Contemporary Practices for Management of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology and Risk of Thromboembolism
3. Implantable Loop Recorders and Advanced Monitoring in SCAF
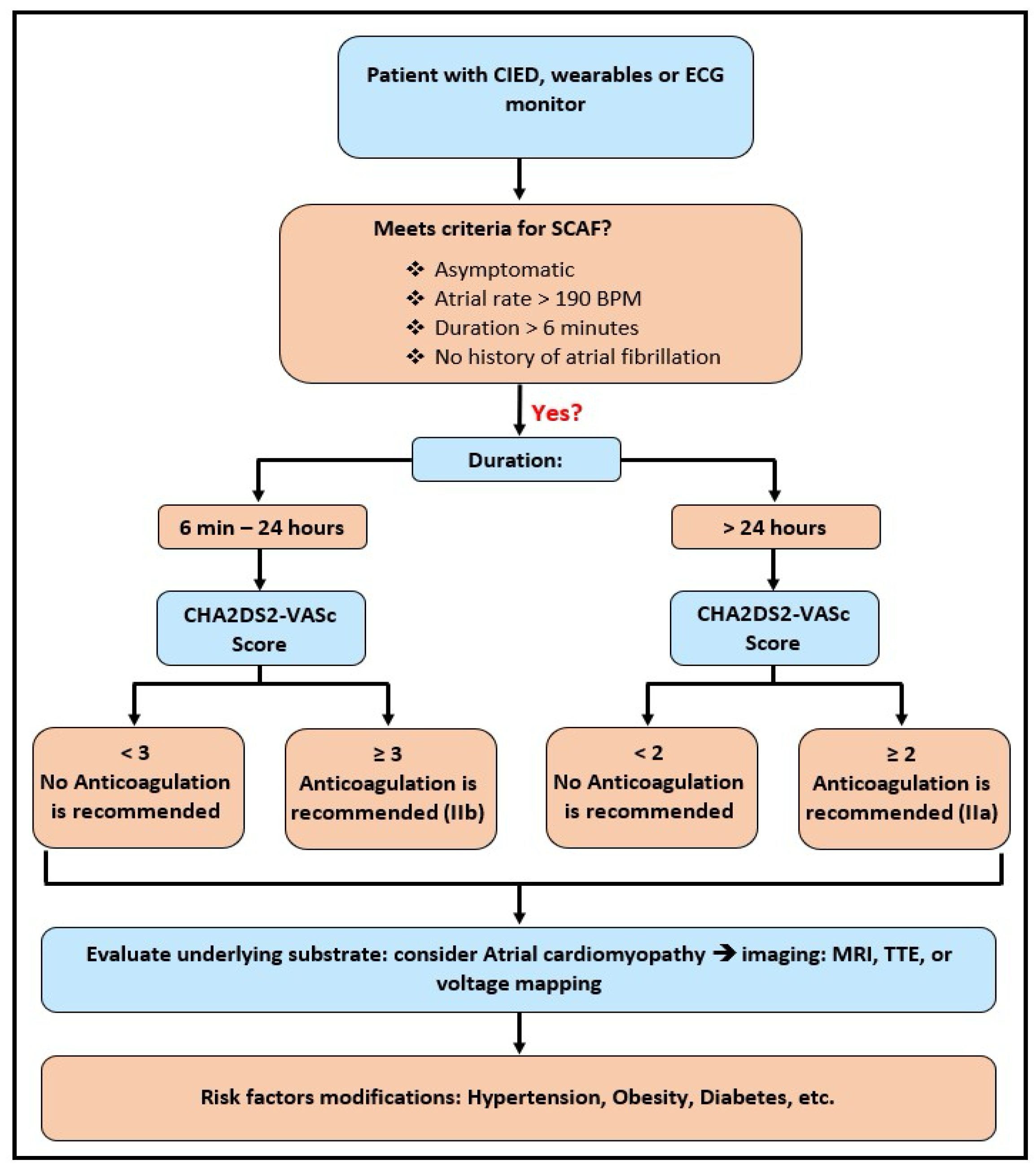
4. Anticoagulation in AHRE/AHRE/SCAF
5. Risk of Progression to Clinical Atrial Fibrillation
6. Heart Failure and SCAF/AHRE
7. Controversies and Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Anticoagulation |
| CIED | Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device |
| CHF | Congestive Heart Failure |
| SCAF | Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation |
| AHRE | Atrial High-Rate Episode |
References
- Simu, G.; Rosu, R.; Cismaru, G.; Puiu, M.; Gusetu, G.; Minciuna, I.; Istratoaie, S.; Tomoaia, R.; Zdrenghea, D.; Pop, D. Atrial high-rate episodes: A comprehensive review. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2021, 32, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.M.; Ruff, C.T. Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulation: Weighing the Absolute Risks and Benefits. Circulation 2024, 149, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorenek, B.C.; Bax, J.; Boriani, G.; Chen, S.A.; Dagres, N.; Glotzer, T.V.; Healey, J.S.; Israel, C.W.; Kudaiberdieva, G.; Levin, L.; et al. Device-detected subclinical atrial tachyarrhythmias: Definition, implications and management-an European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) consensus document, endorsed by Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS) and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulación Cardíaca y Electrofisiología (SOLEACE). Europace 2017, 19, 1556–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glotzer, T.V.; Daoud, E.G.; Wyse, D.G.; Singer, D.E.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Hilker, C.; Miller, C.; Qi, D.; Ziegler, P.D. The relationship between daily atrial tachyarrhythmia burden from implantable device diagnostics and stroke risk: The TRENDS study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotzer, T.V.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Zimmerman, J.; Sweeney, M.O.; Yee, R.; Marinchak, R.; Cook, J.; Paraschos, A.; Love, J.; Radoslovich, G.; et al. Atrial high rate episodes detected by pacemaker diagnostics predict death and stroke: Report of the Atrial Diagnostics Ancillary Study of the MOde Selection Trial (MOST). Circulation 2003, 107, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnani, J.W.; Rienstra, M.; Lin, H.; Sinner, M.F.; Lubitz, S.A.; McManus, D.D.; Dupuis, J.; Ellinor, P.T.; Benjamin, E.J. Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2011, 124, 1982–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; He, J.; Han, Y.; Han, S.; Li, P.; Liao, H.; Guo, J. Global burden of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2021. Europace 2024, 26, euae195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perino, A.C.; Fan, J.; Askari, M.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Keung, E.; Raitt, M.H.; Piccini, J.P.; Ziegler, P.D.; Turakhia, M.P. Practice Variation in Anticoagulation Prescription and Outcomes After Device-Detected Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2019, 139, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.S.; Sharma, M.; Connolly, S.J.; Wang, J.; Gold, M.R.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Lau, C.P.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Morillo, C.; Capucci, A.; et al. Stroke type and severity in patients with subclinical atrial fibrillation: An analysis from the Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Evaluation in Pacemaker Patients and the Atrial Fibrillation Reduction Atrial Pacing Trial (ASSERT). Am. Heart J. 2018, 201, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Healey, J.S.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Wang, J.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Gold, M.R.; Capucci, A.; Lau, C.-P.; Morillo, C.A.; Hobbelt, A.H.; et al. Duration of device-detected subclinical atrial fibrillation and occurrence of stroke in ASSERT. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierucci, N.; Mariani, M.V.; Iannetti, G.; Maffei, L.; Coluccio, A.; Laviola, D.; Palombi, M.; Trivigno, S.; Spadafora, L.; Chourda, E.; et al. Atrial Cardiomyopathy: New Pathophysiological and Clinical Aspects. Minerva Cardiol. Angiol. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecha, S.; Wilke, I.; Yildirim, Y.; Reichenspurner, H.; Aydin, M.A. Implantable loop recorder monitoring in patients with cryptogenic stroke—Detection and treatment of different clinically relevant arrhythmias. J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 60, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cersosimo, A.; Chimenti, C.; Zanon, F.; Antonelli, M.; Ricci, R.; Favale, S.; Iacopino, S.; Molon, G.; Lucci, D.; Vinelli, A.; et al. Predictive value of left and right atrial strain for the detection of device-detected atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke and implantable cardiac monitor. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 435, 133368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, J.S.; Lopes, R.D.; Granger, C.B.; Alings, M.; Rivard, L.; McIntyre, W.F.; Atar, D.; Birnie, D.H.; Boriani, G.; Camm, A.J.; et al. Apixaban for Stroke Prevention in Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Toennis, T.; Goette, A.; Camm, A.J.; Diener, H.C.; Becher, N.; Bertaglia, E.; Lundqvist, C.B.; Borlich, M.; Brandes, A.; et al. Anticoagulation with Edoxaban in Patients with Atrial High-Rate Episodes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoamanesh, A.; Field, T.S.; Coutts, S.B.; Sharma, M.; Gladstone, D.; Hart, R.G.; Boriani, G.; Wright, D.J.; Sticherling, C.; Birnie, D.H.; et al. Apixaban versus aspirin for stroke prevention in people with subclinical atrial fibrillation and a history of stroke or transient ischaemic attack: Subgroup analysis of the ARTESiA randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2025, 24, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; Granger, C.B.; Wojdyla, D.M.; McIntyre, W.F.; Alings, M.; Mani, T.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Rivard, L.; Atar, D.; Birnie, D.H.; et al. Apixaban vs Aspirin According to CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc Score in Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation: Insights From ARTESiA. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 84, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, G.A.; Lee, K.; Sweeney, M.; Leon, A.; Yee, R.; Ellenbogen, K.; Greer, S.; Wilber, D.; Silverman, R.; Marinchak, R.; et al. The mode selection trial (MOST) in sinus node dysfunction: Design, rationale, and baseline characteristics of the first 1000 patients. Am. Heart J. 2000, 140, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.A.; Conen, D.; Van Gelder, I.C.; McIntyre, W.F.; Crijns, H.J.; Wang, J.; Gold, M.R.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Lau, C.P.; Capucci, A.; et al. Progression of Device-Detected Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation and the Risk of Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, A.-L.; Ge, G.; Ma, M.; Zhi, H.; Wang, L.-N. Atrial fibrillation burden and the risk of stroke: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Park, H.W.; Choi, E.K.; Park, J.K.; Kim, J.B.; Kang, K.W.; Shim, J.; Joung, B.; Park, K.M. Clinical Outcomes of Rhythm Control Strategies for Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation According to the Quality-of-Life Score: The CODE-AF (Comparison Study of Drugs for Symptom Control and Complication Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation) Registry. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e025956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Ghanta, S.N.; Mueller, J.; Mansour, M.; Chen, Z.; Puente, C.; Ha, Y.M.; Tarun, T.; Dhar, G.; Sivakumar, K.; et al. Artificial Intelligence, Wearables and Remote Monitoring for Heart Failure: Current and Future Applications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Ghanta, S.N.; Clausen, A.; Saluja, P.; Sivakumar, K.; Dhar, G.; Chang, Q.; De Mazumder, D.; Rabbat, M.G.; Greene, S.J.; et al. Contemporary Applications of Machine Learning for Device Therapy in Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2022, 10, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, E.; Jessup, M.; Callans, D.J. Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Circulation 2009, 119, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Brueckmann, M.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Ezekowitz, M.; Fräßdorf, M.; Hijazi, Z.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Mahfoud, F.; Schmieder, R.E.; Schumacher, H.; et al. Cardiovascular outcomes, bleeding risk, and achieved blood pressure in patients on long-term anticoagulation with the thrombin antagonist dabigatran or warfarin: Data from the RE-LY trial. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2848–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Heckbert, S.R.; Ding, J.; Spragg, D.; Calkins, H.; Shah, S.; Szklo, M.; Post, W.S.; Sharma, K. Prevalence of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2024, 12, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinarita, R.; Niwano, S.; Fukaya, H.; Oikawa, J.; Nabeta, T.; Matsuura, G.; Arakawa, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Shirakawa, Y.; Horiguchi, A.; et al. Burden of Implanted-Device-Detected Atrial High-Rate Episode Is Associated with Future Heart Failure Events—Clinical Significance of Asymptomatic Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Implantable Cardiac Electronic Devices. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahwash, R.; Butler, J.; Khan, M.S.; Chalasani, P.; Bertolet, B.; Gravelin, L.; Lambert, C.; Sarkar, S.; Van Dorn, B.; Laechelt, A.; et al. Incidence of Cardiac Arrhythmias Identified by Insertable Cardiac Monitors in Patients with Symptomatic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Heart Fail. 2025, 13, 102527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.B.; Reddy, V.Y.; Komtebedde, J.; Wegerich, S.W.; Sekaric, J.; Swarup, V.; Walton, A.; Laurent, G.; Chetcuti, S.; Rademann, M.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Burden and Atrial Shunt Therapy in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2023, 11, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doundoulakis, I.; Gavriilaki, M.; Tsiachris, D.; Arsenos, P.; Antoniou, C.-K.; Dimou, S.; Soulaidopoulos, S.; Farmakis, I.; Akrivos, E.; Stoiloudis, P.; et al. Atrial High-Rate Episodes in Patients with Devices Without a History of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022, 36, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Study Comparison: | ||
|---|---|---|
| NOAH-AFNET 6 vs. | ARTESIA | |
| Year | 2023 | 2023 |
| Inclusion criteria | At least one episode of device-detected SCAF lasting at least 6 minutes with a heart rate of at least 170 bpm + At least one other stroke risk factor like age, CHF, etc. | At least one episode of device-detected SCAF lasting at least 6 minutes up to 24 hours + Age of 55 or older + No history of clinical AF. |
| Study groups | Edoxaban Vs Placebo | Apixaban Vs Aspirin (ASA) |
| Sample Size | 2608 (1:1) | 4012 (1:1) |
| Mean CHA2DS2-VASc score | 4 | 3.9 |
| Median follow up (months) | 21 | 42 |
| Mean age (years) | 78 | 76.8 |
| Median duration of AHREs (hours) | 2.8 | 1.47 |
| Results | Higher bleeding in Edoxaban group with no significant difference in stroke & thromboembolism | Apixaban reduced the risk of stroke & thromboembolism significantly compared to ASA alone but increased the risk of major bleeding |
| Limitations | Study terminated early due to safety concerns. Confounding bias due to presence of multiple stroke risk factors in patients enrolled in the trial. | Results can only be extrapolated to patients with existing risk factors for stroke/systemic embolism (confounding bias). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhwarat, B.; Darwish, O.; Ghanta, S.N.; Rana, A.; Gautam, N.; Al’Aref, S.J.; Devabhaktuni, S. Contemporary Practices for Management of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155222
Alhwarat B, Darwish O, Ghanta SN, Rana A, Gautam N, Al’Aref SJ, Devabhaktuni S. Contemporary Practices for Management of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155222
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhwarat, Buthainah, Omar Darwish, Sai Nikhila Ghanta, Aakash Rana, Nitesh Gautam, Subhi J. Al’Aref, and Subodh Devabhaktuni. 2025. "Contemporary Practices for Management of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155222
APA StyleAlhwarat, B., Darwish, O., Ghanta, S. N., Rana, A., Gautam, N., Al’Aref, S. J., & Devabhaktuni, S. (2025). Contemporary Practices for Management of Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155222





