Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Pathophysiological Insights, Subphenotypes, and Clinical Implications—A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Pathophysiology of ARDS
3.1. Alveolo-Capillary Barrier Dysfunction
3.2. Dysregulated Pulmonary Inflammation
3.3. Mechanical Stimuli in ARDS
4. Subphenotypes in ARDS
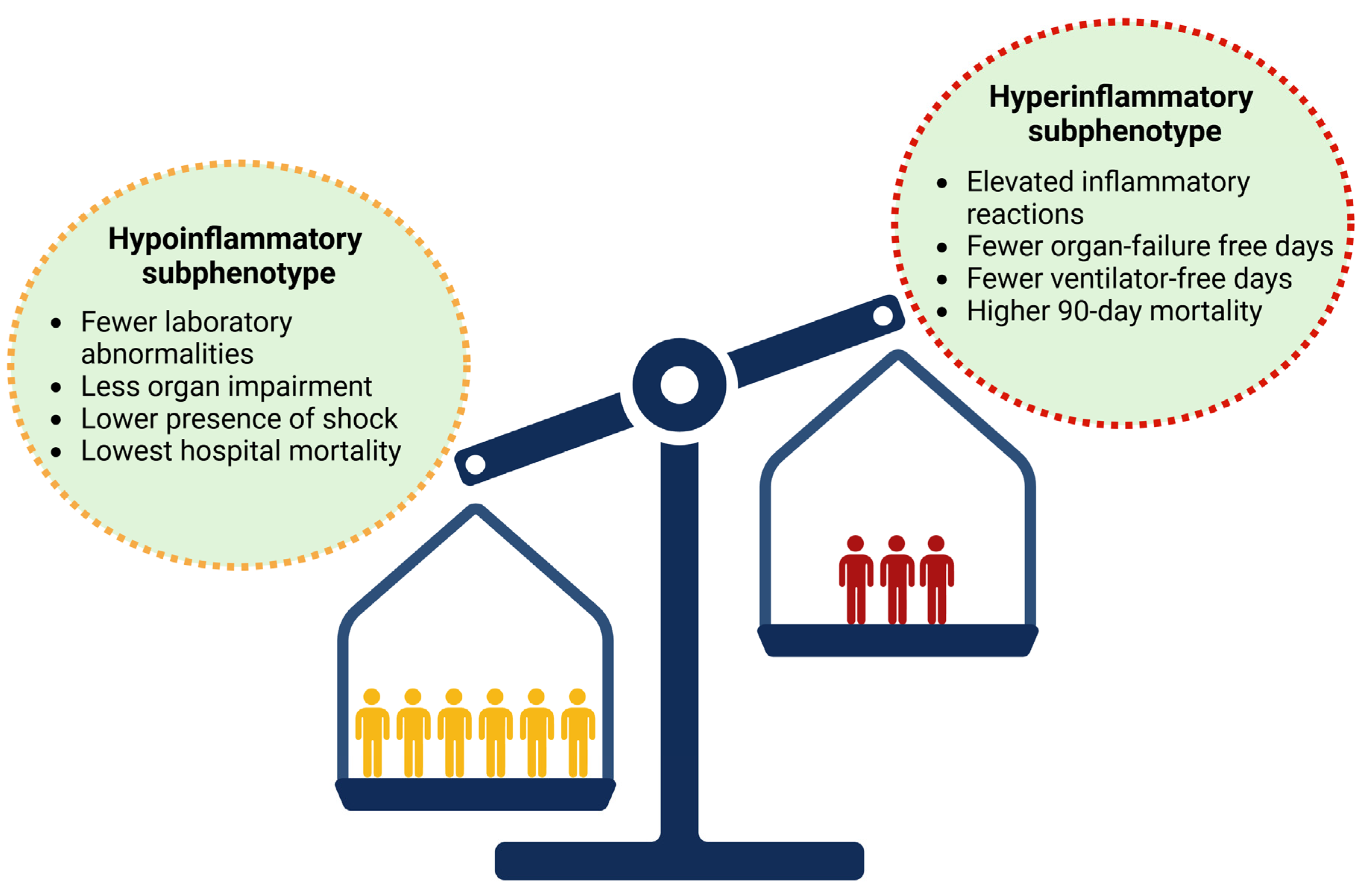
4.1. Biological Subphenotypes
4.2. Subphenotypes by Etiology and Clinical Parameters
4.3. Subphenotypes by Physiological Parameters
4.4. Subphenotypes by Radiographic Patterns
4.5. Cardiovascular Subphenotypes
5. Therapeutic Management Based on ARDS Subphenotypes
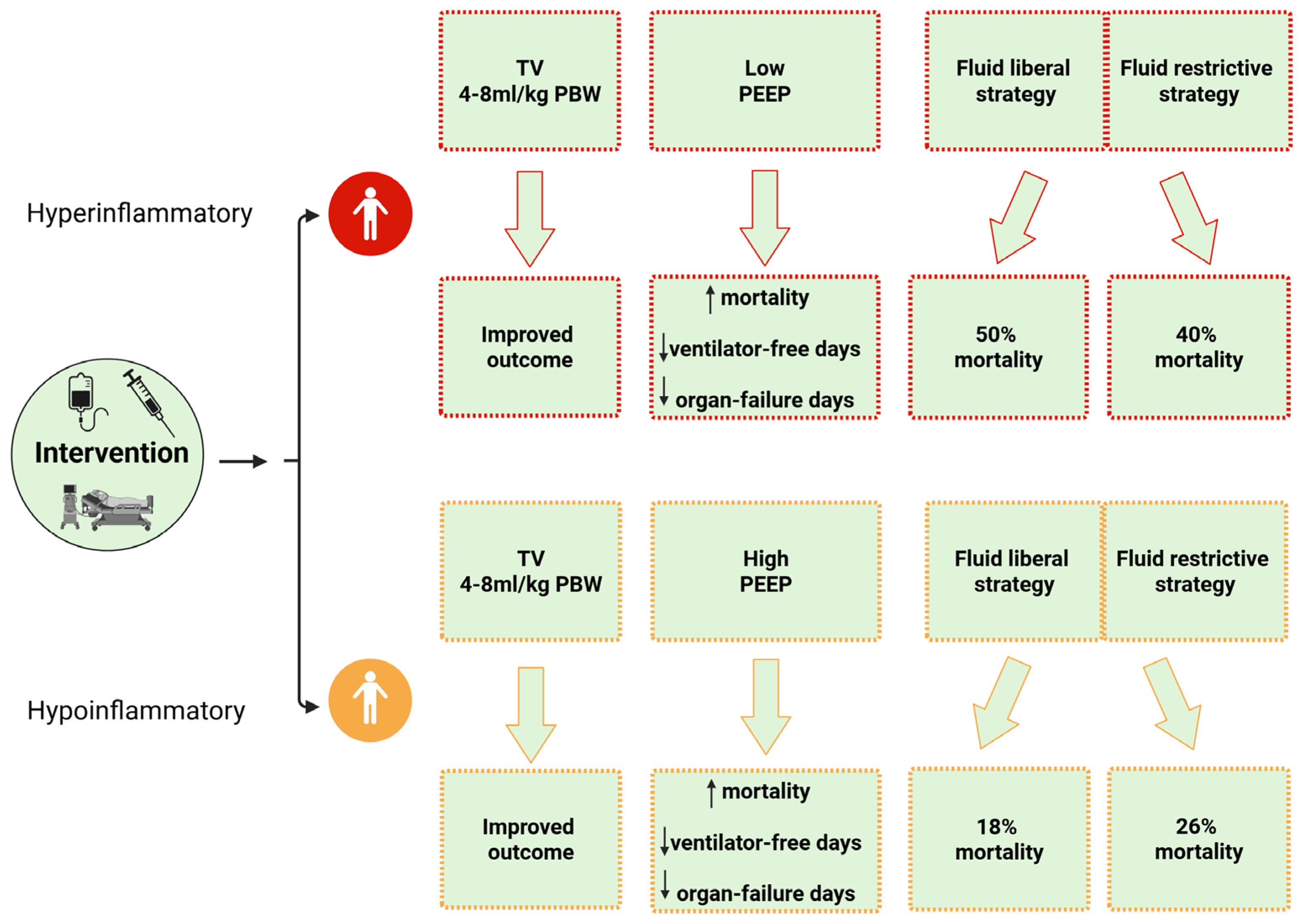
5.1. Ventilation Strategy
5.1.1. Tidal Volume
5.1.2. Positive End-Expiratory Pressure
5.2. Fluid Management
5.3. Statins
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Force, A.D.T.; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estenssoro, E.; Dubin, A.; Laffaire, E.; Canales, H.; Saenz, G.; Moseinco, M.; Pozo, M.; Gomez, A.; Baredes, N.; Jannello, G.; et al. Incidence, clinical course, and outcome in 217 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Bos, L.D. Pathophysiology of the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Insights from Clinical Studies. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 795–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Arabi, Y.; Arroliga, A.C.; Bernard, G.; Bersten, A.D.; Brochard, L.J.; Calfee, C.S.; Combes, A.; Daniel, B.M.; Ferguson, N.D.; et al. A New Global Definition of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Madotto, F.; Pham, T.; Nagata, I.; Uchida, M.; Tamiya, N.; Kurahashi, K.; Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; for the LUNG-SAFE Investigators and the ESICM Trials Group; et al. Epidemiology and patterns of tracheostomy practice in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in ICUs across 50 countries. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derwall, M.; Martin, L.; Rossaint, R. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: Pathophysiology, current clinical practice, and emerging therapies. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, B.; van Laak, V.; Eitel, J.; Suttorp, N. Innate immune recognition in infectious and noninfectious diseases of the lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 1294–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Cassatella, M.A.; Costantini, C.; Jaillon, S. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Neely, G.G.; Yaghubian-Malhami, R.; Perkmann, T.; van Loo, G.; Ermolaeva, M.; Veldhuizen, R.; Leung, Y.H.; Wang, H.; et al. Identification of oxidative stress and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling as a key pathway of acute lung injury. Cell 2008, 133, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Ware, L.B.; Zimmerman, G.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Brain-lung interactions and mechanical ventilation in patients with isolated brain injury. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesnel, C.; Nardelli, L.; Piednoir, P.; Lecon, V.; Marchal-Somme, J.; Lasocki, S.; Bouadma, L.; Philip, I.; Soler, P.; Crestani, B.; et al. Alveolar fibroblasts in acute lung injury: Biological behaviour and clinical relevance. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, R.P.; Bellingan, G.; Webb, S.; Puddicombe, A.; Goldsack, N.; McAnulty, R.J.; Laurent, G.J. Fibroproliferation occurs early in the acute respiratory distress syndrome and impacts on outcome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, K.E.; Swenson, E.R. Pathophysiology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19 Lung Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 749–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashbaugh, D.G.; Bigelow, D.B.; Petty, T.L.; Levine, B.E. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet 1967, 2, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Exploring the lung-gut direction of the gut-lung axis in patients with ARDS. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Brodie, D.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA 2018, 319, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.G.; Calfee, C.S. ARDS Subphenotypes: Understanding a Heterogeneous Syndrome. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee, C.S.; Delucchi, K.; Parsons, P.E.; Thompson, B.T.; Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A.; Network, N.A. Subphenotypes in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Latent class analysis of data from two randomised controlled trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersten, A.D.; Edibam, C.; Hunt, T.; Moran, J.; The Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials Group. Incidence and mortality of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in three Australian States. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Y.A.; Fan, E.; Ferguson, N.D. Precision Medicine and Heterogeneity of Treatment Effect in Therapies for ARDS. Chest 2021, 160, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, J.M.; Jabaudon, M.; Lefrant, J.Y.; Jaber, S.; Quenot, J.P.; Langeron, O.; Ferrandiere, M.; Grelon, F.; Seguin, P.; Ichai, C.; et al. Personalised mechanical ventilation tailored to lung morphology versus low positive end-expiratory pressure for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in France (the LIVE study): A multicentre, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.C.; Alipanah-Lechner, N.; Bos, L.D.; Dianti, J.; Diaz, J.V.; Finfer, S.; Fujii, T.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Goligher, E.C.; Gong, M.N.; et al. From ICU Syndromes to ICU Subphenotypes: Consensus Report and Recommendations for Developing Precision Medicine in the ICU. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effros, R.M.; Mason, G.R. An end to “ARDS”. Chest 1986, 89, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.F.; Matthay, M.A.; Luce, J.M.; Flick, M.R. An expanded definition of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, G.R.; Artigas, A.; Brigham, K.L.; Carlet, J.; Falke, K.; Hudson, L.; Lamy, M.; Legall, J.R.; Morris, A.; Spragg, R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, N.J.; Gattinoni, L.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet 2021, 398, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Arabi, Y.M.; Beitler, J.R.; Mercat, A.; Herridge, M.; Randolph, A.G.; Calfee, C.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Folkesson, H.G.; Clerici, C. Lung epithelial fluid transport and the resolution of pulmonary edema. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 569–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fein, A.; Grossman, R.F.; Jones, J.G.; Overland, E.; Pitts, L.; Murray, J.F.; Staub, N.C. The value of edema fluid protein measurement in patients with pulmonary edema. Am. J. Med. 1979, 67, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. Clinical practice. Acute pulmonary edema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2788–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.R.; Ma, A.C.; Tavener, S.A.; McDonald, B.; Goodarzi, Z.; Kelly, M.M.; Patel, K.D.; Chakrabarti, S.; McAvoy, E.; Sinclair, G.D.; et al. Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, N.C. Pulmonary edema: Physiologic approaches to management. Chest 1978, 74, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuebler, W.M.; Ying, X.; Singh, B.; Issekutz, A.C.; Bhattacharya, J. Pressure is proinflammatory in lung venular capillaries. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuckton, T.J.; Alonso, J.A.; Kallet, R.H.; Daniel, B.M.; Pittet, J.F.; Eisner, M.D.; Matthay, M.A. Pulmonary dead-space fraction as a risk factor for death in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Gut-derived immune cells and the gut-lung axis in ARDS. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener-Kronish, J.P.; Albertine, K.H.; Matthay, M.A. Differential responses of the endothelial and epithelial barriers of the lung in sheep to Escherichia coli endotoxin. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.R.; Kasper, J.; van der Aa, S.; Andeweg, A.C.; Zaaraoui-Boutahar, F.; Goeijenbier, M.; Richard, M.; Herold, S.; Becker, C.; Scott, D.P.; et al. Influenza virus damages the alveolar barrier by disrupting epithelial cell tight junctions. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, J.L.; Islam, M.N.; Parker, D.; Prince, A.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bhattacharya, J. Disruption of staphylococcal aggregation protects against lethal lung injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suki, B.; Hubmayr, R. Epithelial and endothelial damage induced by mechanical ventilation modes. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClendon, J.; Jansing, N.L.; Redente, E.F.; Gandjeva, A.; Ito, Y.; Colgan, S.P.; Ahmad, A.; Riches, D.W.H.; Chapman, H.A.; Mason, R.J.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha Signaling Promotes Repair of the Alveolar Epithelium after Acute Lung Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 1772–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspal, M.; Zemans, R.L. Mechanisms of ATII-to-ATI Cell Differentiation during Lung Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. The Role of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1264913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, M.; Liao, X.; Gao, S.; Hua, J.; Wu, X.; Guo, Q.; Xu, W.; Sun, J.; He, Y.; et al. Locally organised and activated Fth1(hi) neutrophils aggravate inflammation of acute lung injury in an IL-10-dependent manner. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Fessler, M.B. Regulatory mechanisms of neutrophil migration from the circulation to the airspace. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4095–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.R.; King, L.S.; D’Alessio, F.R. Diverse macrophage populations mediate acute lung inflammation and resolution. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L709–L725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parissis, J.T.; Adamopoulos, S.; Rigas, A.; Kostakis, G.; Karatzas, D.; Venetsanou, K.; Kremastinos, D.T. Comparison of circulating proinflammatory cytokines and soluble apoptosis mediators in patients with chronic heart failure with versus without symptoms of depression. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 1326–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Mao, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Sepsis and ARDS: The Dark Side of Histones. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 205054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wen, T.; Song, J.; Xie, D.; Wu, L.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, P.; Wen, Z. Extracellular histones are clinically relevant mediators in the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogner, K.; Wolff, T.; Pleschka, S.; Plog, S.; Gruber, A.D.; Kalinke, U.; Walmrath, H.D.; Bodner, J.; Gattenlohner, S.; Lewe-Schlosser, P.; et al. Macrophage-expressed IFN-beta contributes to apoptotic alveolar epithelial cell injury in severe influenza virus pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.A.; Wray, C.M.; McAuley, D.F.; Schwendener, R.; Matthay, M.A. Alveolar macrophages contribute to alveolar barrier dysfunction in ventilator-induced lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L1191–L1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, M.; Lomas-Neira, J.; Venet, F.; Chung, C.S.; Ayala, A. Pathogenesis of indirect (secondary) acute lung injury. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2011, 5, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, L.K.; Schuppert, A.; Uhlig, S. Inflammatory processes during acute respiratory distress syndrome: A complex system. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2018, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finigan, J.H. The coagulation system and pulmonary endothelial function in acute lung injury. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 77, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, C.; Millar, A.B.; Medford, A.R. Advances in understanding of the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respiration 2015, 89, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U.; Annane, D.; Chrousos, G.P.; Marik, P.E.; Sinclair, S.E. Activation and regulation of systemic inflammation in ARDS: Rationale for prolonged glucocorticoid therapy. Chest 2009, 136, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Giunta, F.; Suter, P.M.; Slutsky, A.S. Mechanical ventilation as a mediator of multisystem organ failure in acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA 2000, 284, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury in patients with acute brain injury: The triple-hit hypothesis. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Makris, D.; Fotakopoulos, G.; Tsilioni, I.; Befani, C.; Liakos, P.; Zygoulis, P.; Zakynthinos, E. High-Tidal-Volume Mechanical Ventilation and Lung Inflammation in Intensive Care Patients With Normal Lungs. Am. J. Crit. Care 2020, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitler, J.R.; Malhotra, A.; Thompson, B.T. Ventilator-induced Lung Injury. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Pesenti, A.; Avalli, L.; Rossi, F.; Bombino, M. Pressure-volume curve of total respiratory system in acute respiratory failure. Computed tomographic scan study. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 136, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, L.N.; Slutsky, A.S. Ventilator-induced injury: From barotrauma to biotrauma. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1998, 110, 482–488. [Google Scholar]
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network; Brower, R.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; Wheeler, A. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, L.T.; Marini, J.J. Optimized ventilation power to avoid VILI. J. Intensive Care 2023, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.L.; Scharffenberg, M.; Rocco, P.R.M. Understanding the mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury using animal models. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2023, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.B.; Meade, M.O.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brochard, L.; Costa, E.L.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Stewart, T.E.; Briel, M.; Talmor, D.; Mercat, A.; et al. Driving pressure and survival in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, D.L.; Chen, L.; Dres, M.; Brochard, L. Should we use driving pressure to set tidal volume? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2017, 23, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Pesenti, A. The concept of “baby lung”. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Amato, M.B.P.; Kavanagh, B.P.; Fujino, Y. Impact of spontaneous breathing during mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. ARDS associated acute brain injury: From the lung to the brain. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slutsky, A.S.; Tremblay, L.N. Multiple system organ failure. Is mechanical ventilation a contributing factor? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1721–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotz, F.B.; Slutsky, A.S.; van Vught, A.J.; Heijnen, C.J. Ventilator-induced lung injury and multiple system organ failure: A critical review of facts and hypotheses. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahakis, N.E.; Schroeder, M.A.; Limper, A.H.; Hubmayr, R.D. Stretch induces cytokine release by alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, L167–L173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Tonetti, T.; Cressoni, M.; Cadringher, P.; Herrmann, P.; Moerer, O.; Protti, A.; Gotti, M.; Chiurazzi, C.; Carlesso, E.; et al. Ventilator-related causes of lung injury: The mechanical power. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Del Sorbo, L.; Goligher, E.C.; Hodgson, C.L.; Munshi, L.; Walkey, A.J.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Amato, M.B.P.; Branson, R.; Brower, R.G.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Society of Intensive Care Medicine/Society of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline: Mechanical Ventilation in Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, H.C.; Calfee, C.S.; Thompson, B.T.; Angus, D.C.; Liu, V.X. Toward Smarter Lumping and Smarter Splitting: Rethinking Strategies for Sepsis and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Trial Design. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Sinha, P.; O’Kane, C.M.; Gordon, A.C.; Calfee, C.S.; McAuley, D.F. Subphenotypes in critical care: Translation into clinical practice. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee, C.S.; Delucchi, K.L.; Sinha, P.; Matthay, M.A.; Hackett, J.; Shankar-Hari, M.; McDowell, C.; Laffey, J.G.; O’Kane, C.M.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome subphenotypes and differential response to simvastatin: Secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famous, K.R.; Delucchi, K.; Ware, L.B.; Kangelaris, K.N.; Liu, K.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Calfee, C.S.; the ARDS Network. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Subphenotypes Respond Differently to Randomized Fluid Management Strategy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute ARDS Clinical Trials Network. Rosuvastatin for sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Delucchi, K.L.; Thompson, B.T.; McAuley, D.F.; Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S.; for the NHLBI ARDS Network. Latent class analysis of ARDS subphenotypes: A secondary analysis of the statins for acutely injured lungs from sepsis (SAILS) study. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Delucchi, K.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhuo, H.; Abbott, J.; Wang, C.; Wickersham, N.; McNeil, J.B.; Jauregui, A.; Ke, S.; et al. Latent class analysis-derived subphenotypes are generalisable to observational cohorts of acute respiratory distress syndrome: A prospective study. Thorax 2022, 77, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Neyton, L.; Sarma, A.; Wu, N.; Jones, C.; Zhuo, H.; Liu, K.D.; Sanchez Guerrero, E.; Ghale, R.; Love, C.; et al. Molecular Phenotypes of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in the ROSE Trial Have Differential Outcomes and Gene Expression Patterns That Differ at Baseline and Longitudinally over Time. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slim, M.A.; van Amstel, R.B.E.; Bos, L.D.J.; Cremer, O.L.; Consortium, M.; Wiersinga, W.J.; van der Poll, T.; van Vught, L.A. Inflammatory subphenotypes previously identified in ARDS are associated with mortality at intensive care unit discharge: A secondary analysis of a prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabaudon, M.; Blondonnet, R.; Pereira, B.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Lichtenstern, C.; Mauri, T.; Determann, R.M.; Drabek, T.; Hubmayr, R.D.; Gajic, O.; et al. Plasma sRAGE is independently associated with increased mortality in ARDS: A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, A.D.; Compton, C.C.; Poste, G. The National Biomarker Development Alliance accelerating the translation of biomarkers to the clinic. Biomark. Med. 2014, 8, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bime, C.; Camp, S.M.; Casanova, N.; Oita, R.C.; Ndukum, J.; Lynn, H.; Garcia, J.G.N. The acute respiratory distress syndrome biomarker pipeline: Crippling gaps between discovery and clinical utility. Transl. Res. 2020, 226, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, P.; Rietdijk, W.; Somhorst, P.; Endeman, H.; Gommers, D. A systematic review of biomarkers multivariately associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome development and mortality. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Laorden, M.I.; Lorente, J.A.; Flores, C.; Slutsky, A.S.; Villar, J. Biomarkers for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: How to make the diagnosis more precise. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Cui, H.; Li, P.; Fan, H.; Guo, L. Circulating Pulmonary-Originated Epithelial Biomarkers for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, C. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1903–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Moses, H.L. Biomarker Tests for Molecularly Targeted Therapies--The Key to Unlocking Precision Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Calfee, C.S. Phenotypes in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Moving towards precision medicine. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, R.; Madotto, F.; Laffey, J.G.; van Haren, F.M.P. Compliance Phenotypes in Early Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome before the COVID-19 Pandemic. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.M.; Chen, C.W.; Hsiue, T.R.; Lin, W.C. Timing of acute respiratory distress syndrome onset is related to patient outcome. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2009, 108, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Tejera, P.; Frank, A.J.; Wei, Y.; Su, L.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, F.; Bajwa, E.K.; et al. Late-onset moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome is associated with shorter survival and higher mortality: A two-stage association study. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Chiumello, D.; Caironi, P.; Busana, M.; Romitti, F.; Brazzi, L.; Camporota, L. COVID-19 pneumonia: Different respiratory treatments for different phenotypes? Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; D’Onofrio, D.; Chiumello, D.; Paolo, S.; Chiara, G.; Capelozzi, V.L.; Barbas, C.S.; Chiaranda, M.; Gattinoni, L. Pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute respiratory distress syndrome are different. Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 2003, 42, 48s–56s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee, C.S.; Janz, D.R.; Bernard, G.R.; May, A.K.; Kangelaris, K.N.; Matthay, M.A.; Ware, L.B. Distinct molecular phenotypes of direct vs indirect ARDS in single-center and multicenter studies. Chest 2015, 147, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Shaver, C.M.; Zhao, Z.; Koyama, T.; Calfee, C.S.; Bastarache, J.A.; Ware, L.B. Clinical Predictors of Hospital Mortality Differ Between Direct and Indirect ARDS. Chest 2017, 151, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, O.; Rana, R.; Winters, J.L.; Yilmaz, M.; Mendez, J.L.; Rickman, O.B.; O’Byrne, M.M.; Evenson, L.K.; Malinchoc, M.; DeGoey, S.R.; et al. Transfusion-related acute lung injury in the critically ill: Prospective nested case-control study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.R.H.; Cohen, M.J.; Holcomb, J.B.; Pritts, T.A.; Gomaa, D.; Fox, E.E.; Branson, R.D.; Callcut, R.A.; Cotton, B.A.; Schreiber, M.A.; et al. Risk Factors for the Development of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Following Hemorrhage. Shock 2018, 50, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawley, J.A.; Tignanelli, C.J.; Werner, N.L.; Kasotakis, G.; Mandell, S.P.; Glass, N.E.; Dries, D.J.; Costantini, T.W.; Napolitano, L.M. American Association for the Surgery of Trauma/American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma clinical protocol for management of acute respiratory distress syndrome and severe hypoxemia. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 95, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfee, C.S.; Eisner, M.D.; Ware, L.B.; Thompson, B.T.; Parsons, P.E.; Wheeler, A.P.; Korpak, A.; Matthay, M.A.; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Trauma-associated lung injury differs clinically and biologically from acute lung injury due to other clinical disorders. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, C.C.; Gong, M.N.; Zhai, R.; Chen, F.; Bajwa, E.K.; Clardy, P.F.; Gallagher, D.C.; Thompson, B.T.; Christiani, D.C. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of sepsis-related vs non-sepsis-related ARDS. Chest 2010, 138, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevransky, J.E.; Martin, G.S.; Shanholtz, C.; Mendez-Tellez, P.A.; Pronovost, P.; Brower, R.; Needham, D.M. Mortality in sepsis versus non-sepsis induced acute lung injury. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, R.G.; Lanken, P.N.; MacIntyre, N.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; National Heart, L.; Blood Institute, A.C.T.N. Higher versus lower positive end-expiratory pressures in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Clinical Trials Network. Comparison of two fluid-management strategies in acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2564–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, X.; Ma, X.; Han, C.; Guo, N.; Peng, Y.; Liu, H.; Ju, Y.; Luo, X.; et al. Identification of distinct clinical phenotypes of acute respiratory distress syndrome with differential responses to treatment. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.D.; Glidden, D.V.; Eisner, M.D.; Parsons, P.E.; Ware, L.B.; Wheeler, A.; Korpak, A.; Thompson, B.T.; Chertow, G.M.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. Predictive and pathogenetic value of plasma biomarkers for acute kidney injury in patients with acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 2755–2761. [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas, B.A.; Rezoagli, E.; Pham, T.; Madotto, F.; Guiard, E.; Fanelli, V.; Bellani, G.; Griffin, M.D.; Ranieri, M.; Laffey, J.G.; et al. Impact of Early Acute Kidney Injury on Management and Outcome in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Secondary Analysis of a Multicenter Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, C.R.; Gupta, S.; Miano, T.A.; Roche, M.; Hsu, J.; Yang, W.; Holena, D.N.; Reilly, J.P.; Schrauben, S.J.; Leaf, D.E.; et al. Identification of Distinct Clinical Subphenotypes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19. Chest 2021, 160, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, M.A.; Fabian, T.C.; Davis, K.A.; Gavin, T.J. Early and late acute respiratory distress syndrome: Two distinct clinical entities. J. Trauma 1999, 46, 361–366, discussion 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valda Toro, P.L.; Willmore, A.; Wu, N.E.; Delucchi, K.L.; Jauregui, A.; Sinha, P.; Liu, K.D.; Hendrickson, C.M.; Sarma, A.; Neyton, L.P.A.; et al. Rapidly improving ARDS differs clinically and biologically from persistent ARDS. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazian, L.; Forel, J.M.; Gacouin, A.; Penot-Ragon, C.; Perrin, G.; Loundou, A.; Jaber, S.; Arnal, J.M.; Perez, D.; Seghboyan, J.M.; et al. Neuromuscular blockers in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, C.; Reignier, J.; Richard, J.C.; Beuret, P.; Gacouin, A.; Boulain, T.; Mercier, E.; Badet, M.; Mercat, A.; Baudin, O.; et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute PETAL Clinical Trials Network. Early Neuromuscular Blockade in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolo, G.; Collino, F.; Vasques, F.; Rapetti, F.; Tonetti, T.; Romitti, F.; Cressoni, M.; Chiumello, D.; Moerer, O.; Herrmann, P.; et al. Reclassifying Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel Garcia, P.D.; Caccioppola, A.; Coppola, S.; Pozzi, T.; Ciabattoni, A.; Cenci, S.; Chiumello, D. Latent class analysis to predict intensive care outcomes in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A proposal of two pulmonary phenotypes. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H.; Pettenuzzo, T.; Aoyama, K.; Pinto, R.; Englesakis, M.; Fan, E. Association of Driving Pressure With Mortality Among Ventilated Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellani, G.; Grassi, A.; Sosio, S.; Gatti, S.; Kavanagh, B.P.; Pesenti, A.; Foti, G. Driving Pressure Is Associated with Outcome during Assisted Ventilation in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitker, L.; Talmor, D.; Richard, J.C. Imaging the acute respiratory distress syndrome: Past, present and future. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, L.R.; Fumagalli, R.; Tagliabue, P.; Tagliabue, M.; Ferrario, M.; Gattinoni, L.; Pesenti, A. Adult respiratory distress syndrome due to pulmonary and extrapulmonary causes: CT, clinical, and functional correlations. Radiology 1999, 213, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sheng, S.; Luo, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z. Acute respiratory distress syndrome heterogeneity and the septic ARDS subgroup. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1277161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, J.M.; Grasso, S.; Chanques, G.; Aufort, S.; Futier, E.; Sebbane, M.; Jung, B.; Gallix, B.; Bazin, J.E.; Rouby, J.J.; et al. Lung morphology predicts response to recruitment maneuver in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puybasset, L.; Gusman, P.; Muller, J.C.; Cluzel, P.; Coriat, P.; Rouby, J.J. Regional distribution of gas and tissue in acute respiratory distress syndrome. III. Consequences for the effects of positive end-expiratory pressure. CT Scan ARDS Study Group. Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2000, 26, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.R.; Wells, A.U.; Suntharalingam, G.; Rubens, M.B.; Evans, T.W.; Hansell, D.M. Acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by pulmonary and extrapulmonary injury: A comparative CT study. Radiology 2001, 218, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikado, K.; Suga, M.; Muranaka, H.; Gushima, Y.; Miyakawa, H.; Tsubamoto, M.; Johkoh, T.; Hirata, N.; Yoshinaga, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; et al. Prediction of prognosis for acute respiratory distress syndrome with thin-section CT: Validation in 44 cases. Radiology 2006, 238, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, A.; Scemama, U.; Bourenne, J.; Daviet, F.; Coiffard, B.; Persico, N.; Adda, M.; Guervilly, C.; Hraiech, S.; Chaumoitre, K.; et al. Chest CT scan and alveolar procollagen III to predict lung fibroproliferation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieillard-Baron, A.; Matthay, M.; Teboul, J.L.; Bein, T.; Schultz, M.; Magder, S.; Marini, J.J. Experts’ opinion on management of hemodynamics in ARDS patients: Focus on the effects of mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketcham, S.W.; Sedhai, Y.R.; Miller, H.C.; Bolig, T.C.; Ludwig, A.; Co, I.; Claar, D.; McSparron, J.I.; Prescott, H.C.; Sjoding, M.W. Causes and characteristics of death in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geri, G.; Vignon, P.; Aubry, A.; Fedou, A.L.; Charron, C.; Silva, S.; Repesse, X.; Vieillard-Baron, A. Cardiovascular clusters in septic shock combining clinical and echocardiographic parameters: A post hoc analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotalia, M.; Ali, M.; Alderman, J.E.; Bansal, S.; Patel, J.M.; Bangash, M.N.; Parekh, D. Cardiovascular Subphenotypes in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 51, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotalia, M.; Ali, M.; Alderman, J.E.; Patel, J.M.; Parekh, D.; Bangash, M.N. Cardiovascular subphenotypes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonitis whose lungs are mechanically ventilated: A single-centre retrospective observational study. Anaesthesia 2022, 77, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuba, M.T.; Hockstein, M.A.; Rey, D.A.; Duggal, A.; Deliberato, R.O. ARDS Subphenotypes Exhibit Different Right Ventricular-Pulmonary Arterial Coupling Profiles. Chest Crit. Care 2025, 3, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Dugar, S.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Schleicher, M.; Collier, P.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Duggal, A. The impact of right ventricular injury on the mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jin, F.; Pan, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, H. The effects of low tidal ventilation on lung strain correlate with respiratory system compliance. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deans, K.J.; Minneci, P.C.; Suffredini, A.F.; Danner, R.L.; Hoffman, W.D.; Ciu, X.; Klein, H.G.; Schechter, A.N.; Banks, S.M.; Eichacker, P.Q.; et al. Randomization in clinical trials of titrated therapies: Unintended consequences of using fixed treatment protocols. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Ball, L.; Barbas, C.S.V.; Bellomo, R.; Burns, K.E.A.; Einav, S.; Gattinoni, L.; Laffey, J.G.; Marini, J.J.; Myatra, S.N.; et al. Personalized mechanical ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, M.; Wenstedt, E.F.E.; Tsonas, A.M.; Buiteman-Kruizinga, L.A.; van Meenen, D.M.P.; Korsten, H.H.M.; Horn, J.; Paulus, F.; Bindels, A.; Schultz, M.J.; et al. Effectiveness, safety and efficacy of INTELLiVENT-adaptive support ventilation, a closed-loop ventilation mode for use in ICU patients—A systematic review. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahetya, S.K.; Mancebo, J.; Brower, R.G. Fifty Years of Research in ARDS. Vt Selection in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briel, M.; Meade, M.; Mercat, A.; Brower, R.G.; Talmor, D.; Walter, S.D.; Slutsky, A.S.; Pullenayegum, E.; Zhou, Q.; Cook, D.; et al. Higher vs lower positive end-expiratory pressure in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2010, 303, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Caironi, P.; Cressoni, M.; Chiumello, D.; Ranieri, V.M.; Quintel, M.; Russo, S.; Patroniti, N.; Cornejo, R.; Bugedo, G. Lung recruitment in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Marini, J.J. In search of the Holy Grail: Identifying the best PEEP in ventilated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, A.B.; Suzumura, É.A.; Laranjeira, L.N.; Paisani, D.M.; Damiani, L.P.; Guimarães, H.P.; Romano, E.R.; Regenga, M.M.; Taniguchi, L.N.T.; Teixeira, C.; et al. Effect of Lung Recruitment and Titrated Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) vs Low PEEP on Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuba, M.T.; Bulgarelli, L.; Duggal, A.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Zampieri, F.G.; Rey, D.A.; Lucena, W.D.R.; Maia, I.S.; Paisani, D.M.; Laranjeira, L.N.; et al. Differential Effect of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure Strategies in Patients With ARDS: A Bayesian Analysis of Clinical Subphenotypes. Chest 2024, 166, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, N.; Sahetya, S.; Munshi, L.; Summers, C.; Abrams, D.; Beitler, J.; Bellani, G.; Brower, R.G.; Burry, L.; Chen, J.T.; et al. An Update on Management of Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, G.; Calfee, C.S.; Camporota, L.; Poole, D.; Amato, M.B.P.; Antonelli, M.; Arabi, Y.M.; Baroncelli, F.; Beitler, J.R.; Bellani, G.; et al. ESICM guidelines on acute respiratory distress syndrome: Definition, phenotyping and respiratory support strategies. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 727–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Fluid management strategies in critically ill patients with ARDS: A narrative review. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Steingrub, J.S.; Douglas, I.S.; Matthay, M.A.; Wright, P.; Peterson, M.W.; Rock, P.; Hyzy, R.C.; et al. Acute kidney injury in patients with acute lung injury: Impact of fluid accumulation on classification of acute kidney injury and associated outcomes. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2665–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, M.E.; Christie, J.D.; Lanken, P.N.; Biester, R.C.; Thompson, B.T.; Bellamy, S.L.; Localio, A.R.; Demissie, E.; Hopkins, R.O.; Angus, D.C. The adult respiratory distress syndrome cognitive outcomes study: Long-term neuropsychological function in survivors of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manitsopoulos, N.; Orfanos, S.E.; Kotanidou, A.; Nikitopoulou, I.; Siempos, I.; Magkou, C.; Dimopoulou, I.; Zakynthinos, S.G.; Armaganidis, A.; Maniatis, N.A. Inhibition of HMGCoA reductase by simvastatin protects mice from injurious mechanical ventilation. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.A.; Thomas, C.B.; O’Neal, H.R. Do aspirin and statins prevent severe sepsis? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, D.F.; Laffey, J.G.; O’Kane, C.M.; Perkins, G.D.; Mullan, B.; Trinder, T.J.; Johnston, P.; Hopkins, P.A.; Johnston, A.J.; McDowell, C.; et al. Simvastatin in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagendran, M.; McAuley, D.F.; Kruger, P.S.; Papazian, L.; Truwit, J.D.; Laffey, J.G.; Thompson, B.T.; Clarke, M.; Gordon, A.C. Statin therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome: An individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, P.; Bailey, M.; Bellomo, R.; Cooper, D.J.; Harward, M.; Higgins, A.; Howe, B.; Jones, D.; Joyce, C.; Kostner, K.; et al. A multicenter randomized trial of atorvastatin therapy in intensive care patients with severe sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyamsundar, M.; McKeown, S.T.; O’Kane, C.M.; Craig, T.R.; Brown, V.; Thickett, D.R.; Matthay, M.A.; Taggart, C.C.; Backman, J.T.; Elborn, J.S.; et al. Simvastatin decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation in healthy volunteers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambon, A.; Guervilly, C.; Delteil, C.; Potere, N.; Bachelier, R.; Tellier, E.; Abdili, E.; Leprince, M.; Giani, M.; Polidoro, I.; et al. Caspase-1 activation, IL-1/IL-6 signature and IFNgamma-induced chemokines in lungs of COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1493306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.B.; Strieter, R.M.; Martin, D.P.; Steinberg, K.P.; Milberg, J.A.; Maunder, R.J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Walz, A.; Hudson, L.D.; Martin, T.R. Inflammatory cytokines in patients with persistence of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinay, T.; Kim, Y.S.; Howrylak, J.; Hunninghake, G.M.; An, C.H.; Fredenburgh, L.; Massaro, A.F.; Rogers, A.; Gazourian, L.; Nakahira, K.; et al. Inflammasome-regulated cytokines are critical mediators of acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.Y.; Goodman, R.B.; Steinberg, K.P.; Ruzinski, J.T.; Radella, F., 2nd; Park, D.R.; Pugin, J.; Skerrett, S.J.; Hudson, L.D.; Martin, T.R. Cytokine balance in the lungs of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet-Martin, S.; Jourdain, B.; Gibert, C.; Elbim, C.; Chastre, J.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A. Interactions between neutrophils and cytokines in blood and alveolar spaces during ARDS. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, L.; Vozza, E.G.; Bryant, C.E.; Summers, C. Role of inflammasomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Thorax 2025, 80, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.J.M.; Tan, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Lee, J.H.; Leong, J.Y.; Yeo, J.G.; Lee, Y.H. Large scale cytokine profiling uncovers elevated IL12-p70 and IL-17A in severe pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, S.; Beldi-Ferchiou, A.; Bendib, I.; Surenaud, M.; Fourati, S.; Frapard, T.; Rivoal, S.; Razazi, K.; Carteaux, G.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; et al. Uncontrolled Innate and Impaired Adaptive Immune Responses in Patients with COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie-Majd, A.; Maca, T.; Bucek, R.A.; Valent, P.; Muller, M.R.; Husslein, P.; Kashanipour, A.; Minar, E.; Baghestanian, M. Simvastatin reduces expression of cytokines interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in circulating monocytes from hypercholesterolemic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hot, A.; Lavocat, F.; Lenief, V.; Miossec, P. Simvastatin inhibits the pro-inflammatory and pro-thrombotic effects of IL-17 and TNF-alpha on endothelial cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutzouri, E.; Liberopoulos, E.N.; Tellis, C.C.; Milionis, H.J.; Tselepis, A.D.; Elisaf, M.S. Comparison of the effect of simvastatin versus simvastatin/ezetimibe versus rosuvastatin on markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.M.; Spiel, A.O.; Jilma, B.; Wolzt, M.; Muller, M. In-vivo effects of simvastatin and rosuvastatin on global gene expression in peripheral blood leucocytes in a human inflammation model. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2008, 18, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.Y.; Xiao, Y.W.; Jiang, G.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Effect of atorvastatin versus rosuvastatin on levels of serum lipids, inflammatory markers and adiponectin in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleemann, R.; Princen, H.M.; Emeis, J.J.; Jukema, J.W.; Fontijn, R.D.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Kooistra, T.; Havekes, L.M. Rosuvastatin reduces atherosclerosis development beyond and independent of its plasma cholesterol-lowering effect in APOE*3-Leiden transgenic mice: Evidence for antiinflammatory effects of rosuvastatin. Circulation 2003, 108, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, T.J.; Hibbert, K.A. Recent advances in the understanding and management of ARDS. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglini, D.; Fazzini, B.; Silva, P.L.; Cruz, F.F.; Ball, L.; Robba, C.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Pelosi, P. Challenges in ARDS Definition, Management, and Identification of Effective Personalized Therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liao, X. Sepsis subphenotypes: Bridging the gaps in sepsis treatment strategies. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1546474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, N.; Chang, S.Y. Pharmacologic Treatments for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Clin. 2021, 37, 877–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Delucchi, K.L.; McAuley, D.F.; O’Kane, C.M.; Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S. Development and validation of parsimonious algorithms to classify acute respiratory distress syndrome phenotypes: A secondary analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.P.; Calfee, C.S.; Christie, J.D. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Phenotypes. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffey, J.G.; Matthay, M.A. Fifty Years of Research in ARDS. Cell-based Therapy for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Biology and Potential Therapeutic Value. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, G.; Linetsky, E.; Correa, D.; Messinger Cayetano, S.; Alvarez, R.A.; Kouroupis, D.; Alvarez Gil, A.; Poggioli, R.; Ruiz, P.; Marttos, A.C.; et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: A double-blind, phase 1/2a, randomized controlled trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Hou, F.; Huang, X.; Li, B.; Qian, Z.R.; Xie, L. Mesenchymal stem cells: Current clinical progress in ARDS and COVID-19. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curley, G.F.; O’Kane, C.M.; McAuley, D.F.; Matthay, M.A.; Laffey, J.G. Cell-based Therapies for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Where Are We Now? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xiao, K.; Xie, L. Advances in the Regulation of Macrophage Polarization by Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Implications for ALI/ARDS Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 928134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, A.M.; Bailey, A.J.M.; Monaghan, M.; Shorr, R.; Lalu, M.M.; Fergusson, D.A.; Allan, D.S. Updated Living Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Treat COVID-19: A Framework for Accelerated Synthesis of Trial Evidence for Rapid Approval-FASTER Approval. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2022, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglini, D.; Iavarone, I.G.; Al-Husinat, L.; Ball, L.; Robba, C.; Silva, P.L.; Cruz, F.F.; Rocco, P.R. Anti-inflammatory therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2023, 32, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, J.V.; John, P.; Graham, P.L.; Moran, J.L.; George, I.A.; Bersten, A. Corticosteroids in the prevention and treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in adults: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 336, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.R.; Pritchard, M.W.; Thomas, C.M.; Smith, A.F. Pharmacological agents for adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, CD004477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U.; Bridges, L.; Shih, M.C.; Marik, P.E.; Siemieniuk, R.A.C.; Kocak, M. Prolonged glucocorticoid treatment is associated with improved ARDS outcomes: Analysis of individual patients’ data from four randomized trials and trial-level meta-analysis of the updated literature. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, R.C.; Horby, P.; Lim, W.S.; Emberson, J.R.; Mafham, M.; Bell, J.L.; Linsell, L.; Staplin, N.; Brightling, C.; Ustianowski, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazini, B.M.; Maia, I.S.; Cavalcanti, A.B.; Berwanger, O.; Rosa, R.G.; Veiga, V.C.; Avezum, A.; Lopes, R.D.; Bueno, F.R.; Silva, M.; et al. Effect of Dexamethasone on Days Alive and Ventilator-Free in Patients With Moderate or Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19: The CoDEX Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, D.; Sasaki, K.; Karkar, A.; Sharif, S.; Lewis, K.; Mammen, M.J.; Alexander, P.; Ye, Z.; Lozano, L.E.C.; Munch, M.W.; et al. Corticosteroids in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 ARDS: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Pu, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Xu, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, G.; Ding, Q. Physiological and clinical variables identify ARDS classes and therapeutic heterogeneity to glucocorticoids: A retrospective study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadanni, G.P.; Calixto, J.B. Recent progress and prospects for anti-cytokine therapy in preclinical and clinical acute lung injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023, 71–72, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaviya, R.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Anti-TNFalpha therapy in inflammatory lung diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 180, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, R.; Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Yan, Q.; Lu, L. Oral IRAK4 inhibitor BAY-1834845 prevents acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Pathophysiological Insights, Subphenotypes, and Clinical Implications—A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155184
Ziaka M, Exadaktylos A. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Pathophysiological Insights, Subphenotypes, and Clinical Implications—A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155184
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiaka, Mairi, and Aristomenis Exadaktylos. 2025. "Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Pathophysiological Insights, Subphenotypes, and Clinical Implications—A Comprehensive Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155184
APA StyleZiaka, M., & Exadaktylos, A. (2025). Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Pathophysiological Insights, Subphenotypes, and Clinical Implications—A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155184





