Atrial Strain Analysis Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation of Typical Atrial Flutter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Echocardiography
2.3. Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Predictors of Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence
3.2. Differences Between Patients in AFL and in Sinus Rhythm During Echocardiography
3.3. Comparison Between Patients Who Received Concomitant AF Ablation and Those Who Did Not
3.4. Comparison Between Patients with AFL and AF Recurrence
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghali, W.A.; Wasil, B.I.; Brant, R.; Exner, D.V.; Cornuz, J. Atrial flutter and the risk of thromboembolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehm-Reese, M.; Kronborg, M.B.; Lukac, P.; Kristiansen, S.B.; Nielsen, J.M.; Johannessen, A.; Jacobsen, P.K.; Djurhuus, M.S.; Riahi, S.; Hansen, P.S.; et al. Recurrent atrial flutter ablation and incidence of atrial fibrillation ablation after first-time ablation for typical atrial flutter: A nation-wide Danish cohort study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 298, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Ruiz, L.A.; Madrid-Miller, A.; Martínez-Flores, J.E.; González-Hermosillo, J.A.; Arenas-Fonseca, J.; Zamorano-Velazquez, N.; Mendoza-Perez, B. Left atrial longitudinal strain by speckle tracking as independent predictor of recurrence after electrical cardioversion in persistent and long standing persistent non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.R.; Yakupoglu, H.Y.; Kralj-Hans, I.; Haldar, S.; Bahrami, T.; Clague, J.; De Souza, A.; Hussain, W.; Jarman, J.; Jones, D.G.; et al. Left Atrial Function Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Ablation of Long-Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, e015352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 16, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badano, L.P.; Kolias, T.J.; Muraru, D.; Abraham, T.P.; Aurigemma, G.; Edvardsen, T.; D’Hooge, J.; Donal, E.; Fraser, A.G.; Marwick, T.; et al. Standardization of left atrial, right ventricular, and right atrial deformation imaging using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: A consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry Task Force to standardize deformation imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, J.-U.; Pedrizzetti, G.; Lysyansky, P.; Marwick, T.H.; Houle, H.; Baumann, R.; Pedri, S.; Ito, Y.; Abe, Y.; Metz, S.; et al. Definitions for a common standard for 2D speckle tracking echocardiography: Consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/industry task force to standardize deformation imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilli, M.; Iannaccone, G.; Russo, M.; Meucci, M.C.; Chiorazzo, G.; Natali, R.; Mango, F.; Bonanni, A.; Montone, R.A.; Graziani, F.; et al. Early improvement of strain imaging parameters predicts long-term response to sacubitril/valsartan in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: An observational prospective study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2023, 387, 131110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, J.; Diaz, J.C.; Di Biase, L.; Kumar, S.; Briceno, D.; Tedrow, U.B.; Valencia, C.R.; Baldinger, S.H.; Koplan, B.; Epstein, L.M.; et al. Atrial fibrillation inducibility during cavotricuspid isthmus-dependent atrial flutter ablation as a predictor of clinical atrial fibrillation. A meta-analysis. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2017, 48, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raafs, A.G.; Vos, J.L.; Henkens, M.T.; Slurink, B.O.; Verdonschot, J.A.; Bossers, D.; Roes, K.; Gerretsen, S.; Knackstedt, C.; Hazebroek, M.R.; et al. Left Atrial Strain Has Superior Prognostic Value to Ventricular Function and Delayed-Enhancement in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, L. Incremental prognostic value of left atrial strain in patients with heart failure. ESC Heat Fail. 2022, 9, 3942–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Khan, F.H.; Remme, E.W.; Ohte, N.; García-Izquierdo, E.; Chetrit, M.; Moñivas-Palomero, V.; Mingo-Santos, S.; Andersen, Ø.S.; Gude, E.; et al. Determinants of left atrial reservoir and pump strain and use of atrial strain for evaluation of left ventricular filling pressure. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannaccone, G.; Graziani, F.; Del Buono, M.G.; Camilli, M.; Lillo, R.; Caffè, A.; Moroni, F.; La Vecchia, G.; Pedicino, D.; Sanna, T.; et al. Left atrial strain analysis improves left ventricular filling pressures non-invasive estimation in the acute phase of Takotsubo syndrome. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 24, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselberg, N.E.; Kagiyama, N.; Soyama, Y.; Sugahara, M.; Goda, A.; Ryo-Koriyama, K.; Batel, O.; Chakinala, M.; Simon, M.A.; Gorcsan, J. The Prognostic Value of Right Atrial Strain Imaging in Patients with Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2021, 34, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Abe, K.; Kamitani, T.; Hosokawa, K.; Kawakubo, M.; Sagiyama, K.; Hida, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Murayama, Y.; Funatsu, R.; et al. Balloon pulmonary angioplasty improves right atrial reservoir and conduit functions in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Kuriakose, D.; Edelstein, I.; Ansari, B.; Oldland, G.; Gaddam, S.; Javaid, K.; Manaktala, P.; Lee, J.; Miller, R.; et al. Right Atrial Phasic Function in Heart Failure With Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singulane, C.C.; Slivnick, J.A.; Addetia, K.; Asch, F.M.; Sarswat, N.; Soulat-Dufour, L.; Mor-Avi, V.; Lang, R.M. Prevalence of Right Atrial Impairment and Association with Outcomes in Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2022, 35, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charisopoulou, D.; Banner, N.R.; Demetrescu, C.; Simon, A.R.; Haley, S.R. Right atrial and ventricular echocardiographic strain analysis predicts requirement for right ventricular support after left ventricular assist device implantation. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brás, P.G.; Cunha, P.S.; Timóteo, A.T.; Portugal, G.; Galrinho, A.; Laranjo, S.; Cruz, M.C.; Valente, B.; Rio, P.; Delgado, A.S.; et al. Evaluation of left atrial strain imaging and integrated backscatter as predictors of recurrence in patients with paroxysmal, persistent, and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation undergoing catheter ablation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2023, 67, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipek, E.G.; Marine, J.E.; Habibi, M.; Chrispin, J.; Lima, J.; Rickard, J.; Spragg, D.; Zimmerman, S.L.; Zipunnikov, V.; Berger, R.; et al. Association of left atrial function with incident atypical atrial flutter after atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipek, E.G.; Habibi, M.; Zghaib, T.; Zimmerman, S.L.; Calkins, H.; Lima, J.; Nazarian, S. Cardiac magnetic resonance-derived right atrial functional analysis in patients with atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2020, 59, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, S.; Liu, Q.; Gulsen, M.R.; Biviano, A.; Wan, E.Y.; Dizon, J.; Saluja, D.; Garan, H.; Yarmohammadi, H. Catheter ablation of typical atrial flutter improves cardiac chamber size and function. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2023, 35, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaselli, M.; Badano, L.P.; Cannone, V.; Radu, N.; Curti, E.; Perelli, F.; Heilbron, F.; Gavazzoni, M.; Rella, V.; Oliverio, G.; et al. Incremental Value of Right Atrial Strain Analysis to Predict Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Electrical Cardioversion. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2023, 36, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbe, A.C.; Miranda, W.R.; Madhavan, M.; Abozied, O.; Younis, A.K.; Ahmed, M.H.; Connolly, H.M.; Deshmukh, A.J. Right atrial dysfunction is associated with atrial arrhythmias in adults with repaired tetralogy of fallot. Am. Heart J. 2023, 263, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.-H.; Tai, C.-T.; Chiang, C.-E.; Tsai, C.-F.; Yu, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Ding, Y.-A.; Chen, S.-A. Recurrent atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation of the cavotricuspid isthmus: A very long-term follow-up of 333 patients. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2002, 7, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipek, E.G.; Marine, J.; Yang, E.; Habibi, M.; Chrispin, J.; Spragg, D.; Berger, R.D.; Calkins, H.; Nazarian, S. Predictors and Incidence of Atrial Flutter After Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 124, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iden, L.; Richardt, G.; Weinert, R.; Groschke, S.; Toelg, R.; Borlich, M. Typical atrial flutter but not fibrillation predicts coronary artery disease in formerly healthy patients. Europace 2021, 23, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrol, M.; Sbragia, P.; Bonello, L.; Lévy, S.; Paganelli, F. Characteristics of isolated atrial flutter versus atrial flutter combined with atrial fibrillation. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 104, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S. Contemporary Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Flutter: A Continuum of Atrial Fibrillation and Vice Versa? Cardiol. Rev. 2017, 25, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldo, A.L. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: Two sides of the same coin! Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 240, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoudi, N.; Cosio, F.; Waldo, A.; Chen, S.; Iesaka, Y.; Lesh, M.; Saksena, S.; Salerno, J.; Schoels, W. Classification of atrial flutter and regular atrial tachycardia according to electrophysiologic mechanism and anatomical bases. A statement from a Joint Expert Group from the Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2001, 12, 852–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldo, A.L.; Feld, G.K. Inter-relationships of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldo, A.L. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, S267–S274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertaglia, E.; Zoppo, F.; Bonso, A.; Proclemer, A.; Verlato, R.; Corò, L.; Mantovan, R.; D’este, D.; Zerbo, F.; Pascotto, P. Long term follow up of radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial flutter: Clinical course and predictors of atrial fibrillation occurrence. Heart 2004, 90, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, S.; Ndrepepa, G.; Dong, J.; Zrenner, B.; Schreieck, J.; Schneider, M.A.; Karch, M.R.; Schmitt, C. Acute and long-term results of radiofrequency ablation of common atrial flutter and the influence of the right atrial isthmus ablation on the occurrence of atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanasio, P.; Budde, T.; Kamieniarz, P.; Tscholl, V.; Nagel, P.; Biewener, S.; Parwani, A.; Boldt, L.-H.; Landmesser, U.; Hindricks, G.; et al. Incidence and patterns of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation of typical atrial flutter-the FLUTFIB study. Europace 2024, 26, euad348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giehm-Reese, M.; Kronborg, M.B.; Lukac, P.; Kristiansen, S.B.; Jensen, H.K.; Gerdes, C.; Kristensen, J.; Nielsen, J.M.; Nielsen, J.C. Recurrent atrial arrhythmia in a randomised controlled trial comparing contact force-guided and contact force-blinded ablation for typical atrial flutter. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, F.J.; Schubert, C.M.; Parvez, B.; Pathak, V.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Wood, M.A. Long-term outcomes after catheter ablation of cavo-tricuspid isthmus dependent atrial flutter: A meta-analysis. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Ding, L.; Zhang, H.; Mi, L.; Yu, F.; Tang, M. Radiofrequency catheter ablation for pulmonary hypertension patients with atrial flutter. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallaglio, P.D.; Anguera, I.; Jiménez-Candil, J.; Peinado, R.; García-Seara, J.; Arcocha, M.F.; Macías, R.; Herreros, B.; Quesada, A.; Hernández-Madrid, A.; et al. Impact of previous cardiac surgery on long-term outcome of cavotricuspid isthmus-dependent atrial flutter ablation. Europace 2016, 18, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguera, I.; Dallaglio, P.; Macías, R.; Jiménez-Candil, J.; Peinado, R.; García-Seara, J.; Arcocha, M.F.; Herreros, B.; Quesada, A.; Hernández-Madrid, A.; et al. Long-Term Outcome After Ablation of Right Atrial Tachyarrhythmias After the Surgical Repair of Congenital and Acquired Heart Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Lisi, M.; Focardi, M.; Reccia, R.; Natali, B.M.; Sparla, S.; Mondillo, S. Left atrial deformation analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography for prediction of cardiovascular outcomes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, R.; Murata, M.; Roberts, R.; Tokuda, H.; Minakata, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Tsuruta, H.; Kimura, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Fukumoto, K.; et al. Left atrial strain is a powerful predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: Study of a heterogeneous population with sinus rhythm or atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall Population (n = 62) | No AA Recurrence (n = 41) | AA Recurrence (n = 21) | p-Value (Sig.2-Tailed) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| Female sex (n, %) | 18 (29%) | 8 (19.5%) | 10 (47.6%) | 0.021 |
| Age (years) | 64.8 ± 13.2 | 63.4 ± 13.9 | 67.4 ± 11.4 | 0.356 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.9 ± 4.5 | 26.7 ± 4.4 | 27.5 ± 4.7 | 0.484 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 34 (58.4%) | 23 (56%) | 11 (52.4%) | 0.781 |
| Diabetes mellitus (n, %) | 9 (14.5%) | 5 (12.2%) | 4 (19%) | 0.469 |
| Current smoker (n, %) | 9 (14.5%) | 5 (12.2%) | 4 (19%) | 0.469 |
| CAD (n, %) | 6 (9.7%) | 6 (14.6%) | 0 (0%) | 0.065 |
| COPD (n, %) | 6 (9.7%) | 4 (9.8%) | 2 (9.5%) | 0.977 |
| Concomitant AF ablation (n, %) | 27 (43.5%) | 14 (34.1%) | 13 (61.9%) | 0.051 |
| Beta-blockers (n, %) | 49 (79%) | 32 (78%) | 17 (80.9%) | 0.929 |
| AADs (n, %) | 22 (35.5%) | 11 (26.8%) | 11 (52.4%) | 0.055 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 0.944 |
| ECG features | ||||
| HR (bpm) | 93.5 ± 33.2 | 91.9 ± 31.7 | 96.5 ± 36.7 | 0.704 |
| QRS (ms) | 119.2 ± 31 | 119.5 ± 34.4 | 118.6 ± 23.8 | 0.577 |
| Echocardiography | ||||
| LVEDV (mL) | 99.2 ± 31.1 | 101 ± 33.8 | 95.7 ± 25.1 | 0.679 |
| LVEF (%) | 50.5 ± 13.1 | 50.8 ± 13.9 | 49.7 ± 11.7 | 0.579 |
| LAVi (mL/m2) | 40.1 ± 15.9 | 39.6 ± 13.4 | 41.1 ± 14.4 | 0.559 |
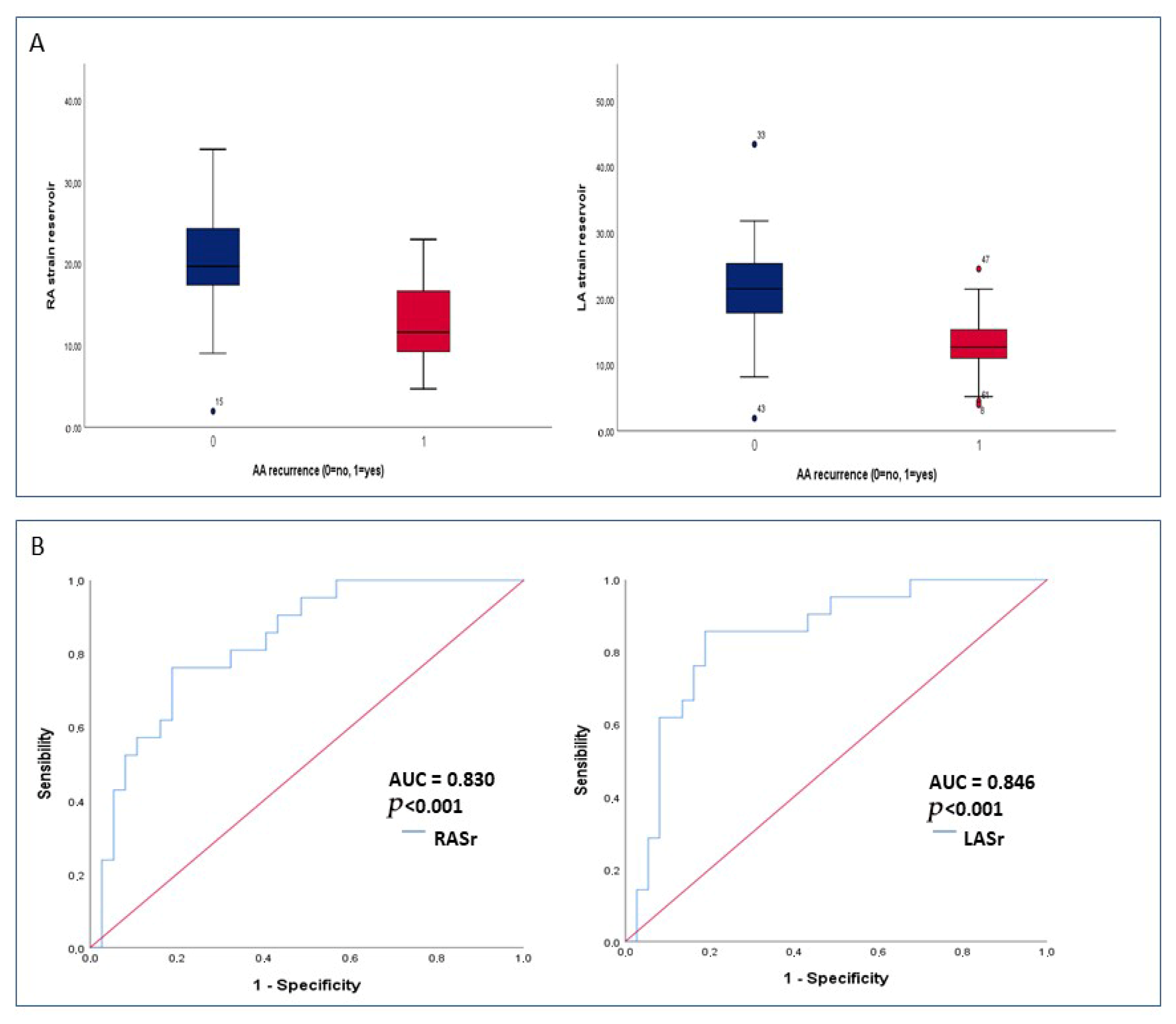
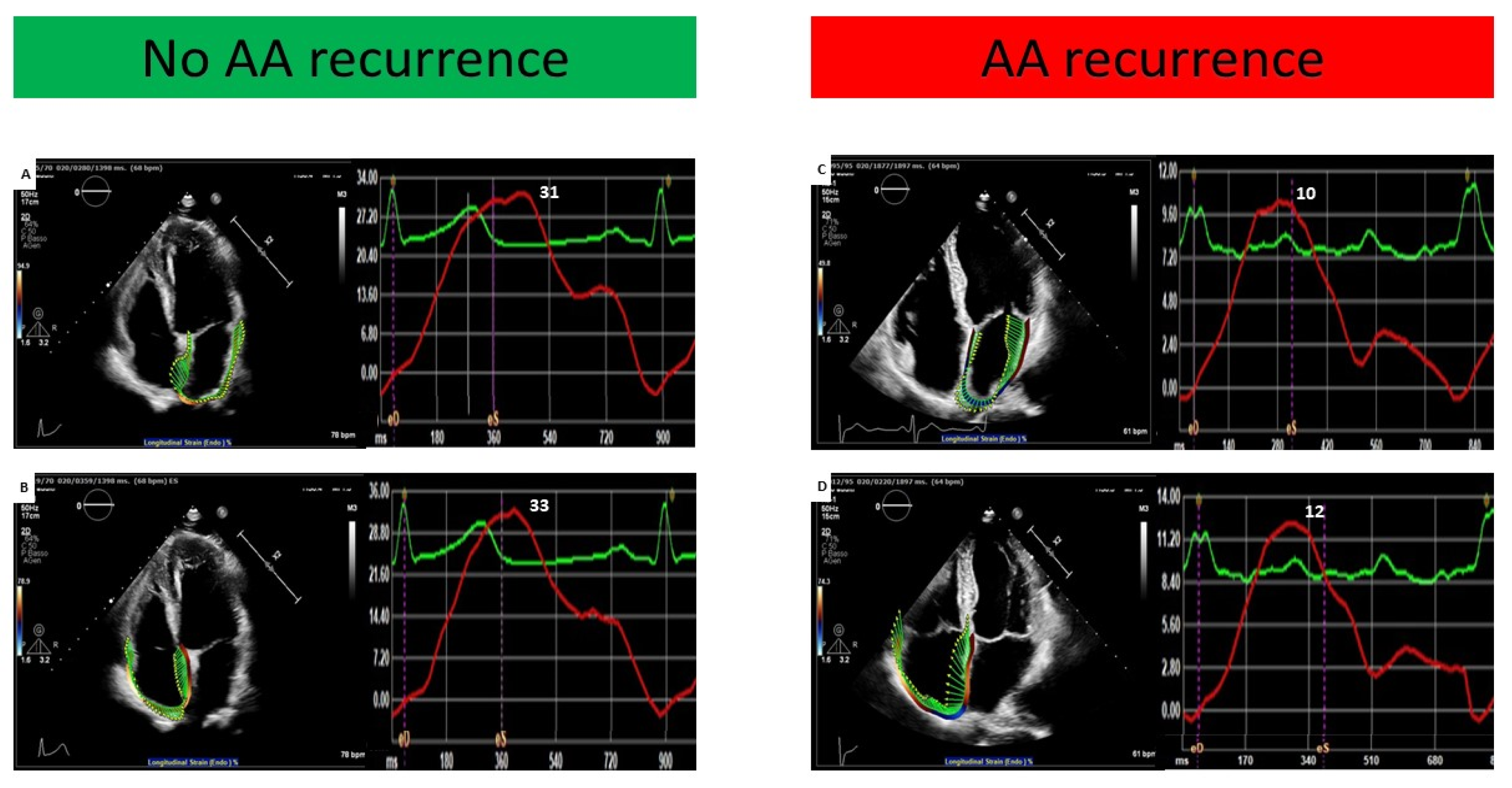
| LASr (%) | 18.8 ± 8.7 | 22.1 ± 8.5 | 13.5 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 18.2 ± 4.1 | 18.6 ± 3.9 | 17.6 ± 4.4 | 0.295 |
| PASP (mmHg) | 33.2 ± 8.5 | 32.3 ± 9 | 32.2 ± 4.4 | 0.914 |
| RVFAC (%) | 32.3 ± 11.1 | 30.8 ± 9.8 | 34.9 ± 13.1 | 0.203 |
| RV mid-diameter (mm) | 29.8 ± 6.2 | 30.2 ± 7 | 29.1 ± 4.4 | 0.949 |
| RAVi (mL/m2) | 30.2 (21.4–41.5) | 31.3 (21.6–40.3) | 35.6 (20.8–50.5) | 0.489 |
| RASr (%) | 17.6 ± 6.9 | 20.3 ± 6.3 | 12.8 ± 5.3 | <0.001 |
| At least moderate MR (n, %) | 7 (11.3%) | 3 (7.3%) | 4 (19%) | 0.167 |
| At least moderate TR (n, %) | 6 (9.7%) | 2 (4.9%) | 4 (19%) | 0.074 |
| Univariable | Multivariable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Clinical variables | ||||
| Age | 1.034 (0.996–1.074) | 0.078 | ||
| Sex | 2.208 (0.890–5.475) | 0.087 | ||
| Hypertension | 0.686 (0.278–1.693) | 0.413 | ||
| History of CAD | 2.425 (0.11–55.178) | 0.419 | ||
| History of COPD | 0.529 (0.117–2.398) | 0.409 | ||
| Concomitant AF | 1.886 (0.767–4.636) | 0.167 | ||
| AADs | 1.736 (0.718–4.198) | 0.221 | ||
| Echocardiographic variables | ||||
| LVEDV | 0.996 (0.981–1.012) | 0.640 | ||
| LVEF | 0.982 (0.946–1.019) | 0.339 | ||
| LAVi | 0.995 (0.982–1.007) | 0.395 | ||
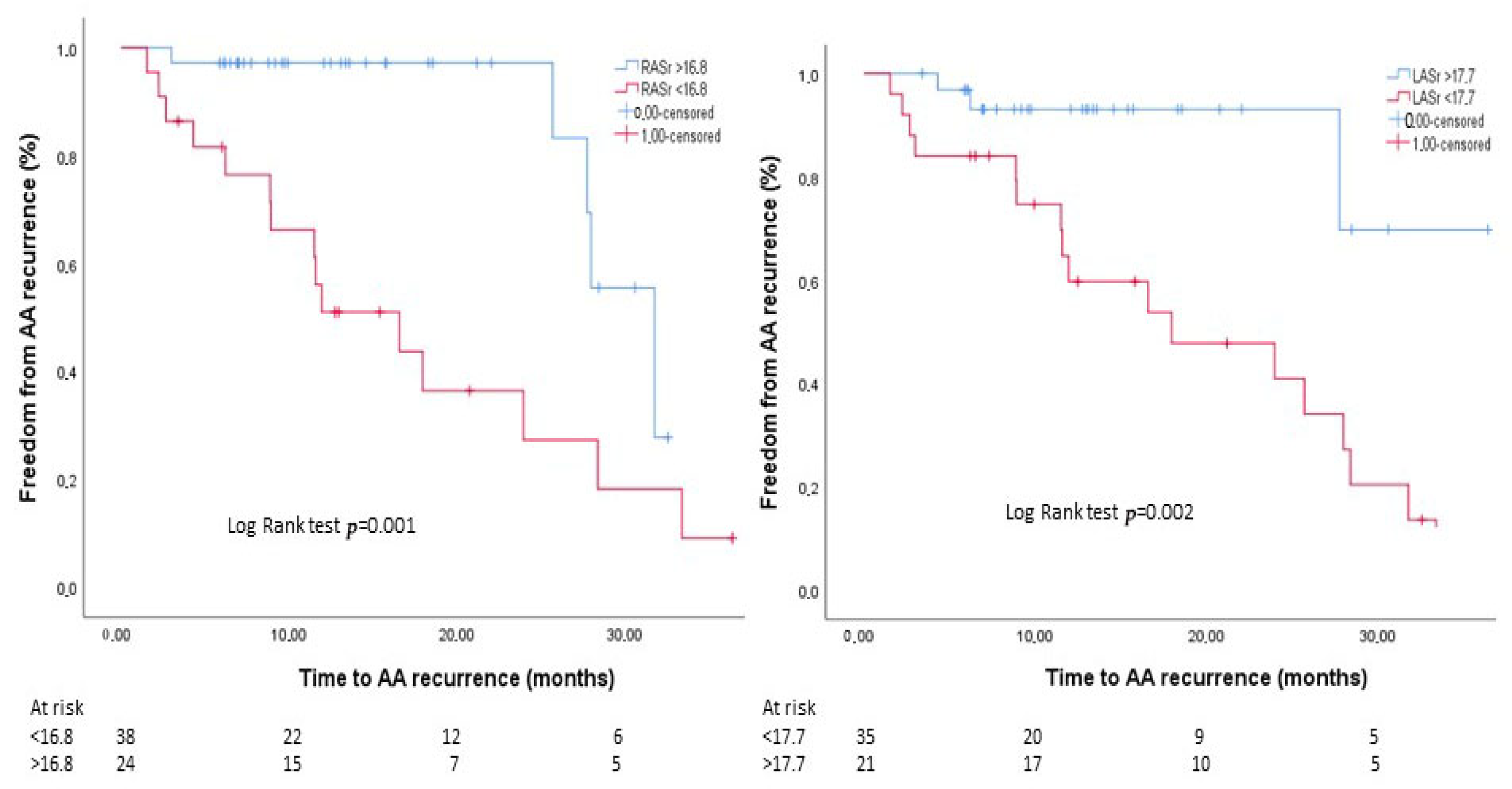
| LASr | 0.890 (0.828–0.957) | 0.002 | 0.919 (0.852–0.992) | 0.03 |
| TAPSE | 0.918 (0.825–1.023) | 0.122 | ||
| RAVi | 1.020 (0.994–1.046) | 0.128 | ||
| RASr | 0.878 (0.812–0.950) | 0.001 | 0.904 (0.831–0.984) | 0.02 |
| At least moderate MR | 0.460 (0.151–1.405) | 0.173 | ||
| At least moderate TR | 0.350 (0.109–1.121) | 0.077 | ||
| Variables | SR During Echocardiography 36 pts | AFL During Echocardiography 26 pts | p-Value (Sig.2-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVEDV (mL) | 95.7 ± 28.5 | 103.6 ± 34.2 | 0.369 |
| LVEF (%) | 54 ± 13.5 | 45.7 ± 11.1 | 0.005 |
| LAVi (mL/m2) | 37.1 ± 11.2 | 42.7 ± 17.5 | <0.001 |
| LASr (%) | 20.4 ± 9.3 | 17.8 ± 7.5 | 0.189 |
| RV mid-diameter (mm) | 29.1 ± 6.7 | 30.7 ± 5.5 | 0.149 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 18.9 ± 3.8 | 17.4 ± 4.3 | 0.277 |
| RAVi (mL/m2) | 22.9 (13.2–33.1) | 31.2 (24.7–45.4) | 0.015 |
| RASr (%) | 18.5 ± 7.9 | 16.5 ± 5.4 | 0.159 |
| AA recurrence | 11 (31%) | 10 (38%) | 0.516 |
| Isolated CTIA 35 pts | CTIA + AF Ablation 27 pts | p-Value (Sig.2-Tailed) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Female sex (n, %) | 12 (34.3%) | 6 (22.2%) | 0.299 |
| Age (years) | 62.9 ± 14.7 | 67.2 ± 10.7 | 0.356 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.7 ± 3.9 | 27.3 ± 5.2 | 0.926 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 18 (51.4%) | 16 (59.2%) | 0.539 |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 6 (17.1%) | 3 (11.1%) | 0.504 |
| CAD (n, %) | 4 (11.4%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.595 |
| COPD (n, %) | 3 (8.5%) | 3 (11.1%) | 0.737 |
| Beta-blockers (n, %) | 27 (77.1%) | 22 (81.4%) | 0.468 |
| AADs (n, %) | 8 (22.9%) | 14 (51.8%) | 0.013 |
| Echocardiography | |||
| LVEDV (mL) | 99.1 ± 33.2 | 99.5 ± 28.8 | 0.747 |
| LVEF (%) | 50.2 ± 13.9 | 50.8 ± 12 | 0.959 |
| LAVi (mL/m2) | 41.8 ± 13.9 | 40.2 ± 18.5 | 0.332 |
| LASr (%) | 18.9 ± 6.7 | 18.5 ± 10.7 | 0.444 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 18.1 ± 4.3 | 18.4 ± 3.8 | 0.653 |
| RAVi (mL/m2) | 33.2 (25–40) | 32.1 (21.4–42) | 0.551 |
| RASr (%) | 17.2 ± 6.7 | 18 ± 7.3 | 0.790 |
| At least moderate MR | 5 (14.3%) | 2 (27.4%) | 0.396 |
| At least moderate TR | 4 (11.4%) | 2 (27.4%) | 0.595 |
| AFL at Fup 11 pts | AF at Fup 10 pts | p-Value (Sig.2-Tailed) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Female sex (n, %) | 5 (45.5%) | 5 (50%) | 0.835 |
| Age (years) | 67.8 ± 12.8 | 66.9 ± 11 | 0.863 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.7 ± 3.4 | 28.3 ± 5.8 | 0.705 |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 5 (45.5%) | 6 (60%) | 0.781 |
| Diabetes (n, %) | 0 (0%) | 4 (40%) | 0.020 |
| CAD (n, %) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.065 |
| COPD (n, %) | 1 (9%) | 1 (10%) | 0.977 |
| Concomitant AF ablation (n, %) | 7 (63.6%) | 6 (60%) | 0.835 |
| Beta-blockers (n, %) | 8 (78%) | 9 (80.9%) | 0.314 |
| AADs (n, %) | 6 (26.8%) | 5 (52.4%) | 0.055 |
| Echocardiography | |||
| LVEDV (mL) | 97.1 ± 21.3 | 94.2 ± 30 | 0.497 |
| LVEF (%) | 51.3 ± 12.3 | 47.9 ± 11.3 | 0.512 |
| LAVi (mL/m2) | 22.6 (12–35) | 28 (13.2–41) | 0.512 |
| LASr (%) | 13.2 ± 5.9 | 12.6 ± 4.5 | 0.973 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 17.8 ± 5.3 | 17.3 ± 3.4 | 0.863 |
| RAVi (mL/m2) | 29.25 (11.9–41.6) | 28 (14.2–39.5) | 0.809 |
| RASr (%) | 12.5 ± 4.8 | 13.2 ± 6 | 0.863 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannaccone, G.; Scacciavillani, R.; Graziani, F.; Tusa, F.; Piccinni, C.; Gabrielli, F.A.; Narducci, M.L.; Perna, F.; Camilli, M.; Meucci, M.C.; et al. Atrial Strain Analysis Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation of Typical Atrial Flutter. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155247
Iannaccone G, Scacciavillani R, Graziani F, Tusa F, Piccinni C, Gabrielli FA, Narducci ML, Perna F, Camilli M, Meucci MC, et al. Atrial Strain Analysis Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation of Typical Atrial Flutter. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155247
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannaccone, Giulia, Roberto Scacciavillani, Francesca Graziani, Filippo Tusa, Carlo Piccinni, Francesca Augusta Gabrielli, Maria Lucia Narducci, Francesco Perna, Massimiliano Camilli, Maria Chiara Meucci, and et al. 2025. "Atrial Strain Analysis Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation of Typical Atrial Flutter" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155247
APA StyleIannaccone, G., Scacciavillani, R., Graziani, F., Tusa, F., Piccinni, C., Gabrielli, F. A., Narducci, M. L., Perna, F., Camilli, M., Meucci, M. C., Montone, R. A., Bencardino, G., Lanza, G. A., Pelargonio, G., & Lombardo, A. (2025). Atrial Strain Analysis Predicts Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence Following Cavotricuspid Isthmus Ablation of Typical Atrial Flutter. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5247. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155247







