Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASM | antiseizure medication |
| SII | systemic inflammatory index |
| NLR | neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio |
| PLR | platelet–lymphocyte ratio |
| FAR | fibrinogen–albumin ratio |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| HMGB-1 | high mobility group box-1 |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| IL | interleukin |
| LEV | levetiracetam |
| VPA | valproate |
| LTG | lamotrigine |
| TPM | topiramate |
| OXC | oxcarbazepine |
| CBZ | carbamazepine |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| TGF | transforming growth factor |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| HDAC | histone deacetylase |
References
- Park, K.I. Understanding epileptogenesis from molecules to network alteration. Encephalitis 2024, 4, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Tang, J.; Du, W.; Du, Y.F.; Liu, H.J. Systemic immunoinflammatory index and prognostic nutrition index for predicting pathologic responses of patients with advanced gastric cancer after neoadjuvant therapy for advanced gastric cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 3922–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, L.; Polat, E.C.; Baran, C.; Boylu, A.; Erkoc, M.; Otunctemur, A. Systemic Inflammatory Index: A Promising Non-Invasive Marker for the Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy prior to Cystectomy. Urol. Int. 2024, 108, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Peng, J.J. Systemic inflammatory index as a predictive marker for the severity of coronary artery disease in individuals with chronic kidney disease. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2024, 21, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, S.; Fischer, I.; Naderi, S.; Faghih Jouibari, M.; Abdolreza, S.; Karimialavijeh, E.; Aslzadeh, S.; Mashayekhi, M.; Zojaji, M.; Kahlert, U.D.; et al. Systemic Inflammatory Index Is a Novel Predictor of Intubation Requirement and Mortality after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Nie, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Serum Folate, Vitamin B12 Levels, and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Correlate with Motor Performance in Parkinson’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 665075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondo, G.; Aprile, D.; De Marchi, F.; Sarasso, B.; Serra, P.; Borasio, G.; Rojo, E.; Arenillas, J.F.; Comi, C. Investigating the Prognostic Role of Peripheral Inflammatory Markers in Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Mojena, Y.; Rodríguez-Córdova, Y.; Dominguez-Barrios, Y.; León-Arcia, K.; Miranda-Becerra, D.; Gonzalez-Zaldivar, Y.; Guerra-Bustillos, G.; Ziemann, U.; Auburger, G.; Rodríguez-Labrada, R.; et al. Peripheral Inflammation Links with the Severity of Clinical Phenotype in Spinocerebellar Ataxia 2. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, S.F.; Bolayır, A.; Cigdem, B.; Yildiz, B. The role of systemic immune inflammatory index in showing active lesion in patients with multiple sclerosis: SII and other inflamatuar biomarker in radiological active multiple sclerosis patients. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Cui, X.; Zhang, S. The value of the systemic immune-inflammation index in assessing disease severity in autoimmune encephalitis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrubaru, I.; Motoc, A.; Moise, M.L.; Miutescu, B.; Citu, I.M.; Pingilati, R.A.; Popescu, D.E.; Dumitru, C.; Gorun, F.; Olaru, F.; et al. The Predictive Role of Maternal Biological Markers and Inflammatory Scores NLR, PLR, MLR, SII, and SIRI for the Risk of Preterm Delivery. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.Q.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhang, S.R.; Ma, Y.Z.; Fu, J.J.; Yang, T.M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Burgunder, J.M.; Shang, H.F. The characteristic and prognostic role of blood inflammatory markers in patients with Huntington’s disease from China. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1374365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, K.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Yang, K.; Xu, J.; Yang, Q.; Huang, X.; et al. Prognosis of Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Endovascular Thrombectomy is Influenced by Systemic Inflammatory Index Through Malignant Brain Edema. Clin. Interv. Aging 2022, 17, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, A.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. The relationship between systemic inflammation index, systemic immune-inflammatory index, and inflammatory prognostic index and 90-day outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. J. Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrieri, L.; Mercatali, L.; Ibrahim, T.; Fausti, V.; Dall’Agata, M.; Riva, N.; Ranallo, N.; Pasini, G.; Tazzari, M.; Foca, F.; et al. Immuno markers in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients underwent Stupp protocol after neurosurgery: A retrospective series. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 164, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cai, X.; Yao, D.; Jing, J.; Mei, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, A.; Meng, X.; Li, H.; et al. Association of inflammatory markers with cerebral small vessel disease in community-based population. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.W.; Kwon, H.M.; Jeong, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, H. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with white matter hyperintensity volume. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.H.L.; Sanfilippo, P.; Colman, B.; Perucca, P.; Kwan, P.; O’Brien, T.J.; Monif, M. Development and validation of a peripheral cell ratio and lactate score for differentiating status epilepticus from prolonged psychogenic nonepileptic seizures. Epilepsia Open 2023, 8, 1460–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.I.; Hwang, S.; Son, H.; Moon, J.; Lee, S.T.; Jung, K.H.; Jung, K.Y.; Chu, K.; Lee, S.K. Prognostication in Epilepsy with Integrated Analysis of Blood Parameters and Clinical Data. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Dhariwal, M.A.; Ageel, A.M.; Qureshi, S. Evaluation of the antiinflammatory activity of sodium valproate in rats and mice. Gen. Pharmacol. 1996, 27, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Chu, L.W.; Cheng, K.I.; Hsieh, S.L.; Juan, Y.S.; Wu, B.N. Valproate reduces neuroinflammation and neuronal death in a rat chronic constriction injury model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyama, T.; Okada, K.; Lipton, J.M.; Matsubara, T.; Hayashi, T.; Furukawa, S. Sodium valproate inhibits production of TNF-alpha and IL-6 and activation of NF-kappaB. Brain Res. 2000, 857, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Qiu, X.Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, T.M.; Traub, R.J.; Feng, H.N.; Cao, D.Y. Valproate attenuates somatic hyperalgesia induced by orofacial inflammation combined with stress through inhibiting spinal IL-6 and STAT1 phosphorylation. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 208, 110889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinborn, B.; Zarowski, M.; Winczewska-Wiktor, A.; Wójcicka, M.; Młodzikowska-Albrecht, J.; Losy, J. Concentration of Il-1β, Il-2, Il-6, TNFα in the blood serum in children with generalized epilepsy treated by valproate. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, S.; Bauer, S.; Hagge, M.; Knake, S.; Olmes, D.G.; Tackenberg, B.; Rosenow, F.; Hamer, H.M. Chronic valproate or levetiracetam treatment does not influence cytokine levels in humans. Seizure 2014, 23, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiah, I.S.; Yatham, L.N.; Yeh, C.B.; Ravindran, A.V. Effect of valproate on plasma levels of interleukin-6 in healthy male humans. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 20, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Taniguchi, R.; Matsuo, T.; Oguro, A.; Vogel, C.F.A.; Yamazaki, T.; Ishihara, Y. Suppressive effects of levetiracetam on neuroinflammation and phagocytic microglia: A comparative study of levetiracetam, valproate and carbamazepine. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 708, 134363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.D.; Buijs, R.M.; Sitges, M. The anti-seizure drugs vinpocetine and carbamazepine, but not valproic acid, reduce inflammatory IL-1β and TNF-α expression in rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmurowska-Michałowska, H.; Szuster-Ciesielska, A.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M.; Dubas-Slemp, H. The influence of carbamazepine on cytokine and superoxide anion production in blood leukocytes of healthy volunteers. Ann. Univ. Mariae Curie Sklodowska Med. 2004, 59, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Salimi, A.; Sabetkasaei, M.; Raisi, H.; Labibi, F.; Ameli, H.; Khazaei-Poul, Y.; Zarei, M.; Mottaghi, K.; Safari, F.; Nazem-Bokaei, A.; et al. Carbamazepine effects on pain management and serum IL-6, IL-10 evaluation in addicted patients undergoing surgery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 812, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.; Rossoni, G.; Sacerdote, P.; Panerai, A.E.; Berti, F. Carbamazepine exerts anti-inflammatory effects in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 294, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, G.; Liang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhong, G.; Huang, C.; Lin, P.; Kuang, Z. Therapeutic Impact of Serum Inflammatory Cytokines and S-100Β Levels in Patients With Acute Secondary Epilepsy Treated With Sodium Valproate. Am. J. Ther. 2025, 32, e92–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Guo, S.X.; Li, J.R.; Du, H.G.; Wang, C.H.; Zhang, J.M.; Wu, Q. Topiramate attenuates early brain injury following subarachnoid haemorrhage in rats via duplex protection against inflammation and neuronal cell death. Brain Res. 2015, 1622, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Xie, M.; Li, Y.; Gong, X.; Li, J. Topiramate Reverses Physiological and Behavioral Alterations by Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Rat Model Through Inhibiting TNF Signaling Pathway. Neuromolecular Med. 2020, 22, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Sun, J.; Hao, F.; Tang, W.; Li, X.; Guo, D.; Liu, X. Effects of Sodium Valproate Combined with Lamotrigine on Quality of Life and Serum Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Poststroke Secondary Epilepsy. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stienen, M.N.; Haghikia, A.; Dambach, H.; Thöne, J.; Wiemann, M.; Gold, R.; Chan, A.; Dermietzel, R.; Faustmann, P.M.; Hinkerohe, D.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of the anticonvulsant drug levetiracetam on electrophysiological properties of astroglia are mediated via TGFβ1 regulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Arfeen, M.; Rabbani, S.I.; Shariq, A.; Amirthalingam, P. Levetiracetam Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Chemobrain by Enhancing Cholinergic Transmission and Reducing Neuroinflammation Using an Experimental Rat Model and Molecular Docking Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Komori, R.; Nakatani, M.; Ochi, S.; Yokota-Nakatsuma, A.; Matsumoto, J.; Takata, F.; Dohgu, S.; Ishihara, Y.; Itoh, K. Levetiracetam Suppresses the Infiltration of Neutrophils and Monocytes and Downregulates Many Inflammatory Cytokines during Epileptogenesis in Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Han, T.T.; Chang, Y.H.; Cui, X.C. Levetiracetam attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive impairment and microglia polarization by suppressing neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1145819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thöne, J.; Ellrichmann, G.; Faustmann, P.M.; Gold, R.; Haghikia, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of levetiracetam in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labh, R.; Gupta, R.; Narang, M.; Halder, S.; Kar, R. Effect of valproate and add-on levetiracetam on inflammatory biomarkers in children with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 125, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulcebi, M.I.; Kendirli, T.; Turgan, Z.A.; Patsalos, P.N.; Onat Yilmaz, F. The effect of serum levetiracetam concentrations on therapeutic response and IL1-beta concentration in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 148, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Duan, R.; Chen, W.; Huang, T.; et al. The association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte to monocyte ratio with post-thrombolysis early neurological outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Hou, H.; Li, L.; Yong, L.; Zhang, S.; Yan, L.; Huang, X.; Wu, J. Neutrophil Percentage-to-Albumin Ratio: A Good Parameter for the Evaluation of the Severity of Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis at Admission and Prediction of Short-Term Prognosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 847200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çırakoğlu, Ö.F.; Yılmaz, A.S. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with increased carotid intima-media thickness in hypertensive patients. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2021, 43, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Deng, H.; Lei, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Sha, D. The prognostic value of fibrinogen to albumin ratio in malignant tumor patients: A meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 985377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Dai, Q.; Chang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Gu, R.; Zheng, H.; Hu, L.; Xu, B.; Wang, L. The association between fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio (FAR) and adverse prognosis in patients with acute decompensated heart failure at different glucose metabolic states. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, M.B.; Teja Reddy, A.; Nagaraju, B.; Arumugaperumal, D.; Ashwini, M.S. Study of Fibrinogen Albumin Ratio in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Cureus 2024, 16, e74977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, Y.; Zong, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K.; Song, Y.; Ye, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Song, B.; et al. Serum fibrinogen/albumin ratio and early neurological deterioration in patients with recent small subcortical infarction. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2396072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkink, W.R.; Walgaard, C.; Kuitwaard, K.; Tio-Gillen, A.P.; van Doorn, P.A.; Jacobs, B.C. Association of Albumin Levels With Outcome in Intravenous Immunoglobulin-Treated Guillain-Barré Syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, T.J.; Jun, J.S.; Moon, J.; Jung, K.H.; Park, K.I.; Chu, K.; Lee, S.K. High albumin level is a predictor of favorable response to immunotherapy in autoimmune encephalitis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Tajima, H.; Hironori, H.; Nakagawara, H.; Ohnishi, I.; Takamura, H.; Ninomiya, I.; Kitagawa, H.; Fushida, S.; Tani, T.; et al. Sodium valproate blocks the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 autocrine loop and attenuates the TGF-β1-induced collagen synthesis in a human hepatic stellate cell line. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 28, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kömürcü, H.F.; Erkalaycı, C.; Gozke, E. Hemogram and inflammatory indices in pain-free periods in migraine patients without aura. Neurol. Res. 2025, 47, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, M.; Maejima, Y.; Nakagama, S.; Shiheido-Watanabe, Y.; Tamura, N.; Hirao, K.; Isobe, M.; Sasano, T. Neutrophil extracellular traps-mediated Beclin-1 suppression aggravates atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage autophagy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 876147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahrendorf, M.; Swirski, F.K. Immunology. Neutrophil-macrophage communication in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Science 2015, 349, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Liu, K.; Wake, H.; Teshigawara, K.; Yoshino, T.; Takahashi, H.; Mori, S.; Nishibori, M. Therapeutic effects of anti-HMGB1 monoclonal antibody on pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.X.; Huang, L.D.; Jiang, Y.M.; Gutkind, J.S.; Manji, H.K.; Chen, G. The mood stabilizer valproic acid activates mitogen-activated protein kinases and promotes neurite growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31674–31683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; French, J.; Bartfai, T.; Baram, T.Z. The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Vezzani, A.; O’Brien, T.J.; Jette, N.; Scheffer, I.E.; de Curtis, M.; Perucca, P. Epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.S.; Peng, J.; Murugan, M.; Feng, L.J.; Liu, J.L.; Eyo, U.B.; Zhou, L.J.; Mogilevsky, R.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.J. Chemokine CCL2-CCR2 Signaling Induces Neuronal Cell Death via STAT3 Activation and IL-1beta Production after Status Epilepticus. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 7878–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, R.L.; Crichton, S.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Yi, Q.; Li, L.; Hankey, G.J.; Rothwell, P.M.; Markus, H.S. Sodium Valproate, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Is Associated With Reduced Stroke Risk After Previous Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2018, 49, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Rowe, M.; Ren, M.; Hong, J.S.; Chen, P.S.; Chuang, D.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in a rat permanent ischemic model of stroke: Multiple mechanisms of action. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, E.; Parodi, L.; Narasimhalu, K.; Wolking, S.; Harloff, A.; Georgakis, M.K.; Rosand, J.; Anderson, C.D. Genetic variation supports a causal role for valproate in prevention of ischemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2024, 19, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Drug-Naïve | 5 ASM User | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (female–male) | 383:455 | 431:513 | 1.000 |
| Age at epilepsy onset | 37.9 ± 21.3 | 24.9 ± 17.0 | <0.001 |
| Age at sampling | 41.4 ± 19.8 | 34.0 ± 15.4 | <0.001 |
| Epilepsy duration | 3.4 ± 7.2 | 8.9 ± 10.5 | <0.001 |
| Seizure frequency in the past 3 months | 6.8 ± 19.5 | 10.1 ± 22.3 | 0.02 |
| Seizure classification | |||
| Generalized | 661 (78.9%) | 726 (76.9%) | 0.496 |
| Focal | 135 (16.1%) | 140 (14.8%) | 0.346 |
| Epilepsy etiology | 0.629 | ||
| Genetic | 117 (14.0%) | 136 (14.4%) | |
| Hypoxic | 1 (0.1%) | 4 (0.4%) | |
| Immune | 44 (5.3%) | 40 (4.2%) | |
| Infectious | 27 (3.2%) | 24 (2.5%) | |
| Metabolic | 2 (0.2%) | 1 (0.1%) | |
| Structural | 285 (34.0%) | 341 (36.1%) | |
| Unknown | 362 (43.2%) | 398 (42.2%) | |
| History of febrile seizures | 45 (5.4%) | 93 (9.9%) | 0.001 |
| MRI lesion (+) | 347 (46.0%) | 417 (52.3%) | 0.015 |
| Time since last seizure | <0.001 | ||
| ~1 week | 379 (46.7%) | 275 (29.3%) | |
| 1 week~1 month | 245 (30.2%) | 365 (39.0%) | |
| ≥1 month | 188 (23.2%) | 297 (31.7%) | |
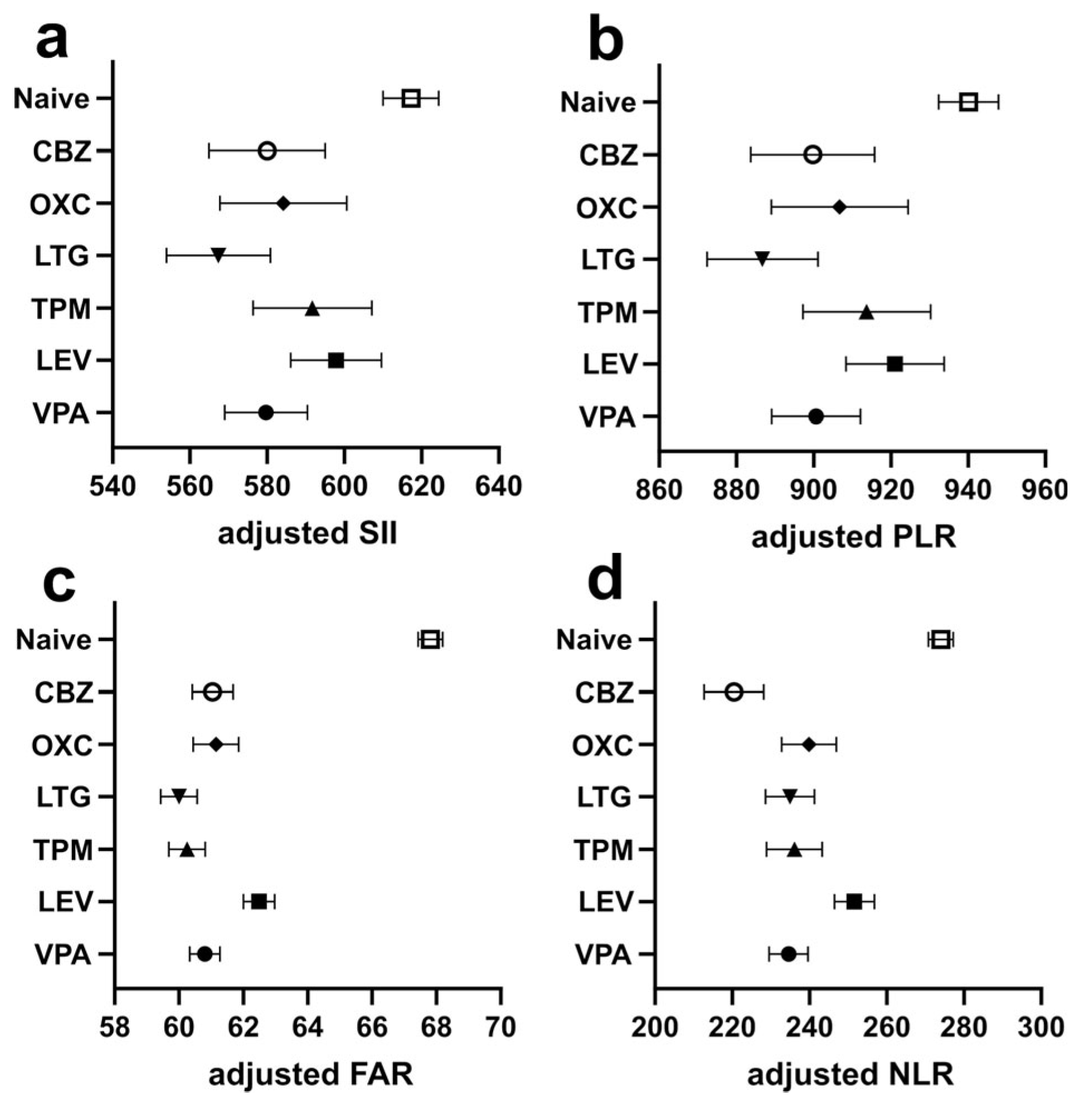
| 1 SII | 687.2 ± 901.1 | 511.6 ± 591.9 | <0.001 |
| 2 PLR | 1016.0 ± 956.4 | 827.8 ± 650.8 | <0.001 |
| 3 NLR | 297.6 ± 392.5 | 215.6 ± 206.3 | <0.001 |
| 4 FAR | 69.9 ± 25.9 | 60.6 ± 20.0 | <0.001 |
| Standardized β Coefficient (p Value) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SII 1 | PLR 2 | NLR 3 | FAR 4 | |
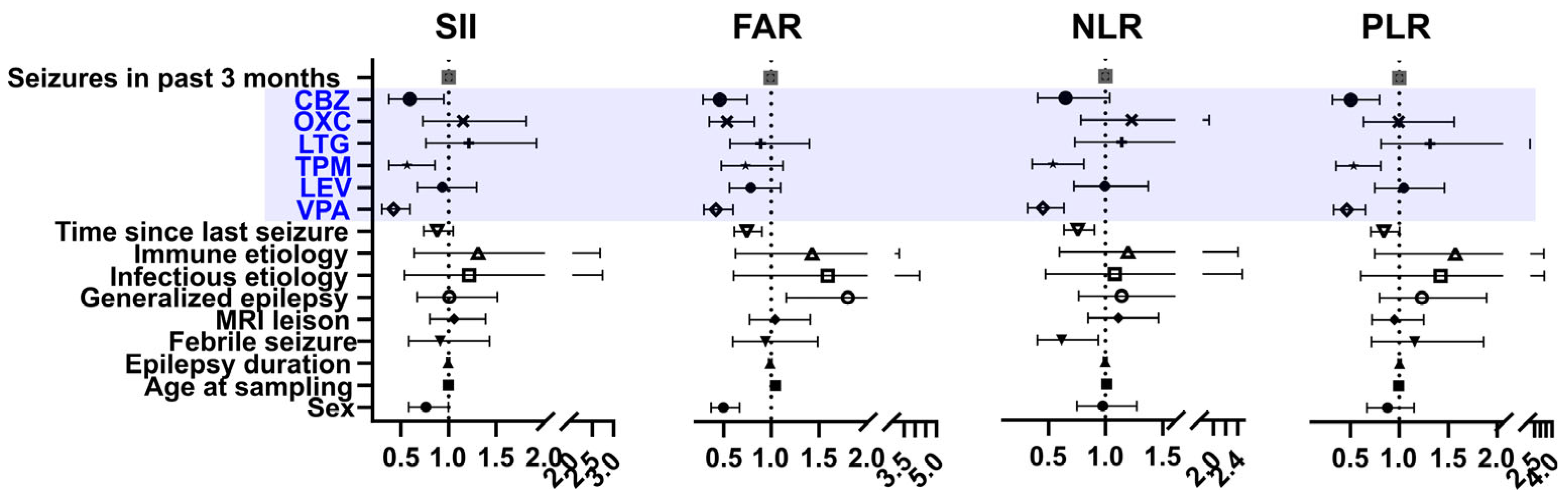
| Sex | - | - | - | −0.065 (0.013) |
| Epilepsy duration | −0.044 (0.147) | −0.039 (0.19) | −0.043 (0.118) | −0.063 (0.030) |
| Number of seizures in the past 3 months | −0.076 (0.007) | −0.08 (0.002) | −0.086 (0.001) | −0.043 (0.114) |
| Onset age | - | 0.009 (0.76) | - | - |
| Febrile seizures | −0.042 (0.125) | −0.039 (0.124) | −0.043 (0.085) | −0.012 (0.634) |
| MRI lesion (+) | 0.036 (0.201) | - | - | 0.078 (0.004) |
| Age at sampling | −0.001 (0.983) | - | 0.061 (0.021) | 0.329 (<0.001) |
| Time since last seizure | −0.17 (<0.001) | −0.172 (<0.001) | −0.215 (<0.001) | −0.117 (<0.001) |
| Generalized epilepsy | −0.021 (0.468) | - | −0.031 (0.241) | 0.158 (0.022) |
| Infectious etiology | 0.163 (<0.001) | 0.157 (<0.001) | 0.155 (<0.001) | 0.183 (<0.001) |
| Immune etiology | 0.076 (0.005) | 0.077 (0.002) | 0.051 (0.041) | 0.031 (0.235) |
| Structural etiology | - | 0.008 (0.767) | - | - |
| Genetic etiology | - | - | - | −0.083 (0.237) |
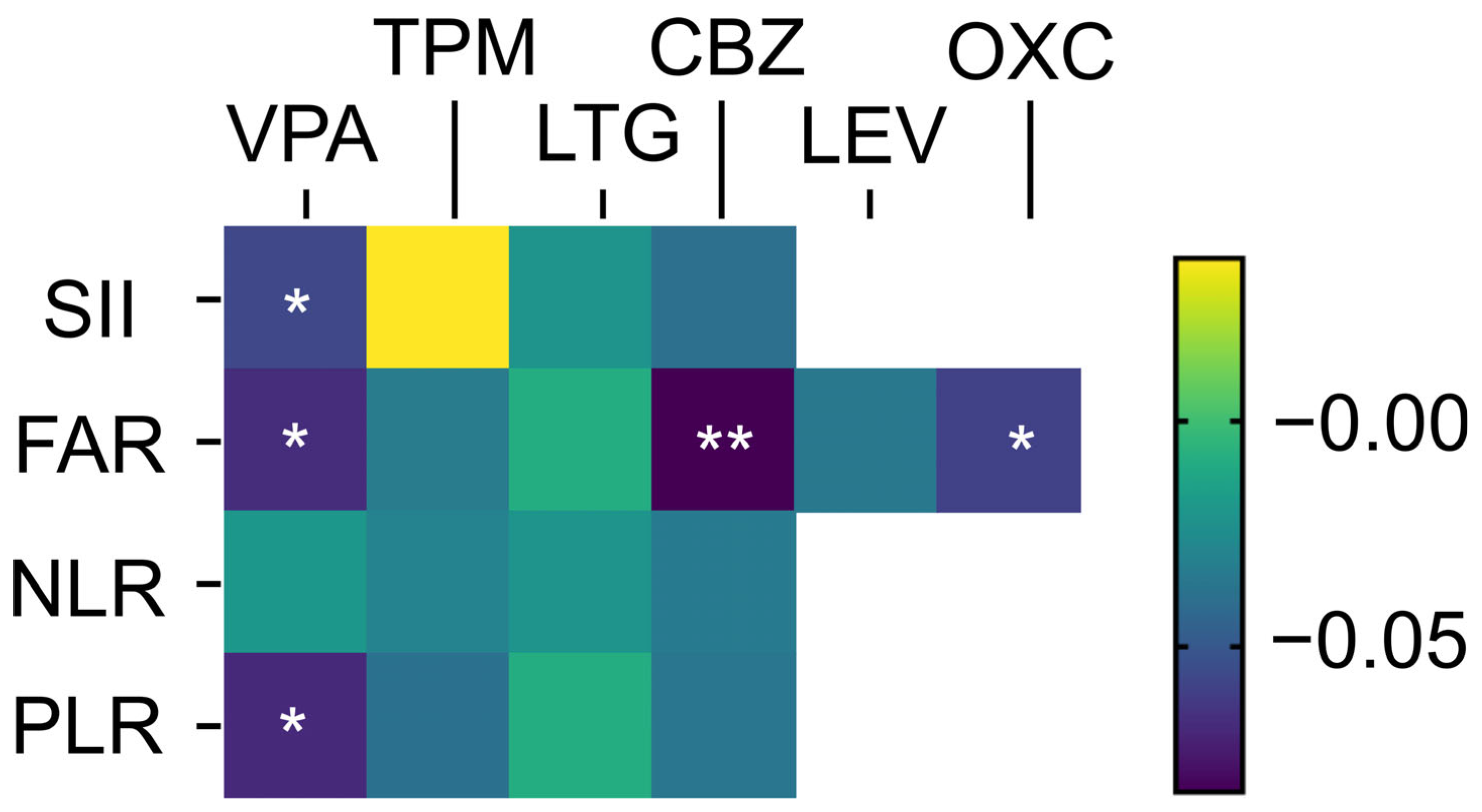
| Valproate | −0.057 (0.048) | −0.068 (0.016) | −0.02 (0.475) | −0.067 (0.025) |
| Topiramate | −0.036 (0.246) | −0.038 (0.191) | −0.03 (0.287) | −0.033 (0.279) |
| Lamotrigine | −0.021 (0.476) | −0.009 (0.749) | −0.021 (0.436) | −0.009 (0.745) |
| Carbamazepine | −0.039 (0.181) | −0.036 (0.185) | −0.034 (0.199) | −0.082 (0.005) |
| Oxcarbazepine | - | - | - | −0.059 (0.042) |
| Levetiracetam | - | - | - | −0.035 (0.258) |
| Polytheraphy | −0.016 (0.677) | −0.006 (0.860) | −0.021 (0.540) | −0.014 (0.762) |
| Antiseizure Medications | Mediators |
|---|---|
| Valproate | 1 HMGB-1, 2 MMP-9, 3 IL-6, 4 TGF-β1, 5 NF-κb, 6 NLRP3, 7 JAK/STAT, 8 HDAC |
| Carbamazepine | IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, 9 TNF-α |
| Topiramate | IL-1β, IL-6, NF-κb |
| Levetiracetam | TGF-β, 10 COX-2, NF-κb, TNF-α, IL-1β |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.-I.; Hwang, S.; Son, H.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Chu, K.; Jung, K.-Y.; Lee, S.K. Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155190
Park K-I, Hwang S, Son H, Yu H, Kim J, Chu K, Jung K-Y, Lee SK. Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155190
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kyung-Il, Sungeun Hwang, Hyoshin Son, Hyunah Yu, Jua Kim, Kon Chu, Ki-Young Jung, and Sang Kun Lee. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155190
APA StylePark, K.-I., Hwang, S., Son, H., Yu, H., Kim, J., Chu, K., Jung, K.-Y., & Lee, S. K. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Across Multiple Antiseizure Medications: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study of 1782 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5190. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155190






