The Role of Probiotics in Preventing Gestational Diabetes: An Umbrella Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation of the Research Question
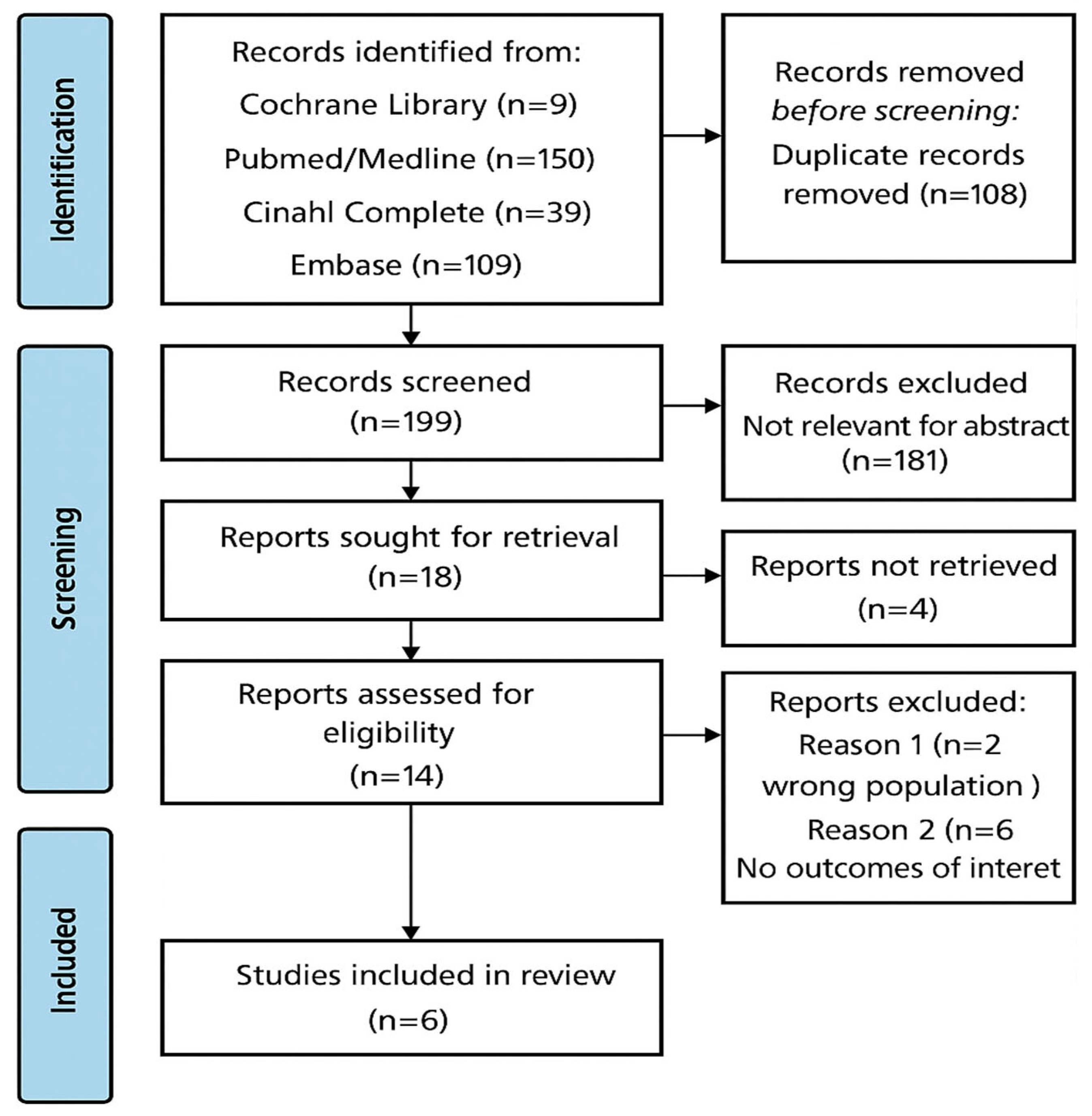
2.2. Transparency and Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Evaluation of Risk of Bias and Methodological Quality of Studies
2.5. Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Studies Included
3.2. Overview of Probiotic Effects on GD and Maternal Outcomes
3.3. Quality of Included Studies
3.4. Efficacy of Probiotics in Preventing GD
3.5. Improvement of Metabolic Parameters
3.6. Effects on Maternal and Neonatal Complications
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Perspective for Clinical Practice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheung, N.W.; Jiang, S.; Athayde, N. Impact of the IADPSG criteria for gestational diabetes, and of obesity, on pregnancy outcomes. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 58, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Gestational diabetes mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, e49–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, E.C.; Denison, F.C.; Norman, J.E.; Reynolds, R.M. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Mechanisms, treatment, and complications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, A.M.; Dunne, F. Optimal management of diabetes during pregnancy. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 8, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchior, H.; Kurch-Bek, D.; Mund, M. The prevalence of gestational diabetes: A population-based analysis of a nationwide screening program. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, H.; Abusanana, S.; Mussa, B.M.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Stojanovska, L.; Mohamad, M.N.; Saleh, S.T.; Ali, H.I.; Cheikh Ismail, L. The role of lifestyle interventions in the prevention and treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus. Medicina 2023, 59, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A. Screening for gestational diabetes: An overview. J. Obstet. Med. 2017, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eades, C.E.; Cameron, D.M.; Evans, J.M. Prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus in Europe: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 129, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, J.; McPhee, A.J.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P.; Shepherd, E. Screening for gestational diabetes mellitus based on different risk profiles and settings for improving maternal and infant health. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 8, CD007222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, V.; Muñoz, S.E.; Gil, C.; Román, M.D. Maternal dietary components in the development of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of observational studies to timely promotion of health. Nutr. J. 2023, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, E.; Crane, M.; Tieu, J.; Han, S.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Diet and exercise interventions for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, CD010443; Erratum in Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD010443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, J.R.; Ghildayal, N.; Hivert, M.F.; Redman, L.M. Lifestyle interventions in pregnancy targeting GD prevention: Looking ahead to precision medicine. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.J.; Qin, F.Y.; Hu, C.L.; Zhu, M.; Tian, C.Q.; Li, L. Is gestational diabetes mellitus an independent risk factor for macrosomia: A meta-analysis? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 291, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, O.; Yogev, Y.; Most, O.; Xenakis, E.M. Gestational diabetes: The consequences of not treating. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 192, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boney, C.M.; Verma, A.; Tucker, R.; Vohr, B.R. Metabolic syndrome in childhood: Association with birthweight, maternal obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics 2005, 115, e290–e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muche, A.A.; Olayemi, O.O.; Gete, Y.K. Prevalence and determinants of gestational diabetes mellitus in Africa based on the updated international diagnostic criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Public Health 2019, 77, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Espinola, F.J.; Berglund, S.K.; García-Valdés, L.; Segura, M.T.; Jerez, A.; Campos, D.; Moreno-Torres, R.; Rueda, R.; Catena, A.; Pérez-García, M.; et al. Maternal obesity, overweight, and gestational diabetes affect the offspring neurodevelopment at 6 and 18 months of age: A follow-up from the PREOBE cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulos, A.S.; Blair, R.; Peters, A.L. Management of Preexisting Diabetes in Pregnancy: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 1811–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, P.; Cullinan, J.; O’Neill, C.; AD Collaborators. Modeling the independent effects of gestational diabetes mellitus on maternity care and costs. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Zolezzi, I.; Samuel, T.M.; Spieldenner, J. Maternal nutrition: Opportunities in the prevention of gestational diabetes. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.; Jelsma, J.G.; Galjaard, S.; Devlieger, R.; van Assche, A.; Jans, G.; Corcoy, R.; Adelantado, J.M.; Dunne, F.; Desoye, G.; et al. Results from a European multicenter randomized trial of physical activity and/or healthy eating to reduce the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: The DALI lifestyle pilot. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.A.; Moreira, T. Physical therapy and gestational diabetes: An evaluation of exercise protocols. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2018, 22, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiburcio, J.B.; Filho, J.P.; Torres, R.E.H. The role of exercise in gestational diabetes management. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2014, 27, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangelosi, G.; Acito, M.; Grappasonni, I.; Nguyen, C.T.T.; Tesauro, M.; Pantanetti, P.; Morichetti, L.; Ceroni, E.; Benni, A.; Petrelli, F. Yoga or Mindfulness on Diabetes: Scoping Review for Theoretical Experimental Framework. Ann. Ig. 2024, 36, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, D.K.; Zhang, C.; Van Dam, R.M.; Bowers, K.; Hu, F.B. Physical activity before and during pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, E.; Gomersall, J.C.; Tieu, J.; Han, S.; Crowther, C.A.; Middleton, P. Combined diet and exercise interventions for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD010443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafne, S.N.; Salvesen, K.Å.; Romundstad, P.R.; Eggebø, T.M.; Carlsen, S.M.; Mørkved, S. Regular exercise during pregnancy to prevent gestational diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 119, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanabria-Martínez, G.; García-Hermoso, A.; Poyatos-León, R.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Sánchez-López, M.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Effectiveness of physical activity interventions on preventing gestational diabetes mellitus and excessive maternal weight gain: A meta-analysis. BJOG 2015, 122, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Kishore, S. Effect of physical activity during pregnancy on gestational diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 22, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, M.J.; Guelfi, K.J.; Hunter, T.; Wallman, K.E.; Fournier, P.A.; Newnham, J.P. Supervised home-based exercise may attenuate the decline of glucose tolerance in obese pregnant women. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W.C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S.E.; Hamman, R.F.; Lachin, J.M.; Walker, E.A.; Nathan, D.M. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guelfi, K.J.; Ong, M.J.; Crisp, N.A.; Fournier, P.A.; Wallman, K.E.; Grove, J.R.; Doherty, D.A.; Newnham, J.P. Regular exercise to prevent the recurrence of gestational diabetes mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 128, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarde, A.; Lewis-Mikhael, A.M.; Moayyedi, P.; Stearns, J.C.; Collins, S.M.; Beyene, J.; McDonald, S.D. Pregnancy outcomes in women taking probiotics or prebiotics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, R.; Prasad, K.; Lemos, J.R.N.; Arevalo, G.; Hirani, K. Unveiling Gestational Diabetes: An Overview of Pathophysiology and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Anna, R.; Santamaria, A.; Di Benedetto, A.; Scilipoti, A.; Santamaria, A.; Interdonato, M.L.; Petrella, E.; Neri, I.; Pintaludi, B.; Corrado, F.; et al. Myo-inositol in the prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.J.; Crowther, C.A.; Alsweiler, J.; Brown, J. Antenatal dietary supplementation with myo-inositol in women during pregnancy for preventing gestational diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 12, CD011507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Anna, R.; Scilipoti, A.; Giordano, D.; Caruso, C.; Cannata, M.L.; Interdonato, M.L.; Corrado, F.; Di Benedetto, A. Myo-inositol supplementation and onset of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant women with a family history of type 2 diabetes: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Ashraf, A. Role of vitamin D in insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity for glucose homeostasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 351385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Y.; Shu, J.; Fu, X.H.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Ji, M.X.; Liu, X.M.; Yu, T.T.; Sheng, J.Z.; Huang, H.F. Improving the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions for gestational diabetes prevention: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. BJOG 2019, 126, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Ji, X.; Zhang, L.; Hou, Z.; Li, C.; Tong, Y. Fish Oil Supplementation does not Reduce Risks of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension, or Pre-Eclampsia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, J.M.; Grivell, R.M.; Deussen, A.R.; Haguet, W.M. Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 7, CD010564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomba, S.; Santagni, S.; Falbo, A.; La Sala, G.B. Complications and challenges associated with polycystic ovary syndrome: Current perspectives. Int. J. Women’s Health 2015, 7, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E. Probiotics: Definition, sources, selection, and uses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46 (Suppl. 2), S58–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, H.S.; Kuan, C.Y.; Ewe, J.A.; Fung, W.-Y.; Liong, M.-T. The improvement of hypertension by probiotics: Effects on cholesterol, diabetes, renin, and phytoestrogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3755–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa-Pacher, A. Research questions with PICO: A universal mnemonic. Publications 2022, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Porritt, K.; Pilla, B.; Jordan, Z. (Eds.) JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020; Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Gates, M.; Gates, A.; Pieper, D.; Fernandes, R.M.; Tricco, A.C.; Moher, D.; Brennan, S.E.; Li, T.; Pollock, M.; Lunny, C. Reporting guideline for overviews of reviews of healthcare interventions: Development of the PRIOR statement. BMJ 2022, 378, e070849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromataris, E.; Fernandez, R.; Godfrey, C.M.; Holly, C.; Khalil, H.; Tungpunkom, P. Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sguanci, M.; Mancin, S.; Piredda, M.; De Marinis, M.G. Protocol for conducting a systematic review on diagnostic accuracy in clinical research. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: A new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019, 2019, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Sowden, A.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Brennan, S.E.; Ellis, S.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Ryan, R.; Shepperd, S.; Thomas, J.; et al. Synthesis without Meta-Analysis (SWiM) in Systematic Reviews: Reporting Guideline. BMJ 2020, 368, l6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S. Probiotics for the prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Biomol. Biomed. 2024, 24, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdizade Ari, M.; Teymouri, S.; Fazlalian, T.; Asadollahi, P.; Afifirad, R.; Sabaghan, M.; Valizadeh, F.; Ghanavati, R.; Darbandi, A. The effect of probiotics on gestational diabetes and its complications in pregnant mother and newborn: A systematic review and meta-analysis during 2010–2020. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakmehr, A.; Ejtahed, H.; Shirzad; Hemmatabadi, M.; Farhat, S.; Larijani, B. Preventive effect of probiotics supplementation on occurrence of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1031915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, C.; Yu, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, J. Effects of probiotic supplementation on glucose metabolism in pregnant women without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2022, 13, 8388–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masulli, M.; Vitacolonna, E.; Fraticelli, F.; Della Pepa, G.; Mannucci, E.; Monami, M. Effects of probiotic supplementation during pregnancy on metabolic outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.J.; Barrett, H.L.; Price, S.A.; Callaway, L.K.; Dekker Nitert, M. Probiotics for preventing gestational diabetes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 4, CD009951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccotti, G.; Meneghin, F.; Aceti, A.; Barone, G.; Callegari, M.L.; Di Mauro, A.; Fantini, M.P.; Gori, D.; Indrio, F.; Maggio, L.; et al. Probiotics for prevention of atopic diseases in infants: Sys-tematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy 2015, 70, 1356–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, G.S.; Lapinski, R.H.; Wein, R.; Lee, D. Race/ethnicity and other risk factors for gestational diabetes. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 135, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liese, A.D.; Schulz, M.; Fang, F.; Wolever, T.M.; D’Algostino, R.B., Jr.; Sparks, K.C.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, carbohydrate, and fiber intake and measures of insulin sensitivity, secretion, and adiposity in the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GonzálEz -Quintero, V.H.; Istwan, N.B.; Rhea, D.J.; Rodriguez, L.I.; Cotter, A.; Carter, J.; Mueller, A.; Stanziano, G.J. The impact of glycemic control on neonatal outcome in singleton pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogozińska, E.; Chamillard, M.; Hitman, G.A.; Khan, K.S.; Thangaratinam, S. Nutritional manipulation for the primary prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomised studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, M.; Miller, C. A diet containing food rich in soluble and insoluble fiber improves glycemic control and reduces hyperlipidemia among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, F.; D’aNna, R.; Di Vieste, G.; Giordano, D.; Pintaudi, B.; Santamaria, A.; Di Benedetto, A. The effect of myoinositol supplementation on insulin resistance in patients with gestational diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria, A.; Alibrandi, A.; Di Benedetto, A.; Pintaudi, B.; Corrado, F.; Facchinetti, F.; D’Anna, R. Clinical and Metabolic Outcomes in Pregnant Women at Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Supplemented with Myo-Inositol: A Secondary Analysis from 3 RCTs. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 219, 300.e1–300.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procter, S.B.; Campbell, C.G. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Nutrition and lifestyle for a healthy pregnancy outcome. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, J.C.; Butler, C.L.; Sorensen, T.K.; Lee, I.-M.; Thompson, M.L.; Miller, R.S.; Frederick, I.O.; Willialms, M.A. A case-control study of maternal recreational physical activity and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 66, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, L.M.; Nobles, C.; Ertel, K.A.; Chasan-Taber, L.; Whitcomb, B.W. Physical activity interventions in pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangelosi, G.; Mancin, S.; Pantanetti, P.; Nguyen, C.T.T.; Palomares, S.M.; Biondini, F.; Sguanci, M.; Petrelli, F.; Cangelosi, G.; Mancin, S.; et al. Lifestyle medicine case manager nurses for type two diabetes patients: An overview of a job description framework—A narrative review. Diabetology 2024, 5, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangelosi, G.; Grappasonni, I.; Pantanetti, P.; Scuri, S.; Garda, G.; Thu, N.C.T.; Petrelli, F. Nurse case manager lifestyle medicine (NCMLM) in the type two diabetes patient concerning post COVID-19 pandemic management: Integrated-scoping literature review. Ann. Ig. 2022, 34, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangelosi, G.; Grappasonni, I.; Nguyen, C.T.T.; Acito, M.; Pantanetti, P.; Benni, A.; Petrelli, F. Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) and lifestyle medicine (LM) for support and care of patients with type II diabetes in the COVID-19 era: A cross-observational study. Acta Biomed. 2023, 94, e2023189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Peng, S.; Li, M.; Ao, X.; Liu, Z. The efficacy and safety of probiotics for allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 848279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentz, A.; Müller, L. Probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in adulthood: A systematic review. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2022, 31, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayesha, I.E.; Monson, N.R.; Klair, N.; Patel, U.; Saxena, A.; Patel, D.; Venugopal, S.; Ayesha, I.E. Probiotics and their role in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (short-term versus long-term effect): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e46741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farren, M.; Daly, N.; McKeating, A.; Kinsley, B.; Turner, M.J.; Daly, S. The prevention of gestational diabetes mellitus with antenatal oral inositol supplementation: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancin, S.; Mazzoleni, B. Probiotics as adjuvant therapy in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2023, 16, 2393–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettocchi, S.; Comotti, A.; Elli, M.; De Cosmi, V.; Berti, C.; Alberti, I.; Mazzocchi, A.; Rosazza, C.; Agostoni, C.; Milani, G.P. Probiotics and fever duration in children with upper respiratory tract infections: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e250669, Erratum in JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2516123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Cangelosi, G.; Scuri, S.; Thu, N.C.T.; Debernardi, G.; Benni, A.; Vesprini, A.; Rocchi, R.; De Carolis, C.; Pantanetti, P.; et al. Food knowledge of patients at the first access to a Diabetology center. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Sachdeva, M.; Dhar, S.; Ganjoo, A.; Shah, B.; Pandhi, D.; Lahiri, K.; Agarwal, R.; Jagadeesan, S.; Mane, P.; et al. Delphi Consensus Statement on the Role of Probiotics in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Cureus 2024, 16, e64583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Feng, H.; Mao, X.L.; Deng, Y.J.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, S.M. The effects of probiotics supplementation on glycaemic control among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, L.; Tian, P.; Jin, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhu, M. The Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Glucolipid Metabolism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Chiou, J. Potential Benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics for Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Ye, H.; Yang, X.; Shen, L.; Dang, X.; Liu, X.; Gong, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Ge, X.; et al. Probiotic Clostridium butyricum ameliorates cognitive impairment in obesity via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 115, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, S.M.; Ferrara, G.; Sguanci, M.; Gazineo, D.; Godino, L.; Palmisano, A.; Paderno, A.; Vrenna, G.; Faraglia, E.; Petrelli, F.; et al. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Technologies on Nutritional Care in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Ren. Nutr. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loy, M.H.; Usseglio, J.; Lasalandra, D.; Gold, M.A. Probiotic Use in Children and Adolescents with Overweight or Obesity: A Scoping Review. Child Obes. 2023, 19, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Tsilingiris, D.; Panagopoulos, F.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Evangelopoulos, A.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. The Role of Next-Generation Probiotics in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Disorders: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sguanci, M.; Mancin, S.; Gazzelloni, A.; Diamanti, O.; Ferrara, G.; Palomares, S.M.; Parozzi, M.; Petrelli, F.; Cangelosi, G. The Internet of Things in the Nutritional Management of Patients with Chronic Neurological Cognitive Impairment: A Scoping Review. Healthcare 2024, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhalima, K.; Beunen, K.; Siegelaar, S.E.; Painter, R.; Murphy, H.R.; Feig, D.S.; Donovan, L.E.; Polsky, S.; Buschur, E.; Levy, C.J.; et al. Management of type 1 diabetes in pregnancy: Update on lifestyle, pharmacological treatment, and novel technologies for achieving glycaemic targets. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 490–508, Erratum in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantanetti, P.; Cangelosi, G.; Palomares, S.M.; Ferrara, G.; Biondini, F.; Mancin, S.; Caggianelli, G.; Parozzi, M.; Sguanci, M.; Petrelli, F. Real-World Life Analysis of a Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Smart Insulin Pen System in Type 1 Diabetes: A Cohort Study. Diabetology 2025, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Han, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C.; Jiang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H. Machine Learning Prediction Models for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e26634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Ang, L.T.; Ho, C.; Soh, S.E.; Tan, K.H.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Godfrey, K.M.; Chan, S.-Y.; Chong, Y.S.; Eriksson, J.G.; et al. Machine Learning-Derived Prenatal Predictive Risk Model to Guide Intervention and Prevent the Progression of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus to Type 2 Diabetes: Prediction Model Development Study. JMIR Diabetes 2022, 7, e32366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Zhu, C.; Lai, M.; Weng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; He, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Large-for-Gestational-Age Infants in Mothers with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e1631–e1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vudathaneni, V.K.P.; Lanke, R.B.; Mudaliyar, M.C.; Movva, K.V.; Kalluri, L.M.; Boyapati, R.; Mounika, K.L. The Impact of Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring on Healthcare Delivery: A Comprehensive Evaluation. Cureus 2024, 16, e55534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.Y.; Ding, X.; Hirst, J.E.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Mackillop, L.; Clifton, D.A. Digital Health and Machine Learning Technologies for Blood Glucose Monitoring and Management of Gestational Diabetes. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 17, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, S.; Chang, H.-J.; Worthington, C.; Kushniruk, A.; Ibáñez-Carrasco, F.; Davies, H.; McKee, G.; Brown, A.; Gilbert, M.; Iyamu, I. Digital Competencies and Training Approaches to Enhance the Capacity of Practitioners to Support the Digital Transformation of Public Health: Rapid Review of Current Recommendations. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024, 10, e52798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamani, S.; Waterfield, K.C.; Austin, R.; Singletary, V.; Odowa, Y.; Miles-Richardson, S.; Winters, T.; Powers, B.; LaRoche, F.; Trachet, S.; et al. Training in Public Health Informatics and Technology Leveraging a Multi-institutional Partnership Model and Emphasizing Experiential Learning. Appl. Clin. Inform. 2024, 15, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| First Author | Publication Year | Studies (n) | Study Design Included |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. [54] | 2024 | 14 | RCTs |
| Mahdizade Ari et al. [55] | 2022 | 28 | RCTs |
| Pakmehr et al. [56] | 2022 | 10 | RCTs |
| Zhang et al. [57] | 2022 | 12 | RCTs |
| Davidson et al. [59] | 2021 | 7 | RCTs |
| Masulli et al. [58] | 2020 | 17 | RCTs |
| Author (Year) | Population | Intervention | Comparator | Outcomes Reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. (2024) [54] | 3527 pregnant women, aged 27–34 years, BMI 21–39 kg/m2, mostly in early pregnancy; 14 RCTs conducted in 10 countries | Probiotic supplementation (various strains including L. rhamnosus, B. lactis, S. thermophilus), 1–50 × 109 CFU/day, started during 1st or 2nd trimester | Placebo (12 RCTs) or no additional treatment (2 RCTs) | Incidence of GDM; subgroup analyses by BMI and age |
| Mahdizade Ari et al. (2022) [55] | 6014 pregnant women with or without GDM; 25 RCTs (various countries) | Oral probiotic supplementation (various strains; mean duration 4–12 weeks) | Placebo | Incidence of GDM; fasting plasma glucose (FPG); insulin; HOMA-IR; neonatal outcomes (birth weight, prematurity) |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [57] | 2213 pregnant women without diabetes; 12 RCTs (China, Iran, Finland, Australia, others) | Probiotic supplementation (various strains; 4–12 weeks duration) | Placebo | GDM incidence; fasting blood glucose (FBG); insulin; HOMA-IR; QUICKI; 1 h and 2 h OGTT |
| Masulli et al. (2020) [58] | 2968 pregnant women with or without GDM, mean age ~29.4 years, mean BMI ~28.5 kg/m2; 17 RCTs (various countries) | Probiotic supplementation (various strains, mostly L. rhamnosus, B. lactis, L. salivarius, etc.), duration ~11.5 weeks | Placebo | Incidence of GDM; fasting plasma glucose (FPG); fasting insulin; HOMA index; maternal and fetal outcomes |
| Pakmehr et al. (2022) [56] | 2921 healthy pregnant women without previously diagnosed glucose disturbances; 10 RCTs | Probiotic supplementation (various strains, especially multi-strain; dose, timing and duration varied) | Placebo | Primary: Incidence of GDM. Secondary: maternal and infant outcomes (e.g., preeclampsia, cesarean, macrosomia, NICU, prematurity) |
| Davidson et al. (2021) [59] | Pregnant women without pre-existing diabetes; studies from Australia, Finland, Iran, Ireland, and New Zealand; 7 RCTs | Probiotic supplementation (various strains, doses, forms, mostly capsules; initiated before 20 weeks of gestation) | Placebo | GDM diagnosis; pre-eclampsia; hypertensive disorders; cesarean section; gestational weight gain; large-for-gestational-age infants; neonatal outcomes |
| Author (Year) | No. RCTs (n Participants) | Outcome | Relative Effect (RR/OR, 95% CI) | Absolute Effect | I2 | τ2 | GRADE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. (2024) [54] | 14 RCTs (3527 women) | GDM incidence | RR: 0.71 (95% CI: 0.52–0.96) | ARR: –5.3%; Probiotics 13.1%, Placebo 18.4% | 73% | NR | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (inconsistency) |
| Mahdizade Ari et al. (2022) [55] | 25 RCTs (6014 women) | GDM incidence | RR: 0.73 (95% CI: 0.58–0.91) | ARR: –5.8%; Event rates not reported | 65% | 0.03 | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (heterogeneity) |
| 25 RCTs (6014 women) | FPG | MD: –3.10 mg/dL (95% CI: –5.21 to –0.98) | – | 87% | 4.7 | ⬤⬤◯◯ Low (inconsistency, imprecision) | |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [57] | 12 RCTs (2213 women) | GDM incidence | RR: 0.62 (95% CI: 0.39–0.99) | ARR: –4.9%; Event rates not reported | 58% | 0.01 | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (some inconsistency) |
| 12 RCTs (2213 women) | FBG | MD: –2.52 mg/dL (95% CI: –4.61 to –0.44) | – | 72% | 2.1 | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (imprecision) | |
| Masulli et al. (2020) [58] | 17 RCTs (2968 women) | GDM incidence | OR: 0.77 (95% CI: 0.51–1.16) | Not statistically significant | 62% | NR | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (wide CI) |
| 15 RCTs (n not specified) | FPG | MD: –1.05 mg/dL (95% CI: –1.95 to –0.16) | Minimal, not clinically relevant | 45% | NR | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (precision) | |
| Pakmehr et al. (2022) [56] | 10 RCTs (2921 women) | GDM incidence | RR: 0.67 (95% CI: 0.47–0.95) | ARR: –4.5%; Probiotics 8.4%, Placebo 12.9% | NR | NR | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (data limited) |
| Davidson et al. (2021) [59] | 6 RCTs (1440 women) | GDM incidence | RR: 0.80 (95% CI: 0.54–1.20) | Not reported | NR | NR | ⬤⬤◯◯ Low (inconsistency, imprecision) |
| 4 RCTs (955 women) | Pre-eclampsia | RR: 1.85 (95% CI: 1.04–3.29) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤⬤⬤ High (robust effect) | |
| 6 RCTs (1520 women) | Caesarean section | RR: 1.00 (95% CI: 0.86–1.17) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤⬤⬤ High (no effect) | |
| 4 RCTs (853 women) | Weight gain in pregnancy | MD: 0.30 kg (95% CI: –0.67 to 1.26) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (inconsistency) | |
| 4 RCTs (919 women) | Large-for-gestational age | RR: 0.99 (95% CI: 0.72–1.36) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤⬤◯ Moderate (imprecision) | |
| 3 RCTs (709 women) | Perinatal mortality | RR: 0.33 (95% CI: 0.01–8.02) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤◯◯ Low (very serious imprecision) | |
| 2 RCTs (623 women) | Morbidity composite | RR: 0.69 (95% CI: 0.36–1.35) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤◯◯ Low (very serious imprecision) | |
| 2 RCTs (586 women) | Neonatal hypoglycaemia | RR: 1.15 (95% CI: 0.69–1.92) | – | NR | NR | ⬤⬤◯◯ Low (inconsistency, imprecision) | |
| 2 RCTs (320 women) | Neonatal adiposity | MD: −0.04 kg & −0.10% | Not pooled | – | – | ⬤⬤◯◯ Low (imprecision) |
| Items | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Include | Score (Mean) |
| Li et al., 2024 [54] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 100% |
| Mahdizade Ari et al, 2022 [55] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 100% |
| Zhang et al., 2022 [57] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 100% |
| Masulli et al., 2020 [58] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 100% |
| Pakmehr et al., 2022 [56] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 100% |
| Davidson et al., 2021 [59] | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | 91% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosmai, S.; Morales Palomares, S.; Chiari, C.; Cattani, D.; Mancin, S.; Gibellato, A.; Valsecchi, A.; Sguanci, M.; Petrelli, F.; Cangelosi, G.; et al. The Role of Probiotics in Preventing Gestational Diabetes: An Umbrella Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145168
Cosmai S, Morales Palomares S, Chiari C, Cattani D, Mancin S, Gibellato A, Valsecchi A, Sguanci M, Petrelli F, Cangelosi G, et al. The Role of Probiotics in Preventing Gestational Diabetes: An Umbrella Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(14):5168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145168
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosmai, Simone, Sara Morales Palomares, Cristina Chiari, Daniela Cattani, Stefano Mancin, Alberto Gibellato, Alessandra Valsecchi, Marco Sguanci, Fabio Petrelli, Giovanni Cangelosi, and et al. 2025. "The Role of Probiotics in Preventing Gestational Diabetes: An Umbrella Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 14: 5168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145168
APA StyleCosmai, S., Morales Palomares, S., Chiari, C., Cattani, D., Mancin, S., Gibellato, A., Valsecchi, A., Sguanci, M., Petrelli, F., Cangelosi, G., Lopane, D., & Mazzoleni, B. (2025). The Role of Probiotics in Preventing Gestational Diabetes: An Umbrella Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(14), 5168. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14145168






