Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: Pathophysiological Mechanism and Clinical Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
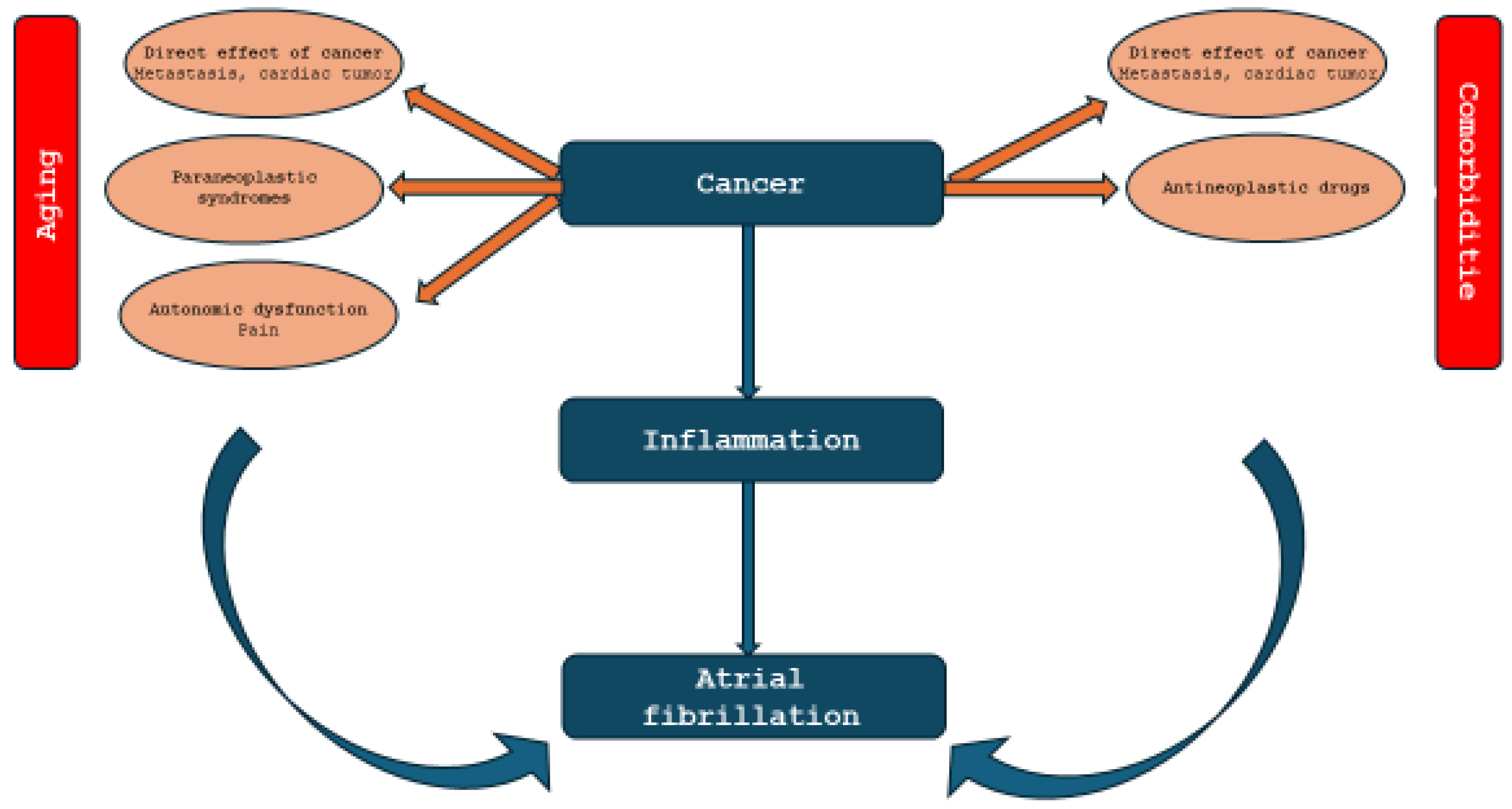
2. Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: Pathophysiological Mechanism
3. Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Cancer Patients
3.1. Thromboembolic Risk
3.2. Bleeding Risk
3.3. Interactions Drugs
3.4. Choice of Anticoagulant Regime
4. Future Perspectives on Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Cancer Patients
4.1. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter Two Inhibitors
4.2. Factor XI Inhibitors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| ATE | Arterial thromboembolism |
| BARC | Bleeding Academic Research Consortium |
| Cardio-CHUVI-AF | Retrospective Observational Registry of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation From Vigo’s Health Area |
| CAR-T | Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy |
| CDK4/6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 |
| CHA2DS2-VA | Congestion, Hypertension, Age ≥ 75, Diabetes mellitus, Vascular disease, Age between 65–74 |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CXCR-4 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DDIs | Drug–drug interactions |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| HAS-BLED | Hypertension, Abnormal liver and renal function, Stroke, Bleeding, Labile international normalized ratio, Elderly, Drugs |
| HER-2 | Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| MACEs | Major adverse cardiac events |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| NOACs | New oral anticoagulants |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| RR | Relative risk |
| SGLT2 | Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 |
| STE | Systemic thromboembolism |
| VKAs | Vitamin K antagonists |
| VTE | Venous Thromboembolism |
References
- Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Molinari, R.; Del Vecchio, G.E.; Tessitore, V.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Atrial Fibrillation: The Need for a Strong Pharmacological Approach. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madnick, D.L.; Fradley, M.G. Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer Patients: Mechanisms and Management. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J. Independent Risk Factors for Atrial Fibrillation in a Population-Based Cohort. JAMA 1994, 271, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauriello, A.; Ascrizzi, A.; Roma, A.S.; Molinari, R.; Caturano, A.; Imbalzano, E.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Effects of Heart Failure Therapies on Atrial Fibrillation: Biological and Clinical Perspectives. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, N.; Kapoor, V.; Ahsan, M.J.; Latif, A.; Ahmed, U.; Mirza, M.; Anwar, F.; Holmberg, M. Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer; Understanding the Mysterious Relationship through a Systematic Review. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2020, 10, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conen, D.; Wong, J.A.; Sandhu, R.K.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.-M.; Buring, J.E.; Albert, C.M. Risk of Malignant Cancer Among Women with New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, C.B.; Lamberts, M.; Carlson, N.; Lock-Hansen, M.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.H.; Schou, M. Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in Different Major Cancer Subtypes: A Nationwide Population-Based 12 Year Follow up Study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D.; Parissis, J.; Filippatos, G. Insights Into Onco-Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Maratea, A.C.; Caturano, A.; Liccardo, B.; Perrone, M.A.; Giordano, A.; Nigro, G.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Serum Lipids, Inflammation, and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiological Links and Clinical Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Ascrizzi, A.; Del Vecchio, G.E.; Benfari, G.; Ilardi, F.; Lisi, M.; Malagoli, A.; Mandoli, G.E.; Pastore, M.C.; et al. Relationship Between Left Atrial Strain and Atrial Fibrillation: The Role of Stress Echocardiography. Diagnostics 2024, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, N.; Kudo, Y.; Aki, D.; Nakagawa, H.; Taniguchi, K. Immunomodulation by Inflammation during Liver and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis and Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A New Immune–Metabolic Viewpoint for Age-Related Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rositch, A.F. Global Burden of Cancer Attributable to Infections: The Critical Role of Implementation Science. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e153–e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, T.A.; Itzkowitz, S.H. Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1807–1816.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Ogata, H.; Nishigaki, R.; Broide, D.H.; Karin, M. Tobacco Smoke Promotes Lung Tumorigenesis by Triggering IKKβ- and JNK1-Dependent Inflammation. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quail, D.F.; Dannenberg, A.J. The Obese Adipose Tissue Microenvironment in Cancer Development and Progression. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukić, M.; Radonjić, T.; Jovanović, I.; Zdravković, M.; Todorović, Z.; Kraišnik, N.; Aranđelović, B.; Mandić, O.; Popadić, V.; Nikolić, N.; et al. Alcohol, Inflammation, and Microbiota in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartung, A.; Yang, J.; Sukhatme, V.P.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Fernandes, D.; Chang, J.; Schmidt, B.A.; Hwang, S.H.; Zurakowski, D.; Huang, S.; et al. Suppression of Chemotherapy-Induced Cytokine/Lipid Mediator Surge and Ovarian Cancer by a Dual COX-2/SEH Inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, H.; Jones, J.D.; Purica, M.C.; Weidner, S.; Koh, A.J.; Kuo, R.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Daignault-Newton, S.; Pienta, K.J.; et al. Apoptosis-Induced CXCL5 Accelerates Inflammation and Growth of Prostate Tumor Metastases in Bone. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 128, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, T.; Chen, J.; She, Q.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Mao, M.; Zuo, Z.; Li, J. Anthracycline-Induced Arrhythmias in Breast Cancer Therapy: A Meta-Analysis of Single-Arm Trials. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartermaine, C.; Ghazi, S.M.; Yasin, A.; Awan, F.T.; Fradley, M.; Wiczer, T.; Kalathoor, S.; Ferdousi, M.; Krishan, S.; Habib, A.; et al. Cardiovascular Toxicities of BTK Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. JACC CardioOncol. 2023, 5, 570–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albini, A.; Pennesi, G.; Donatelli, F.; Cammarota, R.; De Flora, S.; Noonan, D.M. Cardiotoxicity of Anticancer Drugs: The Need for Cardio-Oncology and Cardio-Oncological Prevention. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhl-Polk, A.; Schou, M.; Vistisen, K.K.; Sillesen, A.-S.; Serup-Hansen, E.; Faber, J.; Klausen, T.W.; Bojesen, S.E.; Vaage-Nilsen, M.; Nielsen, D.L. Myocardial Ischemia Induced by 5-Fluorouracil: A Prospective Electrocardiographic and Cardiac Biomarker Study. Oncologist 2021, 26, e403–e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-S.; Feng, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lai, J.-I.; Chao, T.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Tseng, L.-M. The Association of Trastuzumab with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in Breast Cancer Patients in Routine Clinical Practice: A Population-Based Propensity Score Matching and Competing Risk Model Analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 198, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, C.; Zagouri, F.; Tampakis, K.; Georgakopoulou, R.; Manios, E.; Kafouris, P.; Benetos, G.; Koutagiar, I.; Anagnostopoulos, C.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; et al. Vascular Inflammation and Cardiovascular Burden in Metastatic Breast Cancer Female Patients Receiving Hormonal Treatment and CDK 4/6 Inhibitors or Everolimus. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 638895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glen, C.; Tan, Y.Y.; Waterston, A.; Evans, T.R.J.; Jones, R.J.; Petrie, M.C.; Lang, N.N. Mechanistic and Clinical Overview Cardiovascular Toxicity of BRAF and MEK Inhibitors. JACC CardioOncol 2022, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamami, Y.; Niimura, T.; Okada, N.; Koyama, T.; Fukushima, K.; Izawa-Ishizawa, Y.; Ishizawa, K. Factors Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Related Myocarditis. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Goldman, A.; Flynn, J.R.; El-Moghraby, A.; Rehman, M.; Devlin, S.M.; Corona, M.; Landego, I.; Lin, R.J.; Scordo, M.; et al. Atrial Arrhythmias Following CAR-chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy: Incidence, Risk Factors and Biomarker Profile. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 205, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Thurlapati, A.; Thotamgari, S.; Grewal, U.S.; Sheth, A.R.; Gupta, D.; Beedupalli, K.; Dominic, P. Anti-Cancer Drugs Associated Atrial Fibrillation—An Analysis of Real-World Pharmacovigilance Data. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 739044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasome. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.; Li, N.; Dobrev, D. Role of Inflammatory Signaling in Atrial Fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 287, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D. Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation in Active Cancer: What the Cardiologists Think. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fernández, T. CHA2DS2-VASc Score in Cardio-Oncology. JACC CardioOncol 2023, 5, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, M.; Carlson, N.; Fosbøl, E.; Lamberts, M.; Smedegaard, L.; Nielsen, D.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Gislason, G.; Schou, M. CHA2 DS2-VASc Score and Risk of Thromboembolism and Bleeding in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Recent Cancer. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leader, A.; Cohen, N.M.; Afek, S.; Jaschek, R.; Frajman, A.; Ben Zadok, O.I.; Raanani, P.; Lishner, M.; Spectre, G. Arterial Thromboembolism in Patients with AF and CHA2DS2-VASc Score 0–2 with and without Cancer. JACC CardioOncol 2023, 5, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposeiras-Roubin, S.; Abu-Assi, E.; Marchán, A.; Fernández-Sanz, T.; Barreiro-Pardal, C.; Pousa, I.M.; Erquicia, P.D.; Ledo-Piñeiro, A.; González-Bermúdez, I.; Viu, M.M.; et al. Validation of Embolic and Bleeding Risk Scores in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 180, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaber, E.; Orvain, C.; Papadopoulou, V.; Genthon, A.; Daguerre, V.; Barrière, S.; Teste, A.; Tavernier, E.; Daguenet, E.; Chalayer, E. Management of Thrombocytopenia and Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Hematological Malignancy on Chemotherapy: A Binational Prospective Study (TAT Study). J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2025, 58, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradley, M.G.; Beckie, T.M.; Brown, S.A.; Cheng, R.K.; Dent, S.F.; Nohria, A.; Patton, K.K.; Singh, J.P.; Olshansky, B. Recognition, Prevention, and Management of Arrhythmias and Autonomic Disorders in Cardio-Oncology: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, E41–E55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, C.J.; Rodgers, J.E.; Bagnola, A.J.; Beckie, T.M.; Campia, U.; Di Palo, K.E.; Okwuosa, T.M.; Przespolewski, E.R.; Dent, S. Cardio-Oncology Drug Interactions: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e811–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffel, J.; Collins, R.; Antz, M.; Cornu, P.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; Rowell, N.; et al. 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the Use of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2021, 23, 1612–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, B.S.; Dixon, D.L.; Neyens, R.R.; Page, R.L.; Gluckman, T.J. Select Drug-Drug Interactions with Direct Oral Anticoagulants. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnoth, M.J.; Buetehorn, U.; Muenster, U.; Schwarz, T.; Sandmann, S. In Vitro and In Vivo P-Glycoprotein Transport Characteristics of Rivaroxaban. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueck, W.; Kubitza, D.; Becka, M. Co-administration of Rivaroxaban with Drugs That Share Its Elimination Pathways: Pharmacokinetic Effects in Healthy Subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, A.; Ascrizzi, A.; Molinari, R.; Falco, L.; Caturano, A.; D’Andrea, A.; Russo, V. Pharmacogenomics of Cardiovascular Drugs for Atherothrombotic, Thromboembolic and Atherosclerotic Risk. Genes 2023, 14, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Norby, F.L.; Datta, Y.H.; Lutsey, P.L.; MacLehose, R.F.; Chen, L.Y.; Alonso, A. Comparative Effectiveness of Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin in Patients with Cancer and Atrial Fibrillation. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Park, J.; Uhm, J.-S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Pak, H.-N.; Lee, M.-H.; Sung, J.-H.; Joung, B. Bleeding Risk and Major Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer on Oral Anticoagulation Therapy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 203, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitelzweig, S.; Keshishian, A.V.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, A.; Dhamane, A.D.; Luo, X.; Klem, C.; Ferri, M.; Jiang, J.; Yuce, H.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Oral Anticoagulants Among Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Patients With Active Cancer. JACC CardioOncol 2021, 3, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.V.; Magnocavallo, M.; Straito, M.; Piro, A.; Severino, P.; Iannucci, G.; Chimenti, C.; Mancone, M.; Rocca, D.G.D.; Forleo, G.B.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants versus Vitamin K Antagonists in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer a Meta-Analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.Y.; Levine, M.N.; Baker, R.I.; Bowden, C.; Kakkar, A.K.; Prins, M.; Rickles, F.R.; Julian, J.A.; Haley, S.; Kovacs, M.J.; et al. Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin versus a Coumarin for the Prevention of Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Avezum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Špinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastori, D.; Marang, A.; Bisson, A.; Menichelli, D.; Herbert, J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Fauchier, L. Thromboembolism, Mortality, and Bleeding in 2,435,541 Atrial Fibrillation Patients with and without Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancer 2021, 127, 2122–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Chang, P.M.; Tsao, H.; Lin, Y.; Chang, S.; Lo, L.; Tuan, T.; Li, C.; Chao, T.; et al. Incident Thromboembolism and Heart Failure Associated with New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Cancer Patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 165, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, S.; Hasan, M.; Sheikh, Z.M.; Mustafa, F.; Tegeltija, V.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, J. Efficacy of SGLT2 Inhibitors for Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Meta-Analysis in Cancer Patients. Future Cardiol. 2024, 20, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommu, S. The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Heart Failure Outcomes in Nondiabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2024, 83, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Di Mauro, A.; Ferrara, G.; Bruzzese, F.; Palma, G.; Luciano, A.; Canale, M.L.; Bisceglia, I.; Iovine, M.; Cadeddu Dessalvi, C.; et al. Cardio–Renal and Systemic Effects of SGLT2i Dapagliflozin on Short-Term Anthracycline and HER-2-Blocking Agent Therapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, J.P.; Patel, M.R.; Steffel, J.; Ferdinand, K.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Russo, A.M.; Ma, C.S.; Goodman, S.G.; Oldgren, J.; Hammett, C.; et al. Asundexian versus Apixaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 392, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoamanesh, A.; Mundl, H.; Smith, E.E.; Masjuan, J.; Milanov, I.; Hirano, T.; Agafina, A.; Campbell, B.; Caso, V.; Mas, J.L.; et al. Factor XIa Inhibition with Asundexian after Acute Non-Cardioembolic Ischaemic Stroke (PACIFIC-Stroke): An International, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2b Trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.S.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Pieper, K.S.; Shimizu, W.; Potpara, T.; Ruff, C.T.; Kamel, H.; Lewis, B.S.; Cornel, J.H.; Kowey, P.R.; et al. Milvexian vs. Apixaban for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation: The LIBREXIA Atrial Fibrillation Trial Rationale and Design. Am. Heart J. 2024, 277, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Kohs, T.C.L.; Vu, H.H.; Jordan, K.R.; Wang, J.S.H.; Lorentz, C.U.; Tucker, E.I.; Puy, C.; Olson, S.R.; DeLoughery, T.G.; et al. Factor XI Inhibition for the Prevention of Catheter-Associated Thrombosis in Patients with Cancer Undergoing Central Line Placement: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, C.T.; Patel, S.M.; Giugliano, R.P.; Morrow, D.A.; Hug, B.; Kuder, J.F.; Goodrich, E.L.; Chen, S.A.; Goodman, S.G.; Joung, B.; et al. Abelacimab versus Rivaroxaban in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. 2025, 392, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Study Comparing Abelacimab to Apixaban in the Treatment of Cancer-Associated VTE (ASTER). 2024. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05171049 (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Study Comparing Abelacimab to Dalteparin in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal/Genitourinary Cancer and Associated VTE (MAGNOLIA). 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05171075 (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Weitz, J.I.; Tankó, L.B.; Floege, J.; Fox, K.A.A.; Bhatt, D.L.; Thadhani, R.; Hung, J.; Pap, Á.F.; Kubitza, D.; Winkelmayer, W.C. Anticoagulation with Osocimab in Patients with Kidney Failure Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Phase 2 Trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmayer, W.C.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Thadhani, R.I.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Walsh, M.; Pap, Á.F.; Willmann, S.; Thelen, K.; Hodge, S.; Solms, A.; et al. A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluated Antithrombotic Treatment with Fesomersen in Patients with Kidney Failure on Hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Study to EvaLuate the EffIcacy and Safety of AbeLacimab in High-Risk Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Who Have Been Deemed Unsuitable for Oral AntiCoagulation (LILAC-TIMI 76) (LILAC-TIMI 76). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05712200 (accessed on 7 June 2025).
| Drug Class | Proposed Mechanisms |
|---|---|
| Anthracyclines [22] | Oxidative stress-induced cardiomyocyte damage, ion channel dysfunction, myocarditis and cardiac remodeling, autonomic dysfunction |
| Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors [23] | Off-target inhibition of C-terminal Src kinase, structural remodeling and myocardial fibrosis in the atrium, inflammation |
| Alkylating Agents [24] | Elevated inflammatory markers, alteration of intracellular calcium activity, aggravation of pre-existing pro-arrhythmic conditions |
| Anti-metabolites [25] | Endothelial dysfunction and vasospasm, oxidative stress, direct myocardial toxicity, electrophysiologic change |
| HER-2 Antagonists [26] | Disruption of HER2 signaling pathways, structural changes in the heart, cardiac inflammation, and fibrosis |
| CDK4/6 Inhibitors [27] | Alteration of potassium and sodium channel activity, vascular inflammation |
| BRAF/MEK Inhibitors [28] | Structural and electrical remodeling in the heart |
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors [29] | Myocarditis, cardiac inflammation leading to arrhythmias, variable incidence based on specific drug and combination therapy |
| CAR-T-Cell Therapies [30] | Cytokine release syndrome, elevated inflammatory markers |
| Lenalidomide [31] | Exact mechanism for AF is unknown |
| Molecule | Mechanism of Action | The Phase of Clinical Trial |
|---|---|---|
| Asundexian | bind to the active site of FXIa | OCEANIC-AF (NCT05643573) phase 3 [62] PACIFIC-AF (NCT04218266) [63] |
| Milvexian | bind to the active site of FXIa | LIBREXIA-AF trial (NCT05757869) phase 3 [64] |
| Xisomab | antibodies directed against FXI and FXII | (NCT04465760) Phase 2 [65] |
| Abelacimab | antibodies directed against FXI | AZALEA-TIMI 71 (NCT04755283) phase 2b [66] ASTER (NCT05171049) phase 3 [67] MAGNOLIA (NCT05171075) phase 3 [68] |
| Osocimab | antibodies directed against FXI | Phase 2b (NCT04523220) [69] |
| Fesomersen | antisense oligonucleotides | Phase 2b RE-THINC ESRD (NCT04534114) [70] |
| Trial | Sample Size (N) | Drugs | Primary Outcome | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PACIFIC-AF [63] (NCT04218266) | 755 | Asundexian | The composite of major or clinically relevant non-major bleeding. | Rate of incidence for the primary endpoint were 0.50 (90% CI 0.14–1.68) for asundexian 20 mg, 0.16 (0.01–0.99) for asundexian 50 mg, and 0.33 (0.09–0.97) for pooled asundexian versus apixaban. |
| OCEANIC-AF [62] (NCT05643573) | 14,810 | Asundexian | Superiority of asundexian versus to apixaban to major bleeding events. | The trial was stopped prematurely. During trial, Asundexian at a dose of 50 mg once daily was associated with a higher risk of stroke or systemic embolism when compared than apixaban (hazard ratio, 3.79; 95% CI, 2.46 to 5.83). |
| LIBREXIA-AF [64] (NCT05757869) | 15,500 | Milvexian | Non-inferiotity of milvexian versus apixaban for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism. | Ongoing |
| AZALEA-TIMI 71 [66] (NCT04755283) | 1287 | Abelacimab | Major or clinically relevant non-major bleeding. | The trial was stopped early due to a greater-than-anticipated reduction in bleeding events with abelacimab. |
| LILAC-TIMI 76 [71] (NCT05712200) | 1900 | Abelacimab | The composite outcome of ischemic stroke or systemic embolism. | Ongoing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mauriello, A.; Correra, A.; Quagliariello, V.; Iovine, M.; Di Micco, P.; Imbalzano, E.; Giallauria, F.; Giordano, A.; Russo, V.; D’Andrea, A.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: Pathophysiological Mechanism and Clinical Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155600
Mauriello A, Correra A, Quagliariello V, Iovine M, Di Micco P, Imbalzano E, Giallauria F, Giordano A, Russo V, D’Andrea A, et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: Pathophysiological Mechanism and Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155600
Chicago/Turabian StyleMauriello, Alfredo, Adriana Correra, Vincenzo Quagliariello, Martina Iovine, Pierpaolo Di Micco, Egidio Imbalzano, Francesco Giallauria, Antonio Giordano, Vincenzo Russo, Antonello D’Andrea, and et al. 2025. "Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: Pathophysiological Mechanism and Clinical Implications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155600
APA StyleMauriello, A., Correra, A., Quagliariello, V., Iovine, M., Di Micco, P., Imbalzano, E., Giallauria, F., Giordano, A., Russo, V., D’Andrea, A., & Maurea, N. (2025). Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: Pathophysiological Mechanism and Clinical Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155600













