) | 15.5 (11.72) | <0.001 | 4.6 (4.18) | <0.001 |
| Additional Injuries | |||||
| Thorax | 6 (27.3) | 17 (10.8) | 0.041 | 1 (4.8) | 0.095 |
| Abdomen | 3 (13.6) | 3 (1.9) | 0.025 | 0 (0) | 0.233 |
| Extremities | 3 (13.6) | 13 (8.2) | 0.420 | 3 (14.3) | 1.000 |
| Spine | 4 (18.2) | 10 (6.3) | 0.074 | 1 (4.8) | 0.345 |
| Binary Logistic Regression Analysis for Death in the Primary In-Hospital Stay (Comparison to Discharged Patients with a Matching Tolerance of 0.01) | ||||
| Univariate Regression Analysis | Odds Ratio | p | CI: 95% | |
| lower | upper | |||
| Chronological age | 1.018 | 0.017 | 1.003 | 1.032 |
| Time between trauma and surgery | 0.986 | 0.051 | 0.972 | 1.000 |
| Pupil function disturbance | 2.967 | <0.001 | 1.584 | 5.560 |
| Heart rate (beats/minute) on admission | 1.023 | 0.001 | 1.009 | 1.037 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) on admission | 1.007 | 0.017 | 1.001 | 1.013 |
| PTT (Seconds) on admission | 1.039 | <0.001 | 1.016 | 1.062 |
| Quick (%) on admission | 0.971 | <0.001 | 0.958 | 0.985 |
| Platelet count (giga/L) on admission | 0.994 | 0.007 | 0.989 | 0.998 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) on admission | 0.820 | 0.005 | 0.714 | 0.941 |
| Multivariate Regression Analysis | Odds Ratio | p | CI: 95% | |
| lower | upper | |||
| Chronological age | 1.045 | 0.013 | 1.010 | 1.082 |
| Quick (%) on admission | 0.965 | 0.049 | 0.931 | 1.000 |
| Binary Logistic Regression Analysis for Death in the Primary In-Hospital Stay within 24 h (comparison to discharged patients with a matching tolerance of 0.2) | ||||
| Univariate Regression Analysis | Odds Ratio | p | CI: 95% | |
| lower | upper | |||
| Chronological age | 1.023 | 0.055 | 0.999 | 1.047 |
| Additional thorax injury | 3.110 | 0.037 | 1.073 | 9.020 |
| Additional abdominal injury | 8.158 | 0.014 | 1.536 | 43.324 |
| Pupil function disturbance | 5.389 | 0.002 | 1.874 | 15.499 |
| Heart rate (beats/minute) on admission | 1.043 | <0.001 | 1.020 | 1.066 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) on admission | 1.009 | 0.029 | 1.001 | 1.017 |
| PTT (Seconds) on admission | 1.064 | <0.001 | 1.033 | 1.096 |
| Quick (%) on admission | 0.936 | <0.001 | 0.910 | 0.963 |
| Platelet count (giga/L) on admission | 0.993 | 0.033 | 0.986 | 0.999 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) on admission | 0.688 | 0.001 | 0.547 | 0.865 |
| Hematocrit (%) on admission | 0.897 | 0.017 | 0.821 | 0.981 |
| Multivariate Regression Analysis | Odds Ratio | p | CI: 95% | |
| lower | upper | |||
| Chronological age | 1.143 | 0.019 | 1.022 | 1.277 |
| Heart rate (beats/minute) on admission | 1.099 | 0.030 | 1.009 | 1.197 |
| Quick (%) on admission | 0.923 | 0.037 | 0.856 | 0.995 |
| Conditional Logistic Regression Analysis for Death in the Primary In-Hospital Stay (Comparison to Discharged Patients with a Matching Tolerance of 0.01) | ||||
| Univariate Regression Analysis | Odds Ratio | p | CI: 95% | |
| lower | upper | |||
| Time between trauma and surgery (hours) | 0.992 | 0.201 | 0.980 | 1.004 |
| GCS eye opening | 0.880 | 0.311 | 0.687 | 1.127 |
| GCS motor | 0.949 | 0.459 | 0.825 | 1.091 |
| GCS verbal | 0.858 | 0.204 | 0.678 | 1.086 |
| Additional thorax injury | 1.015 | 0.969 | 0.484 | 2.127 |
| Additional abdominal injury | 1.677 | 0.382 | 0.527 | 5.344 |
| Additional injuries of extremities | 0.727 | 0.494 | 0.292 | 1.811 |
| Additional spine injury | 1.494 | 0.316 | 0.682 | 3.272 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 0.999 | 0.814 | 0.992 | 1.007 |
| Heart rate (beats/minute) on admission | 1.004 | 0.334 | 0.996 | 1.013 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) on admission | 1.004 | 0.136 | 0.999 | 1.010 |
| PTT (seconds) on admission | 1.010 | 0.052 | 1.000 | 1.020 |
| Quick (%) on admission | 0.989 | 0.040 | 0.978 | 0.999 |
| Platelet count (giga/L) on admission | 0.999 | 0.439 | 0.995 | 1.002 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) on admission | 1.007 | 0.472 | 0.988 | 1.026 |
| Leukocytes (per µL) on admission | 1.017 | 0.212 | 0.990 | 1.045 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) on admission | 0.938 | 0.240 | 0.843 | 1.044 |
| Hematocrit (%) on admission | 0.983 | 0.477 | 0.939 | 1.030 |
| Conditional Logistic Regression Analysis for Death in the Primary In-Hospital Stay within 24 h (comparison to discharged patients with a matching tolerance of 0.2) | ||||
| Univariate Regression Analysis | Odds Ratio | p | CI: 95% | |
| lower | upper | |||
| Time between trauma and surgery (hours) | 0.985 | 0.457 | 0.948 | 1.024 |
| GCS eye opening | 0.696 | 0.184 | 0.408 | 1.187 |
| GCS motor | 0.803 | 0.161 | 0.591 | 1.091 |
| GCS verbal | 0.698 | 0.148 | 0.429 | 1.136 |
| Additional thorax injury | 1.929 | 0.170 | 0.755 | 4.929 |
| Additional abdominal injury | 2.106 | 0.231 | 0.623 | 7.115 |
| Additional injuries of extremities | 0.974 | 0.966 | 0.288 | 3.290 |
| Additional spine injury | 1.689 | 0.343 | 0.572 | 4.990 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 0.999 | 0.891 | 0.985 | 1.013 |
| Heart rate (beats/minute) | 1.018 | 0.016 | 1.003 | 1.033 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) on admission | 1.004 | 0.374 | 0.995 | 1.014 |
| PTT (seconds) on admission | 1.014 | 0.017 | 1.003 | 1.026 |
| Quick (%) on admission | 0.975 | 0.013 | 0.955 | 0.995 |
| Platelet count (giga/L) on admission | 0.998 | 0.444 | 0.993 | 1.003 |
| Fibrinogen on admission | 1.011 | 0.490 | 0.979 | 1.044 |
| Leukocytes on admission | 1.015 | 0.463 | 0.976 | 1.056 |
| Hemoglobin on admission | 0.874 | 0.132 | 0.733 | 1.042 |
| Hematocrit (%) on admission | 0.948 | 0.129 | 0.884 | 1.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapapa, T.; Petkov, M.; Pala, A.; Woischneck, D.; Schiller, F.; Jesuthasan, S.; Schiller, F.; Bracht, H.; Mayer, B.; Oehmichen, M. Mortality During In-Hospital Stay and the First 24 h After Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multi-Center, Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155540
Kapapa T, Petkov M, Pala A, Woischneck D, Schiller F, Jesuthasan S, Schiller F, Bracht H, Mayer B, Oehmichen M. Mortality During In-Hospital Stay and the First 24 h After Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multi-Center, Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155540
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapapa, Thomas, Martin Petkov, Andrej Pala, Dieter Woischneck, Franziska Schiller, Stefanie Jesuthasan, Frederike Schiller, Hendrik Bracht, Benjamin Mayer, and Marcel Oehmichen. 2025. "Mortality During In-Hospital Stay and the First 24 h After Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multi-Center, Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155540
APA StyleKapapa, T., Petkov, M., Pala, A., Woischneck, D., Schiller, F., Jesuthasan, S., Schiller, F., Bracht, H., Mayer, B., & Oehmichen, M. (2025). Mortality During In-Hospital Stay and the First 24 h After Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Multi-Center, Retrospective Propensity Score-Matched Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155540






